

决策树(二):后剪枝,连续值处理,数据加载器:DataLoader和模型评估 - 单车/
source link: https://www.cnblogs.com/danchegg/p/16908400.html
Go to the source link to view the article. You can view the picture content, updated content and better typesetting reading experience. If the link is broken, please click the button below to view the snapshot at that time.
决策树(二):后剪枝,连续值处理,数据加载器:DataLoader和模型评估
在上一篇文章中,我们实现了树的构造,在下面的内容中,我们将中心放在以下几个方面
1.剪枝
2.连续值处理
3.数据加载器:DataLoader
4.模型评估
一,后剪枝
我选择的是后剪枝,也就是先构造出完整的二叉树,最后在回过头来剪掉其中一部分节点
后剪枝方法:
1.数据量太少的节点剪掉,可以防止减小误差对模型的影响,降低过拟合风险,提高泛化能力
2.限制树的的深度
3.小于先验概率的节点剪掉,如果一个特征判断的能力甚至低于先验概率,那么就没有必要存在
# 后剪枝
def post_pruning(self,tree_dict,data,key=None):
def processing_data(data,col_name,value):
inx=data[col_name]==value
return data[inx]
for k in tree_dict:
# 如果不是叶子节点
if not isinstance(tree_dict[k], str):
if key in self.data.columns:
# 递归遍历所有节点
flag, count = self.post_pruning(tree_dict[k],data=processing_data(data,key,k),key=k)
else:flag, count = self.post_pruning(tree_dict[k], data=data, key=k)
# 如果知道叶子节点可以合并,返回两次找到爷爷节点,把父节点变为save或not save
if count == 1:
return flag, count + 1
elif count == 2:
tree_dict[k] = flag
#叶子节点,判断数据是否大于阈值
elif data.shape[0]<self.num_threshold:
if len(data[data[self.target]==0])>=len(data[self.target])/2:
return "not save",1
else:return "save",1
# 叶子节点,判断是否都相同
elif np.array([v == "save" for v in tree_dict.values()]).all():
return "save", 1
elif np.array([v == "not save" for v in tree_dict.values()]).all():
return "not save", 1
continue
return tree_dict, 0
二,连续值处理
处理方法:
def process_continue_value(x,y,total_entropy):
'''
:param x: data:pd
:param y: data[Survived]:pd
:param total_entropy: int
:return: 处理后的data
'''
data=x["Age"]
total_data=len(data)
mean_list=[]
gain_list=[]
data=np.array(data)
data.sort()
unique_data=np.unique(data)
for i in range(len(unique_data)-1):
mean_list.append((unique_data[i]+unique_data[i+1])/2)
for v in mean_list:
x1_index=np.where(data>=v)[0]
x2_index=np.where(data<v)[0]
kind_y1=y[x1_index]
kind_y2=y[x2_index]
len_kind1=len(kind_y1)
len_kind2 = len(kind_y2)
part_gain=total_entropy-(len_kind1/total_data)*entropy(kind_y1)-(len_kind2/total_data)*entropy(kind_y2)
gain_list.append(part_gain)
x["Age"]=[0 if i<mean_list[np.argmax(gain_list)] else 1 for i in x["Age"]]
return x
三,数据加载器:DataLoader
构造类数据加载器,传入data自动划分好train 和test,传入参数设置train和test比例,随机数种子,实现划分
class DataLoader(object):
def __init__(self,data:"pd",random_seed=None,test_size=0.33):
self.data=data
self.test_size=test_size
self.random_seed=random_seed if random_seed is not None else None
def __getitem__(self, index):
return self.data.iloc[index,:]
def __len__(self):
return len(self.data)
def split_data(self):
if self.random_seed is not None:
np.random.seed(self.random_seed)
train_data_idx=np.random.randint(0,len(self.data),size=int(len(self.data)*(1-self.test_size)))
test_data_idx=np.random.randint(0,len(self.data),size=int(len(self.data)*self.test_size))
train_data=self.data.iloc[train_data_idx,:]
test_data=self.data.iloc[test_data_idx,:]
return train_data,test_data
四,模型评估
模型的好坏我们无法肉眼观察,需要在测试集中测试,按照构建的决策树做决策,与真实值比较,得出准确率
def evaluator(self,tree_dict, test_data: "pd", target_name):
#调换数据顺序,按照信息增益由大到小
columns=test_data.columns
new_columns=[columns[i] for i in self.gain.argsort()[::-1]]
new_columns.append(target_name)
#改变顺序
test_data=test_data.reindex(columns=new_columns)
right=0
#遍历test_data中每一行数据
for index,row in test_data.iterrows():
temp_tree = tree_dict
#根据test_data做选择
for name in new_columns:
choice=row[name]
#如果没有当前分支则跳过
if choice not in temp_tree[name].keys():
value=None
break
value=temp_tree[name][choice]
temp_tree=value
if value in["save","not save"]:
#将y和pred_y同一
value=0 if value=="not save" else 1
break
if value==row[target_name]:
right+=1
accuracy = right/len(test_data)
return accuracy
五,总结
首先,先把代码跑的数据截图展示以下
1.未剪枝准确率:0.3299319727891156
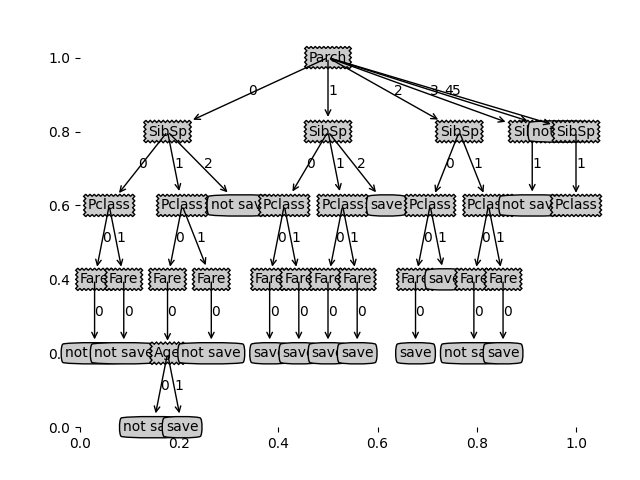
2.剪枝后准确率:0.6190476190476191
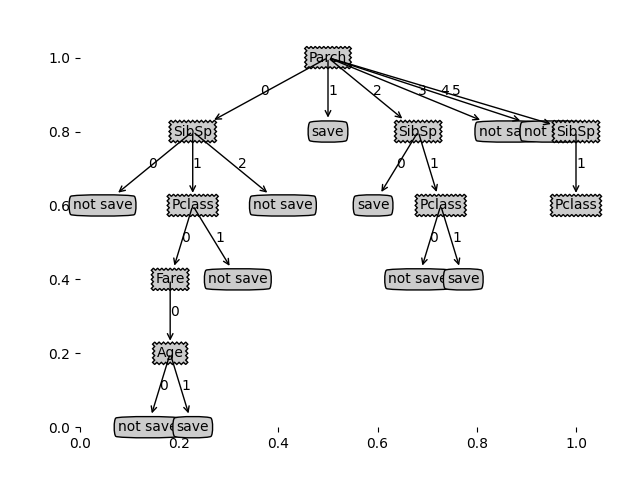
对比分析可见,剪枝后准确率大大提升
总结反思:1.在编写代码时,总是会出现各种错误,只有细心细心再细心,才能走向成功
2.在此次代码中运用大量递归,由于刚开始数据结构掌握的不熟练,吃了很多亏
3.在确定类时,刚开始没有构思好,导致后续整合时,走了弯路。之后最好先画类图,再动手是实现代码
最后,全部代码如下,数据在上一篇文章中已放出
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
from graphviz import Digraph
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import random
# 定义文本框和箭头格式
decisionNode = dict(boxstyle="sawtooth", fc="0.8")
leafNode = dict(boxstyle="round4", fc="0.8")
arrow_args = dict(arrowstyle="<-")
## 绘制带箭头的注解##############
def plotNode(nodeTxt, centerPt, parentPt, nodeType):
createPlot.ax1.annotate(nodeTxt, xy=parentPt, xycoords='axes fraction',
xytext=centerPt, textcoords='axes fraction',
va="center", ha="center", bbox=nodeType, arrowprops=arrow_args)
## PLOTTREE#################################
## 在父子节点间填充文本信息
def plotMidText(cntrPt, parentPt, txtString):
xMid = (parentPt[0] - cntrPt[0]) / 2.0 + cntrPt[0]
yMid = (parentPt[1] - cntrPt[1]) / 2.0 + cntrPt[1]
createPlot.ax1.text(xMid, yMid, txtString)
## 获取叶节点的数目和树的层数#######################
def getNumLeafs(myTree):
numLeafs = 0
firstStr = list(myTree.keys())[0]#找到输入的第一个元素
secondDict = myTree[firstStr]
for key in secondDict.keys():
if type(secondDict[key]).__name__ == 'dict':
numLeafs += getNumLeafs(secondDict[key])
else:
numLeafs += 1
return numLeafs
def getTreeDepth(myTree):
maxDepth = 0
firstStr = list(myTree.keys())[0]
secondDict = myTree[firstStr]
for key in secondDict.keys():
if type(secondDict[key]).__name__ == 'dict':
thisDepth = 1 + getTreeDepth(secondDict[key])
else:
thisDepth = 1
if thisDepth > maxDepth:
maxDepth = thisDepth
return maxDepth
def plotTree(myTree, parentPt, nodeTxt):
# 计算宽与高
numLeafs = getNumLeafs(myTree)
depth = getTreeDepth(myTree)
firstStr = list(myTree.keys())[0]
cntrPt = (plotTree.xOff + (1.0 + float(numLeafs)) / 2.0 / plotTree.totalW, plotTree.yOff)
# 标记子节点属性
plotMidText(cntrPt, parentPt, nodeTxt)
plotNode(firstStr, cntrPt, parentPt, decisionNode)
secondDict = myTree[firstStr]
# 减少y偏移
plotTree.yOff = plotTree.yOff - 1.0 / plotTree.totalD
for key in secondDict.keys():
if type(secondDict[key]) == dict:
plotTree(secondDict[key], cntrPt, str(key))
else:
plotTree.xOff = plotTree.xOff + 1.0 / plotTree.totalW
plotNode(secondDict[key], (plotTree.xOff, plotTree.yOff), cntrPt, leafNode)
plotMidText((plotTree.xOff, plotTree.yOff), cntrPt, str(key))
plotTree.yOff = plotTree.yOff + 1.0 / plotTree.totalD
def process(data):
#数据处理
data.drop("Embarked",inplace=True,axis=1)
x=data[["Age","Pclass","Sex","SibSp","Parch","Fare"]]
y=data["Survived"]
x["Pclass"] = x["Pclass"] - 1
x["SibSp"].fillna(x["SibSp"].mean(),inplace=True)#将缺省的用平均值填充
x["Parch"].fillna(x["Parch"].mean(),inplace=True)
x["Age"].fillna(x["Age"].mean(),inplace=True)
#将大于平均值的设为1
x["Fare"]=[1 if i>np.array(x["Fare"]).mean() else 0 for i in x["Fare"] ]
#将sex转为1和0
x["Sex"]=pd.factorize(x["Sex"])[0].astype(np.uint16)
return x,y
def process_data(data):
data = data[["Age", "Pclass", "Sex", "SibSp", "Parch", "Fare","Survived"]]
#使得Pclass从0开始
data["Pclass"]=data["Pclass"]-1
data["Fare"] = [1 if i > np.max(data["Fare"] / 2) else 0 for i in data["Fare"]]
data["Sex"] = pd.factorize(data["Sex"])[0].astype(np.uint16)
data["SibSp"].fillna(data["SibSp"].mean(),inplace=True)#将缺省的用平均值填充
data["Parch"].fillna(data["Parch"].mean(),inplace=True)
data["Age"].fillna(data["Age"].mean(), inplace=True)
return data
#计算信息熵
def entropy(data):
total_len=len(data)
len_1=np.where(data==1)[0].shape[0]
len_0=len(data)-len_1
# 出现问题:部分数据会返回nan
# 探索原因:当概率很小时,取对数后结果趋于负无穷大。
# 解决方法:改变浮点数的精度为1e - 5
p1=len_1/total_len+1e-5
p0=len_0/total_len+1e-5
entro=-np.sum([p0*np.log2(p0),p1*np.log2(p1)])
return entro
def process_continue_value(x,y,total_entropy):
'''
:param x: data:pd
:param y: data[Survived]:pd
:param total_entropy: int
:return: 处理后的data
'''
data=x["Age"]
total_data=len(data)
mean_list=[]
gain_list=[]
data=np.array(data)
data.sort()
unique_data=np.unique(data)
for i in range(len(unique_data)-1):
mean_list.append((unique_data[i]+unique_data[i+1])/2)
for v in mean_list:
x1_index=np.where(data>=v)[0]
x2_index=np.where(data<v)[0]
kind_y1=y[x1_index]
kind_y2=y[x2_index]
len_kind1=len(kind_y1)
len_kind2 = len(kind_y2)
part_gain=total_entropy-(len_kind1/total_data)*entropy(kind_y1)-(len_kind2/total_data)*entropy(kind_y2)
gain_list.append(part_gain)
x["Age"]=[0 if i<mean_list[np.argmax(gain_list)] else 1 for i in x["Age"]]
return x
#计算信息增益
def gain(total_entropy,x,y):
gain=[]
total_data=len(y)
# #将特征转为数字
# for f in x:
# x[f] = pd.factorize(x[f])[0].astype(np.uint16)
#计算每一个的gain
for feature in x:
# print("\n",feature)
part_entropy = []
for kind in np.unique(x[feature]):
# print("kind:",kind)
x_index=np.where(x[feature]==kind)[0]
kind_y=y[x_index]
len_kind=len(kind_y)
# print("len_kind:",len_kind)
# print("获救人数:",len(np.where(kind_y==1)[0]))
part_entropy.append((len_kind/total_data)*entropy(kind_y))
gain.append(total_entropy-np.sum(part_entropy))
return gain
class TreeNode(object):
def __init__(self,name,parent=None):
self.name=name
self.parent=parent
self.children={}
#重写,返回节点名称
def __repr__(self):
return "TreeNode(%s)"%self.name
def add_child(self,child,idx):
self.children[idx]=child
def print_tree(self,root:"TreeNode",leval=0):
print("第", leval, "层\n")
if root.parent==None:
print(root)
if root.children:
# print(root.name,":",end="")
print(root.children.values())
#将每一层的节点全部输出
#深度优先遍历
for child in root.children.values():
self.print_tree(child,leval+1)
print("\n")
#获得tree的字典
def get_tree_dict(self,root,data=None):
def split_data(data,feature,value):
inx=data[feature]==value
return data[inx]
#如果不是TreeNode类型,其实就是“empty”,就停止向下延伸
if not isinstance(root,TreeNode):
return
#如果没有数据,标记为empty
if data.empty:
return "empty"
#叶子节点时,那种多就标记为哪一种
if root.children=={}:
if len(data[data["Survived"]==0])>=len(data["Survived"])/2:
return "not save"
else :
return "save"
# # 类别完全相同,停止划分
if len(data[data["Survived"]==0])==len(data["Survived"]):
#如果data["Survived"]全为0
return "not save"
elif len(data[data["Survived"]==1])==len(data["Survived"]):
# 如果data["Survived"]全为1
return "save"
tree = {root.name: {}}
for key in root.children:
value=self.get_tree_dict(root.children[key],data=split_data(data,root.name,key))
#如果下个节点为empty,就不生成新的节点
if value=="empty":
continue
#递归,类似于dfs
tree[root.name][key]=value
return tree
class DecisionTree(object):
def __init__(self,gain,data:"pd.DataFrame",target,max_depth=None,num_threshold=5):
self.prior_probability=len(np.where(target==1)[0])/len(target)
self.max_depth=max_depth
self.num_threshold=num_threshold
self.depth=0
self.data=data
# self.gain=np.array(gain.sort(reverse=True))
self.gain=np.array(gain)
self.x=data.drop(target,axis=1)
self.target=target
# 深度优先建树
def init(self):
def dfs(node, map, leval=1):
# leval=0为根节点
if leval < len(map):
# 获取当前
cur_name = map[leval]
node_children = np.unique(self.x[cur_name])
cur_node = TreeNode(cur_name, node)
for i in node_children:
dfs(cur_node, map, leval + 1)
node.add_child(cur_node, i)
else:
return
features_name = [name for name in self.x]
# 逆序
features_index = self.gain.argsort()[::-1]
features_map = {}
# 将信息增益与对应的排名组成字典
for i,key in enumerate(features_index):
features_map[i] = features_name[key]
root = TreeNode(features_map[0])
dfs(root, features_map)
return root
# 后剪枝
def post_pruning(self,tree_dict,data,key=None):
def processing_data(data,col_name,value):
inx=data[col_name]==value
return data[inx]
for k in tree_dict:
# 如果不是叶子节点
if not isinstance(tree_dict[k], str):
if key in self.data.columns:
# 递归遍历所有节点
flag, count = self.post_pruning(tree_dict[k],data=processing_data(data,key,k),key=k)
else:flag, count = self.post_pruning(tree_dict[k], data=data, key=k)
# 如果知道叶子节点可以合并,返回两次找到爷爷节点,把父节点变为save或not save
if count == 1:
return flag, count + 1
elif count == 2:
tree_dict[k] = flag
#叶子节点,判断数据是否大于阈值
elif data.shape[0]<self.num_threshold:
if len(data[data[self.target]==0])>=len(data[self.target])/2:
return "not save",1
else:return "save",1
# 叶子节点,判断是否都相同
elif np.array([v == "save" for v in tree_dict.values()]).all():
return "save", 1
elif np.array([v == "not save" for v in tree_dict.values()]).all():
return "not save", 1
continue
return tree_dict, 0
def evaluator(self,tree_dict, test_data: "pd", target_name):
#调换数据顺序,按照信息增益由大到小
columns=test_data.columns
new_columns=[columns[i] for i in self.gain.argsort()[::-1]]
new_columns.append(target_name)
#改变顺序
test_data=test_data.reindex(columns=new_columns)
right=0
#遍历test_data中每一行数据
for index,row in test_data.iterrows():
temp_tree = tree_dict
#根据test_data做选择
for name in new_columns:
choice=row[name]
#如果没有当前分支则跳过
if choice not in temp_tree[name].keys():
value=None
break
value=temp_tree[name][choice]
temp_tree=value
if value in["save","not save"]:
#将y和pred_y同一
value=0 if value=="not save" else 1
break
if value==row[target_name]:
right+=1
accuracy = right/len(test_data)
return accuracy
def createPlot(inTree):
fig = plt.figure(1, facecolor='white')
fig.clf()
axprops = dict(xticks=[], yticks=[])
createPlot.ax1 = plt.subplot(111, frameon=False) # no ticks
plotTree.totalW = float(getNumLeafs(inTree))
plotTree.totalD = float(getTreeDepth(inTree))
plotTree.xOff = -0.5 / plotTree.totalW
plotTree.yOff = 1.0
plotTree(inTree, (0.5, 1.0), '')
plt.show()
class DataLoader(object):
def __init__(self,data:"pd",random_seed=None,test_size=0.33):
self.data=data
self.test_size=test_size
self.random_seed=random_seed if random_seed is not None else None
def __getitem__(self, index):
return self.data.iloc[index,:]
def __len__(self):
return len(self.data)
def split_data(self):
if self.random_seed is not None:
np.random.seed(self.random_seed)
train_data_idx=np.random.randint(0,len(self.data),size=int(len(self.data)*(1-self.test_size)))
test_data_idx=np.random.randint(0,len(self.data),size=int(len(self.data)*self.test_size))
train_data=self.data.iloc[train_data_idx,:]
test_data=self.data.iloc[test_data_idx,:]
return train_data,test_data
if __name__=="__main__":
train_file = "D:/DataSet/titanic/titanic_train.csv"
test_file = "D:/DataSet/titanic/titanic_test.csv"
# 数据读取
data = pd.read_csv(train_file)
# test = pd.read_csv(test_file)
data=process_data(data)
target_name="Survived"
target = data[target_name]
#总的信息熵
total_entropy = entropy(np.array(target))
#连续值处理
data = process_continue_value(data, target, total_entropy)
#数据加载器
dataloader=DataLoader(data,random_seed=1)
train_data,test_data=dataloader.split_data()
#获得信息增益
gain=gain(total_entropy, train_data.drop(target_name,axis=1), target)
#构造树,设置树的最大深度,每一个节点最少数据量等参数
tree=DecisionTree(np.array(gain),train_data,"Survived",num_threshold=10)
root=tree.init()
#获得书的字典,为后续画图,剪枝准备
tree_dict = root.get_tree_dict(root,tree.data )
#后剪枝
for i in range(3):
tree_dict=tree.post_pruning(tree_dict,tree.data)[0]
# 模型评估
accuracy = tree.evaluator(tree_dict, test_data, target_name)
print(accuracy)
#plt作图
createPlot(tree_dict)
# print(tree_dict)
Recommend
About Joyk
Aggregate valuable and interesting links.
Joyk means Joy of geeK