

源码分析基于 bitcask 的 rosedb 存储引擎初始化和关闭的实现
source link: https://xiaorui.cc/archives/7406
Go to the source link to view the article. You can view the picture content, updated content and better typesetting reading experience. If the link is broken, please click the button below to view the snapshot at that time.
源码分析基于 bitcask 的 rosedb 存储引擎的初始化和关闭的实现
golang bitcask rosedb 存储引擎实现原理系列的文章地址 (更新中)
https://github.com/rfyiamcool/notes#golang-bitcask-rosedb
rosedb 启动实现
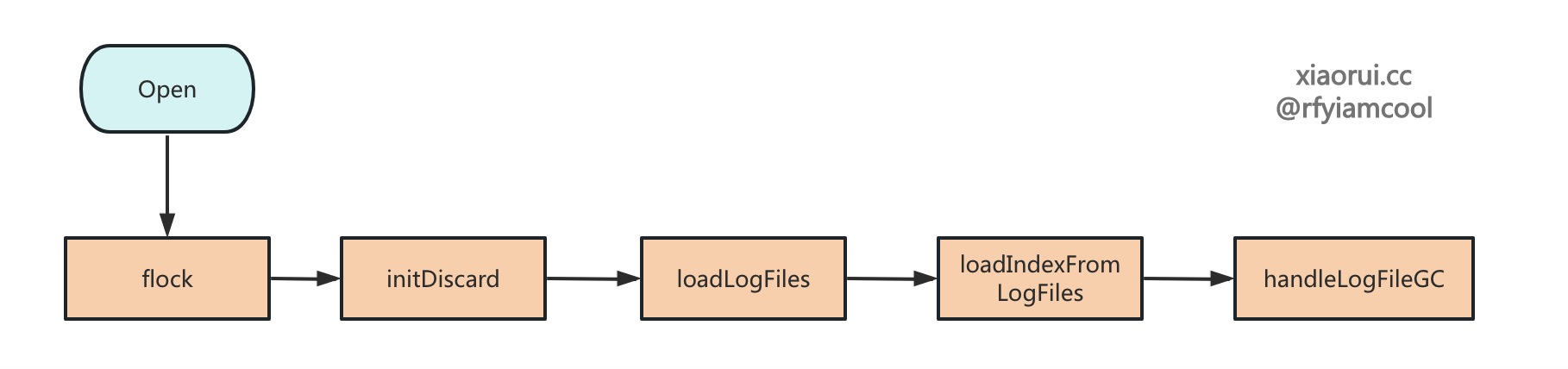
Open 为 Rosedb 的初始化入口,其内部流程如下。
- 创建 rosedb 的 DB 目录 ;
- 使用 flock 实现文件锁,对 db 的目录加锁,保证只有一个 rosedb 实例可以读写 db 文件 ;
- 实例化 rosedb 对象 ;
- 读取所有的 discard 文件 ;
- 加载所有的 logfile 对象,这里只是组织实例化 logfile 对象,不读取其内容 ;
- 对 logfile 进行排序,然后读取 logfile 内的数据,并把数据添加到内存索引结构里 ;
- 开启 GC 垃圾回收器,默认每 8 个小时执行一波垃圾回收。
func Open(opts Options) (*RoseDB, error) {
// 如果 dbpath 不存在则创建.
if !util.PathExist(opts.DBPath) {
if err := os.MkdirAll(opts.DBPath, os.ModePerm); err != nil {
return nil, err
}
}
// 使用 flock 实现文件锁,对 db 的目录加锁,保证只有一个 rosedb 实例可以读写 db 文件。
lockPath := filepath.Join(opts.DBPath, lockFileName)
lockGuard, err := flock.AcquireFileLock(lockPath, false)
if err != nil {
return nil, err
}
// 实例化 rosedb 对象
db := &RoseDB{
activeLogFiles: make(map[DataType]*logfile.LogFile),
archivedLogFiles: make(map[DataType]archivedFiles),
opts: opts,
fileLock: lockGuard,
strIndex: newStrsIndex(),
listIndex: newListIdx(),
hashIndex: newHashIdx(),
setIndex: newSetIdx(),
zsetIndex: newZSetIdx(),
}
// 读取所有的 discard 文件.
if err := db.initDiscard(); err != nil {
return nil, err
}
// 加载所有的 logfile 对象,这里只是组织实例化 logfile 对象,不读取其内容.
if err := db.loadLogFiles(); err != nil {
return nil, err
}
// 对 logfile 进行排序,然后读取 logfile 内的数据,并把数据添加到内存索引结构里.
if err := db.loadIndexFromLogFiles(); err != nil {
return nil, err
}
// 开启 GC 垃圾回收.
go db.handleLogFileGC()
return db, nil
}
读取 discard 数据
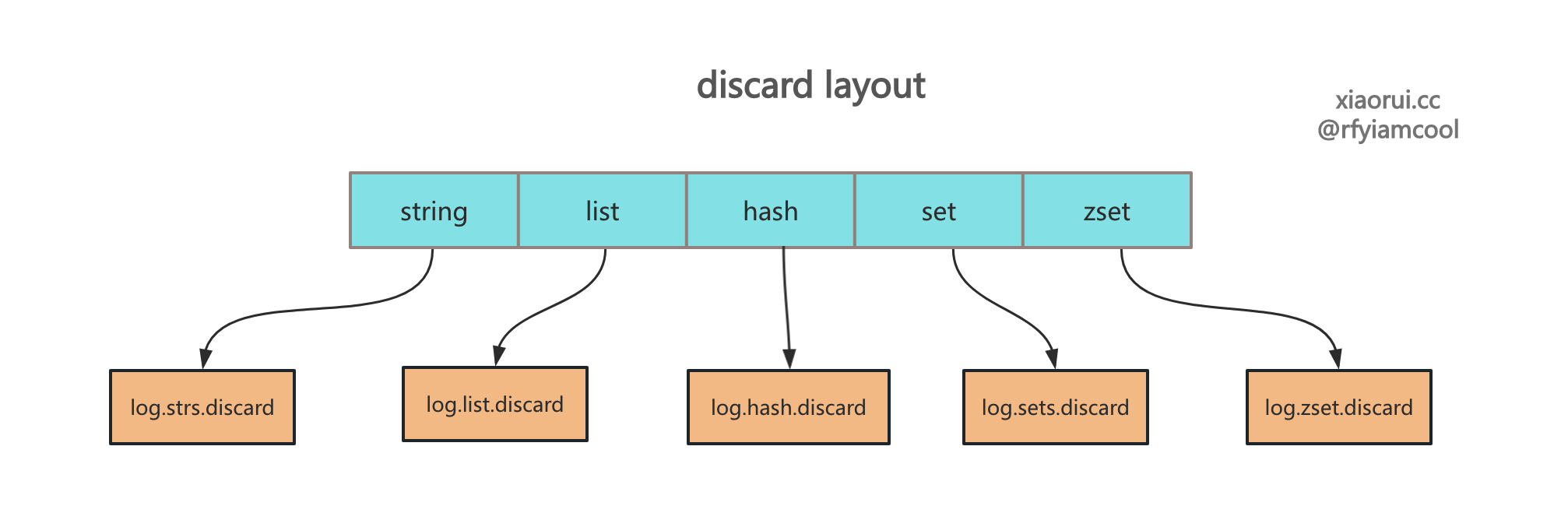
读取各个 dataType 的 discard 数据,然后全局的构建 discard 统计信息。newDiscard 方法内部会按照 discard record 格式读取文件中的统计信息,然后启动一个协程来接收 discard 事件并写入统计文件。
func (db *RoseDB) initDiscard() error {
discardPath := filepath.Join(db.opts.DBPath, discardFilePath)
// ...
discards := make(map[DataType]*discard)
// 读取各个 dataType 的 discard 数据.
for i := String; i < logFileTypeNum; i++ {
name := logfile.FileNamesMap[logfile.FileType(i)] + discardFileName
dis, err := newDiscard(discardPath, name, db.opts.DiscardBufferSize)
if err != nil {
return err
}
discards[i] = dis
}
db.discards = discards
return nil
}
加载所有的 logfile 日志文件
加载所有的 logfile 对象,这里只是组织实例化 logfile 对象,不读取其内容。
func (db *RoseDB) loadLogFiles() error {
// 加锁,放锁
db.mu.Lock()
defer db.mu.Unlock()
// 获取目录下 logfile 列表.
fileInfos, err := ioutil.ReadDir(db.opts.DBPath)
if err != nil {
return err
}
fidMap := make(map[DataType][]uint32)
for _, file := range fileInfos {
// rosedb 的 logfile 文件名前缀是 `log.type`,
if strings.HasPrefix(file.Name(), logfile.FilePrefix) {
splitNames := strings.Split(file.Name(), ".")
// 获取 logfile 的 file id.
fid, err := strconv.Atoi(splitNames[2])
if err != nil {
return err
}
// 获取 logfile 的 dataType
typ := DataType(logfile.FileTypesMap[splitNames[1]])
fidMap[typ] = append(fidMap[typ], uint32(fid))
}
}
db.fidMap = fidMap
// 遍历各个 dataType 的 logfile 列表
for dataType, fids := range fidMap {
if db.archivedLogFiles[dataType] == nil {
db.archivedLogFiles[dataType] = make(archivedFiles)
}
// 正序排序,旧日志文件在前面.
sort.Slice(fids, func(i, j int) bool {
return fids[i] < fids[j]
})
opts := db.opts
for i, fid := range fids {
ftype, iotype := logfile.FileType(dataType), logfile.IOType(opts.IoType)
// 构建 logfile 对象
lf, err := logfile.OpenLogFile(opts.DBPath, fid, opts.LogFileSizeThreshold, ftype, iotype)
if err != nil {
return err
}
// 最新的日志文件是活跃的 logfile,其他日志文件是归档集合里.
if i == len(fids)-1 {
db.activeLogFiles[dataType] = lf
} else {
db.archivedLogFiles[dataType][fid] = lf
}
}
}
return nil
}
读取 logfile 里的数据并添加到索引
loadIndexFromLogFiles 用来遍历读取 logfile 里的所有数据,并添加到内存的索引里。
为什么说 bitcask 模型不适合大存储模型 ? 就是因为其需要在内存里构建全量的索引,当数据特别多的时候,单单索引的开销也很大,还有启动时需要扫描所有的 logfile 文件内的数据来构建索引。当使用 sata 这类机械盘做存储时,假设 Disk磁盘吞吐在 200MB 左右,那么读取 20GB 的 DB 数据少说需要 100 秒。如果 DB 文件在 100GB,差不多需要近 10 分钟加载时间。
func (db *RoseDB) loadIndexFromLogFiles() error {
iterateAndHandle := func(dataType DataType, wg *sync.WaitGroup) {
defer wg.Done()
fids := db.fidMap[dataType]
if len(fids) == 0 {
return
}
// 对 logfile 正排序,旧的文件优先处理.
sort.Slice(fids, func(i, j int) bool {
return fids[i] < fids[j]
})
// 遍历 logfile 集合.
for i, fid := range fids {
var logFile *logfile.LogFile
if i == len(fids)-1 {
logFile = db.activeLogFiles[dataType]
} else {
logFile = db.archivedLogFiles[dataType][fid]
}
if logFile == nil {
logger.Fatalf("log file is nil, failed to open db")
}
// 初始化偏移量
var offset int64
for {
// 从偏移量读取 entry,其内部先读取 entry header,再根据 ksize 和 vsize 获取 kv 键值数据.
entry, esize, err := logFile.ReadLogEntry(offset)
if err != nil {
// 如果文件读到头,则跳出
if err == io.EOF || err == logfile.ErrEndOfEntry {
break
}
}
// 构建 valuePos 文件偏移量信息
pos := &valuePos{fid: fid, offset: offset}
// 把数据添加到 dataType 相关的索引里.
db.buildIndex(dataType, entry, pos)
// 累加偏移量
offset += esize
}
// 如果遍历到最新的 logfile, 则原子保存当前的活跃日志文件的 offset.
if i == len(fids)-1 {
atomic.StoreInt64(&logFile.WriteAt, offset)
}
}
}
wg := new(sync.WaitGroup)
wg.Add(logFileTypeNum)
// 为每个 dataType 启动给协程来加载数据,并构建索引.
for i := 0; i < logFileTypeNum; i++ {
go iterateAndHandle(DataType(i), wg)
}
wg.Wait()
return nil
}
rosedb 的关闭的实现
// Close db and save relative configs.
func (db *RoseDB) Close() error {
db.mu.Lock()
defer db.mu.Unlock()
if db.fileLock != nil {
// 关闭 flock 文件锁
_ = db.fileLock.Release()
}
// 对各个 dataType 的活跃文件执行同步落盘和关闭操作.
for _, activeFile := range db.activeLogFiles {
_ = activeFile.Close()
}
// 关闭归档文件对象
for _, archived := range db.archivedLogFiles {
for _, file := range archived {
_ = file.Sync()
_ = file.Close()
}
}
// 关闭 discard 管道,discard 内部协程会收尾并退出.
for _, dis := range db.discards {
dis.closeChan()
}
// 重置空对象
atomic.StoreUint32(&db.closed, 1)
db.strIndex = nil
db.hashIndex = nil
db.listIndex = nil
db.zsetIndex = nil
db.setIndex = nil
return nil
}
Recommend
About Joyk
Aggregate valuable and interesting links.
Joyk means Joy of geeK
