

SpringBoot静态资源配置原理详解
source link: https://www.51cto.com/article/751125.html
Go to the source link to view the article. You can view the picture content, updated content and better typesetting reading experience. If the link is broken, please click the button below to view the snapshot at that time.
环境:Springboot2.7.10
默认情况下,Spring Boot从类路径中的/static(或/public或/resources或/META-INF/resources)目录或ServletContext的根目录中提供静态内容。它使用来自Spring MVC的ResourceHttpRequestHandler,因此可以通过添加自己的WebMvcConfigurer并覆盖addResourceHandlers方法来修改该行为。
默认情况下,资源映射在/**上,但是你可以使用spring.mvc.static-path-pattern配置属性进行修改。例如,将所有资源重新定位到/resources/**可以实现如下:
默认静态资源路径
spring:
web:
resources:
static-locations:
- classpath:/META-INF/resources/
- classpath:/resources/
- classpath:/static/
- classpath:/public/目录结构如下:
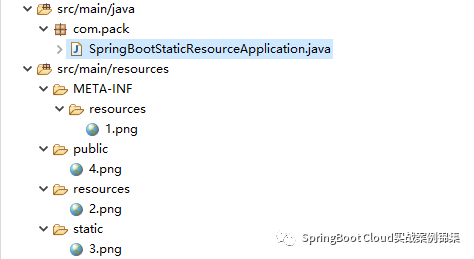
默认访问路径:http://localhost:8080/xxx.yy
修改访问路径
spring:
mvc:
static-path-pattern: /res/**如上修改后访问路径:
http://localhost:8080/res/xxx.yy
注意:如果你使用的是旧版本Springboot,这里的静态资源配置是spring.resources.static-locations
添加静态资源路径
spring:
web:
resources:
static-locations:
- classpath:/META-INF/resources/
- classpath:/resources/
- classpath:/static/
- classpath:/public/
- file:///D:/images/上面的:file:///D:/images/
编程方式配置
@Configuration
public class WebConfig implements WebMvcConfigurer {
@Override
public void addResourceHandlers(ResourceHandlerRegistry registry) {
registry.addResourceHandler("/static/**").addResourceLocations("file:///d:/images/") ;
registry.addResourceHandler("/h5/**").addResourceLocations("file:///d:/h5/") ;
}
}上面配置了2个文件系统的资源目录,分别以:/static/**,/h5/**路径进行访问
访问:
http://localhost:8080/static/xxx.yy,http://localhost:8080/h5/xxx。
WebJars静态资源
除了前面提到的“标准”静态资源位置之外,Webjars内容还有一个特殊情况。任何路径在/webjars/**中的资源都是从jar文件中提供的,前提是它们以webjars格式打包的。
如果你的应用程序打包为jar,请不要使用src/main/webapp目录。尽管这个目录是一个常见的标准,但它只适用于war打包,并且如果你生成一个jar,它会被大多数构建工具默默地忽略。
Spring Boot还支持Spring MVC提供的高级资源处理功能,允许使用缓存破坏静态资源或为Webjars使用版本不可知的URL等用例。
要为Webjars使用版本不可知的url,请添加webjars-locator-core依赖项。然后声明你的webjar。以jQuery为例,添加"/webjars/jQuery/jQuery .min.js"会得到"
/webjars/jQuery/x.y.z/jQuery .min.js",其中x.y.z是webjar版本。
为了使用缓存破坏,下面的配置为所有静态资源配置缓存破坏解决方案,有效地在url中添加内容哈希,例如<link href="
/css/spring-2a2d595e6ed9a0b24f027f2b63b134d6.css"/>:
spring:
web:
resources:
chain:
strategy:
content:
enabled: true
paths: "/**"静态资源访问原理
SpringMVC核心组件配置:
@Configuration(proxyBeanMethods = false)
public class DelegatingWebMvcConfiguration extends WebMvcConfigurationSupport {
private final WebMvcConfigurerComposite configurers = new WebMvcConfigurerComposite();
// 注入当前环境中所有的WebMvcConfigurer类型的Bean
@Autowired(required = false)
public void setConfigurers(List<WebMvcConfigurer> configurers) {
if (!CollectionUtils.isEmpty(configurers)) {
// 添加到上面的WebMvcConfigurerComposite中
this.configurers.addWebMvcConfigurers(configurers);
}
}
@Override
protected void addResourceHandlers(ResourceHandlerRegistry registry) {
// 调用WebMvcConfigurerComposite#addResourceHandlers方法,该方法内部
// 遍历所有的WebMvcConfigurer分别调用addResourceHandlers方法
this.configurers.addResourceHandlers(registry);
}
}
class WebMvcConfigurerComposite implements WebMvcConfigurer {
private final List<WebMvcConfigurer> delegates = new ArrayList<>();
@Override
public void addResourceHandlers(ResourceHandlerRegistry registry) {
for (WebMvcConfigurer delegate : this.delegates) {
delegate.addResourceHandlers(registry);
}
}
}Spring提供的一个WebMvcConfigurer实现
public static class WebMvcAutoConfigurationAdapter implements WebMvcConfigurer {
@Override
public void addResourceHandlers(ResourceHandlerRegistry registry) {
// ...
// addResourceHandler注册资源实例
addResourceHandler(registry, "/webjars/**", "classpath:/META-INF/resources/webjars/");
// getStaticPathPattern获取配置文件中spring.mvc.staticPathPattern属性值
addResourceHandler(registry, this.mvcProperties.getStaticPathPattern(), (registration) -> {
// getStaticLocations获取配置文件中spring.web.resources.staticLocations属性值
// 该方法调用后就会将资源访问路径与具体资源路径进行关联
registration.addResourceLocations(this.resourceProperties.getStaticLocations());
if (this.servletContext != null) {
ServletContextResource resource = new ServletContextResource(this.servletContext, SERVLET_LOCATION);
registration.addResourceLocations(resource);
}
});
}
private void addResourceHandler(ResourceHandlerRegistry registry, String pattern, String... locations) {
addResourceHandler(registry, pattern, (registration) -> registration.addResourceLocations(locations));
}
private void addResourceHandler(ResourceHandlerRegistry registry, String pattern, Consumer<ResourceHandlerRegistration> customizer) {
if (registry.hasMappingForPattern(pattern)) {
return;
}
// 创建并获取资源访问模式的的实例
ResourceHandlerRegistration registration = registry.addResourceHandler(pattern);
// 自定义配置
customizer.accept(registration);
// 缓存设置
registration.setCachePeriod(getSeconds(this.resourceProperties.getCache().getPeriod()));
registration.setCacheControl(this.resourceProperties.getCache().getCachecontrol().toHttpCacheControl());
registration.setUseLastModified(this.resourceProperties.getCache().isUseLastModified());
customizeResourceHandlerRegistration(registration);
}
}ResourceHandlerRegistry
public class ResourceHandlerRegistry {
private final List<ResourceHandlerRegistration> registrations = new ArrayList<>();
// 为每一种资源创建ResourceHandlerRegistration实例,添加到List集合中
public ResourceHandlerRegistration addResourceHandler(String... pathPatterns) {
ResourceHandlerRegistration registration = new ResourceHandlerRegistration(pathPatterns);
this.registrations.add(registration);
return registration;
}
}通过上面的源码我们只看到收集容器中所有WebMvcConfigurer类型的Bean,然后分别调用重写的addResourceHandlers方法接着为每一种资源访问路径/xxx创建对应的ResourceHandlerRegistration实例,并且将这些实例添加到ResourceHandlerRegistry中。
这里有2个疑问:
- ResourceHandlerRegistry是如何创建的
- 当访问这些静态资源时对应的HandlerMapping及Adapter又是谁如何与上面的ResourceHandlerRegistration关联的。
ResourceHandlerRegistry创建
上面的
DelegatingWebMvcConfiguration配置类继承WebMvcConfigurationSupport,该父类中有如下方法:
public class WebMvcConfigurationSupport {
// 该Bean是一个HandlerMapping(这是个接口),用来确定当前请求对应的处理器类
@Bean
public HandlerMapping resourceHandlerMapping(
@Qualifier("mvcContentNegotiationManager") ContentNegotiationManager contentNegotiationManager,
@Qualifier("mvcConversionService") FormattingConversionService conversionService,
@Qualifier("mvcResourceUrlProvider") ResourceUrlProvider resourceUrlProvider) {
PathMatchConfigurer pathConfig = getPathMatchConfigurer();
// 这里创建了资源注册器类
ResourceHandlerRegistry registry = new ResourceHandlerRegistry(this.applicationContext, this.servletContext, contentNegotiationManager, pathConfig.getUrlPathHelper());
// 添加注册静态资源,该访问正好被子类DelegatingWebMvcConfiguration重写了
// 而 在上面源码看到,子类就是遍历了容器中所有的WebMvcConfigurer对应的addResourceHandlers方法
// 到这里你就清楚了静态资源的注册入口,接下来就是这些静态资源对应是如何与HandlerMapping关联的
addResourceHandlers(registry);
// 获取HandlerMapping对象
AbstractHandlerMapping handlerMapping = registry.getHandlerMapping();
// ...
return handlerMapping;
}
}通过ResourceHandlerRegistry获取HandlerMapping对象
public class ResourceHandlerRegistry {
protected AbstractHandlerMapping getHandlerMapping() {
// 如果没有配置静态资源,那么就没有必要注册HandlerMapping了,直接返回null
if (this.registrations.isEmpty()) {
return null;
}
Map<String, HttpRequestHandler> urlMap = new LinkedHashMap<>();
// 遍历上面注册的所有静态资源对应的ResourceHandlerRegistration
for (ResourceHandlerRegistration registration : this.registrations) {
// 将ResourceHandlerRegistration对象转换为ResourceHttpRequestHandler对象
ResourceHttpRequestHandler handler = getRequestHandler(registration);
for (String pathPattern : registration.getPathPatterns()) {
// 以配置的访问路径为key,对应的ResourceHttpRequestHandler为处理句柄
// 当一个请求过来如果匹配了当前的模式,那么就会用对应的ResourceHttpRequestHandler对象进行处理
urlMap.put(pathPattern, handler);
}
}
return new SimpleUrlHandlerMapping(urlMap, this.order);
}
private ResourceHttpRequestHandler getRequestHandler(ResourceHandlerRegistration registration) {
// 获取
ResourceHttpRequestHandler handler = registration.getRequestHandler();
handler.setServletContext(this.servletContext);
handler.setApplicationContext(this.applicationContext);
try {
// 执行初始化
handler.afterPropertiesSet();
}
return handler;
}
}
public class ResourceHandlerRegistration {
protected ResourceHttpRequestHandler getRequestHandler() {
// 创建对象
ResourceHttpRequestHandler handler = new ResourceHttpRequestHandler();
// ...
// 设置路径
handler.setLocationValues(this.locationValues);
handler.setLocations(this.locationsResources);
if (this.cacheControl != null) {
handler.setCacheControl(this.cacheControl);
}
// ... 这里缓存设置
return handler;
}
}ResourceHttpRequestHandler对应的HandlerAdapter对象
public class HttpRequestHandlerAdapter implements HandlerAdapter {
@Override
public boolean supports(Object handler) {
// ResourceHttpRequestHandler实例HttpRequestHandler子类
return (handler instanceof HttpRequestHandler);
}
@Override
@Nullable
public ModelAndView handle(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, Object handler) throws Exception {
// 直接调用ResourceHttpRequestHandler#handleRequest方法
((HttpRequestHandler) handler).handleRequest(request, response);
return null;
}
}Recommend
About Joyk
Aggregate valuable and interesting links.
Joyk means Joy of geeK