

聊一聊装饰者模式_知了一笑的技术博客_51CTO博客
source link: https://blog.51cto.com/cicadasmile/5885526
Go to the source link to view the article. You can view the picture content, updated content and better typesetting reading experience. If the link is broken, please click the button below to view the snapshot at that time.
是你,还是你,一切都有你!—— 装饰者模式
装饰者模式(Decorator Pattern)允许向一个现有的对象扩展新的功能,同时不改变其结构。主要解决直接继承下因功能的不断横向扩展导致子类膨胀的问题,无需考虑子类的维护。
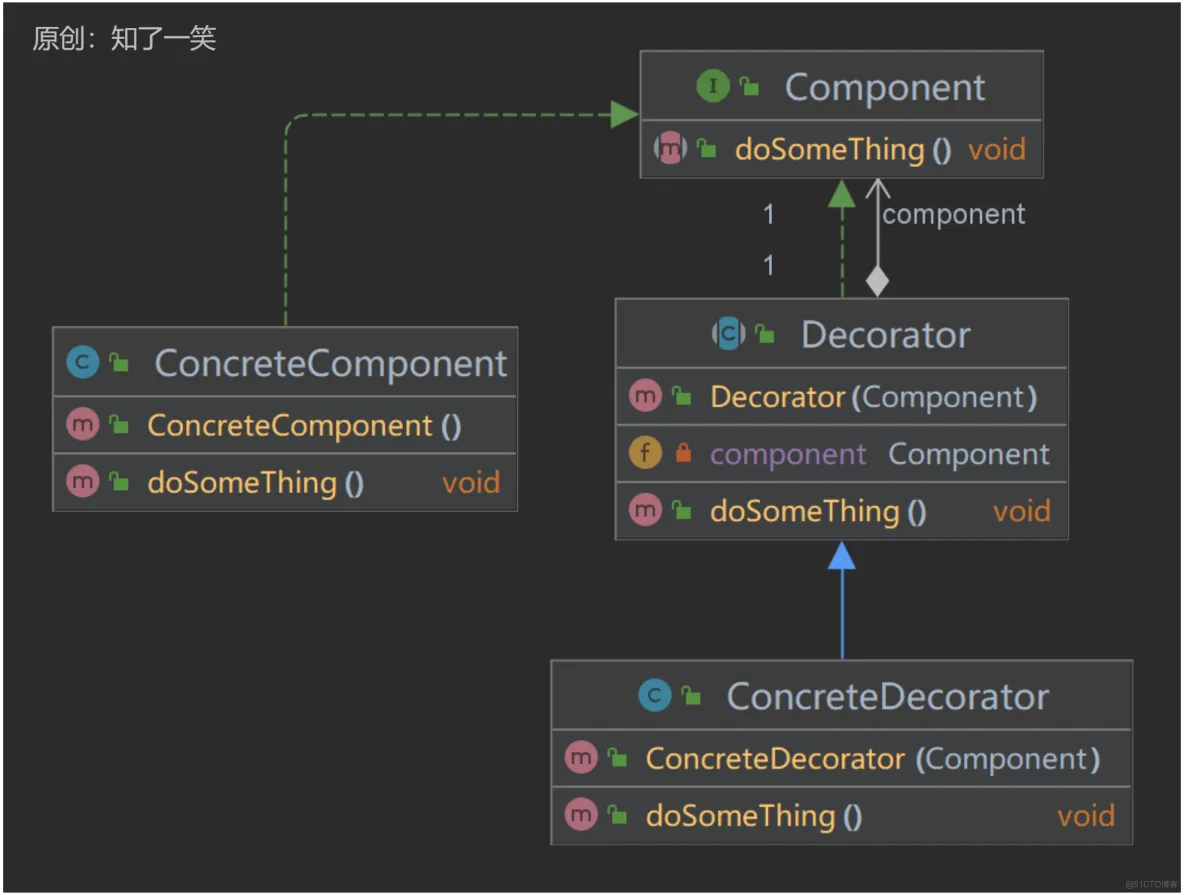
装饰者模式有4种角色:
- 抽象构件角色(Component):具体构件类和抽象装饰者类的共同父类。
- 具体构件角色(ConcreteComponent):抽象构件的子类,装饰者类可以给它增加额外的职责。
- 装饰角色(Decorator):抽象构件的子类,具体装饰类的父类,用于给具体构件增加职责,但在子类中实现。
- 具体装饰角色(ConcreteDecorator):具体装饰类,定义了一些新的行为,向构件类添加新的特性。
二、入门案例
2.1、类图
2.2、基础类介绍
// 抽象构件角色
public interface Component {
void doSomeThing();
}
// 具体构件角色
public class ConcreteComponent implements Component {
@Override
public void doSomeThing() {
System.out.println("处理业务逻辑");
}
}
// 装饰者类
public abstract class Decorator implements Component {
private Component component;
public Decorator(Component component) {
this.component = component;
}
@Override
public void doSomeThing() {
// 调用处理业务逻辑
component.doSomeThing();
}
}
// 具体装饰类
public class ConcreteDecorator extends Decorator {
public ConcreteDecorator(Component component) {
super(component);
}
@Override
public void doSomeThing() {
System.out.println("业务逻辑功能扩展");
super.doSomeThing();
}
}
当然,如果需要扩展更多功能的话,可以再定义其他的ConcreteDecorator类,实现其他的扩展功能。
如果只有一个ConcreteDecorator类,那么就没有必要建立一个单独的Decorator类,而可以把Decorator和ConcreteDecorator的责任合并成一个类。
三、应用场景
1.如风之前在一家保险公司干过一段时间。其中保险业务员也会在自家产品注册账号,进行推销。不过在这之前,他们需要经过培训,导入一张展业资格证书。然后再去推销保险产品供用户下单,自己则通过推销产生的业绩,参与分润,拿对应的佣金。
2.对于上面导证书这个场景,实际上是会根据不同的保险产品,导入不同的证书的。并且证书的类型也不同,对应的解析、校验、执行的业务场景都是不同的。如何去实现呢?当然if-else确实也是一种不错的选择。下面放一段伪代码:
/**
* @author 往事如风
* @version 1.0
* @date 2022/11/17 11:32
* @description
*/
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/certificate")
public class CertificateController {
@Resource
private CommonCertificateService certificateService;
@PostMapping("/import")
public Result<Integer> importFile(@RequestParam MultipartFile file, @RequestParam String productCode) {
return Result.success(certificateService.importCertificate(file, productCode));
}
}
/**
* @author 往事如风
* @version 1.0
* @date 2022/11/17 13:25
* @description
*/
@Service
public class CommonCertificateService {
public Integer importCertificate(MultipartFile file, String productCode) {
// 1、参数非空校验
// 2、通过file后缀判断file类型,支持excel和pdf
// 3、解析file文件,获取数据,统一封装到定义的CertificatePojo类中
// 4、根据产品类型判断导入之前的业务逻辑
if (productCode.equals(DecorateConstants.PRODUCT_A)) {
// 重新计算业绩逻辑
// 重新算业绩类型逻辑
// 一坨坨代码去实现....
}
else if (productCode.equals(DecorateConstants.PRODUCT_B)) {
// 导入证书的代理人自己以及上级身份晋升逻辑
// 业绩计算逻辑
// 一坨坨代码去实现...
} else if (productCode.equals(DecorateConstants.PRODUCT_C)) {
// c产品下的业务逻辑
// 一坨坨代码去实现...
} else {
// 默认的处理逻辑
// 一坨坨代码去实现...
}
// 5、证书数据保存
// 6、代理人信息保存
// 7、相关流水数据保存
// 返回代理人id
Integer agentId = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
return agentId;
}
}
从上面的伪代码看到,所有的业务逻辑是在一起处理的,通过productCode去处理对应产品的相关逻辑。这么一看,好像也没毛病,但是还是被技术大佬给否决了。好吧,如风决定重写。运用装饰者模式,重新处理下了下这段代码。
1、一切再从注解出发,自定义Decorate注解,这里定义2个属性,scene和type
- scene:标记具体的业务场景
- type:表示在该种业务场景下,定义一种具体的装饰器类
/**
* @author 往事如风
* @version 1.0
* @date 2022/11/8 17:44
* @description
*/
@Target({ElementType.TYPE})
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Documented
@Inherited
@Service
public @interface Decorate {
/**
* 具体的业务场景
* @return
*/
String scene();
/**
* 类型:不同业务场景下,不同的装饰器类型
* @return
*/
String type();
}
2、抽象构件接口,BaseHandler,这个是必须滴
/**
* @author 往事如风
* @version 1.0
* @date 2022/11/8 17:07
* @description 抽象处理接口
*/
public interface BaseHandler<T, R> {
/**
* 统一的处理方法
* @param t
* @return
*/
R handle(T t);
}
3、抽象装饰器类,AbstractHandler,持有一个被装饰类的引用,这个引用具体在运行时被指定
/**
* @author 往事如风
* @version 1.0
* @date 2022-11-13 22:10:05
* @desc 抽象父类
*/
public abstract class AbstractHandler<T, R> implements BaseHandler<T, R> {
protected BaseHandler service;
public void setService(BaseHandler service) {
this.service = service;
}
}
4、具体的装饰器类AProductServiceDecorate,主要负责处理“导师证书”这个业务场景下,A产品相关的导入逻辑,并且标记了自定义注解Decorate,表示该类是装饰器类。主要负责对A产品证书导入之前逻辑的增强,我们这里称之为“装饰”。
/**
* @author 往事如风
* @version 1.0
* @date 2022-11-13 23:11:16
* @desc
*/
@Decorate(scene = SceneConstants.CERTIFICATE_IMPORT, type = DecorateConstants.PRODUCT_A)
public class AProductServiceDecorate extends AbstractHandler<MultipartFile, Integer> {
/**
* 重写父类处理数据方法
* @param file
* @return
*/
@Override
public Integer handle(MultipartFile file) {
// 解析
CertificatePojo data = parseData(file);
// 校验
check(data);
// 业绩计算
calAchievement(data.getMobile());
return (Integer) service.handle(data);
}
public CertificatePojo parseData(MultipartFile file) {
// file,证书解析
System.out.println("A产品的证书解析......");
CertificatePojo certificatePojo = new CertificatePojo();
certificatePojo.setMobile("12323");
certificatePojo.setName("张三");
certificatePojo.setMemberNo("req_343242ds");
certificatePojo.setEffectDate("2022-10-31:20:20:10");
return certificatePojo;
}
/**
* 证书数据校验
* @param data
*/
public void check(CertificatePojo data) {
// 数据规范和重复性校验
// .....
System.out.println("A证书数据校验......");
}
/**
* 计算业绩信息
*/
private void calAchievement(String mobile) {
System.out.println("查询用户信息, 手机号:" + mobile);
System.out.println("重新计算业绩...");
}
}
当然,还是其他装饰类,BProductServiceDecorate,CProductServiceDecorate等等,负责装饰其他产品,这里就不举例了。
5、当然还有管理装饰器类的装饰器类管理器DecorateManager,内部维护一个map,负责存放具体的装饰器类
/**
* @author 往事如风
* @version 1.0
* @date 2022/11/15 17:18
* @description 装饰管理器
*/
public class DecorateManager {
/**
* 用于存放装饰器类
*/
private Map<String, AbstractHandler> decorateHandleMap = new HashMap<>();
/**
* 将具体装饰器类放在map中
*
* @param handlerList
*/
public void setDecorateHandler(List<AbstractHandler> handlerList) {
for (AbstractHandler h : handlerList) {
Decorate annotation = AnnotationUtils.findAnnotation(h.getClass(), Decorate.class);
decorateHandleMap.put(createKey(annotation.scene(), annotation.type()), h);
}
}
/**
* 返回具体的装饰器类
*
* @param type
* @return
*/
public AbstractHandler selectHandler(String scene, String type) {
String key = createKey(scene, type);
return decorateHandleMap.get(key);
}
/**
* 拼接map的key
* @param scene
* @param type
* @return
*/
private String createKey(String scene, String type) {
return StrUtil.builder().append(scene).append(":").append(type).toString();
}
}
6、用了springboot,当然需要将这个管理器交给spring的bean容器去管理,需要创建一个配置类DecorateAutoConfiguration
/**
* @author 往事如风
* @version 1.0
* @date 2022-11-12 19:22:41
* @desc
*/
@Configuration
public class DecorateAutoConfiguration {
@Bean
public DecorateManager handleDecorate(List<AbstractHandler> handlers) {
DecorateManager manager = new DecorateManager();
manager.setDecorateHandler(handlers);
return manager;
}
}
7、被装饰的service类,CertificateService,只需要关注自己的核心逻辑就可以
/**
* @author 往事如风
* @version 1.0
* @date 2022/11/8 17:10
* @description 执行证书导入的service
*/
@Service
public class CertificateService implements BaseHandler<CertificatePojo, Integer> {
/**
* 处理导入证书的核心逻辑service
* @param certificate
* @return
*/
@Override
public Integer handle(CertificatePojo certificate) {
System.out.println("核心业务,证书数据:" + JSONUtil.toJsonStr(certificate));
// 1、证书数据保存
// 2、代理人信息保存
// 3、相关流水数据保存
// 其他的一些列核心操作
Integer agentId = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
// 返回代理人id
return agentId;
}
}
8、在原来的controller中,注入管理器类DecorateManager去调用,以及service,也就是被装饰的类。首先拿到装饰器,然后再通过setService方法,传入被装饰的service。也就是具体装饰什么类,需要在运行时才确定。
/**
* @author 往事如风
* @version 1.0
* @date 2022-11-13 23:30:37
* @desc
*/
@RestController
public class WebController {
@Resource
private DecorateManager decorateManager;
@Resource
private CertificateService certificateService;
@PostMapping("/import")
public Result importFile(@RequestParam MultipartFile file, @RequestParam String productCode) {
AbstractHandler handler = decorateManager.selectHandler(SceneConstants.CERTIFICATE_IMPORT, productCode);
if (Objects.isNull(handler)) {
return Result.fail();
}
handler.setService(certificateService);
return Result.success(handler.handle(file));
}
}
下面模拟下代理人导入证书的流程,当选择A产品,productCode传A过来,后端的处理流程。
-
对于A产品下,证书的解析,A产品传的是excel
-
然后数据校验,这个产品下,特有的数据校验
-
最后是核心的业绩重算,只有A产品才会有这个逻辑
当选择B产品,productCode传A过来,后端的处理流程。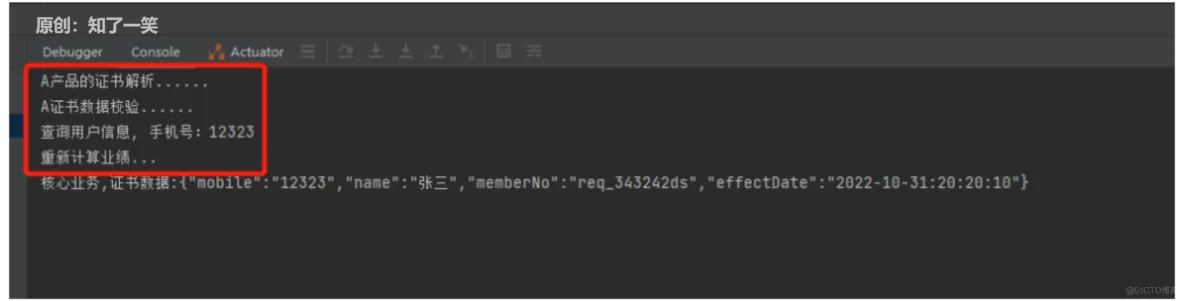
-
对于B产品下,证书的解析,A产品传的是pdf
-
然后数据校验,跟A产品也不同,多了xxx步骤
-
核心是代理人的晋升处理,这部分是B产品独有的
最后说一句,既然都用springboot了,这块可以写一个starter,做一个公用的装饰器模式。如果哪个服务需要用到,依赖这个装饰器的starter,然后标记
Decorate注解,定义对应的scene和type属性,就可以直接使用了。
四、源码中运用
4.1、JDK源码中的运用
来看下IO流中,InputStream、FilterInputStream、FileInputStream、BufferedInputStream的一段代码
public abstract class InputStream implements Closeable {
public abstract int read() throws IOException;
public int read(byte b[], int off, int len) throws IOException {
if (b == null) {
throw new NullPointerException();
} else if (off < 0 || len < 0 || len > b.length - off) {
throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException();
} else if (len == 0) {
return 0;
}
int c = read();
if (c == -1) {
return -1;
}
b[off] = (byte)c;
int i = 1;
try {
for (; i < len ; i++) {
c = read();
if (c == -1) {
break;
}
b[off + i] = (byte)c;
}
} catch (IOException ee) {
}
return i;
}
}
//--------------------------
public class FilterInputStream extends InputStream {
protected FilterInputStream(InputStream in) {
this.in = in;
}
public int read() throws IOException {
return in.read();
}
}
//--------------------------
public class BufferedInputStream extends FilterInputStream {
public BufferedInputStream(InputStream in, int size) {
super(in);
if (size <= 0) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Buffer size <= 0");
}
buf = new byte[size];
}
public BufferedInputStream(InputStream in) {
this(in, DEFAULT_BUFFER_SIZE);
}
public int read() throws IOException {
return in.read();
}
public int read(byte b[], int off, int len) throws IOException {
return in.read(b, off, len);
}
}
//--------------------------
public class FileInputStream extends InputStream {
public int read(byte b[]) throws IOException {
return readBytes(b, 0, b.length);
}
}
再来看下这几个类的类图
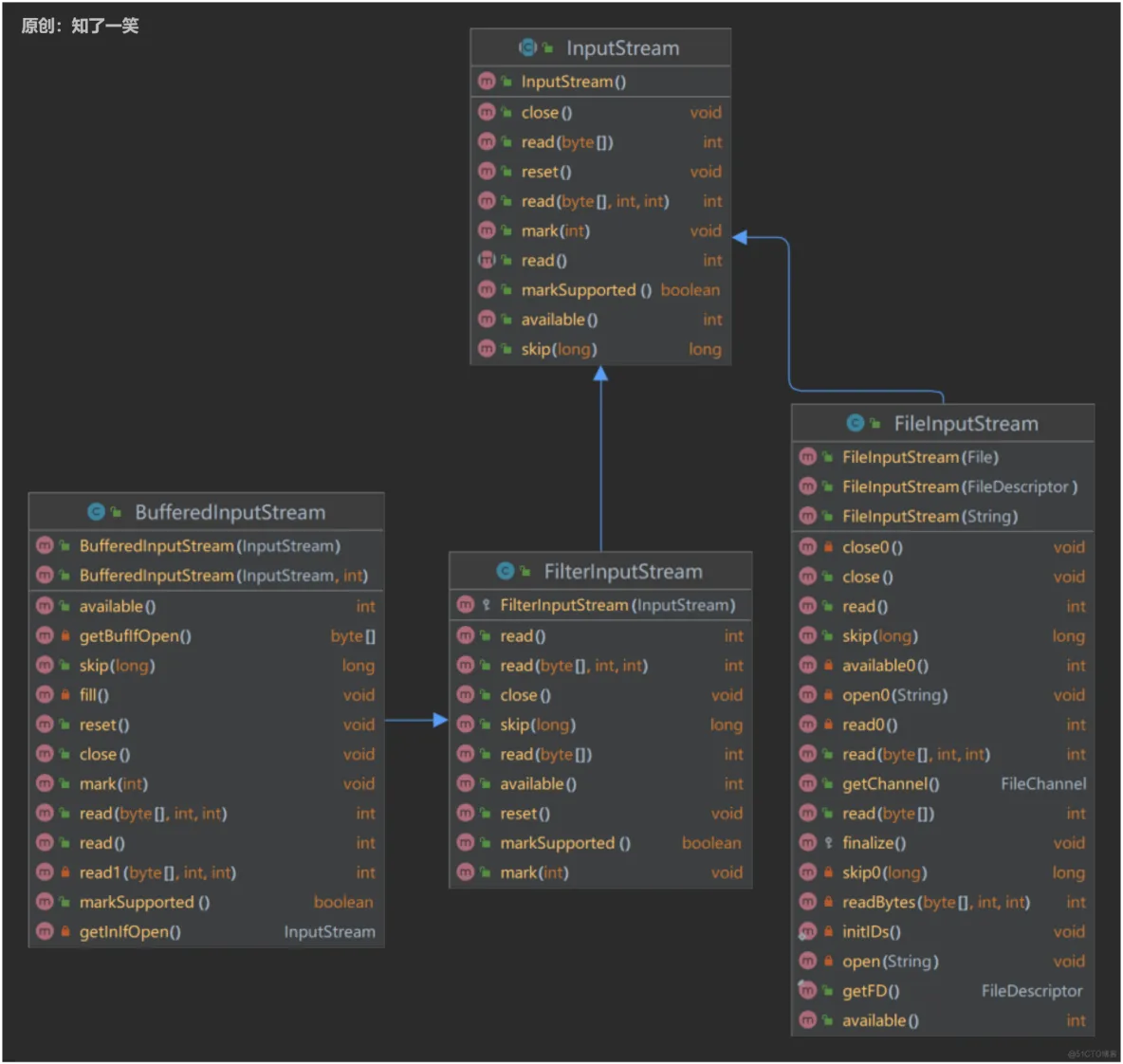
这些类的代码有删改,可以看到BufferedInputStream中定义了很多属性,这些数据都是为了可缓冲读取来作准备的,看到其有构造方法会传入一个InputStream的实例。实际编码如下
//被装饰的对象,文件输入流
InputStream in=new FileInputStream("/data/log/app.log");
//装饰对象,可缓冲
InputStream bufferedIn=new BufferedInputStream(in);
bufferedIn.read();
这里觉得很眼熟吧,其实已经运用了装饰模式了。
4.2、mybatis源码中的运用
在mybatis中,有个接口Executor,顾名思义这个接口是个执行器,它底下有许多实现类,如CachingExecutor、SimpleExecutor、BaseExecutor等等。类图如下:
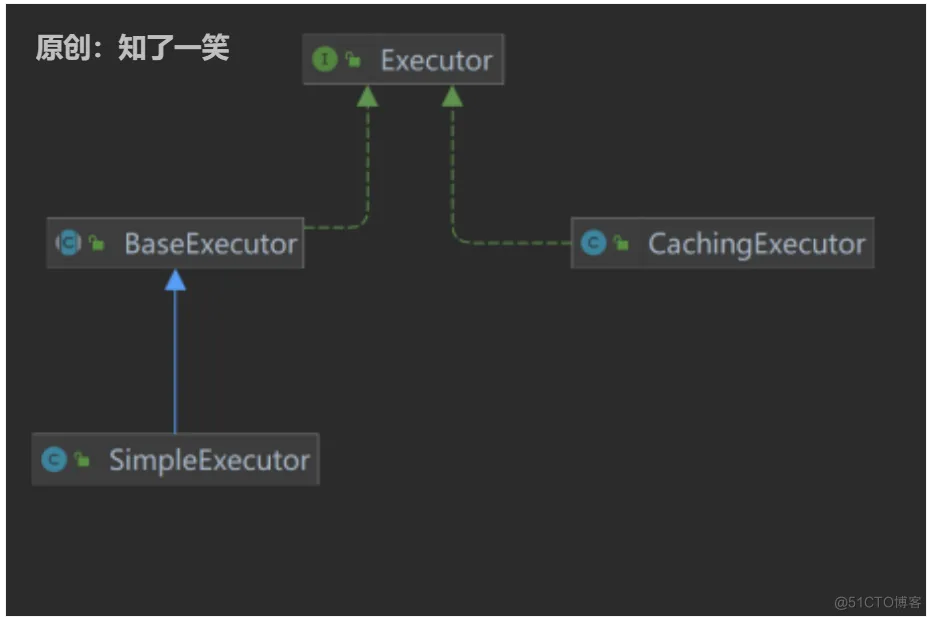
主要看下CachingExecutor类,看着很眼熟,很标准的装饰器。其中该类中的update是装饰方法,在调用真正update方法之前,会执行刷新本地缓存的方法,对原来的update做增强和扩展。
public class CachingExecutor implements Executor {
private final Executor delegate;
private final TransactionalCacheManager tcm = new TransactionalCacheManager();
public CachingExecutor(Executor delegate) {
this.delegate = delegate;
delegate.setExecutorWrapper(this);
}
@Override
public int update(MappedStatement ms, Object parameterObject) throws SQLException {
// 增强内容
// 修改方法就要清空本地的缓存
flushCacheIfRequired(ms);
// 调用原有的方法
return delegate.update(ms, parameterObject);
}
}
再来看下BaseExecutor类,这里有一个update方法,这个是原本的被装饰的update方法。然后再看这个原本的update方法,它调用的doUpdate方法是个抽象方法,用protected修饰。咦,这不就是模板方法么,关于模板方法模式,这里就不展开赘述了。
public abstract class BaseExecutor implements Executor {
protected Executor wrapper;
@Override
public int update(MappedStatement ms, Object parameter) throws SQLException {
ErrorContext.instance().resource(ms.getResource()).activity("executing an update").object(ms.getId());
if (closed) {
throw new ExecutorException("Executor was closed.");
}
clearLocalCache();
return doUpdate(ms, parameter);
}
protected abstract int doUpdate(MappedStatement ms, Object parameter)
throws SQLException;
}
- 通过组合而非继承的方式,动态地扩展一个对象的功能,在运行时可以选择不同的装饰器从而实现不同的功能。
- 有效的避免了使用继承的方式扩展对象功能而带来的灵活性差、子类无限制扩张的问题。
- 具体组件类与具体装饰类可以独立变化,用户可以根据需要新增具体组件类跟装饰类,在使用时在对其进行组合,原有代码无须改变,符合"开闭原则"。
- 这种比继承更加灵活机动的特性,也同时意味着更加多的复杂性。
- 装饰模式会导致设计中出现许多小类 (I/O 类中就是这样),如果过度使用,会使程序变得很复杂。
- 装饰模式是针对抽象组件(Component)类型编程。但是,如果你要针对具体组件编程时,就应该重新思考你的应用架构,以及装饰者是否合适。
六、参考源码
编程文档:
https://gitee.com/cicadasmile/butte-java-note
应用仓库:
https://gitee.com/cicadasmile/butte-flyer-parent
Recommend
About Joyk
Aggregate valuable and interesting links.
Joyk means Joy of geeK