

LangChain 101 - DiscreteTom's Blog
source link: https://discretetom.github.io/posts/langchain/
Go to the source link to view the article. You can view the picture content, updated content and better typesetting reading experience. If the link is broken, please click the button below to view the snapshot at that time.

本文是观看此视频的笔记
LangChain
- 一个编程框架,提供 Python/Javascript/Typescript SDK
- 用来工程化、简化基于 LLM 的应用的开发
- 把和 LLM 的交互抽象为一系列的 Chain
- 通过设置
langchain.debug = True可以查看每个步骤发生了什么
略,就是各种大语言模型
Prompt
为了实现提示词的复用,LangChain 通常不会直接使用 prompt,而是使用 prompt template,并在 template 中预留参数的 slot
from langchain.prompts import ChatPromptTemplate
template_string = """Translate the text \
that is delimited by triple backticks \
into a style that is {style}. \
text: ```{text}```
"""
prompt_template = ChatPromptTemplate.from_template(template_string)
prompt_template.format_messages(style='xxx', text='xxx')
在以上示例中,{style} 和 {text} 就是 slot。ChatPromptTemplate会识别字符串中的这些 slot,并在format_messages的时候填充 slot
Output Parser
如果我们希望 LLM 返回的结果是结构化的,那么我们需要定义一个OutputParser,用来指导 LLM 输出我们想要的格式,然后解析 LLM 的输出
from langchain.output_parsers import ResponseSchema
from langchain.output_parsers import StructuredOutputParser
# define expected response fields
gift_schema = ResponseSchema(name='gift', description='Is this xxx? Answer True if yes, False if no')
# response should have multiple fields
response_schemas = [gift_schema]
# create output parser
output_parser = StructuredOutputParser.from_response_schemas(response_schemas)
# create format instruction prompt string
format_instructions = output_parser.get_format_instructions()
通过以上代码,我们表达了我们希望输出里面包含一个名为gift的字段,这个字段的值应该是一个布尔值,然后让StructuredOutputParser生成一个格式化指令字符串,用来告诉 LLM 我们希望输出的格式
接下来我们需要把 output parser 给出的 format instruction 放到 prompt template 里面,比如
"""\
For the following text, extract the following information:
gift: Was the item purchased as a gift for someone else? \
Answer True if yes, False if not or unknown.
delivery_days: How many days did it take for the product\
to arrive? If this information is not found, output -1.
price_value: Extract any sentences about the value or price,\
and output them as a comma separated Python list.
text: {text}
{format_instructions}
"""
这样 LLM 就会输出可以被 output parser 解析的数据(比如 JSON),我们就可以使用 output parser 来解析输出
output_dict = output_parser.parse(response.content)
Memory
与 LLM 的交互是无状态的,所以为了使 LLM 能够记住之前的信息,每次向 LLM 发出请求都要包含之前的聊天记录。langchain 提供了 Memory 来简化历史信息的管理
from langchain.chains import ConversationChain
from langchain.memory import ConversationBufferMemory
memory = ConversationBufferMemory()
conversation = ConversationChain(
llm=llm,
memory = memory,
verbose=True
)
conversation.predict(input="Hi, my name is Andrew")
conversation.predict(input="What is 1+1?")
conversation.predict(input="What is my name?")
在如上的示例中,所有聊天历史记录都会保存在memory里面,然后在每次向 LLM 发出请求的时候,都会把历史记录放到请求里面。所以当我们问What is my name?的时候,LLM 会知道我们之前说过Hi, my name is Andrew,所以会回答Andrew
我们可以把 memory 里面的数据导出来放到外部数据库,也可以向 memory 导入曾经的历史数据,或者直接向里面写入新的数据
langchain 提供了很多不同功能的 memory 以便我们使用
ConversationBufferMemory:把所有历史记录保存在内存里面ConversationBufferWindowMemory:把最近的历史记录保存在内存里面,超过一定数量的历史记录会被删除(基于消息的滑动窗口)ConversationTokenBufferMemory:把最近的历史记录保存在内存里面,按照 LLM 定义的 token 数量删除历史记录(基于 token 的滑动窗口)ConversationSummaryMemory:使用 LLM 获取历史记录的摘要,然后把摘要保存在内存里面
Chain
使用 Chain 把不同步骤组合起来,这样的话一次输入就可以产生多次 LLM 的调用,用来实现不同的功能
SimpleSequentialChain
最简单的 Chain 是 SimpleSequentialChain,它只是把多个 LLM 调用串联起来,每个 LLM 的输入都是上一个 LLM 的输出
llm = ChatOpenAI(temperature=0.9, model=llm_model)
# prompt template 1
first_prompt = ChatPromptTemplate.from_template(
"What is the best name to describe \
a company that makes {product}?"
)
# Chain 1
chain_one = LLMChain(llm=llm, prompt=first_prompt)
# prompt template 2
second_prompt = ChatPromptTemplate.from_template(
"Write a 20 words description for the following \
company:{company_name}"
)
# chain 2
chain_two = LLMChain(llm=llm, prompt=second_prompt)
# link chains together
overall_simple_chain = SimpleSequentialChain(
chains=[chain_one, chain_two],
verbose=True
)
overall_simple_chain.run(product)
SequentialChain
另一个简单的 Chain 是 SequentialChain,它可以把多个 LLM 调用串联起来,但是没有输出和输入的一一对应关系
# prompt template 1: translate to english
first_prompt = ChatPromptTemplate.from_template(
"Translate the following review to english:"
"\n\n{Review}"
)
# chain 1: input= Review and output= English_Review
chain_one = LLMChain(llm=llm, prompt=first_prompt,
output_key="English_Review"
)
second_prompt = ChatPromptTemplate.from_template(
"Can you summarize the following review in 1 sentence:"
"\n\n{English_Review}"
)
# chain 2: input= English_Review and output= summary
chain_two = LLMChain(llm=llm, prompt=second_prompt,
output_key="summary"
)
# prompt template 3: translate to english
third_prompt = ChatPromptTemplate.from_template(
"What language is the following review:\n\n{Review}"
)
# chain 3: input= Review and output= language
chain_three = LLMChain(llm=llm, prompt=third_prompt,
output_key="language"
)
# prompt template 4: follow up message
fourth_prompt = ChatPromptTemplate.from_template(
"Write a follow up response to the following "
"summary in the specified language:"
"\n\nSummary: {summary}\n\nLanguage: {language}"
)
# chain 4: input= summary, language and output= followup_message
chain_four = LLMChain(llm=llm, prompt=fourth_prompt,
output_key="followup_message"
)
# overall_chain: input= Review
# and output= English_Review,summary, followup_message
overall_chain = SequentialChain(
chains=[chain_one, chain_two, chain_three, chain_four],
input_variables=["Review"],
output_variables=["English_Review", "summary","followup_message"],
verbose=True
)
可以看到,相比于 SimpleSequentialChain,SequentialChain 需要每个子链都指定输出的变量名,也就是 output_key(毕竟每个 LLM 调用只有一个输出),然后在其他子链里面直接在 prompt template 里面使用即可。SequentialChain 会自动根据 prompt 判断调用关系,形成 DAG 图,然后按顺序调用 LLM
Router Chain
用来实现条件判断,然后选择不同的子链进行后续操作
比如我们设计了一个问答机器人,可以回答以下四个门类的问题
physics_template = """You are a very smart physics professor. \
You are great at answering questions about physics in a concise\
and easy to understand manner. \
When you don't know the answer to a question you admit\
that you don't know.
Here is a question:
{input}"""
math_template = """You are a very good mathematician. \
You are great at answering math questions. \
You are so good because you are able to break down \
hard problems into their component parts,
answer the component parts, and then put them together\
to answer the broader question.
Here is a question:
{input}"""
history_template = """You are a very good historian. \
You have an excellent knowledge of and understanding of people,\
events and contexts from a range of historical periods. \
You have the ability to think, reflect, debate, discuss and \
evaluate the past. You have a respect for historical evidence\
and the ability to make use of it to support your explanations \
and judgements.
Here is a question:
{input}"""
computerscience_template = """ You are a successful computer scientist.\
You have a passion for creativity, collaboration,\
forward-thinking, confidence, strong problem-solving capabilities,\
understanding of theories and algorithms, and excellent communication \
skills. You are great at answering coding questions. \
You are so good because you know how to solve a problem by \
describing the solution in imperative steps \
that a machine can easily interpret and you know how to \
choose a solution that has a good balance between \
time complexity and space complexity.
Here is a question:
{input}"""
prompt_infos = [
{
"name": "physics",
"description": "Good for answering questions about physics",
"prompt_template": physics_template
},
{
"name": "math",
"description": "Good for answering math questions",
"prompt_template": math_template
},
{
"name": "History",
"description": "Good for answering history questions",
"prompt_template": history_template
},
{
"name": "computer science",
"description": "Good for answering computer science questions",
"prompt_template": computerscience_template
}
]
为这四个门类创建四个子链,保存在 destination_chains 里面
destination_chains = {}
for p_info in prompt_infos:
name = p_info["name"]
prompt_template = p_info["prompt_template"]
prompt = ChatPromptTemplate.from_template(template=prompt_template)
chain = LLMChain(llm=llm, prompt=prompt)
destination_chains[name] = chain
为这四个子链提供描述,以便放到 prompt template 里面
destinations = [f"{p['name']}: {p['description']}" for p in prompt_infos]
destinations_str = "\n".join(destinations)
以免用户的问题不属于这四个门类,再添加一条默认子链
default_prompt = ChatPromptTemplate.from_template("{input}")
default_chain = LLMChain(llm=llm, prompt=default_prompt)
为 router 设计 prompt template
MULTI_PROMPT_ROUTER_TEMPLATE = """Given a raw text input to a \
language model select the model prompt best suited for the input. \
You will be given the names of the available prompts and a \
description of what the prompt is best suited for. \
You may also revise the original input if you think that revising\
it will ultimately lead to a better response from the language model.
<< FORMATTING >>
Return a markdown code snippet with a JSON object formatted to look like:
```json
{{{{
"destination": string \ name of the prompt to use or "DEFAULT"
"next_inputs": string \ a potentially modified version of the original input
}}}}
```
REMEMBER: "destination" MUST be one of the candidate prompt \
names specified below OR it can be "DEFAULT" if the input is not\
well suited for any of the candidate prompts.
REMEMBER: "next_inputs" can just be the original input \
if you don't think any modifications are needed.
<< CANDIDATE PROMPTS >>
{destinations}
<< INPUT >>
{{input}}
<< OUTPUT (remember to include the ```json)>>"""
可以看到,判断用户的输入属于哪个门类,也是 LLM 的工作之一
然后我们创建 RouterChain
router_template = MULTI_PROMPT_ROUTER_TEMPLATE.format(
destinations=destinations_str
)
router_prompt = PromptTemplate(
template=router_template,
input_variables=["input"],
output_parser=RouterOutputParser(),
)
router_chain = LLMRouterChain.from_llm(llm, router_prompt)
Router 只负责判断用户输入的门类,我们还需要一个 MultiPromptChain 来连接之前创建的四个子链和一个默认子链
chain = MultiPromptChain(
router_chain=router_chain,
destination_chains=destination_chains,
default_chain=default_chain, verbose=True
)
构建完毕,我们可以问它问题了,比如如下一个物理问题
chain.run("What is black body radiation?")
Question and Answer
实现一个从 CSV 中查询某些行的应用:
from langchain.chains import RetrievalQA
from langchain.chat_models import ChatOpenAI
from langchain.document_loaders import CSVLoader
from langchain.vectorstores import DocArrayInMemorySearch
from langchain.indexes import VectorstoreIndexCreator
from IPython.display import display, Markdown
# Load a CSV file into a list of Documents.
# Each document represents one row of the CSV file.
# Every row is converted into a key/value pair and outputted to a new line in the document’s page_content.
file = 'OutdoorClothingCatalog_1000.csv'
loader = CSVLoader(file_path=file)
# create an index wrapper for easy access
index = VectorstoreIndexCreator(
# store embedding vectors in memory
vectorstore_cls=DocArrayInMemorySearch
).from_loaders([loader]) # Create a vectorstore index from loaders.
query ="Please list all your shirts with sun protection \
in a table in markdown and summarize each one."
# query with the default LLM (OpenAI)
response = index.query(query)
display(Markdown(response))
- LLM 对数据进行 embedding,获得向量,并保存到数据库
- LLM 对 query 进行 embedding,获得向量
- 从数据库中找到与 query 向量相似的向量,然后返回对应的数据
- 把数据和 query 交给 LLM,返回人类语言描述的结果
from langchain.document_loaders import CSVLoader
from langchain.embeddings import OpenAIEmbeddings
# load CSV file into documents
loader = CSVLoader(file_path=file)
docs = loader.load()
# index documents with OpenAI embeddings
# and store them in memory
embeddings = OpenAIEmbeddings()
db = DocArrayInMemorySearch.from_documents(
docs,
embeddings
)
# we can embed a query
embed = embeddings.embed_query("Hi my name is Harrison")
# or directly search for similar documents
docs = db.similarity_search(query)
# we need to feed the search results to LLM
# so we create a retriever
retriever = db.as_retriever()
# create a RetrievalQA chain
qa_stuff = RetrievalQA.from_chain_type(
llm=llm,
chain_type="stuff",
retriever=retriever,
verbose=True
)
# now we can run a query
response = qa_stuff.run(query)
Chain Type
上述的示例使用了stuff作为 RetrievalQA 的 chain type,这个 chain type 会把所有搜索结果交给 LLM
如果搜索结果太多/太大,就不好使了。以下是其他 Chain Type
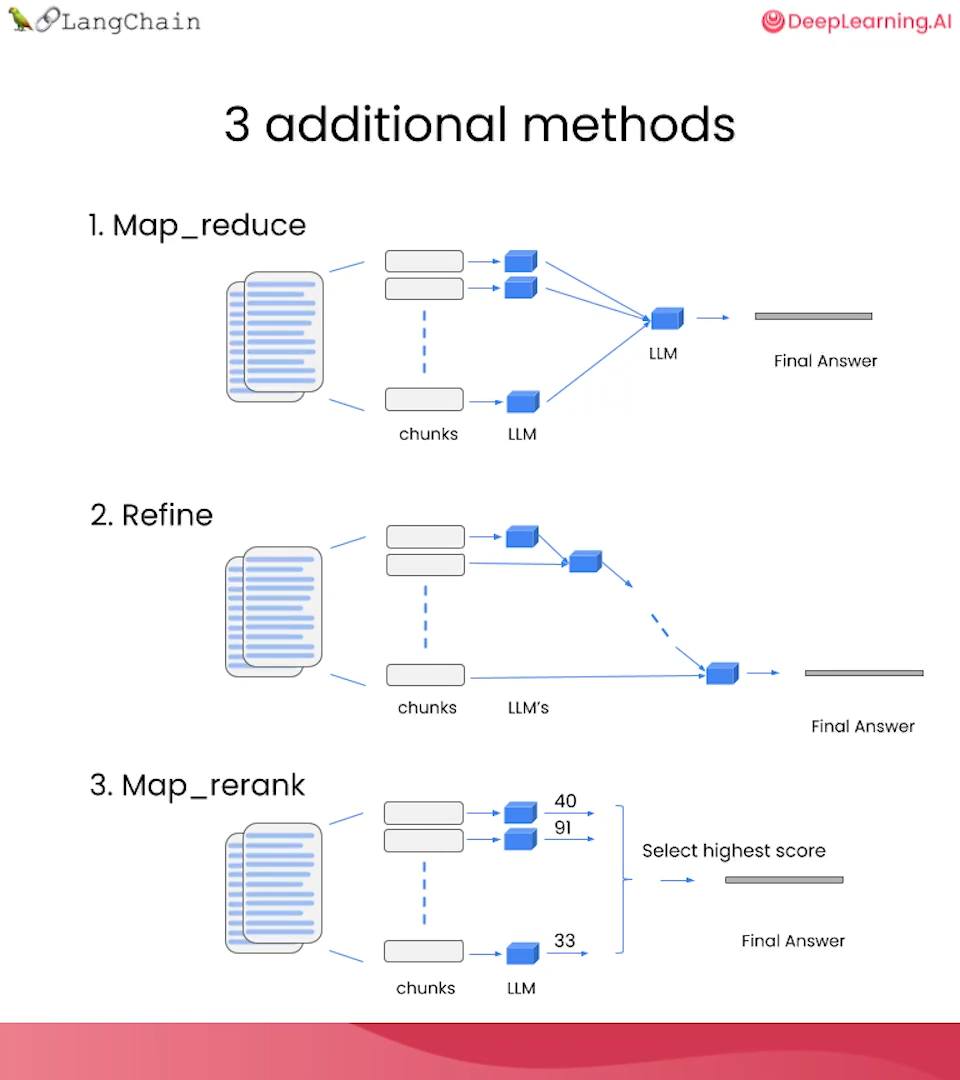
Evaluation
如何评估 LLM 的表现?或者说 LLM 在回答问题上的正确率?
手动给出 ground truth
针对一个 context(比如:数据集),手动给出 query 和 answer
examples = [
{
"query": "Do the Cozy Comfort Pullover Set\
have side pockets?",
"answer": "Yes"
},
{
"query": "What collection is the Ultra-Lofty \
850 Stretch Down Hooded Jacket from?",
"answer": "The DownTek collection"
}
]
使用 LLM 自动化生成 ground truth
使用 QAGenerateChain,从文档中生成 question-answer-pair
from langchain.evaluation.qa import QAGenerateChain
example_gen_chain = QAGenerateChain.from_llm(ChatOpenAI(model=llm_model))
new_examples = example_gen_chain.apply_and_parse(
[{"doc": t} for t in data[:5]]
)
评估 LLM
有了 ground truth,就可以对 LLM 的返回结果进行评估了
# get predict results
predictions = qa.apply(examples)
# compare predictions with ground truth
from langchain.evaluation.qa import QAEvalChain
eval_chain = QAEvalChain.from_llm(llm)
graded_outputs = eval_chain.evaluate(examples, predictions)
因为 LLM 的随机性,使用 QAGenerateChain 生成的答案,和 RetrievalQA 找到的答案,可能表达方式不一样,但是表达的意思是一样的,所以使用 QAEvalChain 评估二者的意思是否相同
Agents
使用 Agents 和外部环境交互,从而实现更多的功能
为了消除随机性,可以把 LLM 的 temperature 设置为 0,以确保 LLM 返回的结果的准确性
以下为一个示例
from langchain.agents.agent_toolkits import create_python_agent
from langchain.agents import load_tools, initialize_agent
from langchain.agents import AgentType
from langchain.tools.python.tool import PythonREPLTool
from langchain.python import PythonREPL
from langchain.chat_models import ChatOpenAI
llm = ChatOpenAI(temperature=0, model=llm_model)
# llm-math是一个使用LLM和计算器解决数学问题的chain
# wikipedia是一个连接维基百科API的chain,用来实现搜索
tools = load_tools(["llm-math","wikipedia"], llm=llm)
agent = initialize_agent(
tools,
llm,
# 使用Chat大模型
# 使用ReAct模型实现prompt engineering
agent=AgentType.CHAT_ZERO_SHOT_REACT_DESCRIPTION,
# 如果LLM的输出无法被解析,则让LLM解析这个输出并进行自动修正
handle_parsing_errors=True,
verbose = True)
现在我们用这个 agent 计算一个数学问题
agent("What is the 25% of 300?")
Agent 会判断:应该使用 Calculator,并且输入是300*0.25。然后调用外部计算器的 API,返回75.0
同理,我们可以让 Agent 帮我们查维基百科,或者执行代码
自定义 tool
非常简单,只需要给一个函数加上@tool装饰器即可
我们必须给函数加上 docstring,这样 Agent 才能知道这个函数的功能,以便在合适的时候调用
from langchain.agents import tool
from datetime import date
@tool
def time(text: str) -> str:
"""Returns todays date, use this for any \
questions related to knowing todays date. \
The input should always be an empty string, \
and this function will always return todays \
date - any date mathmatics should occur \
outside this function."""
return str(date.today())
</div
Recommend
About Joyk
Aggregate valuable and interesting links.
Joyk means Joy of geeK