

请查收这份学习笔记!我从Vue源码中学到的5个JavaScript技巧
source link: http://developer.51cto.com/art/202006/618825.htm
Go to the source link to view the article. You can view the picture content, updated content and better typesetting reading experience. If the link is broken, please click the button below to view the snapshot at that time.

本文转载自公众号“读芯术”(ID:AI_Discovery)
从他人的成果中汲取营养是进步的法则之一,阅读知名框架的源代码可以有效地提高编程水平。最近,笔者开始了一场vue2.x的阅读之旅,从中学到了很多与JS相关的技巧。

独乐乐不如众乐乐,本文就将和你分享我的学习成果。
1.确定任何对象的特定类型
JavaScript中有六种基本数据类型——布尔、数字、字符串、空值、未定义、符号,以及对象数据类型。但是,你知道对象数据类型可以被细分为许多种子类型吗?对象可以是数组、函数、映射等。如果我们想获取特定类型的对象,应该怎么做?
在深入之前,先看看另一个问题:
Object.prototype.toString.call(arg) 和 String(arg)的区别是什么?
两个表达式都试图将参数转换为字符串,但其中存在差异:
String(arg)会尝试调用arg.toString()或arg.valueOf(),所以如果arg或arg prototype重写这两个函数,
Object.prototype.toString.call(arg)和 String(arg)将会得出不同的结果。
const _toString =Object.prototype.toString
var obj = {}obj.toString() // [objectObject]
_toString.call(obj) // [object Object]

在这种情况下,String(arg)就和Object.prototype.toString.call(arg)有同样的效果。
const _toString =Object.prototype.toString
var obj = {}obj.toString = () => '111'obj.toString() // 111
_toString.call(obj) // [object Object]/hello/.toString() // /hello/
_toString.call(/hello/) // [object RegExp]
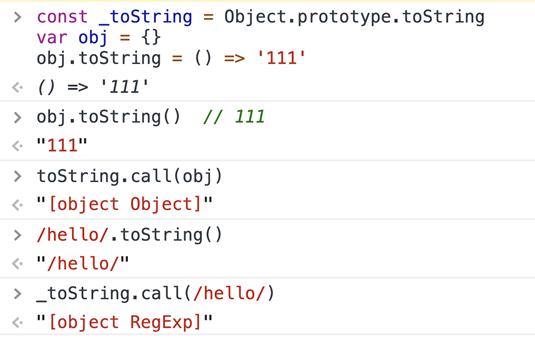
而在这种情况下,String(arg)和Object.prototype.toString.call(arg)得出的结果不同。
ECMAScript有着如下规则:

图源:EcmaScript
对不同的对象调用Object.prototype.toString(),会返回不同结果。

此外,Object.prototype.toString() 的返回值的格式总是‘[object ’ + ‘tag’ +‘] ’。如果只想要中间的tag,就可以通过正则表达式或String.prototype.slice()删除两边的字符。
function toRawType (value) {
const _toString =Object.prototype.toString
return _toString.call(value).slice(8,-1)
}toRawType(null) // "Null"
toRawType(/sdfsd/) //"RegExp"

利用如上函数,就可以得到JavaScript变量的类型。
Vue源代码:
https://github.com/vuejs/vue/blob/6fe07ebf5ab3fea1860c59fe7cdd2ec1b760f9b0/src/shared/util.js(第62行)
2.确定函数是原生的还是自定义的
JavaScript中有两种类型的函数,一种由服务器环境提供,另一种由用户自定义。两种函数在转换为字符串时有不同的结果。
Array.isArray.toString() //"function isArray() { [native code] }"function fn(){}
fn.toString() // "function fn(){}"

原生函数toString总是以function fnName() { [native code] }的格式呈现结果。可以此进行区分。
Vue源代码:
https://github.com/vuejs/vue/blob/6fe07ebf5ab3fea1860c59fe7cdd2ec1b760f9b0/src/shared/util.js(第58行)
3.缓存函数计算结果
如果有这样一个函数:
function computed(str) {
// Suppose the calculation in thefuntion is very time consuming
console.log('2000s have passed')
return 'a result'
}
其目标是缓存函数操作的结果。当函数在之后被调用,如果参数相同,则不再执行该函数,而是直接返回缓存中的结果。我们该如何操作?
编写一个cached函数来包装目标函数。此缓存函数将目标函数作为一个参数,并返回一个新的包装函数。在cached函数中,可以使用Object或Map来缓存上一个函数调用的结果。
示例如下:

Vue源代码:
https://github.com/vuejs/vue/blob/6fe07ebf5ab3fea1860c59fe7cdd2ec1b760f9b0/src/shared/util.js(第153行)
4.将hello-world样式转换为helloWorld样式
当需要在大型项目上进行协作时,我们必须使用通用的代码样式。有些人可能习惯于helloWorld,有人则习惯于hello-world。为解决该问题,可以编写一个函数,将hello-world统一转换为helloWorld。
const camelizeRE = /-(\w)/gconstcamelize = cached((str) => {
return str.replace(camelizeRE, (_, c)=> c ? c.toUpperCase() : '')
})camelize('hello-world')
// "helloWorld"
Vue源代码:
https://github.com/vuejs/vue/blob/6fe07ebf5ab3fea1860c59fe7cdd2ec1b760f9b0/src/shared/util.js(第164行)
5.确定JS运行环境
随着前端的快速发展,JavaScript代码可能会在不同的运行环境中运行。为更好地适应各种运行环境,需要确定当前代码在哪个运行环境中执行。来一起看看Vue如何确定运行环境的吧。
Vue源代码:
https://github.com/vuejs/vue/blob/6fe07ebf5ab3fea1860c59fe7cdd2ec1b760f9b0/src/shared/util.js(第6行)
相信我,多去阅读源代码,你将会得到意想不到的收获。

Recommend
About Joyk
Aggregate valuable and interesting links.
Joyk means Joy of geeK