

怒肝一页,搞定这篇MyBatis 缓存结构(中)
source link: https://my.oschina.net/u/4728925/blog/4816561
Go to the source link to view the article. You can view the picture content, updated content and better typesetting reading experience. If the link is broken, please click the button below to view the snapshot at that time.

主要内容:
一级缓存也叫本地缓存(LocalCache),Mybatis的一级缓存是会话级别(SqlSession)层面进行缓存的。Mybatis的一级缓存是默认开启的。我们开发项目中不需要做任何配置,但是如果想关闭一级缓存,可以使用localCacheScopde=statement来关闭。
如何关闭一级缓存呢?
在BaseExecutor的中,请看下面代码:
为什么说是SqlSession层面缓存?
就是一级缓存的生命周期和一个SqlSession对象的生命周期一样。
下面这段中,就会使用到一级缓存。
SqlSession sqlSession1 = sqlSessionFactory.openSession();
User user1 = sqlSession1.selectOne("com.tian.mybatis.mapper.UserMapper.selectUserById", 1);
User user2 = sqlSession1.selectOne("com.tian.mybatis.mapper.UserMapper.selectUserById", 1);
结果输出:
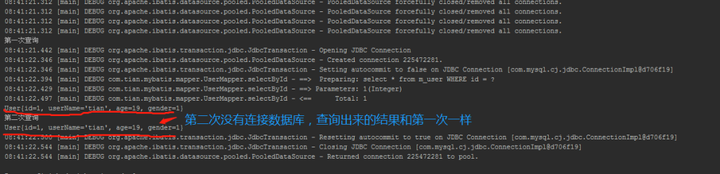
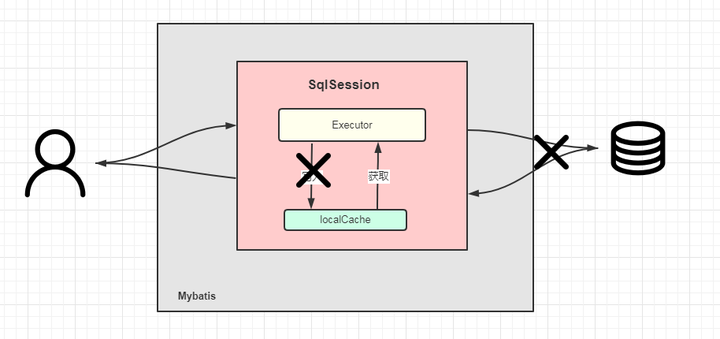
用两张图来总结:
第一次:查数据库,放入到缓存中。
第二次:直接从缓存中获取。
下面这段代码中就使用不到缓存
SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory = new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder().build(inputStream);
sqlSession = sqlSessionFactory.openSession();
sqlSession1 = sqlSessionFactory.openSession();
UserMapper userMapper = sqlSession.getMapper(UserMapper.class);
UserMapper userMapper1 = sqlSession1.getMapper(UserMapper.class);
System.out.println("第一次查询");
System.out.println(userMapper.selectById(1));
User user = new User();
user.setUserName("tian111");
user.setId(1);
userMapper1.updateAuthorIfNecessary(user);
System.out.println("第二次查询");
System.out.println(userMapper.selectById(1));
输出结果:
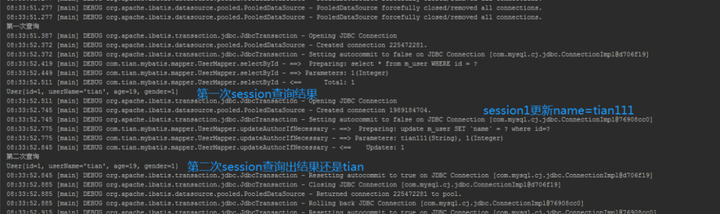
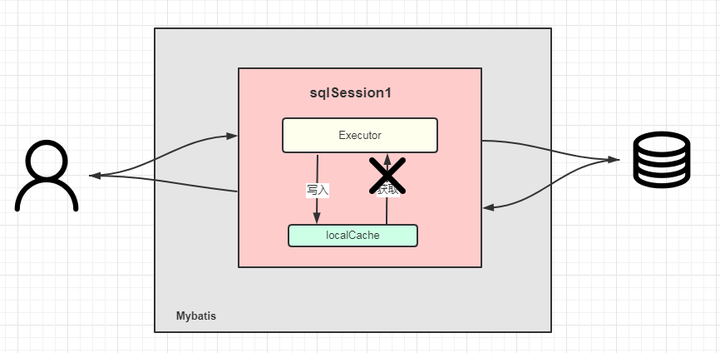
用三张图来总结:
第一次查询:sqlSession1查询数据库,放入到缓存中。
更新:sqlSession2进行更新,注意这里写入的是sqlSession自己的本地缓存。
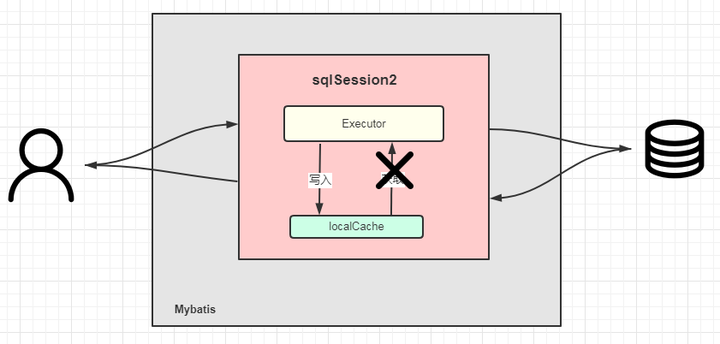
第二次查询:sqlSession1第二次查询。
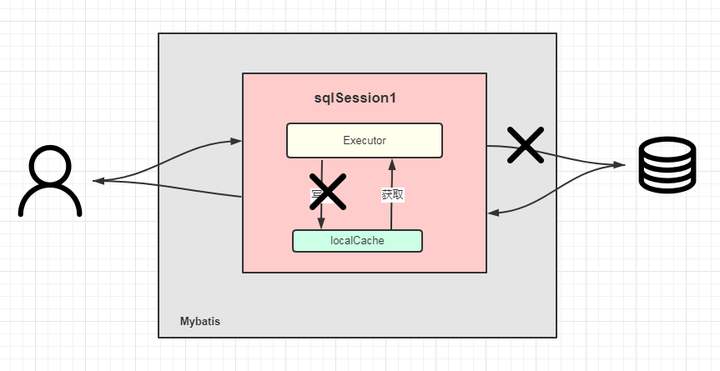
记住是一级缓存只能是同一个SqlSession对象就行了。
一级缓存维护在哪里的?
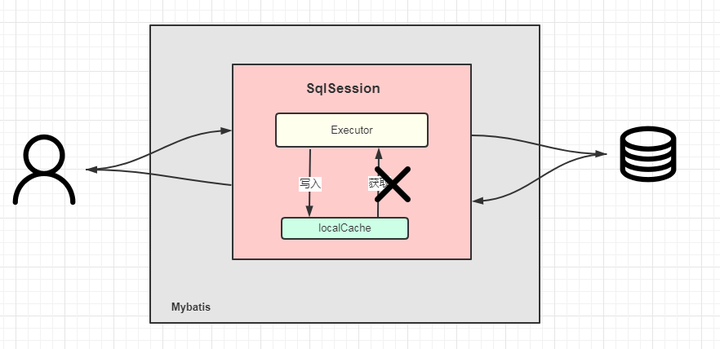
既然一级缓存的生命周期和SqlSession一致,那么我们可以猜想,这个缓存是不是就维护在SqlSession中呢?
SqlSession的默认实现类DefaultSqlSession,在DefaultSqlSession中只有两个属性可能存放缓存:
private final Configuration configuration;
private final Executor executor;
configuration是全局的,肯定不会放缓存。
那就只能把希望寄托于Executor了。由于Executor是个接口,我们可以看看他的实现类:
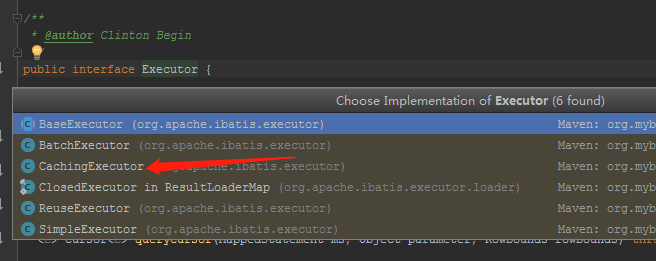
另外这里有个BaseExecutor。有各类也得瞄瞄。一看居然有东西。
public abstract class BaseExecutor implements Executor {
private static final Log log = LogFactory.getLog(BaseExecutor.class);
protected Transaction transaction;
protected Executor wrapper;
protected ConcurrentLinkedQueue<DeferredLoad> deferredLoads;
//熟悉的家伙,基本缓存
protected PerpetualCache localCache;
protected PerpetualCache localOutputParameterCache;
protected Configuration configuration;
protected int queryStack;
private boolean closed;
protected BaseExecutor(Configuration configuration, Transaction transaction) {
this.transaction = transaction;
this.deferredLoads = new ConcurrentLinkedQueue<>();
this.localCache = new PerpetualCache("LocalCache");
this.localOutputParameterCache = new PerpetualCache("LocalOutputParameterCache");
this.closed = false;
this.configuration = configuration;
this.wrapper = this;
}
}
再看看BaseExecutor类图:
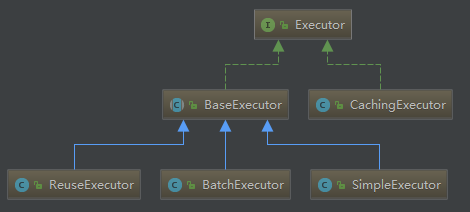
所以这就证明了,这个缓存是维护在SqlSession里。
一级缓存什么时候被清空?
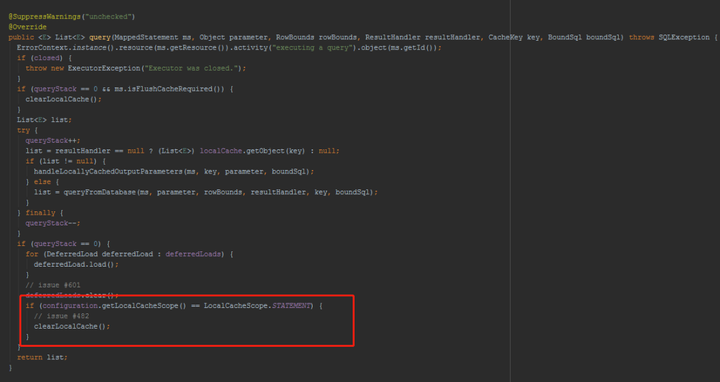
在执行update、insert、delete、flushCache="true"、commit、rollback、LocalCacheScope.STATEMENT等情况下,一级缓存就都会被清空。
@Override
public void clearLocalCache() {
if (!closed) {
localCache.clear();
localOutputParameterCache.clear();
}
}
update时,一级缓存会被清空。delete和insert都是调用这个update。可以从SqlSession的insert、update、delete方法跟踪。
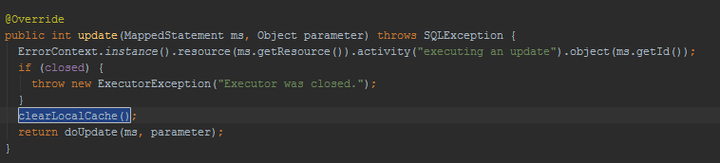
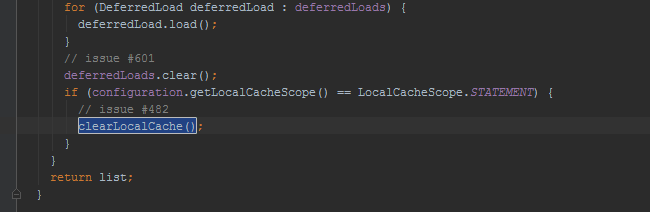
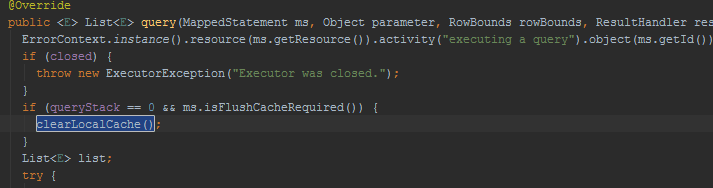
LocalCacheScope.STATEMENT时,一级缓存会被清空。在BaseExecutor里的query方法中:
事务提交回滚时,一级缓存会被清空。
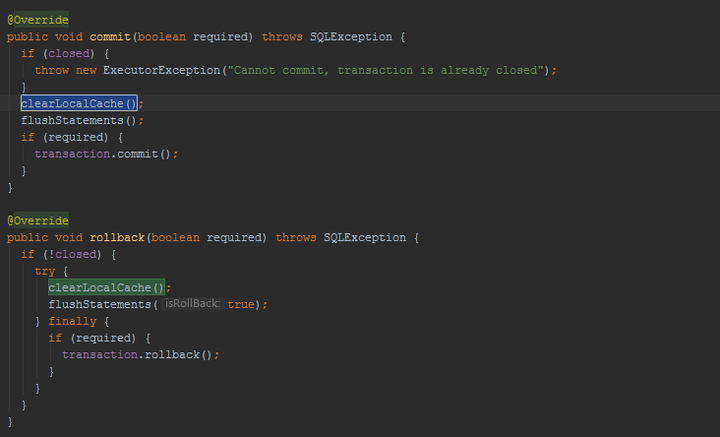
flushCache="true"时,一级缓存会被清空。
一级缓存key是什么?
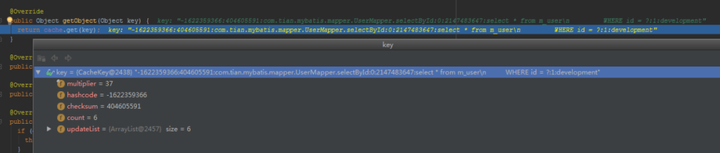
下面就是一级缓存key的创建过程
@Override
public CacheKey createCacheKey(MappedStatement ms, Object parameterObject, RowBounds rowBounds, BoundSql boundSql) {
if (closed) {
throw new ExecutorException("Executor was closed.");
}
CacheKey cacheKey = new CacheKey();
cacheKey.update(ms.getId());
cacheKey.update(rowBounds.getOffset());
cacheKey.update(rowBounds.getLimit());
cacheKey.update(boundSql.getSql());
List<ParameterMapping> parameterMappings = boundSql.getParameterMappings();
TypeHandlerRegistry typeHandlerRegistry = ms.getConfiguration().getTypeHandlerRegistry();
// mimic DefaultParameterHandler logic
for (ParameterMapping parameterMapping : parameterMappings) {
if (parameterMapping.getMode() != ParameterMode.OUT) {
Object value;
String propertyName = parameterMapping.getProperty();
if (boundSql.hasAdditionalParameter(propertyName)) {
value = boundSql.getAdditionalParameter(propertyName);
} else if (parameterObject == null) {
value = null;
} else if (typeHandlerRegistry.hasTypeHandler(parameterObject.getClass())) {
value = parameterObject;
} else {
MetaObject metaObject = configuration.newMetaObject(parameterObject);
value = metaObject.getValue(propertyName);
}
cacheKey.update(value);
}
}
if (configuration.getEnvironment() != null) {
// issue #176
cacheKey.update(configuration.getEnvironment().getId());
}
return cacheKey;
}
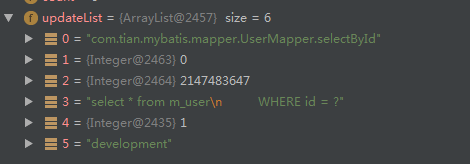
id:com.tian.mybatis.mapper.UserMapper.selectById
key的生成策略:id + offset + limit + sql + param value + environment id,这些值都相同,生成的key就相同。
一级缓存总结
一级缓存的生命周期和SqlSession对象的生命周期一致。所以缓存维护在SqlSession中的属性executor里。
一级缓存默认开启。可以通过修改配置项把一级缓存关掉。
清空一级缓存的方式有:
- update、insert、delete
- flushCache="true"
- commit、rollback
- LocalCacheScope.STATEMENT
Recommend
About Joyk
Aggregate valuable and interesting links.
Joyk means Joy of geeK