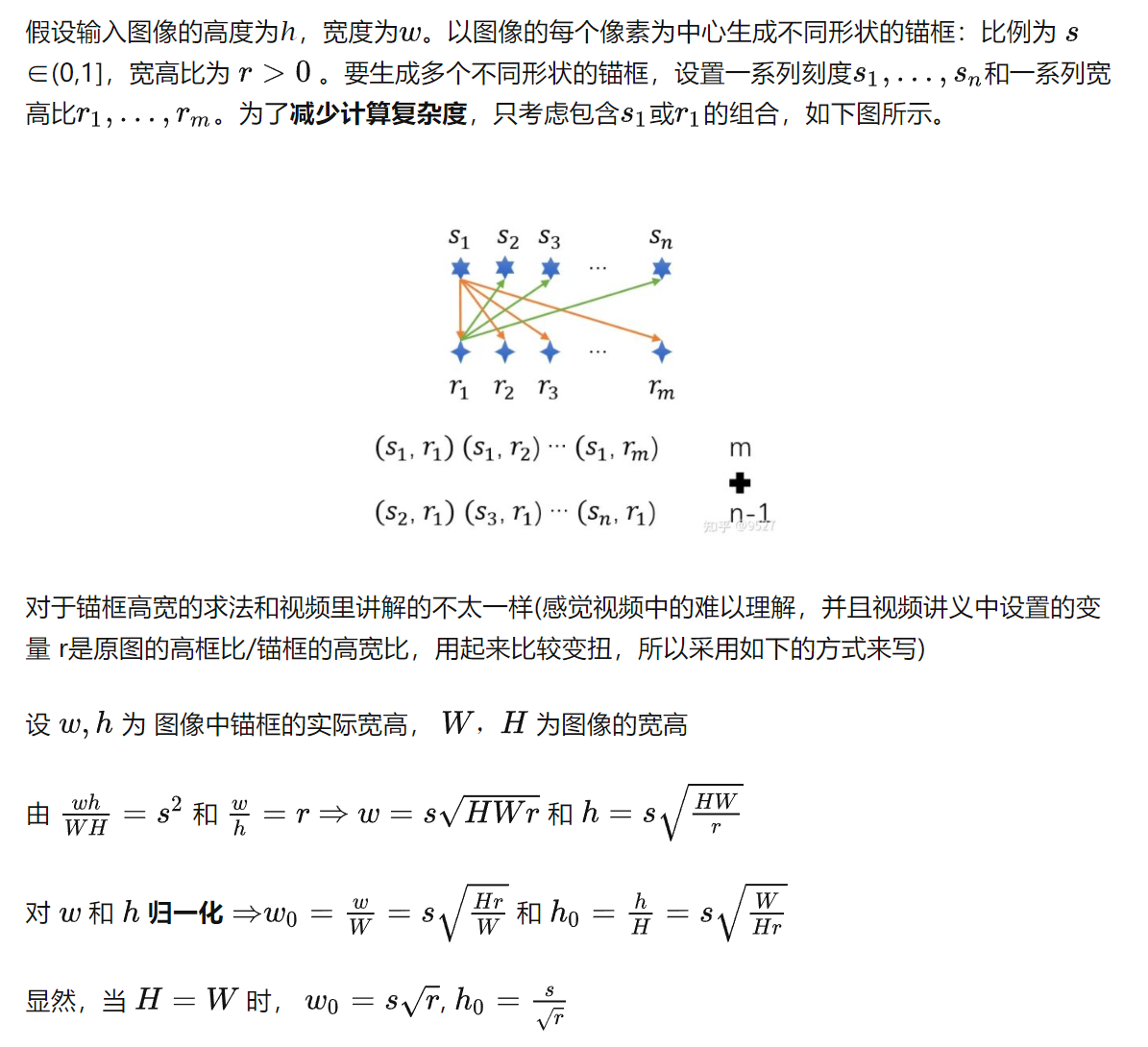
6

目标检测-SSD算法从零实现 - SXQ-BLOG
source link: https://www.cnblogs.com/sxq-blog/p/16672884.html
Go to the source link to view the article. You can view the picture content, updated content and better typesetting reading experience. If the link is broken, please click the button below to view the snapshot at that time.

1. 几个工具函数
def box_corner_to_center(boxes): """从(左上,右下)转换到(中间,宽度,高度)""" x1, y1, x2, y2 = boxes[:, 0], boxes[:, 1], boxes[:, 2], boxes[:, 3] cx = (x1 + x2) / 2 cy = (y1 + y2) / 2 w = x2 - x1 h = y2 - y1 boxes = torch.stack((cx, cy, w, h), axis=-1) return boxes def box_center_to_corner(boxes): """从(中间,宽度,高度)转换到(左上,右下)""" cx, cy, w, h = boxes[:, 0], boxes[:, 1], boxes[:, 2], boxes[:, 3] x1 = cx - 0.5 * w y1 = cy - 0.5 * h x2 = cx + 0.5 * w y2 = cy + 0.5 * h boxes = torch.stack((x1, y1, x2, y2), axis=-1) return boxes def bbox_to_rect(bbox, color): # 将边界框(左上x,左上y,右下x,右下y)格式转换成matplotlib格式: # ((左上x,左上y),宽,高) return plt.Rectangle( xy=(bbox[0], bbox[1]), width=bbox[2]-bbox[0], height=bbox[3]-bbox[1], fill=False, edgecolor=color, linewidth=2) # 显示以图像中一个像素为中心的所有锚框def show_bboxes(axes, bboxes, labels=None, colors=None): """显示所有边界框""" def _make_list(obj, default_values=None): if obj is None: obj = default_values elif not isinstance(obj, (list, tuple)): obj = [obj] return obj labels = _make_list(labels) colors = _make_list(colors, ['b','g','r','m','c']) for i, bbox in enumerate(bboxes): color = colors[i % len(colors)] rect = bbox_to_rect(bbox.detach().numpy(),color) axes.add_patch(rect) if labels and len(labels) > i: text_color = 'k' if color == 'w' else 'w' axes.text(rect.xy[0], rect.xy[1], labels[i], va='center', ha='center', fontsize=9, color=text_color, bbox=dict(facecolor=color, lw=0))
2. 生成锚框
def multibox_prior(img, sizes, ratios): """生成以每个像素为中心具有不同形状的锚框""" in_height, in_width = img.shape[-2:] device, num_sizes, num_ratios = img.device, len(sizes), len(ratios) boxes_per_pixel = (num_sizes + num_ratios - 1) size_tensor = torch.tensor(sizes, device=device) ratio_tensor = torch.tensor(ratios, device=device) # 生成锚框的所有中心点 # 这里以0 1 2为例,中心点是0.5和1.5所以要加上0.5, /in_height是为了进行归一化 center_h = (torch.arange(in_height, device=device) + 0.5) / in_height center_w = (torch.arange(in_width, device=device) + 0.5) / in_width shift_y, shift_x = torch.meshgrid(center_h, center_w, indexing='ij') shift_y, shift_x = shift_y.reshape(-1), shift_x.reshape(-1)#此时shift_y和shift_x一对一地形成了所有中心点下标 # 生成“boxes_per_pixel”个高和宽, # 之后用于创建锚框的四角坐标(xmin,xmax,ymin,ymax) # w为一行,其中每个元素为不同的锚框的宽度 w = torch.cat((sizes[0] * torch.sqrt(in_height * ratio_tensor[:] / in_width), size_tensor[1:] * torch.sqrt(in_height * ratio_tensor[0] / in_width))) # h为一行,其中每个元素为不同的锚框的高度 h = torch.cat((sizes[0] * torch.sqrt(in_width / ratio_tensor[:] / in_height), size_tensor[1:] * torch.sqrt(in_width / ratio_tensor[0] / in_height))) # 除以2来获得半高和半宽 anchor_manipulations = torch.stack((-w, -h, w, h)).T.repeat(in_height * in_width, 1) / 2 # 每个中心点都将有“boxes_per_pixel”个锚框, # 所以生成含所有锚框中心的网格,重复了“boxes_per_pixel”次 out_grid = torch.stack([shift_x, shift_y, shift_x, shift_y], dim=1).repeat_interleave(boxes_per_pixel, dim=0) output = out_grid + anchor_manipulations # 只能返回一张图片的所有锚框 return output.unsqueeze(0) # 1 * 锚框个数 * 4(左上和右下下标)
3. 给锚框打标签
- 首先提供一个计算锚框之间的交并比的函数
# 交并比(IoU)def box_iou(boxes1,boxes2): # 左上右下形式坐标 # boxes1:(boxes1的数量,4), # boxes2:(boxes2的数量,4), """计算两个锚框或边界框列表中成对的交并比""" box_area = lambda boxes: ((boxes[:,2] - boxes[:,0]) * (boxes[:,3] - boxes[:,1])) areas1 = box_area(boxes1) # 锚框1的面积 areas2 = box_area(boxes2) # 锚框2的面积 inter_upperlefts = torch.max(boxes1[:,None,:2],boxes2[:,:2]) inter_lowerrights = torch.min(boxes1[:,None,2:],boxes2[:,2:]) inters = (inter_lowerrights - inter_upperlefts).clamp(min=0) # inter_areasand and union_areas的形状:(boxes1的数量,boxes2的数量) inter_areas = inters[:,:,0] * inters[:,:,1] # 交集的面积 union_areas = areas1[:,None] + areas2 - inter_areas # 并集的面积 return inter_areas / union_areas # num_box1 * num_box2
- 为锚框分配真实边界框,这样之后才能打标签,偏移量和类别,这里只会把所有满足和真实边界框的iou值大于一定范围的锚框分配,未分配的值为-1
# 将真实边界框分配给锚框def assign_anchor_to_bbox(anchors,ground_truth,device,iou_threshold=0.5): """将最接近的真实边界框分配给锚框""" num_anchors, num_gt_boxes = anchors.shape[0], ground_truth.shape[0] jaccard = box_iou(anchors,ground_truth) # 计算所有的锚框和真实边缘框的IOU anchors_bbox_map = torch.full((num_anchors,), -1, dtype=torch.long, device=device) max_ious, indices = torch.max(jaccard, dim=1)#indices为每一个锚框对应的真实的边界框的标号, max_ious为每一个锚框对应的真实边界框的iou anc_i = torch.nonzero(max_ious >= iou_threshold).reshape(-1) #找到所有iou值>0.5的锚框的下标 box_j = indices[max_ious >= iou_threshold]#找到所有iou值>0.5的锚框对应的真实边界框 anchors_bbox_map[anc_i] = box_j #到现在上面的每一个iou>=0.5的锚框都分配了一个真实的边界框,但是此时并不一定每个真实边界框都分配到了一个锚框, #所以下面的代码要对每一个真实边界框进行遍历,并未其分配一个锚框 col_discard = torch.full((num_anchors,),-1) row_discard = torch.full((num_gt_boxes,),-1) for _ in range(num_gt_boxes): max_idx = torch.argmax(jaccard, dim=None) # 找IOU最大的锚框,找的是全局最大的锚框 box_idx = (max_idx % num_gt_boxes).long() anc_idx = (max_idx / num_gt_boxes).long() anchors_bbox_map[anc_idx] = box_idx jaccard[:,box_idx] = col_discard # 把最大Iou对应的锚框在 锚框-类别 矩阵中的一列删掉 jaccard[anc_idx,:] = row_discard # 把最大Iou对应的锚框在 锚框-类别 矩阵中的一行删掉 return anchors_bbox_map#返回每一个分配了边界框的锚框对应的真实边界框的下标
- 接下来就可以给锚框打标签了
def offset_boxes(anchors, assigned_bb, eps=1e-6): """对锚框偏移量的转换""" c_anc = box_corner_to_center(anchors) c_assigned_bb = box_corner_to_center(assigned_bb) offset_xy = 10 * (c_assigned_bb[:, :2] - c_anc[:, :2]) / c_anc[:, 2:] offset_wh = 5 * torch.log(eps + c_assigned_bb[:, 2:] / c_anc[:, 2:]) offset = torch.cat([offset_xy, offset_wh], axis=1) return offset # 尽量使得 offset 让 machine learning 算法好预测 # 标记锚框的类和偏移量def multibox_target(anchors, labels): """使用真实边界框标记锚框""" batch_size, anchors = labels.shape[0], anchors.squeeze(0) batch_offset, batch_mask, batch_class_labels = [], [], [] device, num_anchors = anchors.device, anchors.shape[0] for i in range(batch_size): label = labels[i,:,:] anchors_bbox_map = assign_anchor_to_bbox(anchors,label[:,1:],device) class_labels = torch.zeros(num_anchors, dtype=torch.long,device=device) assigned_bb = torch.zeros((num_anchors,4), dtype=torch.float32,device=device) indices_true =torch.nonzero(anchors_bbox_map >= 0)# 分配了真实边界框的锚框下标 bb_idx = anchors_bbox_map[indices_true] #分配了边界框的锚框对应的真实边界框的下标 class_labels[indices_true] = label[bb_idx,0].long() + 1 #所有锚框对应的类别,0表示背景,>0表示物体, (num_anchors,) assigned_bb[indices_true] = label[bb_idx, 1:] #所有锚框对应的真实的边界框的坐标,num_anchors * 4 bbox_mask = ((anchors_bbox_map >= 0).float().unsqueeze(-1)).repeat(1,4) # num_anchors * 4,没有分配真实边界框的锚框对应4个0,分配的对应4个1 offset = offset_boxes(anchors, assigned_bb) * bbox_mask#乘上bbox_mask是因为有的锚框对应的真实边界框坐标全是0,为了把这部分去掉, num_anchors*4 batch_offset.append(offset.reshape(-1)) batch_mask.append(bbox_mask.reshape(-1)) batch_class_labels.append(class_labels) bbox_offset = torch.stack(batch_offset) #batch_size * (num_anchors*4) bbox_mask = torch.stack(batch_mask) #batch_size * (num_anchors*4) class_labels = torch.stack(batch_class_labels) #batch_size * num_anchors # bbox_offset返回每一个锚框到真实标注框的offset偏移 # bbox_mask为0表示背景锚框,就不用了,>0表示对应真实的物体 # class_labels为锚框对应类的编号 return (bbox_offset, bbox_mask, class_labels)
4. 接下来准备模型
- 首先提供用来预测锚框类别和偏移量的层
因为锚框个数太多,如果把每个锚框都拿出来做回归和分类会导致计算量太大,这里采用的方式是利用通道数作为每一个像素点生成的所有锚框的预测,锚框的标签是利用上面的方式标记的,损失便是由这两者产生的,根据损失的梯度下降,网路便可以学会通道便是锚框的预测结果。
def cls_predictor(num_input_channels, num_anchors, num_classes): """类别预测层 这里卷积核用的是高宽不变的,因为如果每一个像素点都生成多个锚框,在进行分类会导致参数过大, 所以这里省略了这个步骤,直接通过把每一个像素点生成num_anchors*num_classes个通道,就代替了上面的步骤 Args: num_input_channels (_type_):特征图的输入通道 num_anchors (_type_):每一个像素生成多少锚框,num_sizes+num_ratios-1 num_classes (_type_):类别数,要包含背景的 """ return nn.Conv2d(num_input_channels, num_anchors*num_classes, kernel_size=3, padding=1)def offset_predictor(num_input_channels, num_anchors): """边界框预测层 这里卷积核用的是高宽不变的,因为如果每一个像素点都生成多个锚框,在进行预测4个偏移量导致参数过大, 所以这里省略了这个步骤,直接通过把每一个像素点生成num_anchors*4个通道,就代替了上面的步骤 Args: num_input_channels (_type_):特征图的输入通道 num_anchors (_type_):每一个像素生成多少锚框,num_sizes+num_ratios-1 """ return nn.Conv2d(num_input_channels, num_anchors*4, kernel_size=3, padding=1)
def down_sample_blk(in_channels, out_channels): # 高宽减半 blk = [] for _ in range(2): blk.append(nn.Conv2d(in_channels, out_channels, kernel_size=3, padding=1)) blk.append(nn.BatchNorm2d(out_channels)) blk.append(nn.ReLU()) in_channels = out_channels blk.append(nn.MaxPool2d(kernel_size=2)) return nn.Sequential(*blk)def base_net(): # 从输入图像中抽取特征的网络 # channels:3 -> 64 # 高宽减小了8倍 blk = [] num_filters = [3, 16, 32, 64] for i in range(len(num_filters)-1): blk.append(down_sample_blk(num_filters[i], num_filters[i+1])) return nn.Sequential(*blk)def get_blk(i): if i == 0: blk = base_net() elif i == 1: blk = down_sample_blk(64, 128) elif i == 4: blk = nn.AdaptiveMaxPool2d((1, 1)) else: blk = down_sample_blk(128, 128) return blk
- 定义网络中的每层的前向传播函数
def blk_forward(x, blk, size, ratio, cls_predictor, offset_predictor): """为每个块定义前向传播 Args: x (_type_):输入的特征图,batch * channel * h * w blk (_type_):网络 size (_type_):生成锚框的尺寸 ratio (_type_):生成锚框的高宽比 cls_predictor (_type_):用于分类的conv offset_predictor (_type_):用于回归的conv Returns: CNN特征图y;在当前尺度下根据y生成的锚框;预测的这些锚框的类别和偏移量(基于y) """ y = blk(x) # 以下两个预测相当于生成锚框再进行的预测 cls_preds = cls_predictor(y) offset_preds = offset_predictor(y) # 生成锚框 anchors = mb.multibox_prior(y, sizes=size, ratios=ratio) return (y, anchors, cls_preds, offset_preds)
class TinySSD(nn.Module): def __init__(self, num_classes): super().__init__() self.num_classes = num_classes idx_to_in_channels = [64, 128, 128, 128, 128] for i in range(5): setattr(self, f'blk_{i}', get_blk(i)) setattr(self, f'cls_{i}', cls_predictor(idx_to_in_channels[i], num_anchors, self.num_classes)) setattr(self, f'offset_{i}', offset_predictor(idx_to_in_channels[i], num_anchors)) def flatten_pred(self, pred): """把四维的pred展平成二维 先把通道放到最后一维是因为这样对于每一个像素点的预测后面都是连续的值 Args: pred (_type_):一个batch的预测 Returns: 展平后的张量 """ return torch.flatten(pred.permute(0, 2, 3, 1), start_dim=1) def concat_preds(self, preds): return torch.cat([self.flatten_pred(p) for p in preds], dim=1) def forward(self, x): anchors, cls_preds, offset_preds = [None] * 5, [None] * 5, [None] * 5 for i in range(5): x, anchors[i], cls_preds[i], offset_preds[i] = blk_forward( x, getattr(self, f'blk_{i}'), sizes[i], ratios[i], getattr(self, f'cls_{i}'), getattr(self, f'offset_{i}')) # 注意以下的num_all_anchors指的是一个样本在所有特征图上生成的锚框 anchors = torch.cat(anchors, dim=1)# 1*num_all_anchors*4 cls_preds = self.concat_preds(cls_preds)# batch*(num_all_anchors*num_classes) cls_preds = cls_preds.reshape(cls_preds.shape[0], -1, self.num_classes) offset_preds = self.concat_preds(offset_preds)# batch*(num_all_anchors*4) return anchors, cls_preds, offset_preds
- 定义损失函数
cls_loss = nn.CrossEntropyLoss(reduction='none')offset_loss = nn.L1Loss(reduction='none') def calc_loss(cls_preds, cls_labels, offset_preds, offset_labels, offset_masks): batch_size, num_classes = cls_preds.shape[0], cls_preds.shape[2] l1 = cls_loss(cls_preds.reshape(-1, num_classes), cls_labels.reshape(-1)) l1 = l1.reshape(batch_size, -1).mean(dim=1) l2 = offset_loss(offset_preds*offset_masks, offset_labels*offset_masks).mean(dim=1) return l1 + l2
- 定义评测的函数
# 分类准确率函数def cls_eval(cls_preds, cls_labels): # 返回这个batch中所有锚框预测正确的个数 return float((cls_preds.argmax(dim=-1).type(cls_labels.dtype) == cls_labels).sum()) def offset_eval(offset_preds, offset_labels, offset_mask): # 返回这个batch中的所有的锚框预测的偏移量的损失 return float((torch.abs((offset_preds - offset_labels) * offset_mask)).sum())
- 定义训练函数和一些初始化参数
device, net = mb.try_gpu(), TinySSD(num_classes = 2)updater = torch.optim.SGD(net.parameters(), lr = 0.2, weight_decay=0)num_epochs = 10animator = mb.Animator(xlabel='epoch', xlim=[1, num_epochs], legend=['class error', 'offset mae'])net = net.to(device)#blk_forward中会调用sizes和ratios,用来生成锚框用sizes = [[0.2, 0.272], [0.37, 0.447], [0.54, 0.619], [0.71, 0.79], [0.88, 0.961]]ratios = [[1, 2, 0.5]]*5num_anchors = len(sizes[0]) + len(ratios[0]) - 1 for epoch in range(num_epochs): metric = mb.Accumulator(4) net.train() for x, y in train_iter: x, y = x.to(device), y.to(device) y = y / 256 #因为原图就是256*256的,为了把标签归一化 anchors, cls_preds, offset_preds = net(x) #得到批量预测结果和锚框 offset_labels, offset_mask, cls_labels = mb.multibox_target(anchors, y) #得到批量anchors的标签 l = calc_loss(cls_preds, cls_labels, offset_preds, offset_labels, offset_mask) updater.zero_grad() l.mean().backward() updater.step() metric.add(cls_eval(cls_preds, cls_labels), cls_labels.numel(), offset_eval(offset_preds, offset_labels, offset_mask), offset_labels.numel()) cls_err = 1 - metric[0] / metric[1] offset_mae = metric[2] / metric[3] animator.add(epoch+1, (cls_err, offset_mae))
- 首先定义非极大抑制函数
非极大抑制就是把所有的预测框按照置信度从大到小排序,把和最大的预测框的iou值大于一定阈值的预测框设置为背景
def nms(boxes, scores, iou_threshold): #boxes为所有的预测框, scores为每个预测框对应的预测类别概率最大的值 #对预测边界框的置信度进行排序 B = torch.argsort(scores, dim = -1, descending=True)#得到从大到小的预测概率所对应的预测框下标 keep = [] while B.numel()>0: # 直到把所有框都访问过了,再退出循环 i = B[0] # B中的预测概率最大值的下标(对应着相应的预测框) keep.append(i) if B.numel() == 1: break # 所有的iou大于阈值的全部去掉 iou = box_iou(boxes[i,:].reshape(-1,4), boxes[B[1:],:].reshape(-1,4)).reshape(-1) inds = torch.nonzero(iou <= iou_threshold).reshape(-1) #得到所有<阈值的下标 B = B[inds + 1]#+1是因为得到这些与最大概率预测框的iou小于阈值的预测框的在B中的下标,然后把B更新成小于阈值的预测框 return torch.tensor(keep, dtype=torch.long, device=boxes.device)#返回未被抑制的预测框的下标 # 将非极大值抑制应用于预测边界框def multibox_detection(cls_probs,offset_preds,anchors,nms_threshold=0.5,pos_threshold=0.009999999): #cls_probs:每一个预测框对每一类的预测概率,batch * num_classes * num_predicted_bb #offset_preds:batch * num_anchors * 4 device, batch_size = cls_probs.device, cls_probs.shape[0] anchors = anchors.squeeze(0) num_classes, num_anchors = cls_probs.shape[1], cls_probs.shape[2] out = [] for i in range(batch_size): cls_prob, offset_pred = cls_probs[i], offset_preds[i].reshape(-1,4) # num_anchors * 4 predicted_bb = offset_inverse(anchors,offset_pred) # 把预测框拿出来 #下面conf得到不考率背景的每一个预测框的对每一类物体的最大概率值和相应的下标,classid这里变成用0代表第一类物体了 #不考虑背景是因为在抑制的时候防止因为背景框把物体检测的框抑制了 conf, class_id = torch.max(cls_prob ,dim = 0) background_indices = torch.nonzero(class_id == 0).reshape(-1)# 背景预测框的下标 non_background_indices = torch.nonzero(class_id != 0).reshape(-1)# 非背景预测框的下标 non_back_predictbb = predicted_bb[non_background_indices] non_back_conf = conf[non_background_indices] keep = nms(non_back_predictbb, non_back_conf, nms_threshold) # 获取被抑制的预测框 non_keep = [] for idx, _ in enumerate(non_back_predictbb): if idx not in keep: non_keep.append(idx) # 将被抑制的预测框的类别设置为0 class_id[non_background_indices[non_keep]] = 0 # 下面就是把所有预测框重新排列了一下,前面放的没有被抑制的,后面放的被抑制的 all_sorted_indices = torch.cat((non_background_indices[keep], #非背景框 non_background_indices[non_keep],#背景框 background_indices), dim=0)#背景框 class_id = class_id[all_sorted_indices] conf = conf[all_sorted_indices] predicted_bb = predicted_bb[all_sorted_indices] # pos_threshold是一个用于非背景预测的阈值, 如果有预测目标概率小于pos那个值则被视为背景 below_min_idx = (conf < pos_threshold) class_id[below_min_idx] = 0 conf[below_min_idx] = 1 - conf[below_min_idx] # 增加背景的置信度 # 返回预测的信息,共num_anchors行,每一行6个信息,分别为:类别,预测概率值,4个左上右下坐标 pred_info = torch.cat((class_id.unsqueeze(1), conf.unsqueeze(1), predicted_bb), dim=1) out.append(pred_info) return torch.stack(out)#batch*(共num_anchors行,每一行6个信息,分别为:类别,预测概率值,4个左上右下坐标)
- 定义预测函数
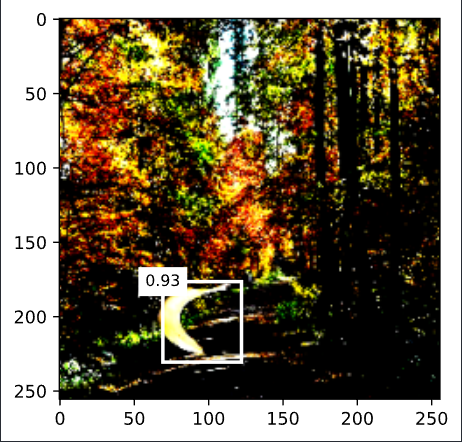
x, y = next(iter(train_iter))x = x[0]img = x.permute(1, 2, 0)x = x.unsqueeze(0) def predict(X): net.eval() net.to(device) X = X.to(device) anchors, cls_preds, offset_preds = net(X) cls_probs = F.softmax(cls_preds, dim=2).permute(0, 2, 1) output = mb.multibox_detection(cls_probs, offset_preds, anchors) idx = [i for i, row in enumerate(output[0]) if row[0] != 0] return output[0, idx]#第0个样本,idx下表对应的锚框 output = predict(x) def display(img, output, threshold): fig = mb.plt.imshow(img) for row in output: score = float(row[1]) if score < threshold: continue h, w = img.shape[0:2] bbox = [row[2:6] * torch.tensor((w, h, w, h), device=row.device)] mb.show_bboxes(fig.axes, bbox, '%.2f' % score, 'w') display(img, output.cpu(), threshold=0.9)
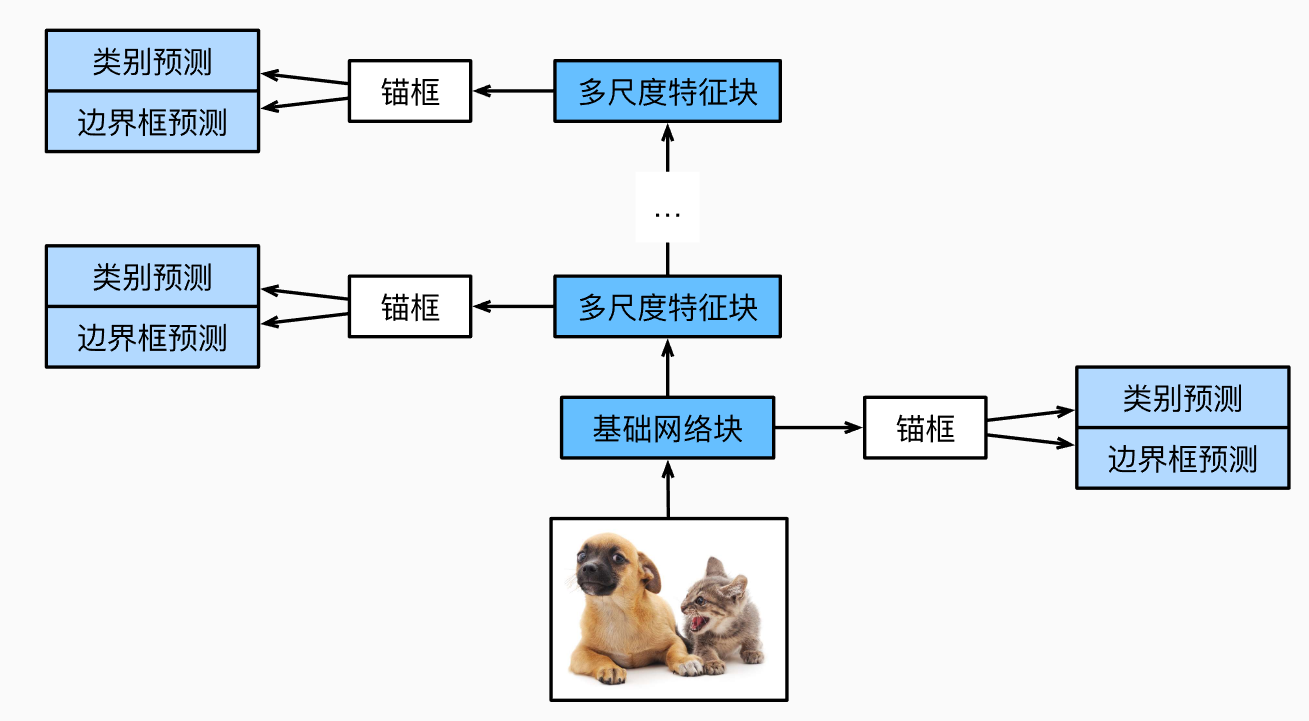
7. SSD原理性分析
SSD通过多尺度的特征图实现对不同大小目标的检测,处在深层的特征图的感受野比较大,所以设置的锚框的sizes较大,卷积核通过对特征图中每一个位置做卷积进而生成该位置处所对应的锚框们的预测,因为在该位置处卷积核的感受野足够大(包含了该位置对应的锚框),所以可以通过该位置的卷积(这个卷积和全连接其实是一样的,把卷积的元素展平就是做的向量内积wT∗xwT∗x,所以这里相当于用卷积去实现局部全连接)去做锚框的预测,因为有锚框的信息在里面,由于感受野很大,所以可以更加准确的预测距离真实边界框的距离(因为卷积核可以看到锚框核真实框的距离信息)
(以上内容完全来自个人理解,不足请不吝指出)
__EOF__
Recommend
About Joyk
Aggregate valuable and interesting links.
Joyk means Joy of geeK