

What did I learn from Google UX Design Specialization?
source link: https://uxplanet.org/what-did-i-learn-from-google-ux-design-specialization-4f3ddc3e0670
Go to the source link to view the article. You can view the picture content, updated content and better typesetting reading experience. If the link is broken, please click the button below to view the snapshot at that time.
What did I learn from Google UX Design Specialization?
Here is the story concluding all my learnings from the google UX Design specialization course.
Overview
I am following my passion as an Artist along with my college in 2019 and after covid hit, Art became my full-time job.
One day while I was searching for inspiration on the internet to draw something, I saw an advertisement related to UX Design and that is where my journey as a UX designer starts.
Upon further research about “How to start with UX Design, I got to know about “The Google UX design" specialization from Coursera and I enrolled myself in the course.
This specialization consists of 7 courses and here I am concluding my learnings from course 2 i.e. Start the UX Design Process: Empathize, Define & Ideate
This story is not about review or feedback on the course but about what I have learnt from this specialization.
Most of us already know what the design thinking process is and the 5 steps included in the design thinking process.
According to Interaction Design Foundation: Design thinking is a non-linear, iterative process that teams use to understand users, challenge assumptions, redefine problems and create innovative solutions to prototype and test
It involves 5 phases which are:
- Empathize
- Define
- Ideate
- Prototype
In course 2 of this specialization, I have understood
- How to empathize with potential users?
- How to define user needs?
- How to ideate solutions for those users' needs?
This course is not only about theory but also includes many hands-on exercises which I am going to include in this story.
Project Prompt (Assignment — 1)
Before coming up to the first step of the design thinking process, I have to choose a prompt for my first portfolio project.
My project prompt for the first portfolio project: Design an e-commerce mobile application focused on artworks & handmade products.
Empathize
Coming on to the first step of the design thinking process i.e. empathising
Empathy: the ability to understand someone else’s feelings or thoughts in a situation.
And it is different from pity and sympathy means empathy goes above pity and sympathy.
If you are empathizing that means you are putting yourself in the place of that person/user i.e. you are experiencing those feelings.
Empathizing with users helps us to solve problems that users have instead of making assumptions by ourselves.
Empathizing is done in many ways such as interviewing them, creating surveys, through empathy maps, user’s personas, user stories etc.
But how do we talk to users?
To talk to users as a designer, we need to first recruit them.
Recruitment can be done through a screener survey which means preparing a list of questions and that list of questions can be prepared with the help of determining the interview goals.
One more important point to consider when preparing a screener survey is to find your target population and that target population should be diverse i.e. it should include people of different age groups, races, gender or culture.
Finding people for an interview depends upon various business constraints as well such as budget, time, type of product and accessibility etc.
Interview goals for my portfolio project (Assignment — 2)
- Understand user/customer behaviour while shopping.
- Problems users face while shopping whether it is online/offline.
- Understand users' emotions and various experiences while shopping especially handmade or handicrafts products.
- Common challenges users face trying to manage shopping and their schedule.
The target population for my portfolio project (Assignment — 3)
- Age Group: — 18–60
- According to a research study — Women are twice as likely as men to purchase handmade goods online.
- The residential sector which dominates the market and is further categorized into home accessories, furniture, jewellery, home textiles and others.
- Region-wise, North America exhibits a clear dominance in the market as consumers in the region are willing to spend substantially on handicrafts, including handmade jewellery, apparel and handcrafted home accessories.
Empathy Maps
Once the exercise of conducting interviews is done, we need to analyse those interviews to get the insights and pain points that a large group of users feel or have.
And that can be done by creating empathy maps.
If goes by definition, an Empathy map is a chart that explains everything designers have learnt about a large group of users that define our target population.
Read more about empathy maps: https://www.nngroup.com/articles/empathy-mapping/#:~:text=Traditional%20empathy%20maps%20are%20split,or%20persona%20in%20the%20middle.
Empathy maps are of two types
- One-user empathy maps: One-user (individual) empathy maps are usually based on a user interview or a user’s log from a diary study.
- Aggregated empathy maps: represent a user segment, rather than one particular user. They are usually created by combining multiple individual empathy maps from users who exhibit similar behaviours and can be grouped into one segment.
Empathy maps help us understand user pain points and problems and also get into users’ mindsets and allow us to know their pain points.
User Personas
As Empathy maps help us to know about users’ pain points, personas help us to identify users’ patterns of behaviour.
Personas are fictional users built based on research.
While researching through interviews or surveys whatever image we formed about our large group of users who have similar interests, goals and concerns are known as personas and that’s why it is fictional because it is based on the image we formed about the large group of users.
In definition terms: Personas are fictional users whose goals and characteristics represent the needs of a larger group of users.
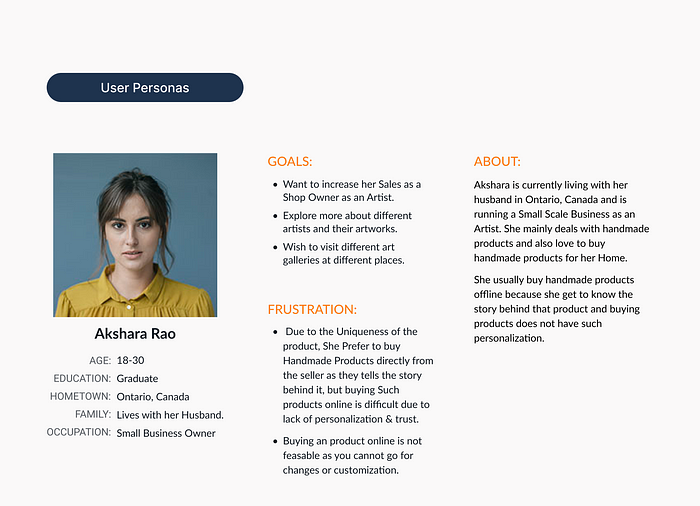
Personas for my portfolio project (Assignment — 4)
After doing secondary research, I have created 2 sets of personas for my portfolio project.

User Stories
User stories help us to choose the design goals/problem statements which are more important to solve at present moment and simultaneously from the business point of view also, we have the budget and capabilities to solve them.
User stories can also be considered as a checklist for solving the problems that large groups of users face.
In definition terms, a User’s Story is a one-sentence fictional story told from a personal point of view to inspire and inform design decisions.
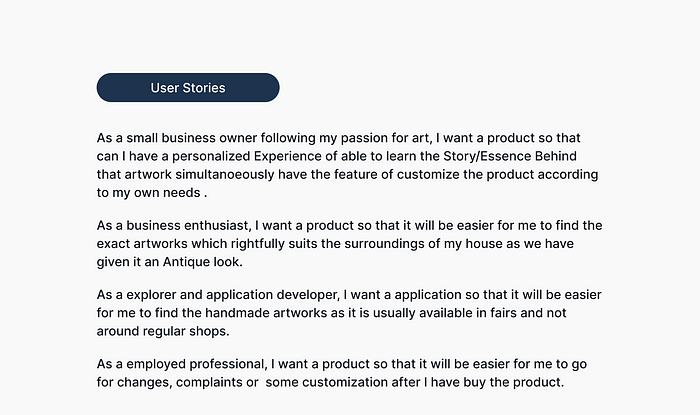
User Stories for my portfolio project (Assignment — 5)
With the help of secondary research and personas, I have created a set of user stories for my portfolio project.
User Journey Map
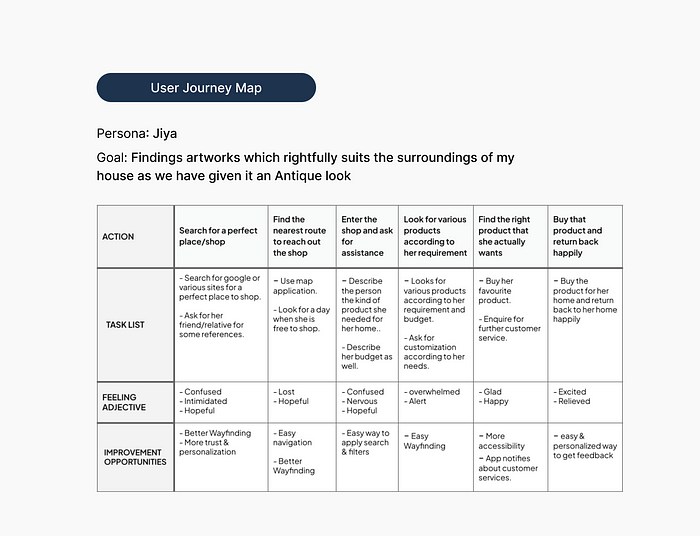
As the name suggests, users' journey is the journey that users go through to achieve their goals i.e. mapping their series of experiences so that we can identify where they face the problems.
User Journey Map for my portfolio project (Assignment — 6)
Define
After empathizing, the next step is to define the user’s needs and problems.
To define the actual user's problems we need to synthesize our research (interviews, personas and user journeys).
It is just like finding the conclusion from research in the form of users' needs and problems.
Problem Statement
Problem statements are a clear definition/description of users' needs.
It is being written so that the whole team including designers, developers and project managers can be aligned on the same page.
Problem Statement for my portfolio project (Assignment — 7)
For defining the problem statement, I have used secondary research along with using the 5 Ws and H framework which means who, what, where, when, why & how.

Hypothesis Statements
After we have written problem statements, we will start brainstorming the solutions i.e. we will make a hypothesis in our mind such as
For eg., If we will take this action then this could be the outcome.
Hypothesis Statement for my portfolio project (Assignment — 8)
Again with the help of secondary research on the internet by reading various articles & blogs, I have come up with hypothesis statements using the if-then formula.

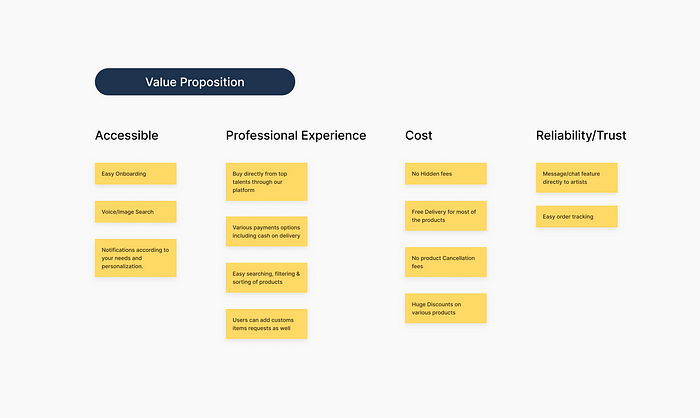
Value Proposition
After we have known our user's needs, it’s important to also know how well our product will meet those needs i.e. to know how and why our users will use our product which is known as the “Value Proposition".
By answering 2 simple questions that are taught in this course to me and considering the user’s needs, I have specified the value proposition for my product.
These questions are:-
- What does my product do?
- Why should the user care?
The 4 core values while deciding the value proposition factors are accessibility, professional experience, cost & reliability/trust.
These core values are decided based on research & insights gathered from that secondary research.
Value Proposition for my portfolio project (Assignment — 9)
Psychology in design
UX designers along with multiple other factors need to understand human psychology while designing because every human is unique in their behaviour and every human will use our product according to their psychology and understanding.
For eg. Feedback loop: when a user clicks on submit button, he/she instantly gets feedback that the task has been completed.
Why it is so?
Because of psychological reasons
Suppose this feedback is not given then the user might be confused about whether the task has been completed or not.
That is why psychology in design is important.
Ideation
Ideation means coming up with lots of ideas on given problem statements with no attempt to judge or evaluate them.
Coming up with lots of ideas is important because we never know which idea can do magic.
After coming up with lots of ideas, we need to evaluate which ideas are feasible for us to apply because as a human we do have a lot of financial, technical and desirable constraints.
Simultaneously our idea should be inclusive so that every user regardless of age, gender, culture etc can use that product.
Ideation can be done with the help of two methods
- Crazy Eights: In this method, we fold a sheet of paper into 8 folds and within 8 minutes we will sketch 8 different designs (1 minute is given to 1 design).
- How might we: It is a design thinking activity which is used to turn problems into opportunities for design. For eg. I can’t find a product I want for my home decor. In the HMW framework, this can be formed such as How Might We choose a product that fits according to the aesthetics of my home?
Competitive Audit
It is an overview of your competitor's strengths and weaknesses.
Competitive Audit can help us to learn from the mistakes of our competitors and simultaneously takes inspiration for what they do the best and how which is why it is important to prepare it for your product as well.
Competitive Audit for my portfolio project (Assignment — 10)
Our competitors mainly include Etsy, amazon handmade & eBay and many more but due to project time constraints, I am only including Etsy's competitive study for mobile applications.

Key Takeaways
- It is not important to follow all the methods you know but since it is my first project, I want to try to practice as many methods as I can.
- The design thinking process is iterative. It may be possible that after starting UI designing or further research, we may make some changes to the value proposition and so on.
Future Scope
- A more detailed competitive study is to be done.
- After completing the 3 stages of the design thinking process, I will move forward to the design & prototype stage.
- Since the design thinking process is iterative, hence in further stages according to the situation & needs we can redo the research, empathize and ideation stage.
Recommend
About Joyk
Aggregate valuable and interesting links.
Joyk means Joy of geeK