

How MVP Development Filters User Needs
source link: https://dzone.com/articles/how-does-mvp-development-filter-user-needs
Go to the source link to view the article. You can view the picture content, updated content and better typesetting reading experience. If the link is broken, please click the button below to view the snapshot at that time.
How MVP Development Filters User Needs
In this blog, we have covered some of the MVP software design practices that filter user needs, enhance consumer engagement, and generate critical business insights.
Join the DZone community and get the full member experience.
Join For FreeThe success of any product depends on how efficiently and effectively it solves the problems of users. Rethinking the traditional development methods to MVP development has taken priority as it helps businesses in creating and capturing value faster by first understanding the requirements of users. In this blog, we have covered some of the MVP software design practices that filter user needs, enhance consumer engagement by prioritizing features and generate insights to measure business value.
Identifying User Needs Through MVP
MVP product development is important to identify the unsaid needs of customers. It helps in gaining insights based on which an MVP can be built to solve the right problem for the right set of people. However, the success of MVP lies in:
- Uncovering long term product potential
- Building a strategy to unlock the potential
To do both, you need metrics based on research. By nature, metrics are considered quantitative but capturing qualitative feedback on the future prospects of the product is equally important. Extracting information based on the user environment and competitor’s research will also bear fruit.
Qualitative Research
The qualitative method is in-depth research on the end-users. It is about understanding their sentiments. It goes deep into not only understanding the needs of the people but also what they and why they think. The focus essentially is on the ‘why’ behind the customer’s behavior.
Face-to-face interviews and group discussions with people can be held for in-depth feedback. The questions that can be asked in the interviews are:
- Is it easy to use?
- Is the design user-friendly?
- What about the features?
- Is the price reasonable?
Quantitative Research
The quantitative research method is all about gathering information through surveys and customer questionnaires. By using these methods, feedback from potential customers can be gathered. The researchers should be careful about the questions when selecting as the results should provide meaningful data. A few questions inquiring about their shopping habits can be asked. Thes can be:
- How often do you go to the retail store?
- What are the products you buy?
- Any specific reasons for buying them?
- From which store do you shop?
Quantitative research helps in creating a clear understanding of how consumers behave. The information gathered can be used in the future as a guide to making better business decisions.
Ethnographic Research
To extract information from customers, traditional market researchers use highly targeted questions but corporate ethnographers observe and listen in an indirect way. Simply put, ethnography is the study of people in their environment. Methods such as face-to-face interviewing, participant observation and more can be used. The main goal of Ethnography is to gain a holistic understanding of a group. Though the method might appear inefficient, it still yields rich data about the use of products.
Consider an example of creating a wearable device to improve movement quality in people with chronic pain. On considering the target market, the first thought which strikes is the adult population. On the contrary, through user interviews, it was brought to light that pain likely impacted the moderately active group. The analysis further revealed that this group was keen on finding a lasting solution that would improve long-term wellness and their eagerness towards trying a new product for pain.
Competitor Research
Competitor research analyzes the weaknesses and strengths of your existing and potential competitors. In addition, it can also provide information regarding their ways of catering to user needs. Once the potential opportunities are identified, only new features and strategies that would work in your business can be incorporated. This will help in reducing MVP’s time-to-market.
Build a Minimum Viable Persona
Before we begin with building a minimum viable persona, let us define “viable”.
Delivering enough value to users so that they use your product can be termed viability. If a specific product is relevant and has business potential then it will be considered viable.
Just like Minimum Viable Product, Minimum Viable Persona brings the most actionable information about users in front. A fictional representation of different user types provides detailed information based on real data, i.e. behavior, goals, and motivations of user types. Having a persona can help in targeting the audience with particular needs and desires.
Considering the example of the B2B audience, it’s just asking to clarify which industry the persona works in, their interests, and preferences. With the data gathered, we can create a product, designed to resonate with a person.
Steps to Build a Minimum Viable Persona
The rationale behind the steps towards building an MVP is to cover the process from research to development. The core areas to be considered remain data material, engagement in personal descriptions, and buy-in from organizations. The steps are:
- Finding Users
- Building a Hypothesis
- Verification
- Finding Patterns
- Constructing Personas
- Defining Situations
- Validation and Buy-in
- Dissemination of Knowledge
- Creating Scenarios
- On-Going Development
Note: A project does not need to follow all the steps as long they are aware of the outlines and the consequences.
Prioritizing Features As Per Users Delight
Focusing on delivering customer value and removing unnecessary features is a necessary part of MVP software design practices. Which features should be incorporated first and what can wait should be carefully considered. A few methods from the ones available in the market are listed below:
The Kano Method
While Prioritizing features, the end goals need to be kept in mind, i.e. to create a minimum viable product that your customers will love. The Kano model helps in weighing features with their potential from the user’s lens. Each feature is broken down into various categories and emotional responses it induces. These are:
- Attractive Needs: These features bring delight, but if not included then the users are not dissatisfied.
- Performance Needs: These features also result in delight but if not present or if they are flawed then users will feel dissatisfaction.
- Basic Needs: As the name suggests, these features are a must-have i.e. the users expect them to be there. Not incorporating these is highly dissatisfying and can lead to a tapered ROI.
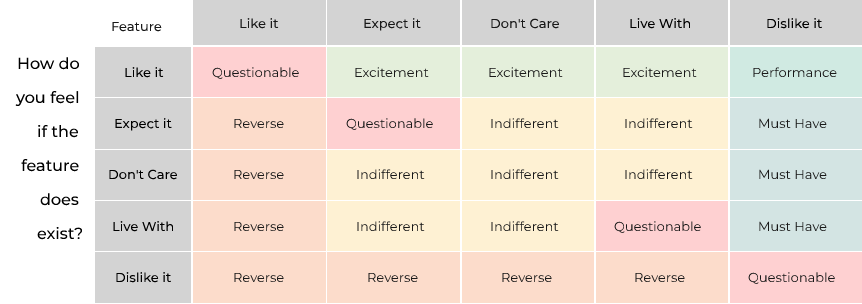
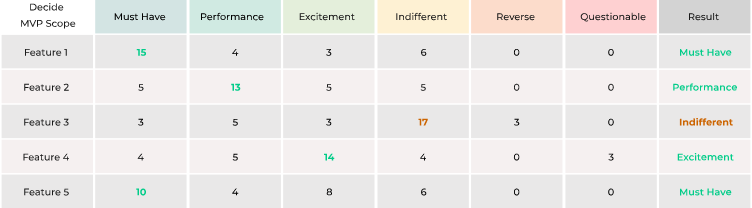

Kano can feel a bit complicated at times, but it certainly brings some interesting insights about the user’s needs.
The RICE Method
Another method to prioritize features based on user needs is the RICE method. It is useful in comparing different users based ideas in a consistent way. Four common factors to consider when evaluating each feature are:
- Reach: This is to measure how many people will be affected in a given period of time using this feature.
- Impact: This is used to measure the impact that the feature will have in terms of meeting the goals and strategy. A scale with multiple choices such as “massive”, “high”, “medium”, “low”, and “minimal” is used.
- Confidence: If you think the product will be impactful, then it is backed by confidence. Again by using multiple-choice scale confidence is measured.
- Effort: This is used to measure the effort required from various teams like design, engineering, and product. It can be measured by person and month.
- The score as a result provides a powerful number, pivotal for prioritizing features.
Priority Score Card
Sometimes features require to be customized based on several factors such as user needs being met. With a Priority Scorecard, a proposed list of parameters with their weights is measured (importance as a percentage of the whole project).
For each feature to be prioritized, assign a score from 1-100 (100 means high impact, 0 means no impact.) So if we are trying to prioritize between, it will appear like this:
Category
Customer Engagement
User Experience
Sales Funnel
Operational Efficiency
Total
Weight
Feature
Score
Rating
New Checkout
Website Redesign
What is great about this method is that the feature list is fine-tuned based on user feedback. While there are a few opinions that can be influenced by how you weigh. But, the method still adds credibility to the roadmap with priorities.
Conclusion
While building an MVP, analyzing data-driven metrics is important but understanding user sentiment and their needs are essential. By prioritizing features based on the needs, one can align their project development to deliver real value to customers.
Recommend
About Joyk
Aggregate valuable and interesting links.
Joyk means Joy of geeK