

C#基于ScottPlot进行可视化
source link: https://www.cnblogs.com/mingupupu/p/17963079
Go to the source link to view the article. You can view the picture content, updated content and better typesetting reading experience. If the link is broken, please click the button below to view the snapshot at that time.

C#基于ScottPlot进行可视化
上一篇文章跟大家分享了用NumSharp实现简单的线性回归,但是没有进行可视化,可能对拟合的过程没有直观的感受,因此今天跟大家介绍一下使用C#基于Scottplot进行可视化,当然Python的代码,我也会同步进行可视化。
Python代码进行可视化
Python代码用matplotlib做了可视化,我就不具体介绍了。
修改之后的python代码如下:
#The optimal values of m and b can be actually calculated with way less effort than doing a linear regression.
#this is just to demonstrate gradient descent
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from matplotlib.animation import FuncAnimation
# y = mx + b
# m is slope, b is y-intercept
def compute_error_for_line_given_points(b, m, points):
totalError = 0
for i in range(0, len(points)):
x = points[i, 0]
y = points[i, 1]
totalError += (y - (m * x + b)) ** 2
return totalError / float(len(points))
def step_gradient(b_current, m_current, points, learningRate):
b_gradient = 0
m_gradient = 0
N = float(len(points))
for i in range(0, len(points)):
x = points[i, 0]
y = points[i, 1]
b_gradient += -(2/N) * (y - ((m_current * x) + b_current))
m_gradient += -(2/N) * x * (y - ((m_current * x) + b_current))
new_b = b_current - (learningRate * b_gradient)
new_m = m_current - (learningRate * m_gradient)
return [new_b, new_m]
def gradient_descent_runner(points, starting_b, starting_m, learning_rate, num_iterations):
b = starting_b
m = starting_m
args_data = []
for i in range(num_iterations):
b, m = step_gradient(b, m, np.array(points), learning_rate)
args_data.append((b,m))
return args_data
if __name__ == '__main__':
points = np.genfromtxt("data.csv", delimiter=",")
learning_rate = 0.0001
initial_b = 0 # initial y-intercept guess
initial_m = 0 # initial slope guess
num_iterations = 10
print ("Starting gradient descent at b = {0}, m = {1}, error = {2}".format(initial_b, initial_m, compute_error_for_line_given_points(initial_b, initial_m, points)))
print ("Running...")
args_data = gradient_descent_runner(points, initial_b, initial_m, learning_rate, num_iterations)
b = args_data[-1][0]
m = args_data[-1][1]
print ("After {0} iterations b = {1}, m = {2}, error = {3}".format(num_iterations, b, m, compute_error_for_line_given_points(b, m, points)))
data = np.array(points).reshape(100,2)
x1 = data[:,0]
y1 = data[:,1]
x2 = np.linspace(20, 80, 100)
y2 = initial_m * x2 + initial_b
data2 = np.array(args_data)
b_every = data2[:,0]
m_every = data2[:,1]
# 创建图形和轴
fig, ax = plt.subplots()
line1, = ax.plot(x1, y1, 'ro')
line2, = ax.plot(x2,y2)
# 添加标签和标题
plt.xlabel('x')
plt.ylabel('y')
plt.title('Graph of y = mx + b')
# 添加网格
plt.grid(True)
# 定义更新函数
def update(frame):
line2.set_ydata(m_every[frame] * x2 + b_every[frame])
ax.set_title(f'{frame} Graph of y = {m_every[frame]:.2f}x + {b_every[frame]:.2f}')
# 创建动画
animation = FuncAnimation(fig, update, frames=len(data2), interval=500)
# 显示动画
plt.show()
实现的效果如下所示:
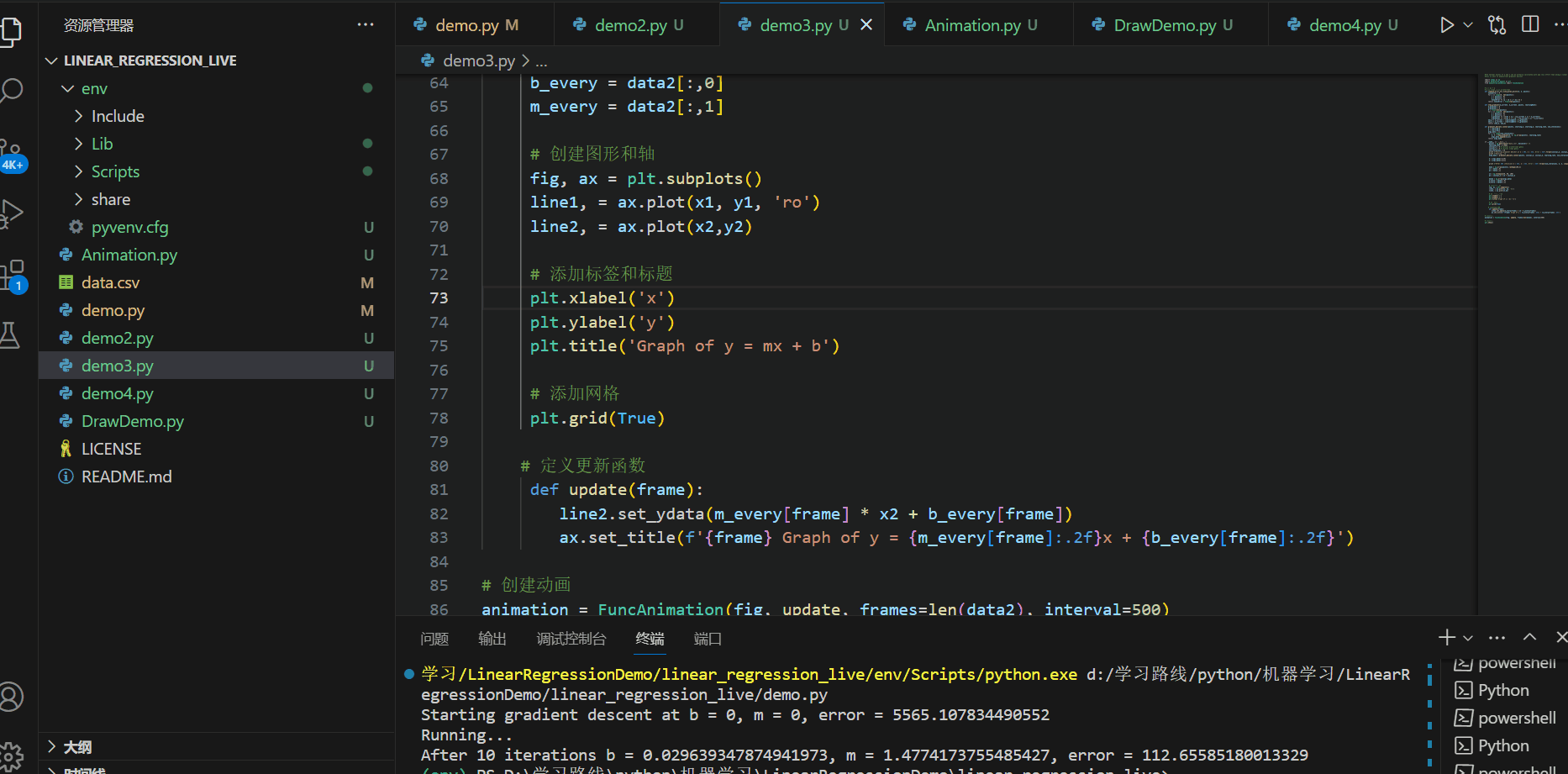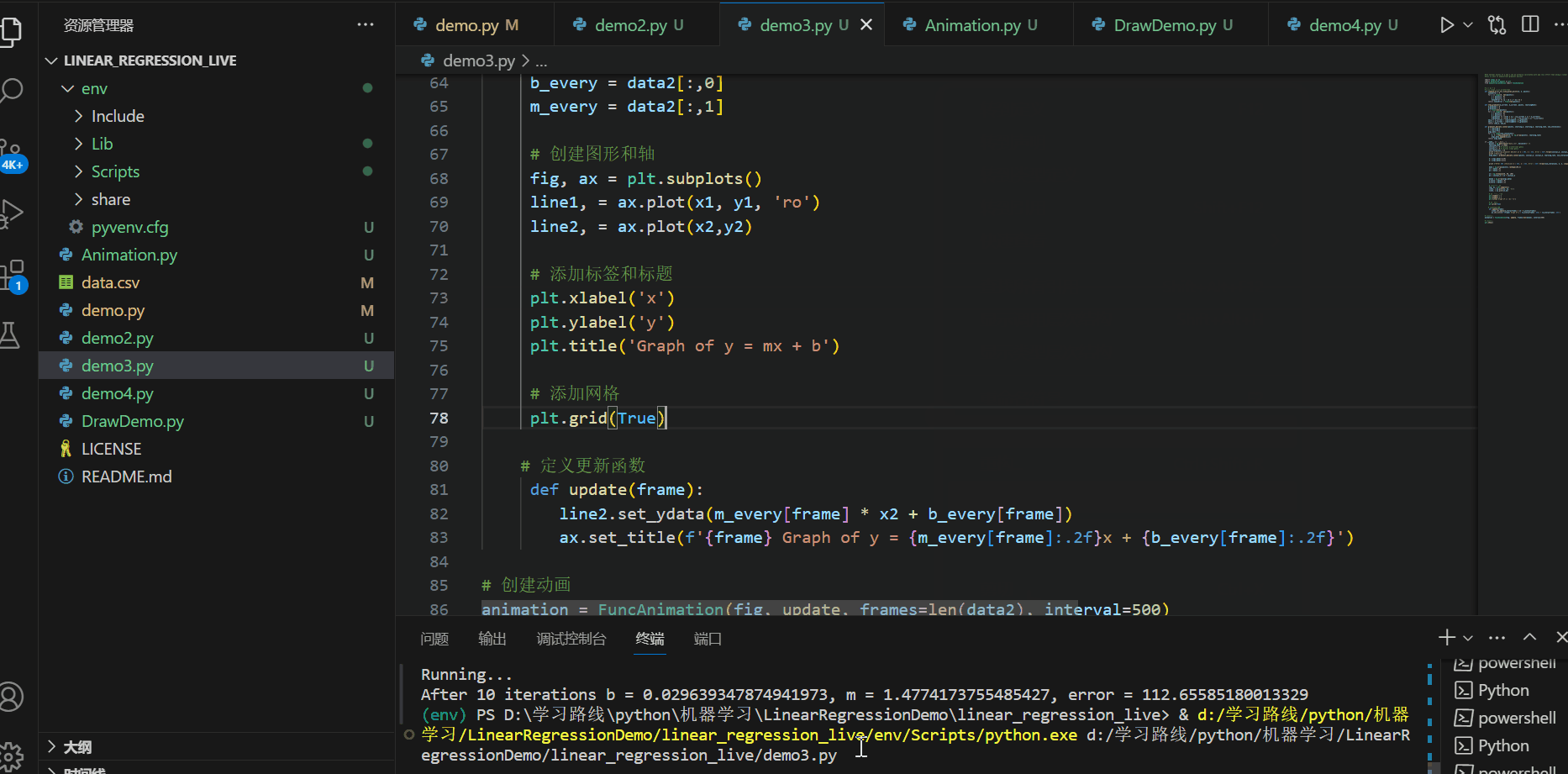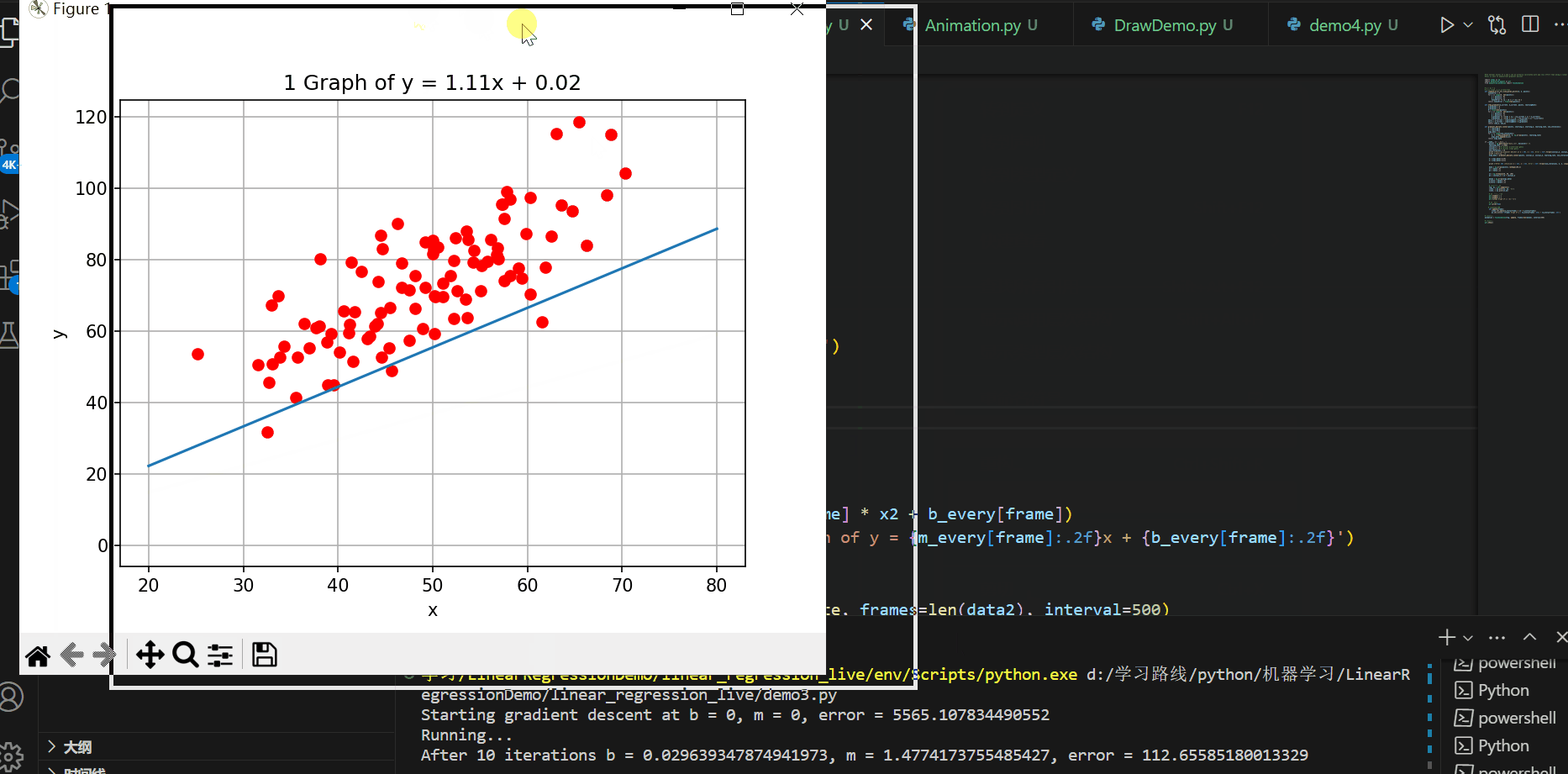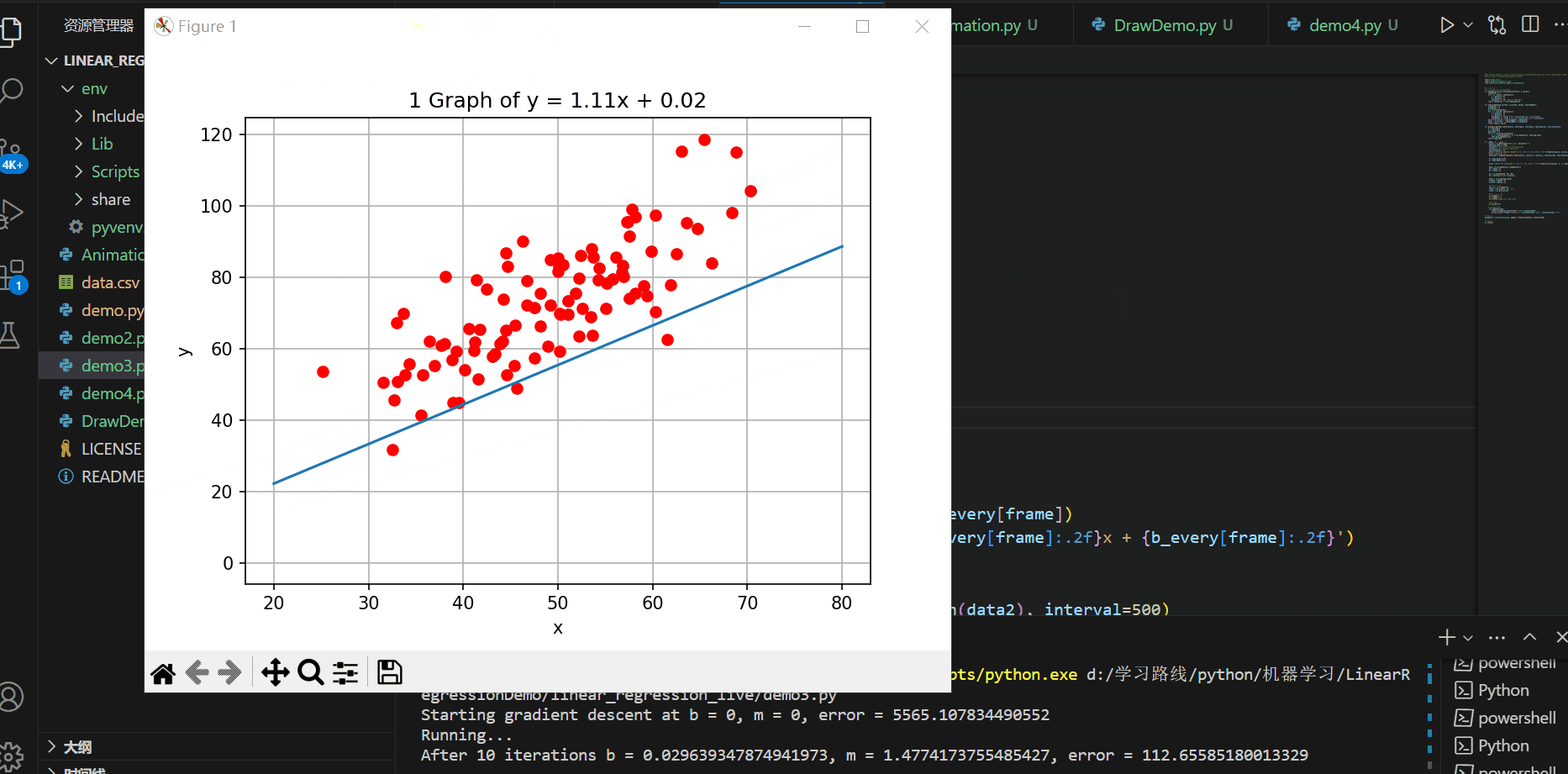

C#代码进行可视化
这是本文重点介绍的内容,本文的C#代码通过Scottplot进行可视化。
Scottplot简介
ScottPlot 是一个免费的开源绘图库,用于 .NET,可以轻松以交互方式显示大型数据集。
控制台程序可视化
首先我先介绍一下在控制台程序中进行可视化。
首先添加Scottplot包:
将上篇文章中的C#代码修改如下:
using NumSharp;
namespace LinearRegressionDemo
{
internal class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
//创建double类型的列表
List<double> Array = new List<double>();
List<double> ArgsList = new List<double>();
// 指定CSV文件的路径
string filePath = "你的data.csv路径";
// 调用ReadCsv方法读取CSV文件数据
Array = ReadCsv(filePath);
var array = np.array(Array).reshape(100,2);
double learning_rate = 0.0001;
double initial_b = 0;
double initial_m = 0;
double num_iterations = 10;
Console.WriteLine($"Starting gradient descent at b = {initial_b}, m = {initial_m}, error = {compute_error_for_line_given_points(initial_b, initial_m, array)}");
Console.WriteLine("Running...");
ArgsList = gradient_descent_runner(array, initial_b, initial_m, learning_rate, num_iterations);
double b = ArgsList[ArgsList.Count - 2];
double m = ArgsList[ArgsList.Count - 1];
Console.WriteLine($"After {num_iterations} iterations b = {b}, m = {m}, error = {compute_error_for_line_given_points(b, m, array)}");
Console.ReadLine();
var x1 = array[$":", 0];
var y1 = array[$":", 1];
var y2 = m * x1 + b;
ScottPlot.Plot myPlot = new(400, 300);
myPlot.AddScatterPoints(x1.ToArray<double>(), y1.ToArray<double>(), markerSize: 5);
myPlot.AddScatter(x1.ToArray<double>(), y2.ToArray<double>(), markerSize: 0);
myPlot.Title($"y = {m:0.00}x + {b:0.00}");
myPlot.SaveFig("图片.png");
}
static List<double> ReadCsv(string filePath)
{
List<double> array = new List<double>();
try
{
// 使用File.ReadAllLines读取CSV文件的所有行
string[] lines = File.ReadAllLines(filePath);
// 遍历每一行数据
foreach (string line in lines)
{
// 使用逗号分隔符拆分每一行的数据
string[] values = line.Split(',');
// 打印每一行的数据
foreach (string value in values)
{
array.Add(Convert.ToDouble(value));
}
}
}
catch (Exception ex)
{
Console.WriteLine("发生错误: " + ex.Message);
}
return array;
}
public static double compute_error_for_line_given_points(double b,double m,NDArray array)
{
double totalError = 0;
for(int i = 0;i < array.shape[0];i++)
{
double x = array[i, 0];
double y = array[i, 1];
totalError += Math.Pow((y - (m*x+b)),2);
}
return totalError / array.shape[0];
}
public static double[] step_gradient(double b_current,double m_current,NDArray array,double learningRate)
{
double[] args = new double[2];
double b_gradient = 0;
double m_gradient = 0;
double N = array.shape[0];
for (int i = 0; i < array.shape[0]; i++)
{
double x = array[i, 0];
double y = array[i, 1];
b_gradient += -(2 / N) * (y - ((m_current * x) + b_current));
m_gradient += -(2 / N) * x * (y - ((m_current * x) + b_current));
}
double new_b = b_current - (learningRate * b_gradient);
double new_m = m_current - (learningRate * m_gradient);
args[0] = new_b;
args[1] = new_m;
return args;
}
public static List<double> gradient_descent_runner(NDArray array, double starting_b, double starting_m, double learningRate,double num_iterations)
{
double[] args = new double[2];
List<double> argsList = new List<double>();
args[0] = starting_b;
args[1] = starting_m;
for(int i = 0 ; i < num_iterations; i++)
{
args = step_gradient(args[0], args[1], array, learningRate);
argsList.AddRange(args);
}
return argsList;
}
}
}
然后得到的图片如下所示:
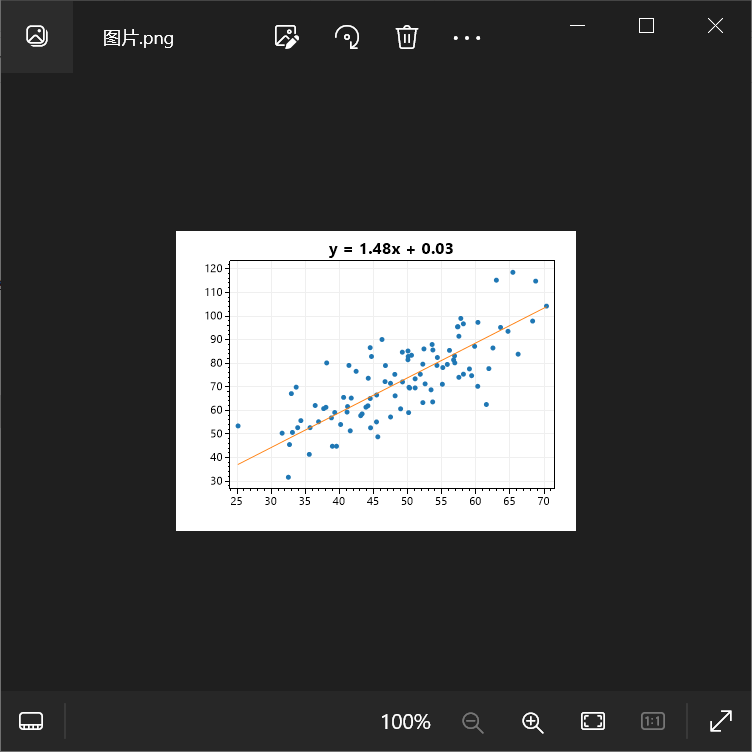
在以上代码中需要注意的地方:
var x1 = array[$":", 0];
var y1 = array[$":", 1];
是在使用NumSharp中的切片,x1表示所有行的第一列,y1表示所有行的第二列。
当然我们不满足于只是保存图片,在控制台应用程序中,再添加一个 ScottPlot.WinForms包:
右键控制台项目选择属性,将目标OS改为Windows:

将上述代码中的
myPlot.SaveFig("图片.png");
var viewer = new ScottPlot.FormsPlotViewer(myPlot);
viewer.ShowDialog();
再次运行结果如下:

winform进行可视化
我也想像Python代码中那样画动图,因此做了个winform程序进行演示。
首先创建一个winform,添加ScottPlot.WinForms包,然后从工具箱中添加FormsPlot这个控件:
有两种方法实现,第一种方法用了定时器:
using NumSharp;
namespace WinFormDemo
{
public partial class Form1 : Form
{
System.Windows.Forms.Timer updateTimer = new System.Windows.Forms.Timer();
int num_iterations;
int count = 0;
NDArray? x1, y1, b_each, m_each;
public Form1()
{
InitializeComponent();
}
private void button1_Click(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
StartLinearRegression();
}
public void StartLinearRegression()
{
//创建double类型的列表
List<double> Array = new List<double>();
List<double> ArgsList = new List<double>();
// 指定CSV文件的路径
string filePath = "你的data.csv路径";
// 调用ReadCsv方法读取CSV文件数据
Array = ReadCsv(filePath);
var array = np.array(Array).reshape(100, 2);
double learning_rate = 0.0001;
double initial_b = 0;
double initial_m = 0;
num_iterations = 10;
ArgsList = gradient_descent_runner(array, initial_b, initial_m, learning_rate, num_iterations);
x1 = array[$":", 0];
y1 = array[$":", 1];
var argsArr = np.array(ArgsList).reshape(num_iterations, 2);
b_each = argsArr[$":", 0];
m_each = argsArr[$":", 1];
double b = b_each[-1];
double m = m_each[-1];
var y2 = m * x1 + b;
formsPlot1.Plot.AddScatterPoints(x1.ToArray<double>(), y1.ToArray<double>(), markerSize: 5);
//formsPlot1.Plot.AddScatter(x1.ToArray<double>(), y2.ToArray<double>(), markerSize: 0);
formsPlot1.Render();
}
static List<double> ReadCsv(string filePath)
{
List<double> array = new List<double>();
try
{
// 使用File.ReadAllLines读取CSV文件的所有行
string[] lines = File.ReadAllLines(filePath);
// 遍历每一行数据
foreach (string line in lines)
{
// 使用逗号分隔符拆分每一行的数据
string[] values = line.Split(',');
// 打印每一行的数据
foreach (string value in values)
{
array.Add(Convert.ToDouble(value));
}
}
}
catch (Exception ex)
{
Console.WriteLine("发生错误: " + ex.Message);
}
return array;
}
public static double compute_error_for_line_given_points(double b, double m, NDArray array)
{
double totalError = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < array.shape[0]; i++)
{
double x = array[i, 0];
double y = array[i, 1];
totalError += Math.Pow((y - (m * x + b)), 2);
}
return totalError / array.shape[0];
}
public static double[] step_gradient(double b_current, double m_current, NDArray array, double learningRate)
{
double[] args = new double[2];
double b_gradient = 0;
double m_gradient = 0;
double N = array.shape[0];
for (int i = 0; i < array.shape[0]; i++)
{
double x = array[i, 0];
double y = array[i, 1];
b_gradient += -(2 / N) * (y - ((m_current * x) + b_current));
m_gradient += -(2 / N) * x * (y - ((m_current * x) + b_current));
}
double new_b = b_current - (learningRate * b_gradient);
double new_m = m_current - (learningRate * m_gradient);
args[0] = new_b;
args[1] = new_m;
return args;
}
public static List<double> gradient_descent_runner(NDArray array, double starting_b, double starting_m, double learningRate, double num_iterations)
{
double[] args = new double[2];
List<double> argsList = new List<double>();
args[0] = starting_b;
args[1] = starting_m;
for (int i = 0; i < num_iterations; i++)
{
args = step_gradient(args[0], args[1], array, learningRate);
argsList.AddRange(args);
}
return argsList;
}
private void button2_Click(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
// 初始化定时器
updateTimer.Interval = 1000; // 设置定时器触发间隔(毫秒)
updateTimer.Tick += UpdateTimer_Tick;
updateTimer.Start();
}
private void UpdateTimer_Tick(object? sender, EventArgs e)
{
if (count >= num_iterations)
{
updateTimer.Stop();
}
else
{
UpdatePlot(count);
}
count++;
}
public void UpdatePlot(int count)
{
double b = b_each?[count];
double m = m_each?[count];
var y2 = m * x1 + b;
formsPlot1.Plot.Clear();
formsPlot1.Plot.AddScatterPoints(x1?.ToArray<double>(), y1?.ToArray<double>(), markerSize: 5);
formsPlot1.Plot.AddScatter(x1?.ToArray<double>(), y2.ToArray<double>(), markerSize: 0);
formsPlot1.Plot.Title($"第{count + 1}次迭代:y = {m:0.00}x + {b:0.00}");
formsPlot1.Render();
}
private void button3_Click(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
updateTimer.Stop();
}
private void Form1_Load(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
}
}
}
简单介绍一下思路,首先创建List<double> argsList用来保存每次迭代生成的参数b、m,然后用
var argsArr = np.array(ArgsList).reshape(num_iterations, 2);
将argsList通过np.array()方法转化为NDArray,然后再调用reshape方法,转化成行数等于迭代次数,列数为2,即每一行对应一组参数值b、m。
b_each = argsArr[$":", 0];
m_each = argsArr[$":", 1];
argsArr[$":", 0]表示每一行中第一列的值,也就是每一个b,argsArr[$":", 1]表示每一行中第二列的值。
double b = b_each[-1];
double m = m_each[-1];
b_each[-1]用了NumSharp的功能表示b_each最后一个元素。
实现效果如下所示:


另一种方法可以通过异步实现:
using NumSharp;
namespace WinFormDemo
{
public partial class Form2 : Form
{
int num_iterations;
NDArray? x1, y1, b_each, m_each;
public Form2()
{
InitializeComponent();
}
private void button1_Click(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
StartLinearRegression();
}
public void StartLinearRegression()
{
//创建double类型的列表
List<double> Array = new List<double>();
List<double> ArgsList = new List<double>();
// 指定CSV文件的路径
string filePath = "你的data.csv路径";
// 调用ReadCsv方法读取CSV文件数据
Array = ReadCsv(filePath);
var array = np.array(Array).reshape(100, 2);
double learning_rate = 0.0001;
double initial_b = 0;
double initial_m = 0;
num_iterations = 10;
ArgsList = gradient_descent_runner(array, initial_b, initial_m, learning_rate, num_iterations);
x1 = array[$":", 0];
y1 = array[$":", 1];
var argsArr = np.array(ArgsList).reshape(num_iterations, 2);
b_each = argsArr[$":", 0];
m_each = argsArr[$":", 1];
double b = b_each[-1];
double m = m_each[-1];
var y2 = m * x1 + b;
formsPlot1.Plot.AddScatterPoints(x1.ToArray<double>(), y1.ToArray<double>(), markerSize: 5);
formsPlot1.Render();
}
static List<double> ReadCsv(string filePath)
{
List<double> array = new List<double>();
try
{
// 使用File.ReadAllLines读取CSV文件的所有行
string[] lines = File.ReadAllLines(filePath);
// 遍历每一行数据
foreach (string line in lines)
{
// 使用逗号分隔符拆分每一行的数据
string[] values = line.Split(',');
// 打印每一行的数据
foreach (string value in values)
{
array.Add(Convert.ToDouble(value));
}
}
}
catch (Exception ex)
{
Console.WriteLine("发生错误: " + ex.Message);
}
return array;
}
public static double compute_error_for_line_given_points(double b, double m, NDArray array)
{
double totalError = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < array.shape[0]; i++)
{
double x = array[i, 0];
double y = array[i, 1];
totalError += Math.Pow((y - (m * x + b)), 2);
}
return totalError / array.shape[0];
}
public static double[] step_gradient(double b_current, double m_current, NDArray array, double learningRate)
{
double[] args = new double[2];
double b_gradient = 0;
double m_gradient = 0;
double N = array.shape[0];
for (int i = 0; i < array.shape[0]; i++)
{
double x = array[i, 0];
double y = array[i, 1];
b_gradient += -(2 / N) * (y - ((m_current * x) + b_current));
m_gradient += -(2 / N) * x * (y - ((m_current * x) + b_current));
}
double new_b = b_current - (learningRate * b_gradient);
double new_m = m_current - (learningRate * m_gradient);
args[0] = new_b;
args[1] = new_m;
return args;
}
public static List<double> gradient_descent_runner(NDArray array, double starting_b, double starting_m, double learningRate, double num_iterations)
{
double[] args = new double[2];
List<double> argsList = new List<double>();
args[0] = starting_b;
args[1] = starting_m;
for (int i = 0; i < num_iterations; i++)
{
args = step_gradient(args[0], args[1], array, learningRate);
argsList.AddRange(args);
}
return argsList;
}
private void Form2_Load(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
}
public async Task UpdateGraph()
{
for (int i = 0; i < num_iterations; i++)
{
double b = b_each?[i];
double m = m_each?[i];
var y2 = m * x1 + b;
formsPlot1.Plot.Clear();
formsPlot1.Plot.AddScatterPoints(x1?.ToArray<double>(), y1?.ToArray<double>(), markerSize: 5);
formsPlot1.Plot.AddScatter(x1?.ToArray<double>(), y2.ToArray<double>(), markerSize: 0);
formsPlot1.Plot.Title($"第{i + 1}次迭代:y = {m:0.00}x + {b:0.00}");
formsPlot1.Render();
await Task.Delay(1000);
}
}
private async void button2_Click(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
await UpdateGraph();
}
}
}
点击更新按钮开始执行异步任务:
private async void button2_Click(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
await UpdateGraph();
}
public async Task UpdateGraph()
{
for (int i = 0; i < num_iterations; i++)
{
double b = b_each?[i];
double m = m_each?[i];
var y2 = m * x1 + b;
formsPlot1.Plot.Clear();
formsPlot1.Plot.AddScatterPoints(x1?.ToArray<double>(), y1?.ToArray<double>(), markerSize: 5);
formsPlot1.Plot.AddScatter(x1?.ToArray<double>(), y2.ToArray<double>(), markerSize: 0);
formsPlot1.Plot.Title($"第{i + 1}次迭代:y = {m:0.00}x + {b:0.00}");
formsPlot1.Render();
await Task.Delay(1000);
}
实现效果如下:
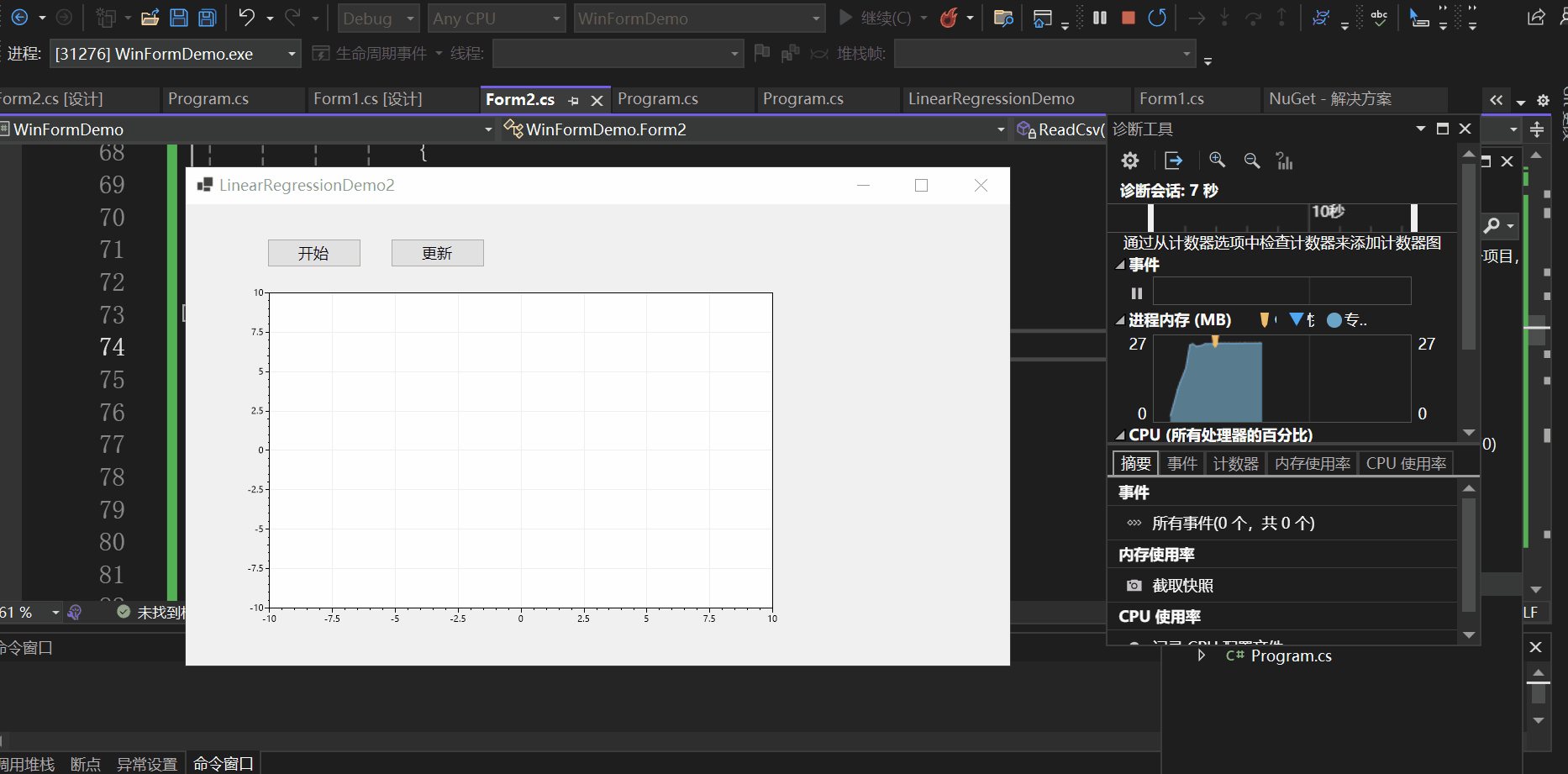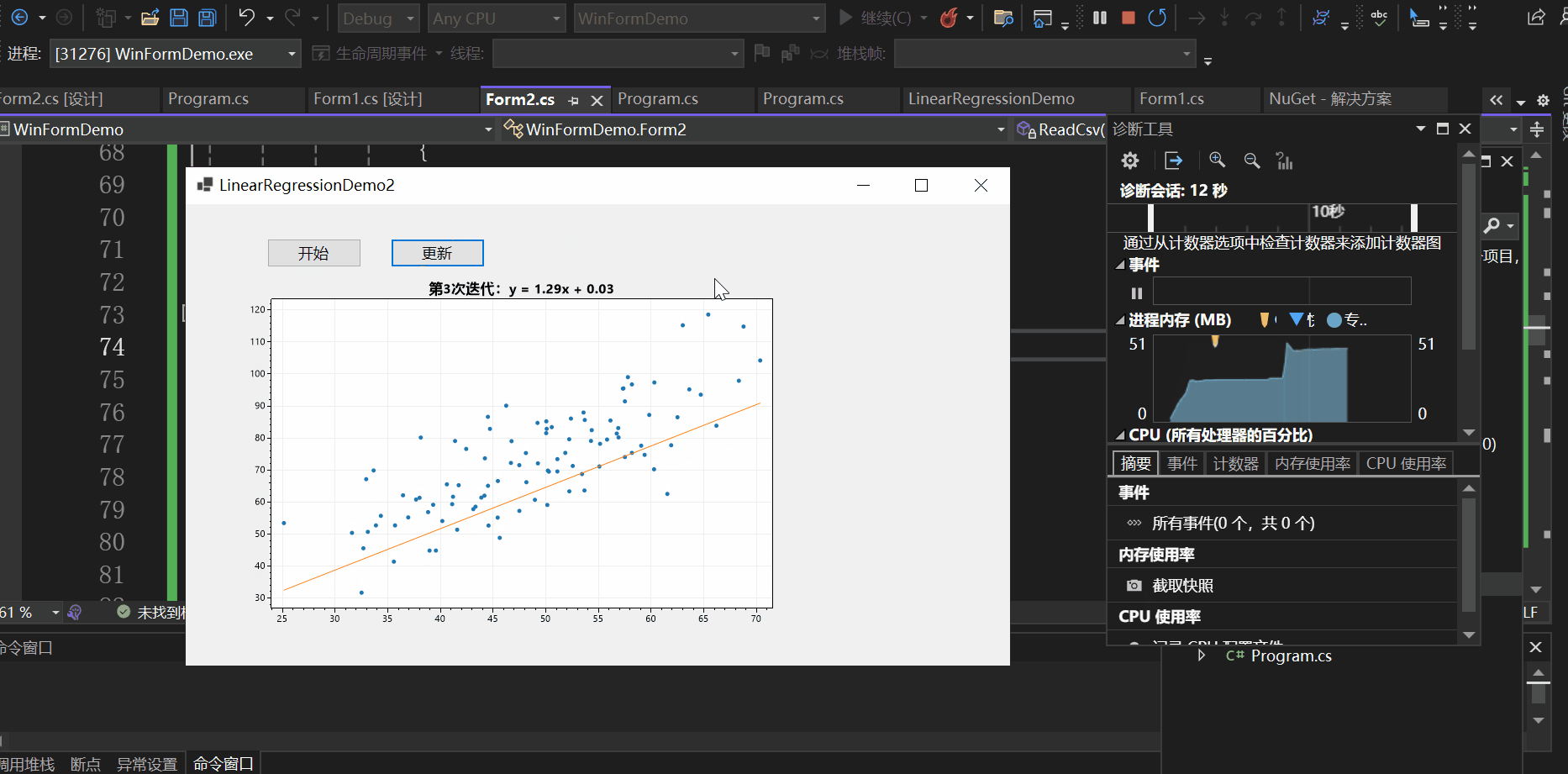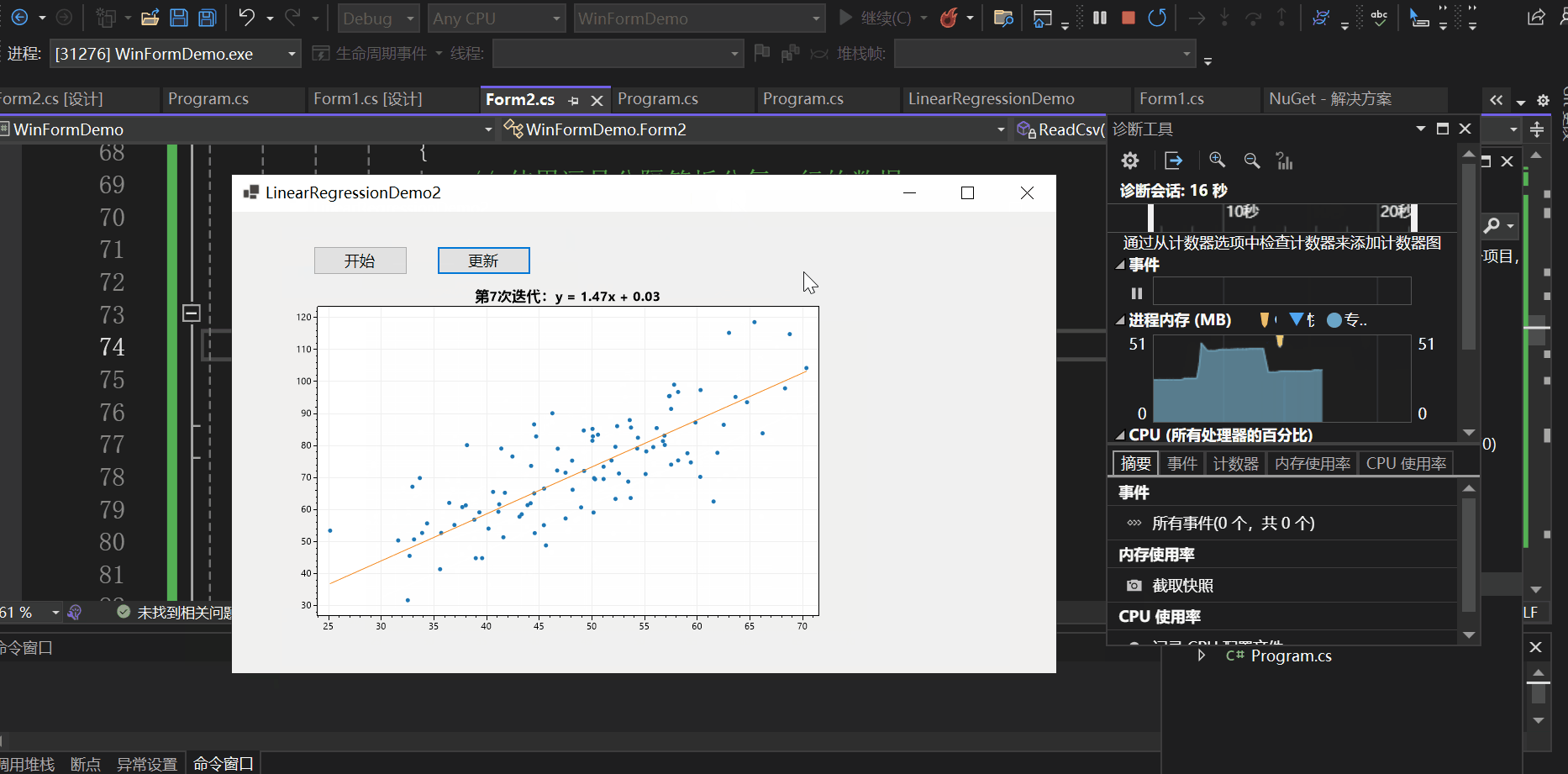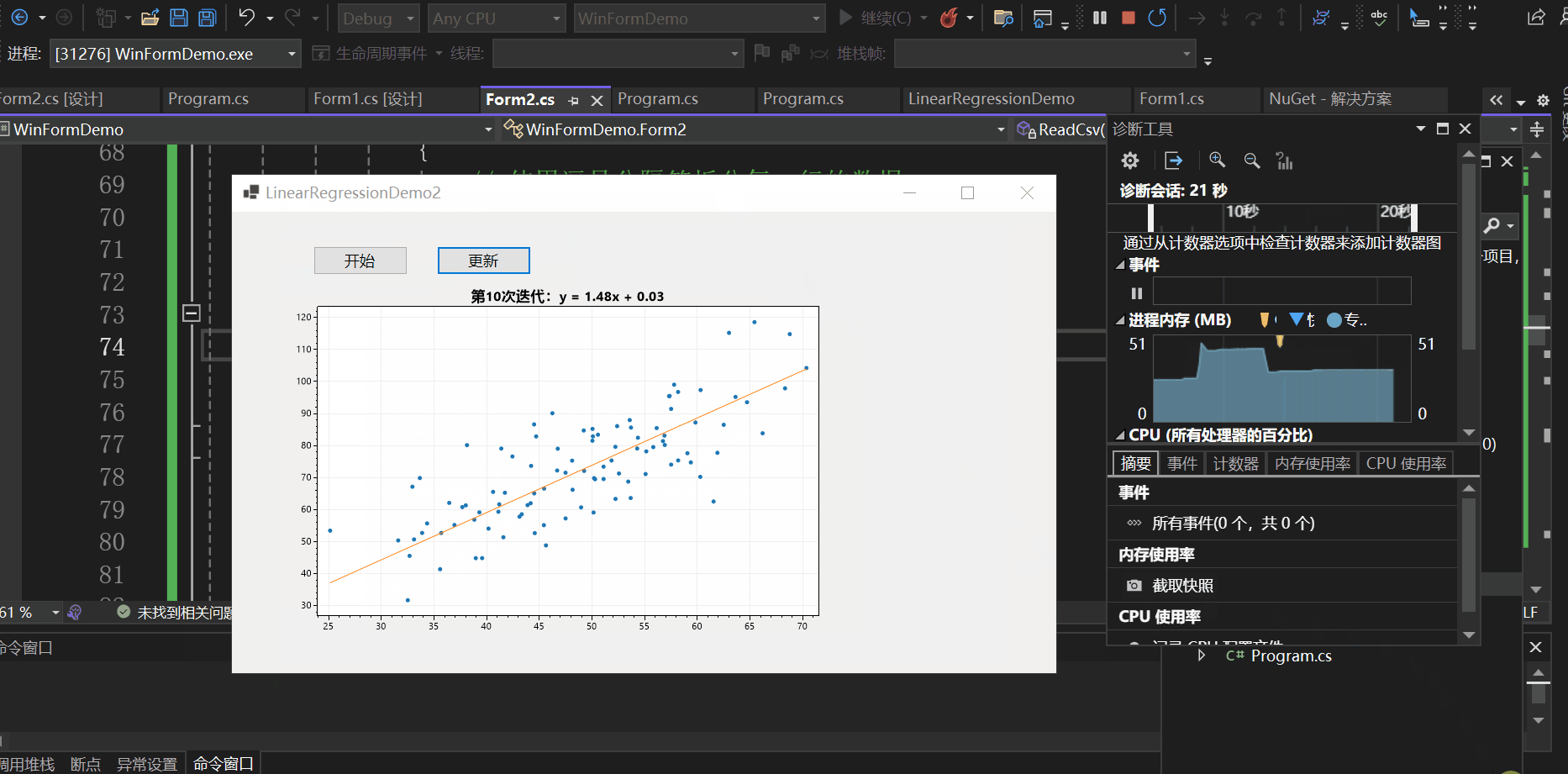
本文以一个控制台应用与一个winform程序为例向大家介绍了C#如何基于ScottPlot进行数据可视化,并介绍了实现动态绘图的两种方式,一种是使用定时器,另一种是使用异步操作,希望对你有所帮助。
Recommend
About Joyk
Aggregate valuable and interesting links.
Joyk means Joy of geeK