

Demonstrating new Arm-based Azure Burstable VMs - Infrastructure Solutions blog...
source link: https://community.arm.com/arm-community-blogs/b/infrastructure-solutions-blog/posts/using-new-microsoft-azure-burstable
Go to the source link to view the article. You can view the picture content, updated content and better typesetting reading experience. If the link is broken, please click the button below to view the snapshot at that time.

Build your web applications with GitHub Actions on new Arm-powered Microsoft Azure Burstable VMs

Arm is building a strong collaboration with the cloud native software ecosystem to ensure open-source projects provide native multi-architecture support to developers. Arm is actively working with community members and contributors to ensure a seamless software development experience. Developers build their applications leveraging Arm’s mature cloud native software ecosystem to deliver better price-performance and efficient energy consumption. Cloud native applications have a varied set of compute requirements. While some require constant high throughput, others such as web servers and development environments, don’t need the full performance of CPU all the time. Arm’s flexible architecture supports this wide range of workloads.
Microsoft burstable VMs announcement
Microsoft is announcing the preview of new Bpsv2 series Burstable Azure VMs powered by Arm Neoverse-based Ampere Altra processors. Burstable VMs provide high levels of CPU performance when it’s needed the most. These VMs are ideal for workloads that require occasional bursts of high performance but operate at a lower performance level most of the time. They are especially useful for workloads that experience unpredictable spikes in demand, such as events or promotions, where burstable VMs can provide the necessary performance without the need for overprovisioning.
The Bpsv2 series virtual machines are the latest generation of Azure Arm-based burstable VMs, providing a baseline level of CPU performance and capable of expanding to higher burst performance as workload volume increases. This is ideal for many applications that do not need the full performance of the CPU continuously, such as development and test servers, low traffic web servers, small databases, micro services, servers for proof-of-concepts, build servers, and code repositories. Burstable VMs accrue credits over time when operating at a lower performance level which can be used to burst to higher performance.
The Azure Arm-based burstable VMs allow developers to take advantage of the cost savings, since they need to pay less for resources compared to general purpose VMs. These VMs provide better price-performance and energy efficiency compared to traditional general purpose VMs. The burstable VMs are an ideal candidate for CI/CD pipelines for development and test environments. Developers can efficiently manage the intermittent demand for additional resources during the build and testing process of a cloud native application with Arm-based burstable VMs. Let’s look at the following use case of building a CI/CD pipeline that showcases how customers can save costs by building their applications with Azure Arm-based burstable VMs.
Azure Arm-based burstable VMs & GitHub actions
Azure Arm-based burstable VMs are used in a GitHub Actions based CI/CD pipeline for managing spikes in resource demands during the build and testing processes. Typically, a self-hosted GitHub Actions runner in a CI/CD pipeline requires build resources only occasionally. So, the runner is sitting idle most of the time while the associated VM in Azure is accruing costs. If we leverage the burstable VMs for the runner, we can save cost and build credits over time that can be used to handle the occasional need for resources.
In this use case, we’re showcasing the CI/CD lifecycle of a Spring Boot based web application using GitHub Actions. Normally the resources of a GitHub Actions runner are sufficient to build, test and run the source code of the application. However, we’re simulating a scenario when there’s a need for additional resources due to a sudden spike in the number of test cases being executed. The overview of the use case is as follows:
- The source code of a web application is hosted in GitHub and the CI/CD lifecycle is managed with GitHub Actions
- A self-hosted GitHub Actions runner is configured on an Arm-based burstable virtual machine in Azure
- The performance of this VM remains below its baseline for majority of time and supports the build and test processes in the CI/CD pipeline
- The VM accumulates credits over time and - using these credits - it bursts above the baseline when there’s a need for a higher number of resources
- After the build and test processes are completed, the VM returns to its baseline performance and starts to build credits again
Configurations
Pre-requisites:
- Azure account with an active subscription
- GitHub account
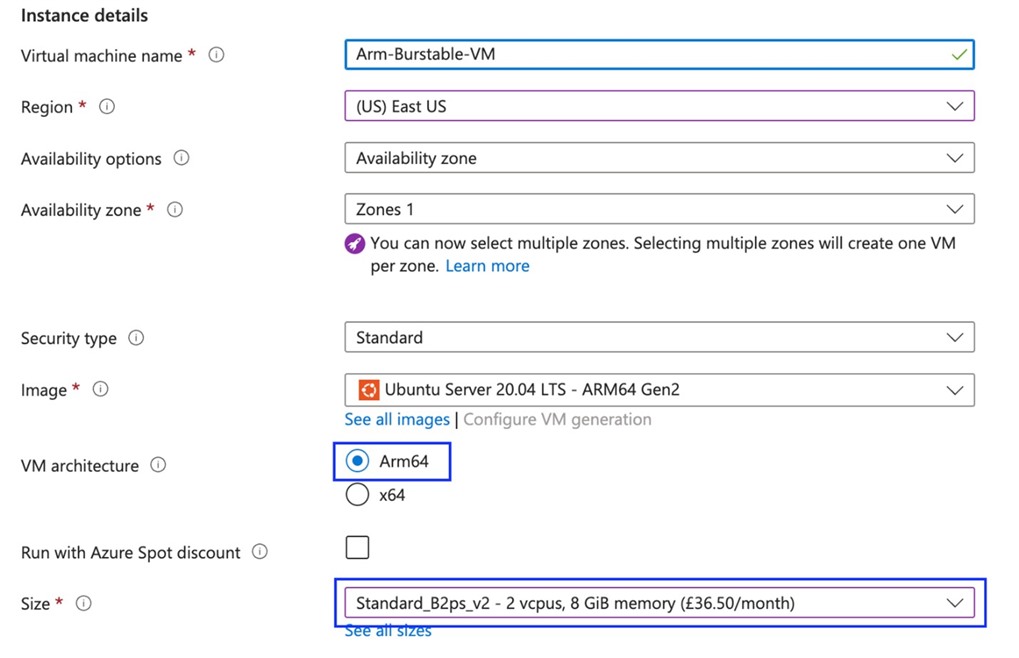
Login to your Azure account and create an Arm-based virtual machine with the following configuration. Make sure to select Arm64 as the architecture and appropriate image as highlighted below:
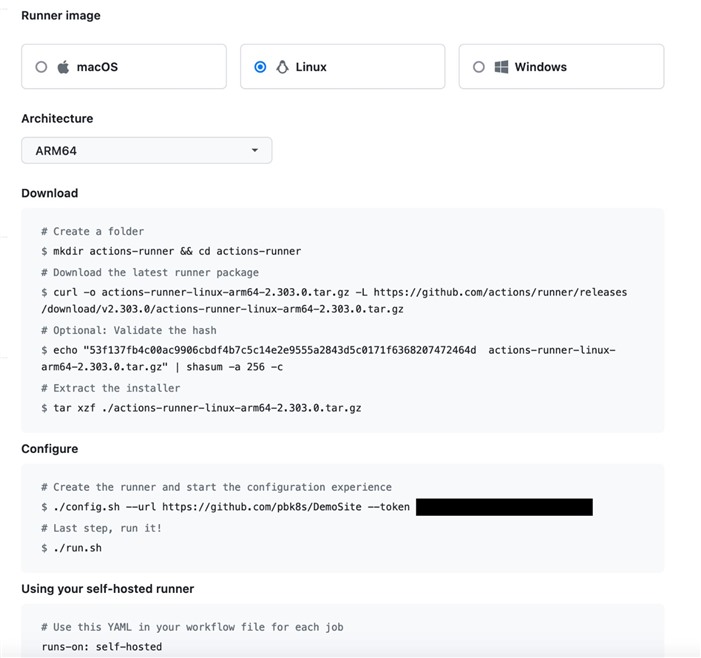
Login to your GitHub account and fork this repository. Afterwards, go the repository settings and register a new self-hosted GitHub Actions Runner. Execute the following commands on the Azure burstable VM and wait for the runner to be in “idle” state.
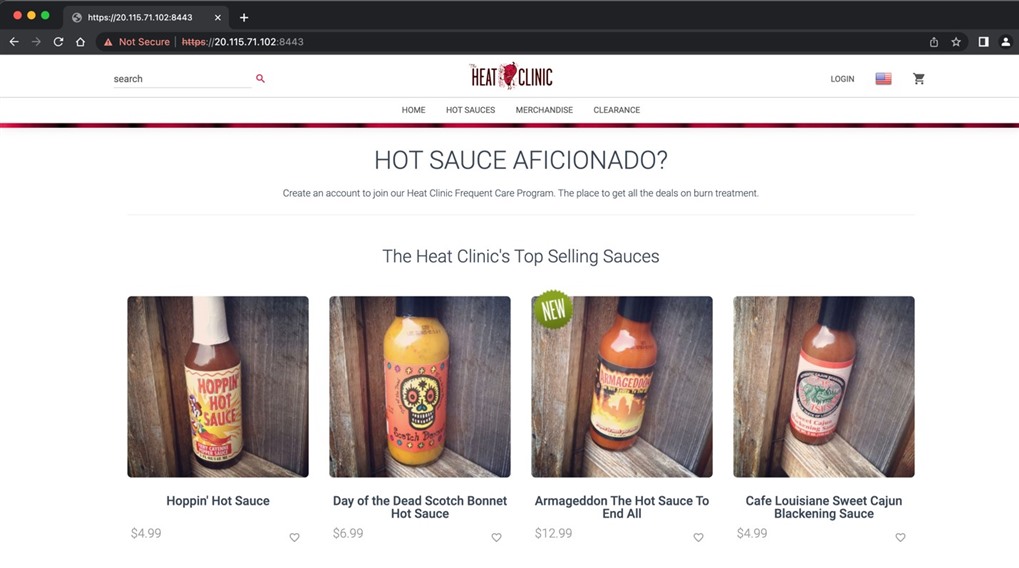
The GitHub Actions Runner is now ready to receive jobs. There is a cool feature in GitHub where you can start visual studio code directly within your browser. Just press . on the repo page and it will immediately start the editor. Modify the application source code and commit the changes. It will automatically trigger the build process in GitHub. We can also monitor it in the Azure VM. Once the build completes successfully, access the application with https://localhost:8443, and the following page should open up.

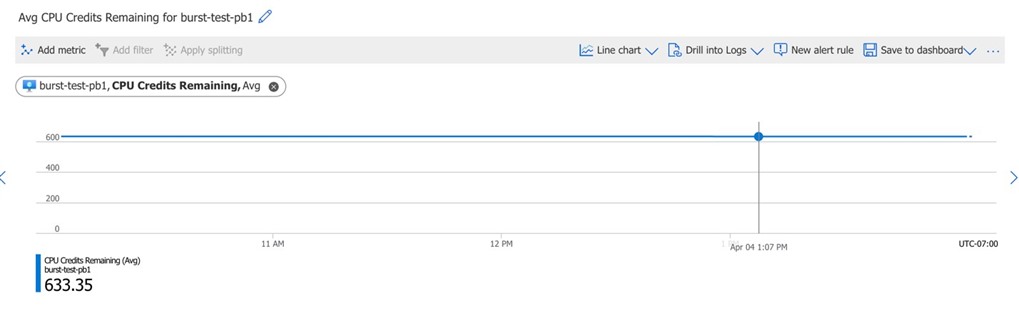
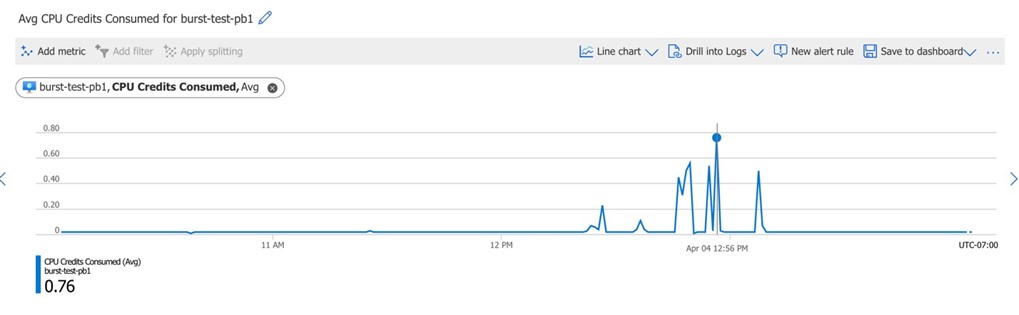
The Burstable VM will accrue credits over time when running below its baseline performance. We can see the accumulated credits on the Azure portal as below:
We did multiple commits to the CI/CD pipeline to see the accumulated credits get utilized. The following screenshot shows the number of credits utilized for the burstable VM:
Recommend
-
 6
6
MapReduce as burstable low-cost CPU About two months ago, when Mike Wickstrand setup a UserVoice instance for Windows Azure, I immediately posted my own suggestion concerning
-
 5
5
This blog post provides some needed background concerning the recent Tetrate and Arm Neoverse announcement. It then shows you how to deploy Tetra...
-
 6
6
Introduction Spark SQL is one of the most used Spark’s modules, providing a simplified programing interface to run Spark computations on a cluster. It comes with query optimizations that help Spark to run more effic...
-
 9
9
LF Edge: Bringing the edge to work
-
 10
10
Synchronization Overview and Case Study on Arm Architecture
-
 5
5
Machine Learning (ML) is one of the fastest growing segments within cloud and edge infrastructure. Within ML, deep learning inference is expected to grow even faster. In this blog, we compare the ML inference performance of three Amazon Web...
-
 4
4
In this blog, we walk through a sample deployment of WordPress (with MySQL) on
-
 5
5
Introduction XGBoost (eXtreme Gradient Boosting) is an open-source machine learning library under Gradient-Boosting Decision Tree (GBDT) framework. XGBoo...
-
 7
7
Announcing WindowsPerf: Open-source performance analysis tool for Windows on Arm
-
 7
7
Introducing the 3rd Generation of Neoverse System IP The Neoverse S3 products introduce our 3rd generation of infrastructure-specific system IP, the ideal foundation for next generation infrastructure SOCs, for...
About Joyk
Aggregate valuable and interesting links.
Joyk means Joy of geeK