

JS手撕(十一) 选择排序、快速排序
source link: https://www.clzczh.top/2022/12/24/js-%E6%89%8B%E6%92%9511/
Go to the source link to view the article. You can view the picture content, updated content and better typesetting reading experience. If the link is broken, please click the button below to view the snapshot at that time.
JS手撕(十一) 选择排序、快速排序
选择排序原理就是每次从未排序序列中选择最小元素,放到已排序序列的末尾。
那么如何选择最小元素,并把最小元素放到已排序序列的末尾?
只需要遍历寻找最小的数,并保存最小数的索引。遍历完之后,让最小数和已排序序列的末尾互换位置即可。
图片来自菜鸟教程
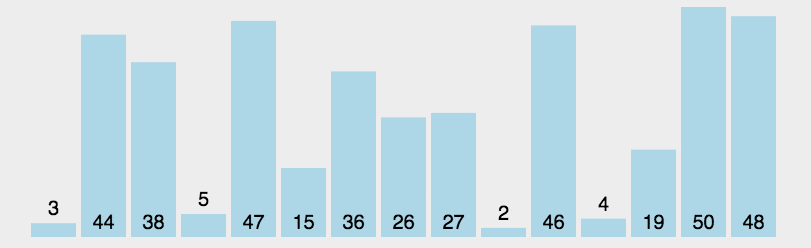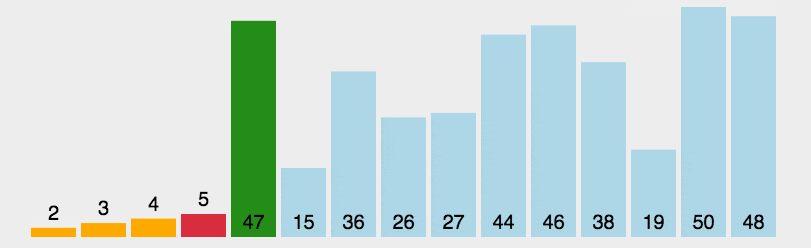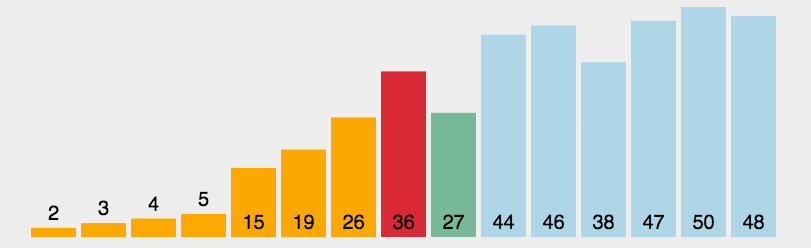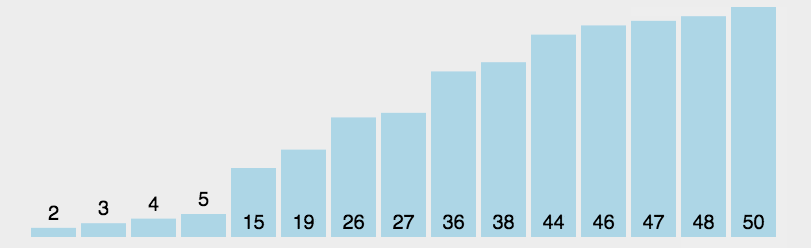
function selectSort(arr) {
const len = arr.length;
let minIndex; // 保存最小数的索引
for (let i = 0; i < len - 1; i++) { // 排好前n-1个,第n个数就是剩下的最大的。
minIndex = i; // 设置最小数的索引的默认值
for (let j = i + 1; j < len; j++) {
if (arr[j] < arr[minIndex]) {
// 遍历的数比之前村的最小数还小,更改最小数的索引位置
minIndex = j;
}
}
// 让最小数和已排序序列的末尾互换位置
[arr[i], arr[minIndex]] = [arr[minIndex], arr[i]];
}
return arr;
}
const selectSort = require('./sort.js');
let arr = [3, 44, 38, 5, 47, 15, 36, 26, 27, 2, 46, 26, 4, 19, 50, 48];
console.log(selectSort(arr))
时间复杂度:O(n²)
排序稳定性:不稳定
这里第一次遇到不稳定的排序。稍微举例子说明一下为什么是不稳定的。
上面一开始2*是在2之后的,排序完之后2*变成在2之前了,所以选择排序是不稳定的。
它是不稳定的关键就是让最小数和已排序序列的末尾互换位置时,可能把大小相同的数中在前面的移动到了后面去。
快速排序原理就是:
从数组中挑出一个元素,称为基准(
pivot)。将所有比基准值小的放在基准前面,所有比基准值大的放在放在基准后面。该操作称为分区操作(
partition)递归地把小于基准值地子序列和大于基准值地子序列排序
图片来自菜鸟教程
function quickSort(arr, l, r) {
if (l >= r) {
return;
}
const partionIndex = partition(arr, l, r);
// 递归排序小于基准值的子数列
quickSort(arr, l, partionIndex - 1);
// 递归排序大于基准值的子数列
quickSort(arr, partionIndex + 1, r);
return arr;
}
function partition(arr, l, r) {
let pivot = l;
let index = l + 1;
for (let i = index; i <= r; i++) {
if (arr[i] < arr[pivot]) {
// 把小于标杆的移到左边
[arr[index], arr[i]] = [arr[i], arr[index]];
index++;
}
}
// 标杆归位
[arr[index - 1], arr[pivot]] = [arr[pivot], arr[index - 1]];
// 返回标杆的位置
return index - 1;
}
快速排序最坏的情况是初始序列已经有序,第一趟排序经过n-1次比较后,第一个元素仍然在原来的位置,第二趟经过n-2次比较厚,也还在原来的位置。依此类推,最后的总比较次数是(n-1) + (n-2) + ... + 1 = n(n-1)/2。即最坏时间复杂度是O(n²)。
至于如何改进,那就是随机取基准。因为上面是一直取第一位为基准,所以就导致了初始序列有序的情况下时间复杂度是O(n²)。而随机取基准就能解决这种情况。
修改起来也很简单,只需要将partition函数那里的pivot修改成取随机数即可,不过还需要将arr[pivot]和arr[l]切换位置,并将pivot设置为l。因为整个算法的逻辑都是按第一位是基准来写的,所以还用之前的逻辑的话,只能随机取值,并把它换到第一位。
// partition函数开始部分
// [l, r]区间取随机数,注意是闭区间
let pivot = Math.floor(Math.random() * (r - l) + l);
[arr[l], arr[pivot]] = [arr[pivot], arr[l]];
pivot = l;
JS特殊实现
主要利用concat方法能用来合并数组,所以使用concat搭配递归调用就能很方便的实现。
function quickSort(arr) {
if (arr.length <= 1) {
// 递归退出条件
return arr;
}
// 随机取基准索引
const pivotIndex = Math.floor(Math.random() * (arr.length - 1));
// 基准值
const pivot = arr.splice(pivotIndex, 1)[0];
const left = [];
const right = [];
for (const item of arr) {
if (item < pivot) {
// 小于基准值的放在基准值左边
left.push(item);
} else {
right.push(item);
}
}
// 递归+concat实现子数组排序
return quickSort(left).concat(pivot, quickSort(right));
}
时间复杂度:O(nlogn)
排序稳定性:不稳定。因为比基准值小的时候,需要换到基准值的左边,这里会引起相同值的相对位置的变换,所以快速排序是不稳定的。
Recommend
About Joyk
Aggregate valuable and interesting links.
Joyk means Joy of geeK