

Understanding Allocations in Go
source link: https://medium.com/eureka-engineering/understanding-allocations-in-go-stack-heap-memory-9a2631b5035d
Go to the source link to view the article. You can view the picture content, updated content and better typesetting reading experience. If the link is broken, please click the button below to view the snapshot at that time.
Understanding Allocations in Go

This is the 18th article of the Eureka Advent Calendar 2020. Yesterday we had a post from
on diversity in Spotify’s recommender systems.Introduction
Thanks to efficient in-built memory management in the Go runtime, we’re generally able to prioritise correctness and maintainability in our programs without much consideration for the details of how allocations are occurring. From time to time though, we may discover performance bottlenecks in our code, and want to look a little deeper.
Anyone who’s run a benchmark with the -benchmem flag will have seen the allocs/op stat in output like the below. In this post we’ll look at what counts as an alloc and what we can do to influence this number.
BenchmarkFunc-8 67836464 16.0 ns/op 8 B/op 1 allocs/op
The stack and heap we know and love
To discuss the allocs/op stat in Go, we’re going to be interested in two areas of memory in our Go programs: the stack and the heap.
In many popular programming environments the stack usually refers to the call stack of a thread. A call stack is a LIFO stack data structure that stores arguments, local variables, and other data tracked as a thread executes functions. Each function call adds (pushes) a new frame to the stack, and each returning function removes (pops) from the stack.
We must be able to safely free the memory of the most recent stack frame when it’s popped. We therefore can’t store anything on the stack that later needs to be referenced elsewhere.

Since threads are managed by the OS, the amount of memory available to a thread stack is typically fixed, e.g. a default of 8MB in many Linux environments. This means we also need to be mindful of how much data ends up on the stack, particularly in the case of deeply-nested recursive functions. If the stack pointer in the diagram above passes the stack guard, the program will crash with a stack overflow error.
The heap is a more complex area of memory that has no relation to the data structure of the same name. We can use the heap on demand to store data needed in our program. Memory allocated here can’t simply be freed when a function returns, and needs to be carefully managed to avoid leaks and fragmentation. The heap will generally grow many times larger than any thread stack, and the bulk of any optimization efforts will be spent investigating heap use.
The Go stack and heap
Threads managed by the OS are completely abstracted away from us by the Go runtime, and we instead work with a new abstraction: goroutines. Goroutines are conceptually very similar to threads, but they exist within user space. This means the runtime, and not the OS, sets the rules of how stacks behave.

Rather than having hard limits set by the OS, goroutine stacks start with a small amount of memory (currently 2KB). Before each function call is executed, a check within the function prologue is executed to verify that a stack overflow won’t occur. In the below diagram, the convert() function can be executed within the limits of the current stack size (without SP overshooting stackguard0).
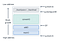
If this wasn’t the case, the runtime would copy the current stack to a new larger space of contiguous memory before executing convert(). This means that stacks in Go are dynamically sized, and can typically keep growing as long as there’s enough memory available to feed them.
The Go heap is again conceptually similar to the threaded model described above. All goroutines share a common heap and anything that can’t be stored on the stack will end up there. When a heap allocation occurs in a function being benchmarked, we’ll see the allocs/ops stat go up by one. It’s the job of the garbage collector to later free heap variables that are no longer referenced.
For a detailed explanation of how memory management is handled in Go, see A visual guide to Go Memory Allocator from scratch.
How do we know when a variable is allocated to the heap?
This question is answered in the official FAQ.
Go compilers will allocate variables that are local to a function in that function’s stack frame. However, if the compiler cannot prove that the variable is not referenced after the function returns, then the compiler must allocate the variable on the garbage-collected heap to avoid dangling pointer errors. Also, if a local variable is very large, it might make more sense to store it on the heap rather than the stack.
If a variable has its address taken, that variable is a candidate for allocation on the heap. However, a basic escape analysis recognizes some cases when such variables will not live past the return from the function and can reside on the stack.
Since compiler implementations change over time, there’s no way of knowing which variables will be allocated to the heap simply by reading Go code. It is, however, possible to view the results of the escape analysis mentioned above in output from the compiler. This can be achieved with the gcflags argument passed to go build. A full list of options can be viewed via go tool compile -help.
For escape analysis results, the -m option (print optimization decisions) can be used. Let’s test this with a simple program that creates two stack frames for functions main1 and stackIt.
func main1() {
_ = stackIt()
}//go:noinline
func stackIt() int {
y := 2
return y * 2
}Since we can can’t discuss stack behaviour if the compiler removes our function calls, the noinline pragma is used to prevent inlining when compiling the code. Let’s take a look at what the compiler has to say about its optimization decisions. The -l option is used to omit inlining decisions.
$ go build -gcflags '-m -l'
# github.com/Jimeux/go-samples/allocations
Here we see that no decisions were made regarding escape analysis. In other words, variable y remained on the stack, and didn’t trigger any heap allocations. We can verify this with a benchmark.
$ go test -bench . -benchmem
BenchmarkStackIt-8 680439016 1.52 ns/op 0 B/op 0 allocs/op
As expected, the allocs/op stat is 0. An important observation we can make from this result is that copying variables can allow us to keep them on the stack and avoid allocation to the heap. Let’s verify this by modifying the program to avoid copying with use of a pointer.
func main2() {
_ = stackIt2()
}//go:noinline
func stackIt2() *int {
y := 2
res := y * 2
return &res
}Let’s see the compiler output.
go build -gcflags '-m -l'
# github.com/Jimeux/go-samples/allocations
./main.go:10:2: moved to heap: res
The compiler tells us it moved the pointer res to the heap, which triggers a heap allocation as verified in the benchmark below
$ go test -bench . -benchmem
BenchmarkStackIt2-8 70922517 16.0 ns/op 8 B/op 1 allocs/op
So does this mean pointers are guaranteed to create allocations? Let’s modify the program again to this time pass a pointer down the stack.
func main3() {
y := 2
_ = stackIt3(&y) // pass y down the stack as a pointer
}
//go:noinline
func stackIt3(y *int) int {
res := *y * 2
return res
}Yet running the benchmark shows nothing was allocated to the heap.
$ go test -bench . -benchmem
BenchmarkStackIt3-8 705347884 1.62 ns/op 0 B/op 0 allocs/op
The compiler output tells us this explicitly.
$ go build -gcflags '-m -l'
# github.com/Jimeux/go-samples/allocations
./main.go:10:14: y does not escape
Why do we get this seeming inconsistency? stackIt2 passes the address of y up the stack to main, where y will be referenced after the stack frame of stackIt2 has already been freed. The compiler is therefore able to judge that y must be moved to the heap to remain alive. If it doesn’t do this, we’ll get a nil pointer in main when attempted to reference y.
stackIt3, on the other hand, passes y down the stack, and y isn’t referenced anywhere outside main3. The compiler is therefore able to judge that y can exist within the stack alone, and doesn’t need to be allocated to the heap. We won’t be able to produce a nil pointer in any circumstances by referencing y.
A general rule we can infer from this is that sharing pointers up the stack results in allocations, whereas sharing points down the stack doesn’t. However, this is not guaranteed, so you’ll still need to verify with gcflags or benchmarks to be sure. What we can say for sure is that any attempt to reduce allocs/op will involve hunting out wayward pointers.
Why do we care about heap allocations?
We’ve learnt a little about what the alloc in allocs/op means, and how to verify if an allocation to the heap is triggered, but why should we care if this stat is non-zero in the first place? The benchmarks we’ve already done can begin to answer this question.
BenchmarkStackIt-8 680439016 1.52 ns/op 0 B/op 0 allocs/op
BenchmarkStackIt2-8 70922517 16.0 ns/op 8 B/op 1 allocs/op
BenchmarkStackIt3-8 705347884 1.62 ns/op 0 B/op 0 allocs/op
Despite the memory requirements of the variables involved being almost equal, the relative CPU overhead of BenchmarkStackIt2 is pronounced. We can get a little more insight by generating flame graphs of the CPU profiles of the stackIt and stackIt2 implementations.


stackIt has an unremarkable profile that runs predictably down the call stack to the stackIt function itself. stackIt2, on the other hand, is making heavy use of a large number of runtime functions that eat many additional CPU cycles. This demonstrates the complexity involved in allocating to the heap, and gives some initial insight into where those extra 10 or so nanoseconds per op are going.
What about in the real world?
Many aspects of performance don’t become apparent without production conditions. Your single function may run efficiently in microbenchmarks, but what impact does it have on your application as it serves thousands of concurrent users?
We’re not going to recreate an entire application in this post, but we will take a look at some more detailed performance diagnostics using the trace tool. Let’s begin by defining a (somewhat) big struct with nine fields.
type BigStruct struct {
A, B, C int
D, E, F string
G, H, I bool
}Now we’ll define two functions: CreateCopy, which copies BigStruct instances between stack frames, and CreatePointer, which shares BigStruct pointers up the stack, avoiding copying, but resulting in heap allocations.
//go:noinline
func CreateCopy() BigStruct {
return BigStruct{
A: 123, B: 456, C: 789,
D: "ABC", E: "DEF", F: "HIJ",
G: true, H: true, I: true,
}
}//go:noinline
func CreatePointer() *BigStruct {
return &BigStruct{
A: 123, B: 456, C: 789,
D: "ABC", E: "DEF", F: "HIJ",
G: true, H: true, I: true,
}
}
We can verify the explanation from above with the techniques used so far.
$ go build -gcflags '-m -l'
./main.go:67:9: &BigStruct literal escapes to heap$ go test -bench . -benchmem
BenchmarkCopyIt-8 211907048 5.20 ns/op 0 B/op 0 allocs/op
BenchmarkPointerIt-8 20393278 52.6 ns/op 80 B/op 1 allocs/op
Here are the tests we’ll use for the trace tool. They each create 20,000,000 instances of BigStruct with their respective Create function.
const creations = 20_000_000
func TestCopyIt(t *testing.T) {
for i := 0; i < creations; i++ {
_ = CreateCopy()
}
}
func TestPointerIt(t *testing.T) {
for i := 0; i < creations; i++ {
_ = CreatePointer()
}
}
Next we’ll save the trace output for CreateCopy to file copy_trace.out, and open it with the trace tool in the browser.
$ go test -run TestCopyIt -trace=copy_trace.out
PASS
ok github.com/Jimeux/go-samples/allocations 0.281s$ go tool trace copy_trace.out
Parsing trace...
Splitting trace...
Opening browser. Trace viewer is listening on http://127.0.0.1:57530
Choosing View trace from the menu shows us the below, which is almost as unremarkable as our flame chart for the stackIt function. Only two of eight potential logical cores (Procs) are utilised, and goroutine G19 spends just about the entire time running our test loop — which is what we want.

Let’s generate the trace data for the CreatePointer code.
$ go test -run TestPointerIt -trace=pointer_trace.out
PASS
ok github.com/Jimeux/go-samples/allocations 2.224sgo tool trace pointer_trace.out
Parsing trace...
Splitting trace...
Opening browser. Trace viewer is listening on http://127.0.0.1:57784
You may have already noticed the test took 2.224s compared to 0.281s for CreateCopy, and selecting View trace displays something much more colourful and busy this time. All logical cores were utilised and there appears to be a lot more heap action, threads, and goroutines than last time.

CreatePointer callsIf we zoom in to a millisecond or so span of the trace, we see many goroutines performing operations related to garbage collection. The quote earlier from the FAQ used the phrase garbage-collected heap because it’s the job of the garbage collector to clean up anything on the heap that is no longer being referenced.

Although Go’s garbage collector is increasingly efficient, the process doesn’t come for free. We can verify visually that the test code stopped completely at times in the above trace output. This wasn’t the case for CreateCopy, since all of our BigStruct instances remained on the stack, and the GC had very little to do.
Comparing the goroutine analysis from the two sets of trace data offers more insight into this. CreatePointer (bottom) spent over 15% of its execution time sweeping or pausing (GC) and scheduling goroutines.


A look at some of the stats available elsewhere in the trace data further illustrates the cost of heap allocation, with a stark difference in the number of goroutines generated, and almost 400 STW (stop the world) events for the CreatePointer test.
+------------+------+---------+
| | Copy | Pointer |
+------------+------+---------+
| Goroutines | 41 | 406965 |
| Heap | 10 | 197549 |
| Threads | 15 | 12943 |
| bgsweep | 0 | 193094 |
| STW | 0 | 397 |
+------------+------+---------+
Do keep in mind though that the conditions of the CreateCopy test are very unrealistic in a typical program, despite the title of this section. It’s normal to see the GC using a consistent amount of CPU, and pointers are a feature of any real program. However, this together with the flame graph earlier gives us some insight into why we may want to track the allocs/op stat, and avoid unnecessary heap allocations when possible.
Summary
Hopefully this post gave some insight into the differences between the stack and heap in a Go program, the meaning of the allocs/op stat, and some of the ways in which we can investigate memory usage.
The correctness and maintainability of our code is usually going to take precedence over tricky techniques to reduce pointer usage and skirt GC activity. Everyone knows the line about premature optimization by now, and coding in Go is no different.
If, however, we do have strict performance requirements or otherwise identify a bottleneck in a program, the concepts and tools introduced here will hopefully be a useful starting point for making the necessary optimizations.
If you want to play around with the simple code examples in this post, check out the source and README on GitHub.
Recommend
About Joyk
Aggregate valuable and interesting links.
Joyk means Joy of geeK