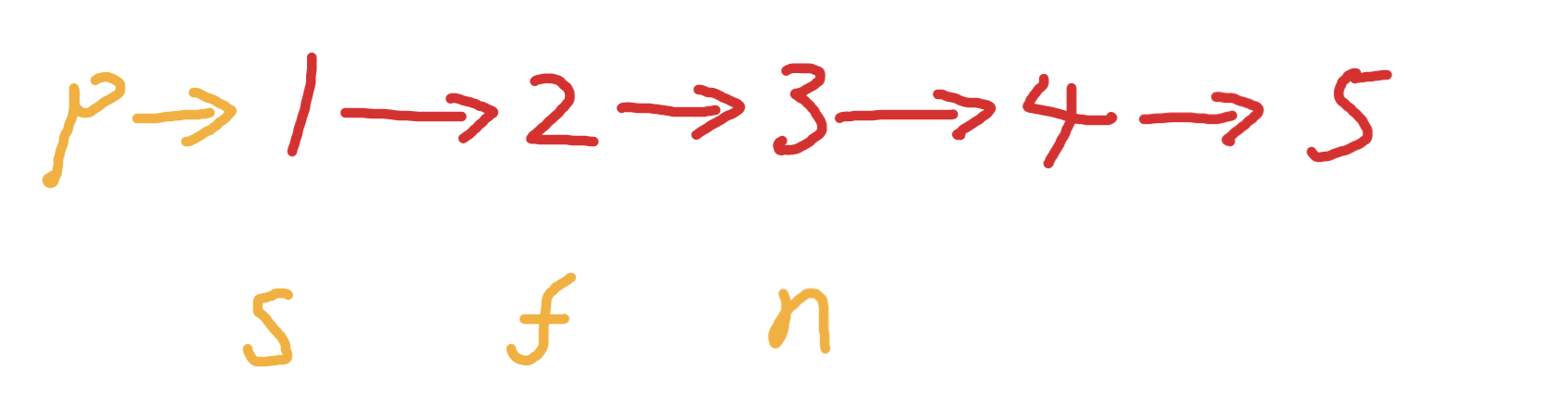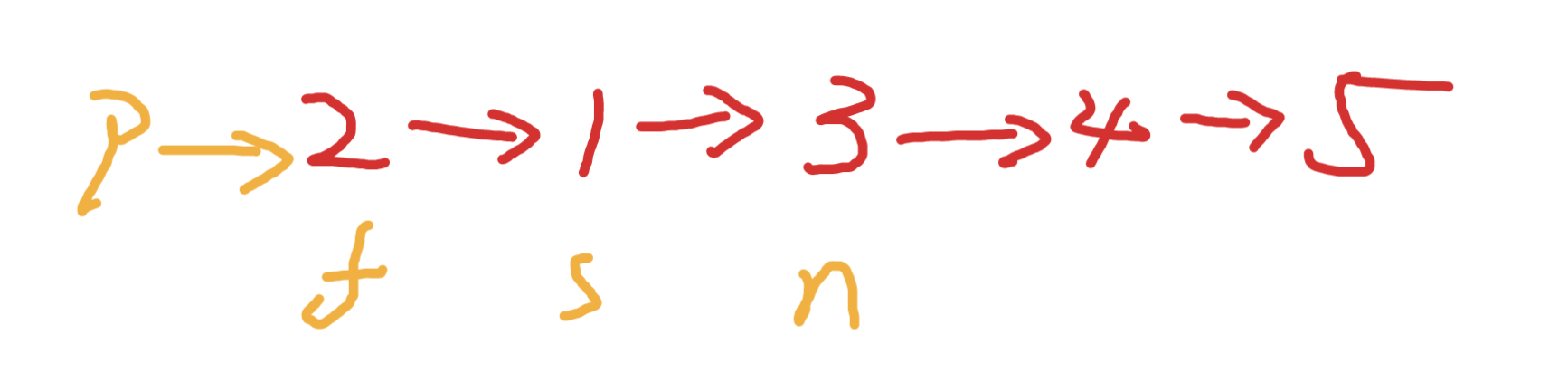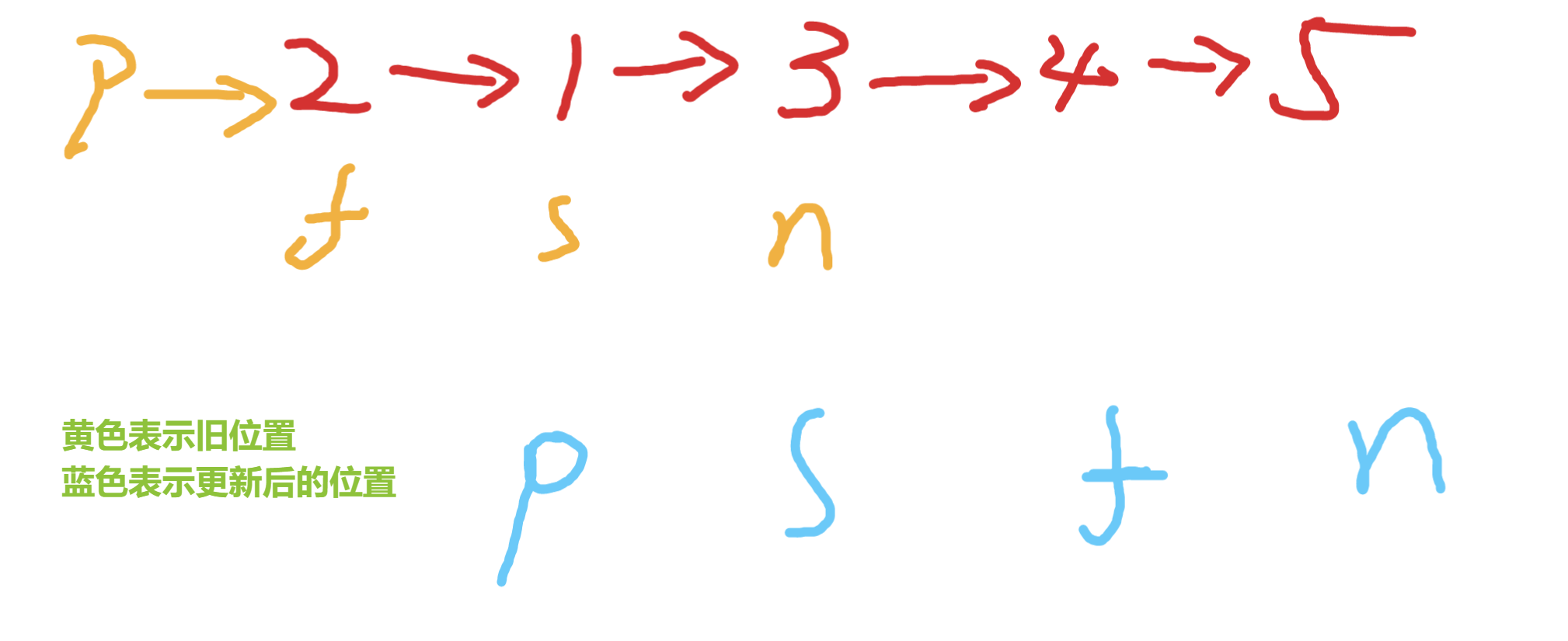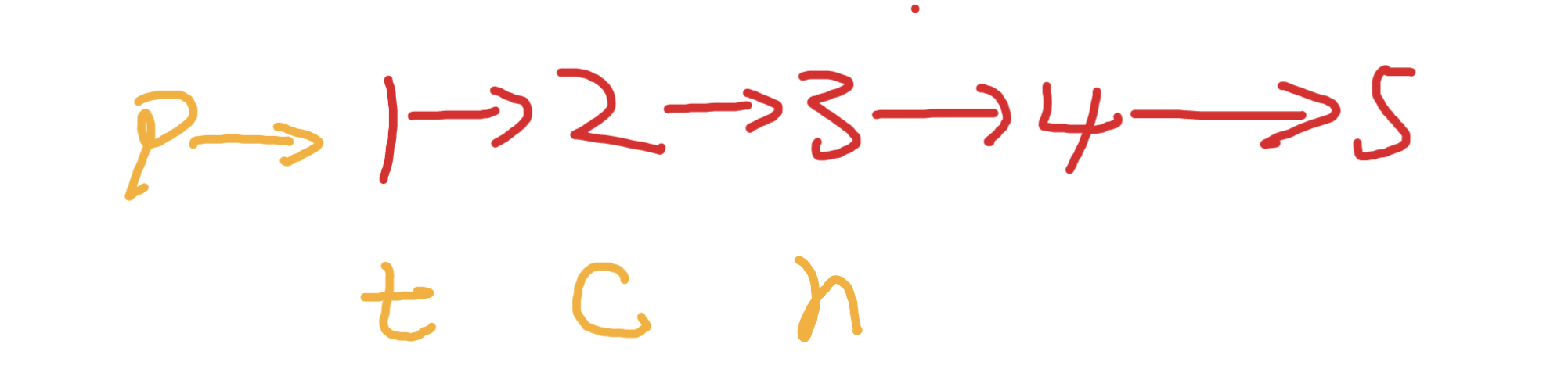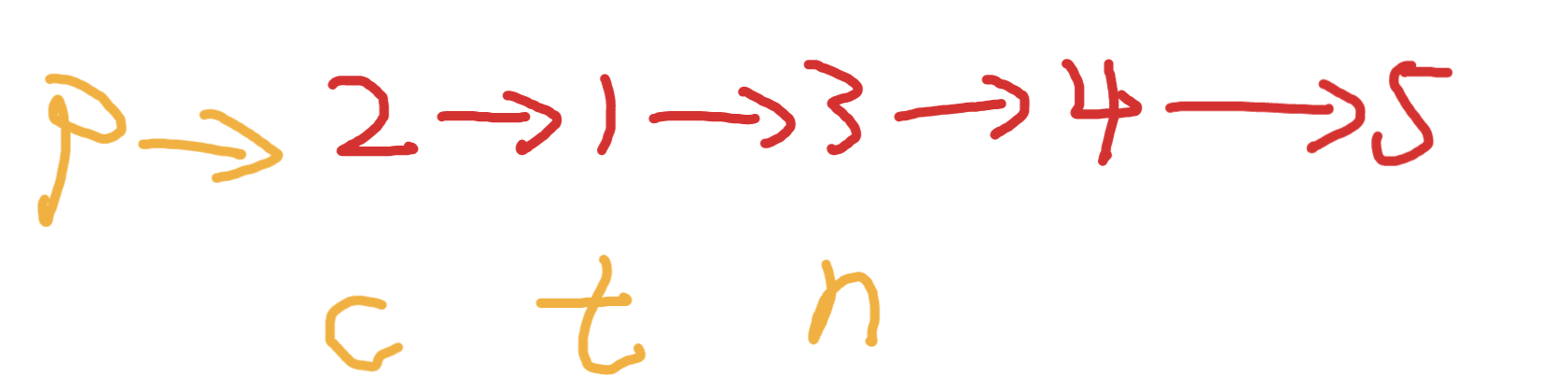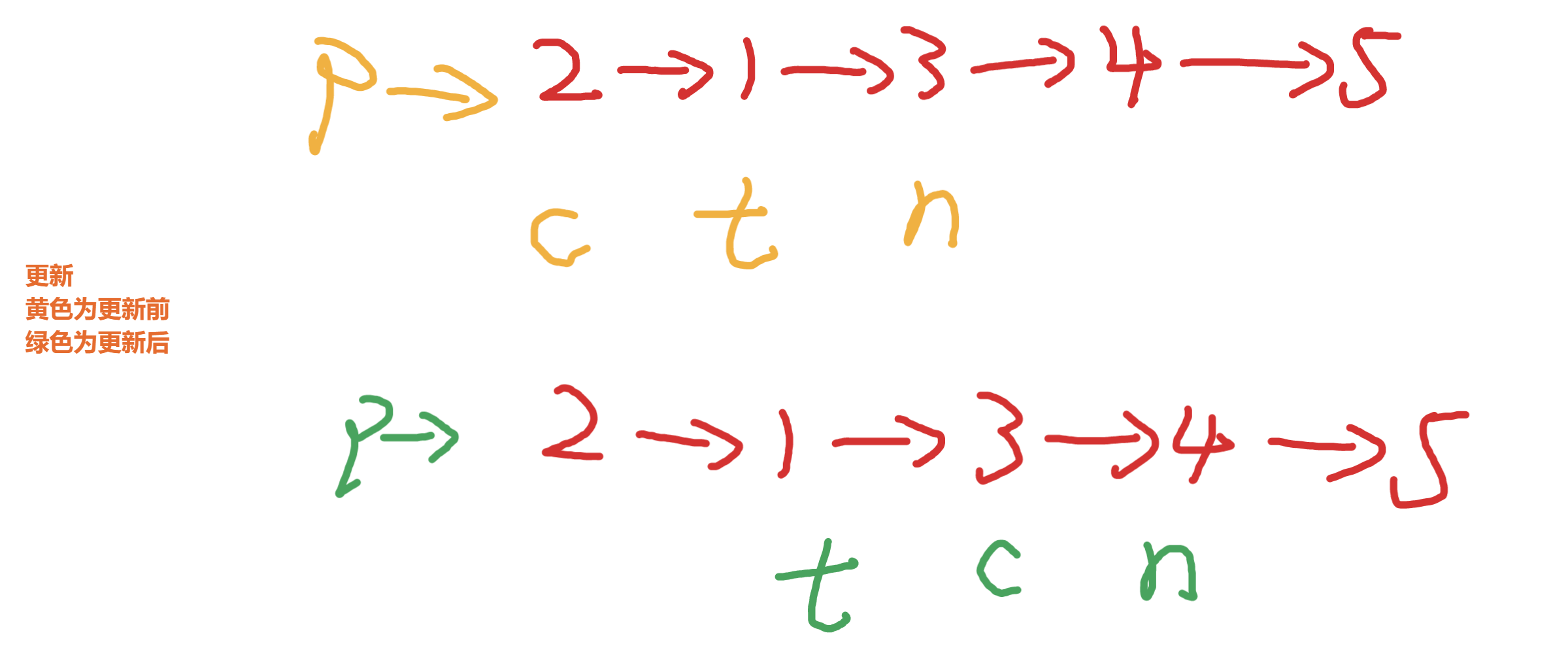18道经典链表题刷题总结——WeetCode1 链表系列 - Cuzzz
source link: https://www.cnblogs.com/cuzzz/p/16907466.html
Go to the source link to view the article. You can view the picture content, updated content and better typesetting reading experience. If the link is broken, please click the button below to view the snapshot at that time.

前言:#
WeetCode = Week leetCode 寓意每周刷点leetCode 题目
链表是我恢复刷题手感最喜欢做的系列,其没用太多的算法思想,单纯考验对指针的理解,和coding能力,但是其中也是有一些技巧的,比如哑节点,这个是非常使用的解题技巧,能避免繁琐的if else 处理头部,下面是笔者本周刷的一些链表题目。下周准备刷单调栈,或者树等其他系列题目。
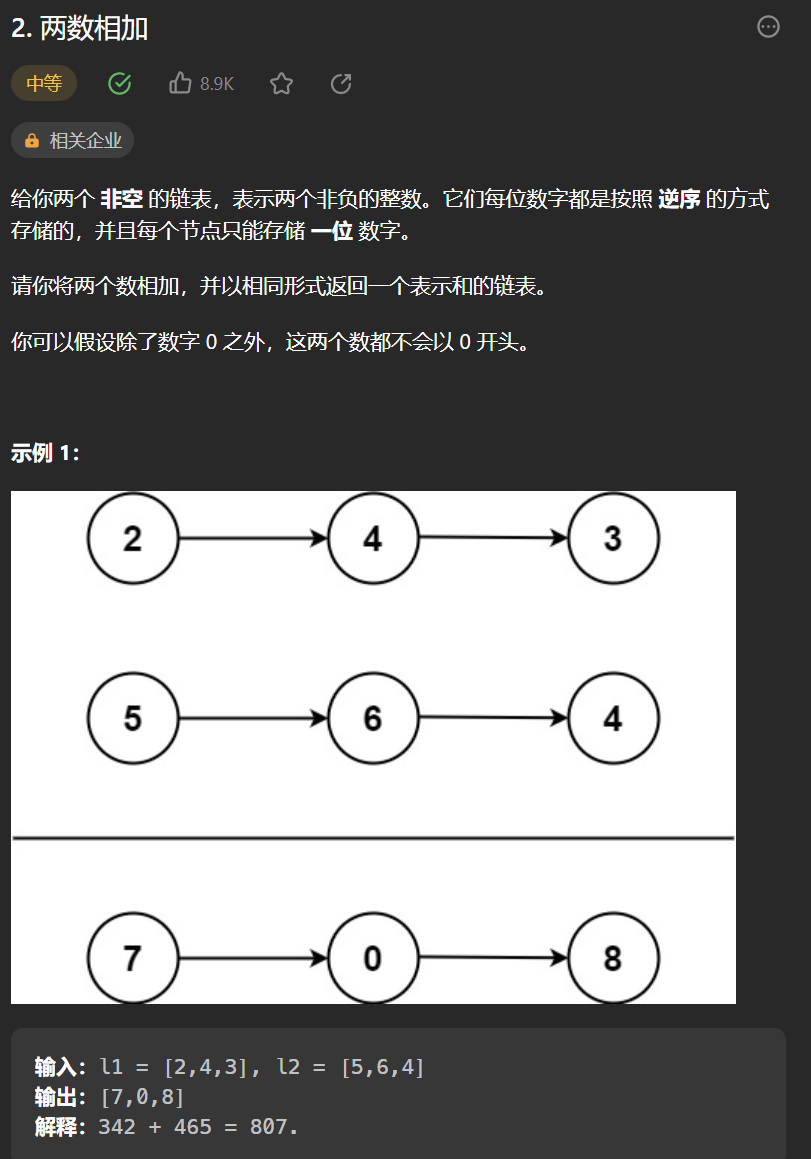
一丶 [ 两数相加](2. 两数相加 - 力扣(Leetcode))#
思路:#
简简单单就是一手模拟,两个指针分别位于两个链表头,然后一起向右,没经过一个节点,就求和得到sum,如果之前存在进位,那么sum需要加1,然后如果sum大于等于10,需要记录存在进位,方便下一轮判断是否需要进位,然后new除一个链表节点,其值位sum%10。
注意:#
-
两个链表同时结束,但是最后两个节点值之和存在进位,比如
1->2->3
2->6->8
这时候答案应该是:3->8->1->
1,注意最后的1,这里我们需要判断,如果二者同时结束,那么需要在末尾加1 -
两个链表不是同时结束,这时候有点合并有序数组的意思,需要继续遍历长的链表,并且还是需要处理进位。比如
1->2->3
2->3->8->6->5
答案应该是 3->5->1->(注意到此存在一个进位3+8>10下一个节点应该是1+6)->7->5
代码:#
public ListNode addTwoNumbers(ListNode l1, ListNode l2) {
//两个链表存在任何一个为null 都返回另外一个
if(l1 == null ){
return l2;
}
if(l2 == null ){
return l1;
}
//记录是否存在进位
boolean hasCarry = false;
//哑巴节点,其next就是头节点
ListNode preHead = new ListNode();
//forward 用来串联求和后生成的节点,其实是结果链表的尾巴
ListNode forward = preHead;
//二者都不为null的时候
while(l1 != null && l2 != null){
//求和 如果之前存在进位 那么需要加1
int sum = (l1.val + l2.val)+ (hasCarry?1:0);
//记录是否进位 为下轮做准备
hasCarry = sum>=10;
//取模
sum = sum%10;
//连接
ListNode newNode = new ListNode(sum);
forward.next = newNode;
//一起向下
forward = forward.next;
l1 = l1.next;
l2 = l2.next;
}
//链表长度相同 且存在进位 那么需要特殊处理
if(l1 == null && l2 == null ){
if(hasCarry){
forward.next = new ListNode(1);
}
return preHead.next;
}
//拿到更长的链表
ListNode longerList = (l1 == null)?l2:l1;
//继续循环
while(longerList != null){
int sum = longerList.val+(hasCarry?1:0);
hasCarry = sum>=10;
sum = sum%10;
ListNode newNode = new ListNode(sum);
forward.next = newNode;
forward = forward.next;
longerList = longerList.next;
}
//如果最后还存在进位 那么new 一个节点
if(hasCarry){
forward.next = new ListNode(1);
}
//返回节点
return preHead.next;
}
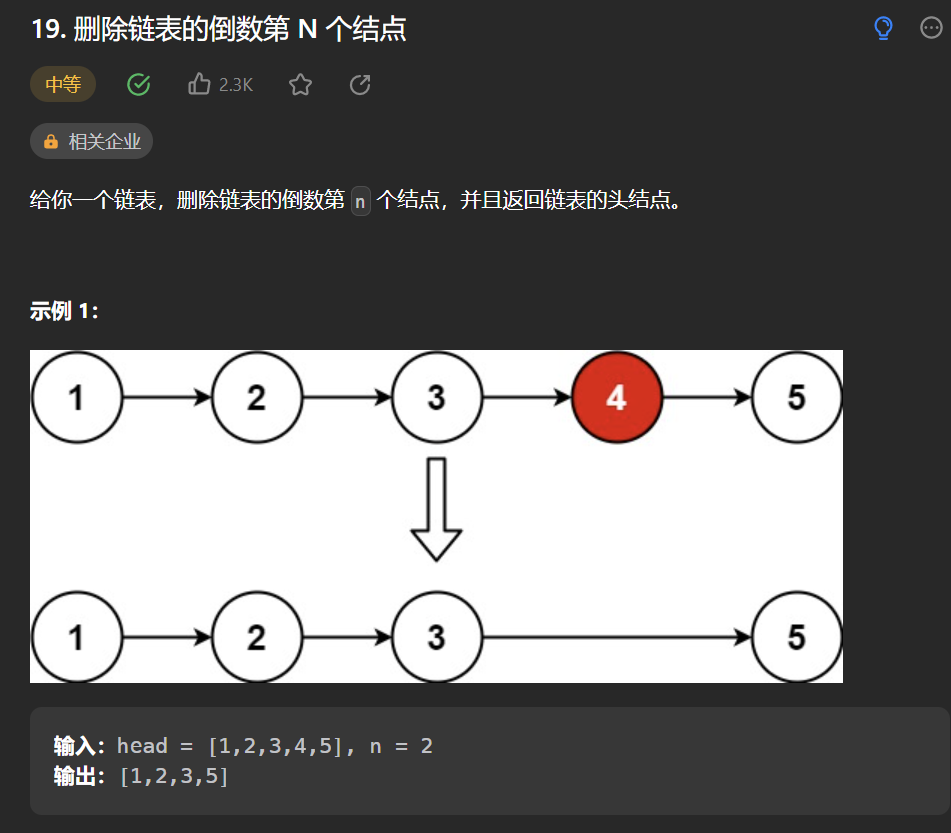
二丶 删除链表的倒数第 N 个结点 #
思路:#
粗暴的思路:先遍历一次拿到链表长度为sz,然后就可以倒数第n是第几个节点了,然后再遍历一次删除即可。但是这样做层次就低了,这时候我们可以使用快慢指针,快指针先走n步,等快指针走到尾部的时候,慢指针就是要删除的倒数第n个节点了。我们可以使用额外的一个指针记录慢指针的前一个,或者使用哑节点,让慢指针从哑节点开始,这样slow最后就是删除节点的前一个
代码:#
public ListNode removeNthFromEnd(ListNode head, int n) {
if(head == null || head.next == null){
return null;
}
//哑节点
ListNode preHead = new ListNode(-1,head);
ListNode fast = head;
ListNode slow = preHead;
//快指针先走
while(n>0){
fast=fast.next;
n--;
}
while(fast!=null){
fast =fast.next;
slow = slow.next;
}
slow.next = slow.next.next;
return preHead.next;
}
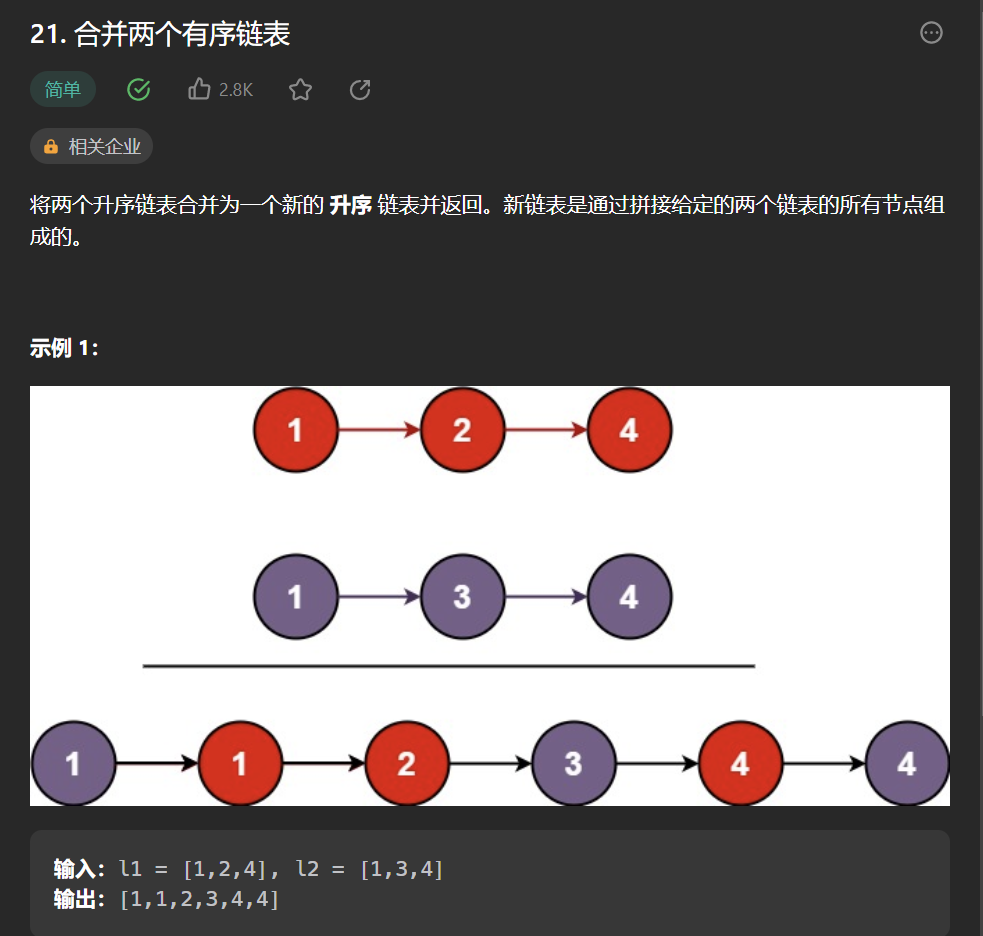
三丶[合并两个有序链表](21. 合并两个有序链表 - 力扣(Leetcode))#
思路:#
没啥好说的,和第一题几乎一模一样
代码:#
public ListNode mergeTwoLists(ListNode list1, ListNode list2) {
if(list1 == null){
return list2;
}
if(list2 == null){
return list1;
}
ListNode preHead = new ListNode();
ListNode tail = preHead;
while(list1 != null && list2 != null){
if(list1.val >= list2.val){
tail.next = list2;
ListNode nextNode = list2.next;
list2.next = null;
list2 = nextNode;
}else {
tail.next = list1;
ListNode nextNode = list1.next;
list1.next = null;
list1 = nextNode;
}
tail = tail.next;
}
tail.next = list1 == null ? list2 : list1;
return preHead.next;
}
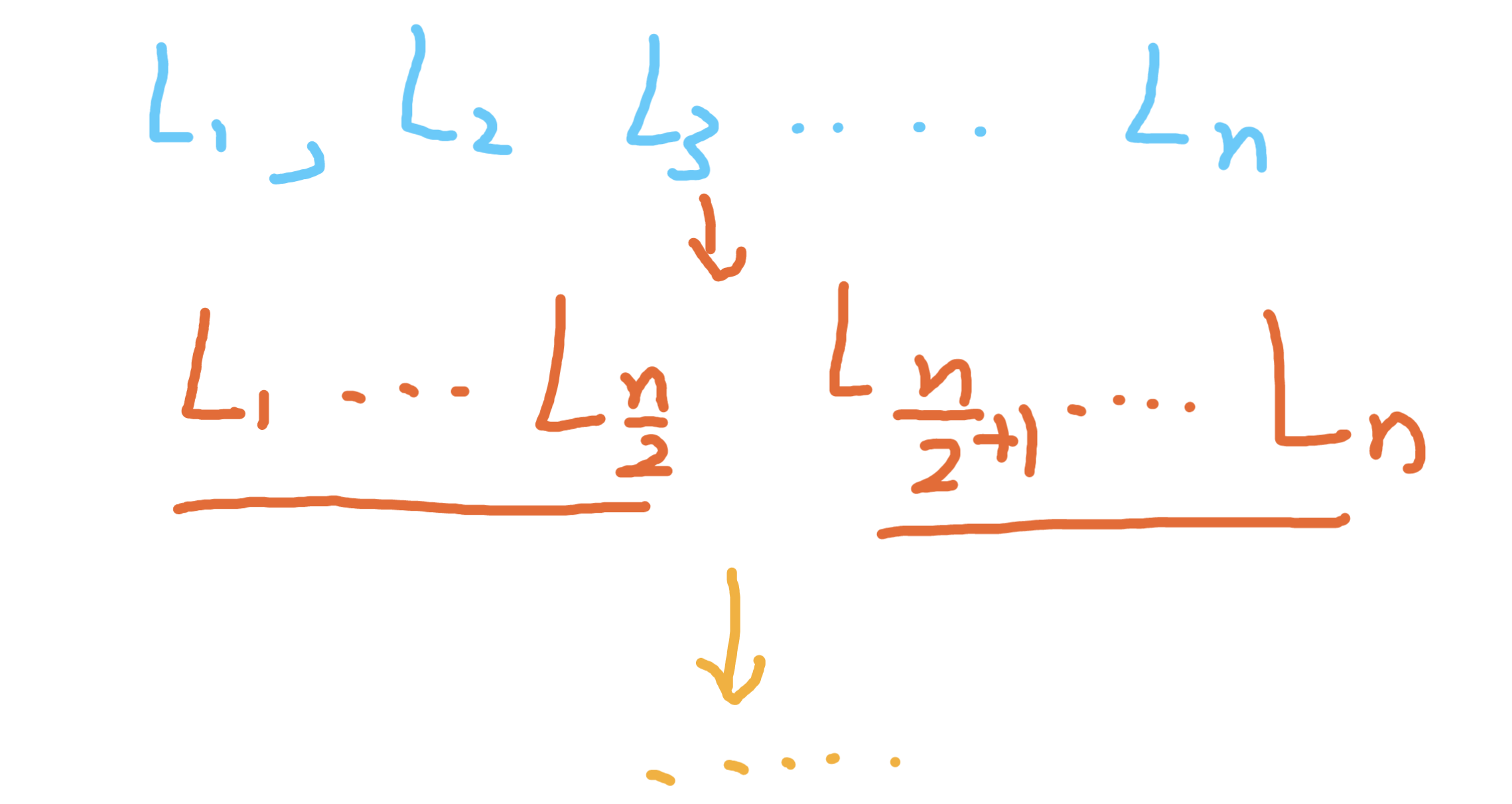
四丶 合并K个升序链表 #
思路&对应代码:#
1.递归,分治#
第三题我们写了合并两个有序链表,我们把大规模的合并k个分解成n个合并2个即可,首先我们把大任务,分解成合并左半部分,和合并右半部分
和归并排序的思路是一致的
- 递归的出口是什么,子任务只有一个链表,只是直接返回一个链表即可,子任务只有两个链表,这时候合并两个链表即可
- 怎么合并两个有序链表,如题三
public ListNode mergeKLists(ListNode[] lists) {
//入参数组为null 返回null
//空数组 返回null
if(lists==null || lists.length==0){
return null;
}
//调用递归方法
return merge2(lists ,0 ,lists.length-1);
}
private ListNode merge2(ListNode[] lists,int start,int end){
//base case 只有一个链表 直接返回一个链表
if(start == end){
return lists[start];
}
//子任务只有两个链表
if(start == end-1){
return mergeTwoLists(lists[start],lists[end]);
}
//分治
int mid = (start+end)/2;
//合并左边
ListNode mergeLeft = merge2(lists,start,mid);
//合并右边
ListNode mergeRight = merge2(lists,mid+1,end);
//把左右合并
return mergeTwoLists(mergeLeft,mergeRight);
}
public ListNode mergeTwoLists(ListNode list1, ListNode list2) {
if(list1 == null){
return list2;
}
if(list2 == null){
return list1;
}
ListNode preHead = new ListNode();
ListNode tail = preHead;
while(list1 != null && list2 != null){
if(list1.val >= list2.val){
tail.next = list2;
ListNode nextNode = list2.next;
list2.next = null;
list2 = nextNode;
}else {
tail.next = list1;
ListNode nextNode = list1.next;
list1.next = null;
list1 = nextNode;
}
tail = tail.next;
}
tail.next = list1 == null ? list2 : list1;
return preHead.next;
}
2.优先队列#
我们想下暴力解法,每次合并一个节点就遍历整个数组找最小节点合并,这种做法慢在哪儿,慢在我们需要找到数组中剩下节点中最小节点,进行合并。那么有没有一种数据结构,可以让拿到最小节点的o(1)时间复杂度昵——优先队列
- 队列优先级是啥——节点的值
- 队列如何初始化——首先放入数组中所有链表的头节点
- 队列如何入队——每次一个节点合并的后都把其next节点进行入队
- 何时停止循环——队列为空、
public ListNode mergeKLists(ListNode[] lists) {
if(lists==null){
return null;
}
if(lists.length==0){
return null;
}
return mergewithHeap(lists);
}
private ListNode mergewithHeap(ListNode[] lists){
//哑节点
ListNode preHead = new ListNode();
//尾巴用于串联这些节点
ListNode tail =preHead;
//优先队列 传入Comparetor 比较val
PriorityQueue<ListNode> heap = new PriorityQueue<ListNode>((l1,l2)->l1.val-l2.val);
//初始化队列
for(int i = 0;i<lists.length;i++){
if(lists[i]!=null){
heap.offer(lists[i]);
}
}
//队列不为空
while(!heap.isEmpty()){
//当前最西澳
ListNode min = heap.poll();
//串联起来
tail.next =min;
//更新尾巴
tail =tail.next;
//继续入队
if(min.next!=null){
heap.offer(min.next);
}
}
return preHead.next;
//这里我把优先队列变量名命为heap 是因为java中的优先队列是基于数组的堆实现
//需要注意入队时offer 出队时poll 并且入队不能是null
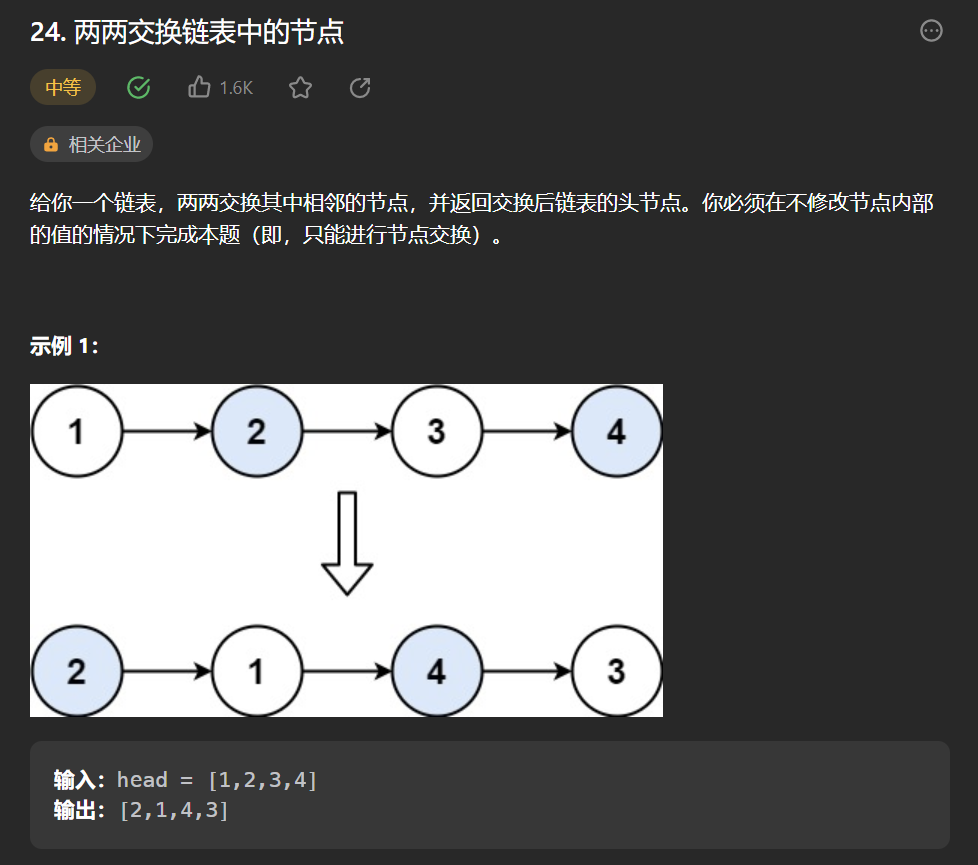
五丶[两两交换链表中的节点](24. 两两交换链表中的节点 - 力扣(Leetcode))#
思路:#
简简单单模拟,初始化如下变量
交换s和f 如下效果
接下来需要更新这些变量
如此往复直到f为null,但是需要注意空指针的处理
代码:#
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* public class ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode next;
* ListNode() {}
* ListNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* ListNode(int val, ListNode next) { this.val = val; this.next = next; }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public ListNode swapPairs(ListNode head) {
//没必要交换
if(head == null || head.next == null){
return head;
}
//只有两个节点
if(head.next.next == null){
ListNode newHead = head.next;
newHead.next = head;
head.next = null;
return newHead;
}
//哑节点
ListNode preHead = new ListNode(-1,head);
ListNode pre = preHead;
ListNode slow = head;
ListNode fast = head.next;
ListNode next = fast.next;
//交换
while(fast != null){
pre.next = fast;
fast.next = slow;
slow.next = next;
if(next == null){
return preHead.next;
}
pre = slow;
slow = next;
fast = slow.next;
if(fast == null){
return preHead.next;
}
next = fast.next;
}
return preHead.next;
}
}
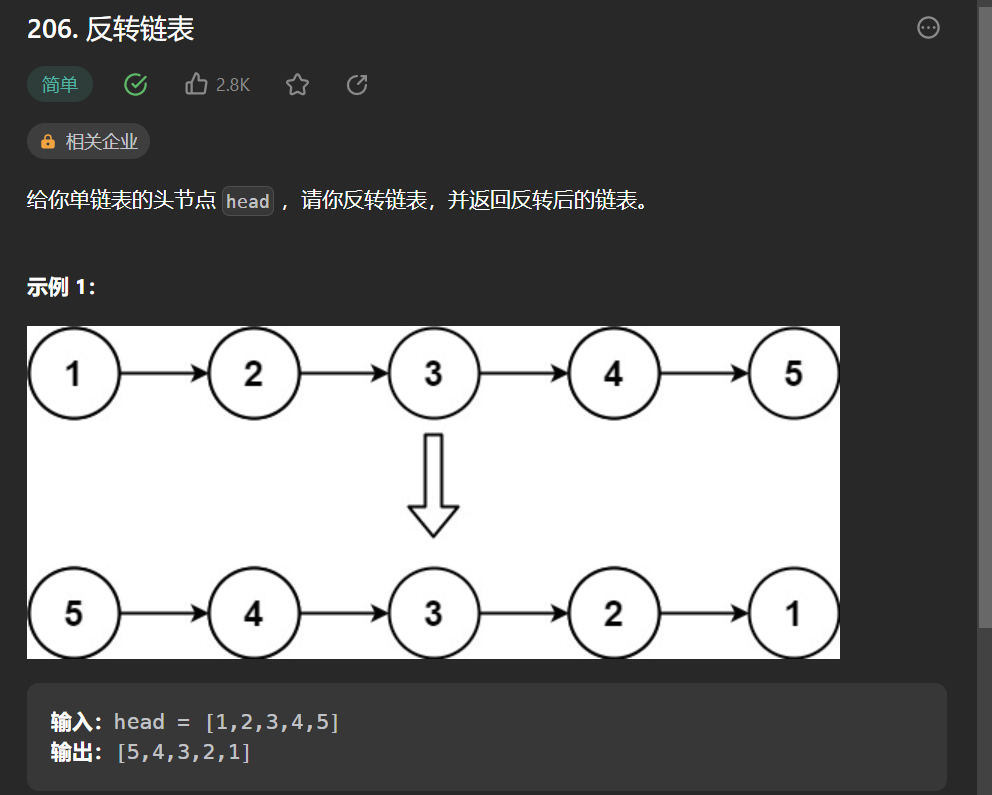
六丶[反转链表](206. 反转链表 - 力扣(Leetcode))#
思路:#
简简单单模拟
先初始化如下节点
代码:#
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* public class ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode next;
* ListNode() {}
* ListNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* ListNode(int val, ListNode next) { this.val = val; this.next = next; }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public ListNode reverseList(ListNode head) {
if(head == null || head.next == null){
return head;
}
//哑节点
ListNode preHead = new ListNode(-1,head);
//当前需要操作的节点
ListNode cur = head.next;
//下一个节点
ListNode next = cur.next;
//尾巴
ListNode tail = preHead.next;
while(cur != null){
//翻转
cur.next = preHead.next;
tail.next = next;
preHead.next = cur;
//更新
cur = next;
if(next == null){
return preHead.next;
}
next = next.next;
}
return preHead.next;
}
}
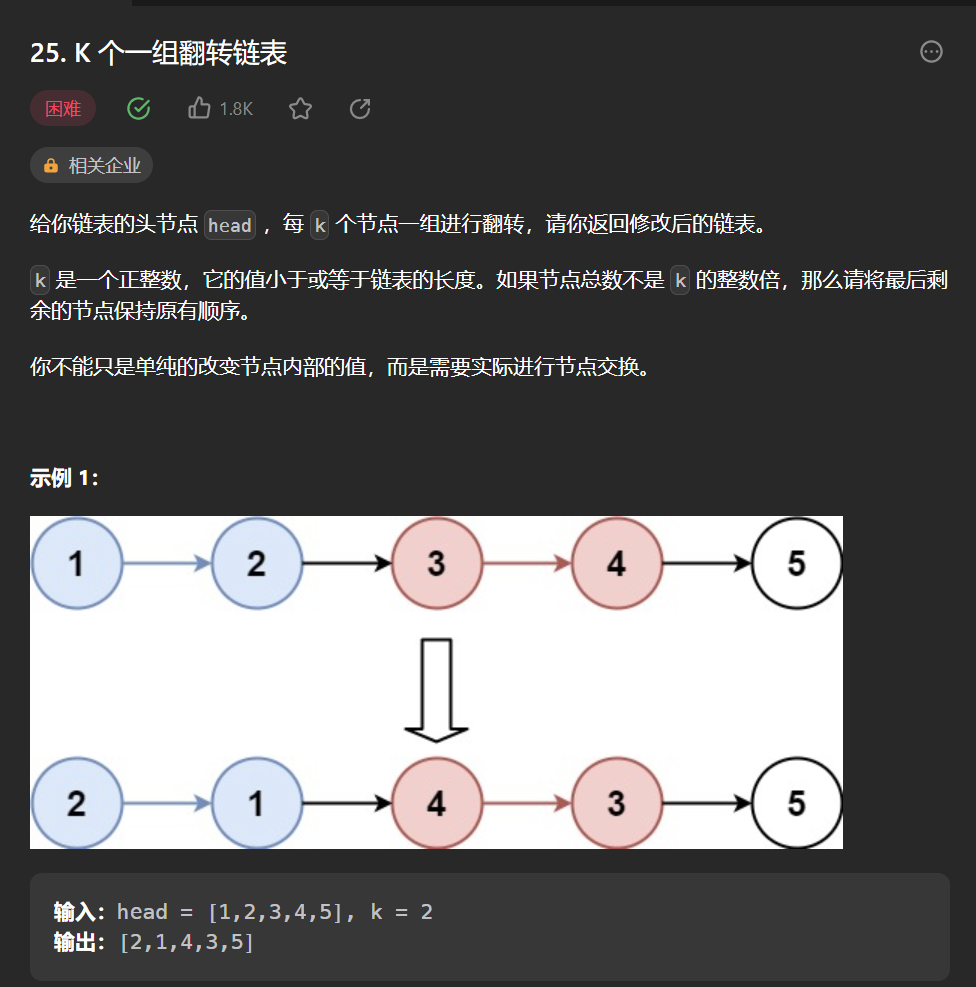
七丶[K 个一组翻转链表](25. K 个一组翻转链表 - 力扣(Leetcode))#
思路:#
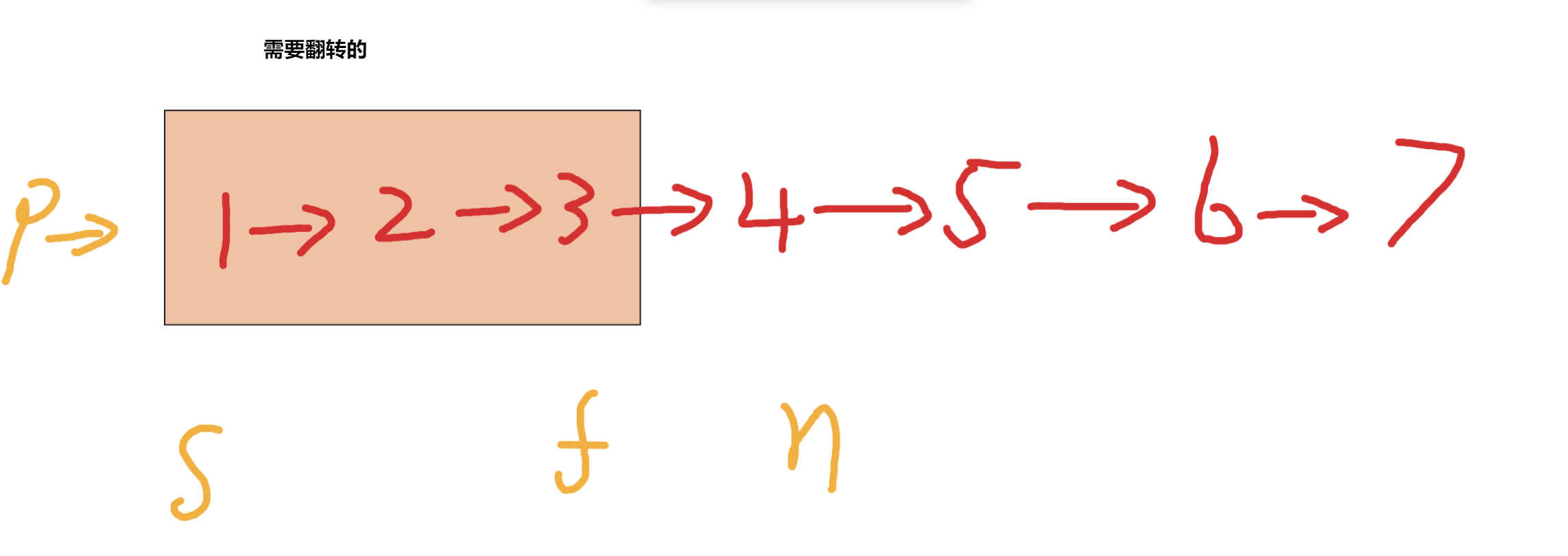
第六题,我们实现了反转链表,那么k个一翻转的逻辑,这个翻转的过程是一样的,接下来我们只需要把这k个节点先摘下来,然后进行翻转,翻转返回新的头和尾巴,然后和原来链表连接起来继续翻转即可
代码:#
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* public class ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode next;
* ListNode() {}
* ListNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* ListNode(int val, ListNode next) { this.val = val; this.next = next; }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public ListNode reverseKGroup(ListNode head, int k) {
//无需翻转的情况
if(head == null || head.next == null || k == 1){
return head;
}
//哑节点
ListNode preHead = new ListNode(-1,head);
//翻转后负责把链表重新连接起来
ListNode pre = preHead;
//翻转 快慢之间的部分
ListNode slow = head;
ListNode fast = findKNext(slow,k);
//如果上来就不足k 个 直接g
if(fast == null){
return preHead.next;
}
//循环翻转
while(fast != null) {
//先保存下 更新的时候需要用
ListNode next = fast.next;
//断开 不然reverseList会一直翻转下去
fast.next = null;
//翻转快慢之间的部分返回翻转后的尾巴
ListNode[] resArray = reverseList(slow);
ListNode rHead = resArray[0];
ListNode rTail = resArray[1];
// 连接 把翻转后的内容连接上去
pre.next = rHead;
rTail.next = next;
//更新
slow = next;
fast = findKNext(slow,k);
pre = rTail;
}
return preHead.next;
}
//node 慢节点。k是题目中的k个一反转,我们要找到fast
//如果不足fast 和 slow 之间一共k个节点(包括自己)
private ListNode findKNext(ListNode node,int k){
while(k>1){
if(node == null){
return null;
}
node = node.next;
k--;
}
return node;
}
//翻转 并返回 头和尾
private ListNode[] reverseList(ListNode head) {
//哑节点
ListNode preHead = new ListNode(-1,head);
//当前需要操作的节点
ListNode cur = head.next;
//下一个节点
ListNode next = cur.next;
//尾巴
ListNode tail = preHead.next;
while(cur != null){
//翻转
cur.next = preHead.next;
tail.next = next;
preHead.next = cur;
//更新
cur = next;
if(next == null){
return new ListNode[]{preHead.next,tail};
}
next = next.next;
}
return new ListNode[]{preHead.next,tail};
}
}
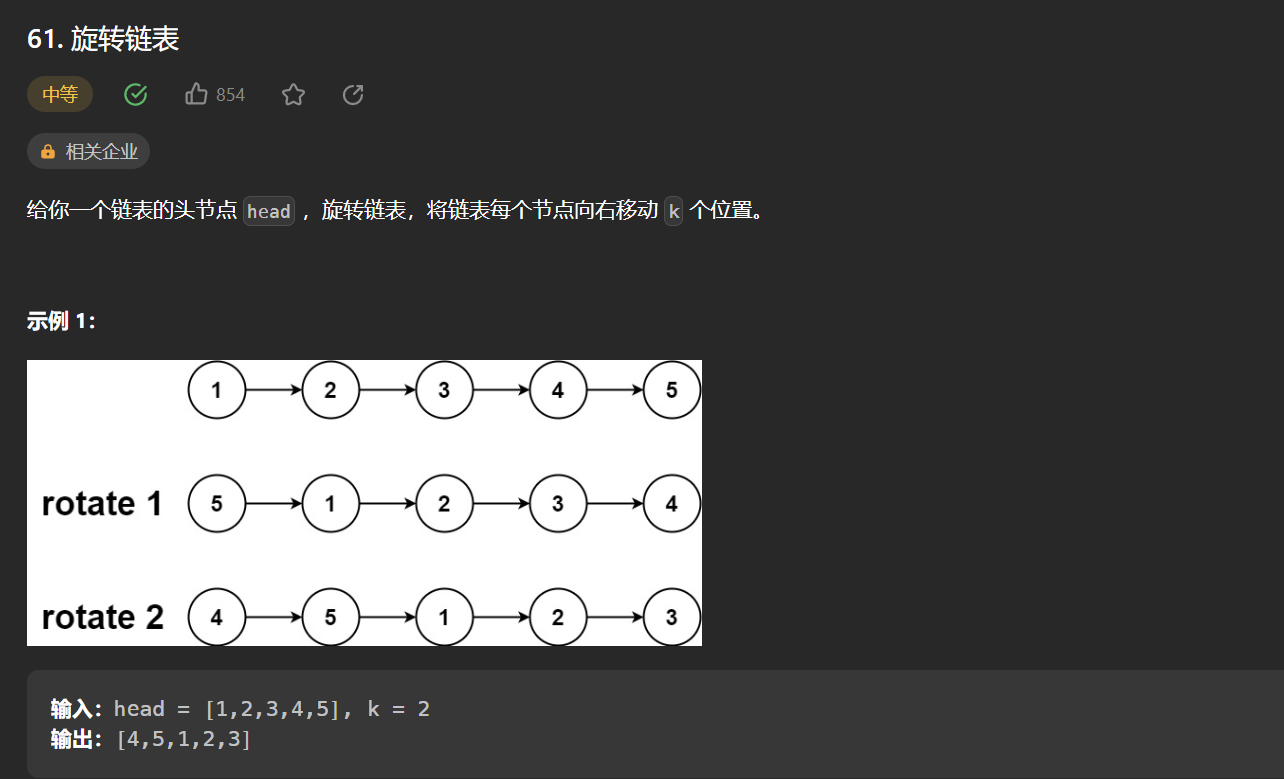
八丶[旋转链表](61. 旋转链表 - 力扣(Leetcode))#
思路:#
首先需要注意的是,如果链表长度为len,向右移动len个位置,其实和原本链表一样,所有其实我们只需要移动k%len个位置即可
移动k个,其实就是把最后k个节点连接到链表头部
代码:#
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* public class ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode next;
* ListNode() {}
* ListNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* ListNode(int val, ListNode next) { this.val = val; this.next = next; }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public ListNode rotateRight(ListNode head, int k) {
if(head == null || head.next==null || k == 0){
return head;
}
//求长度
ListNode lenTemp = head;
int len = 0;
while(lenTemp != null){
lenTemp = lenTemp.next;
len ++;
}
//我们需要旋转的次数
k = k % len;
//刚好整数倍 那么直接返回头
if(k == 0){
return head;
}
//移动k个,其实就是把最后k个节点连接到链表头部
//快慢指针找到倒数第k个的前一个
ListNode fast = head;
ListNode slow = head;
while(k!=0){
fast = fast.next;
k--;
}
while(fast.next!=null){
fast = fast.next;
slow = slow.next;
}
//到这fast 就是尾巴 slow是倒数第k+1个 slow.next 就是新的头
//那么颠倒下倒数k个节点 和 头的位置
ListNode newHead = slow.next;
slow.next = null;
fast.next= head;
return newHead;
}
}
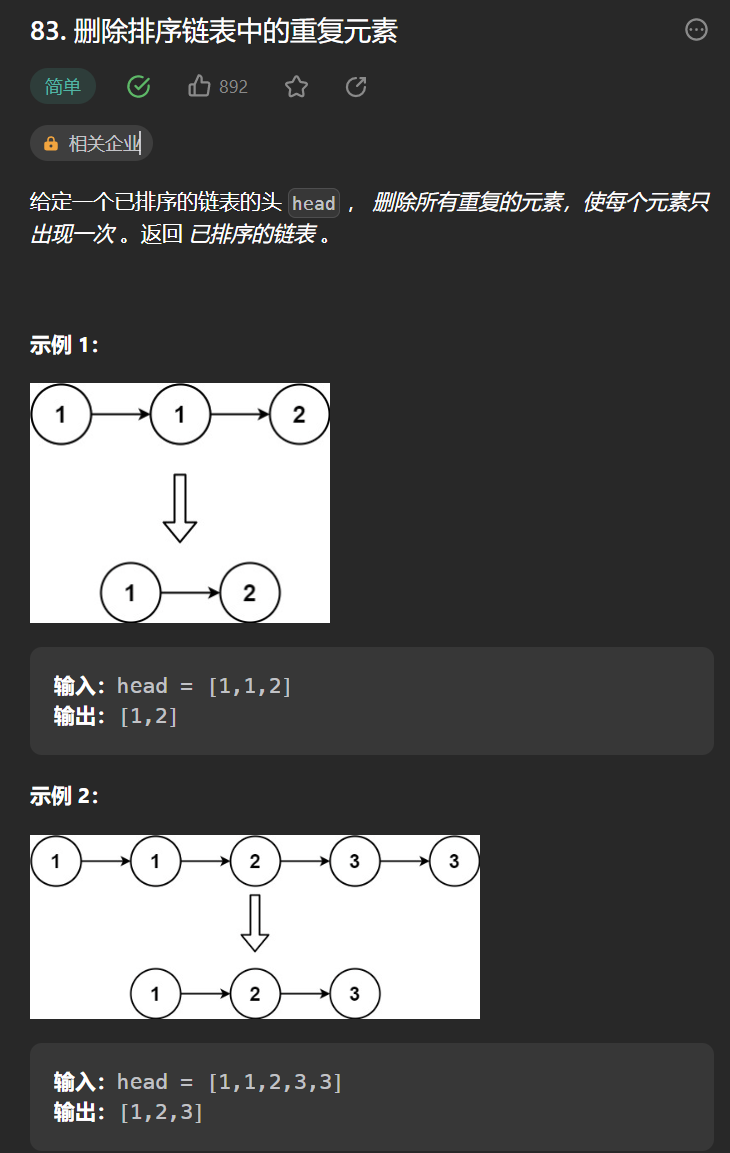
九丶[删除排序链表中的重复元素](83. 删除排序链表中的重复元素 - 力扣(Leetcode))#
思路:#
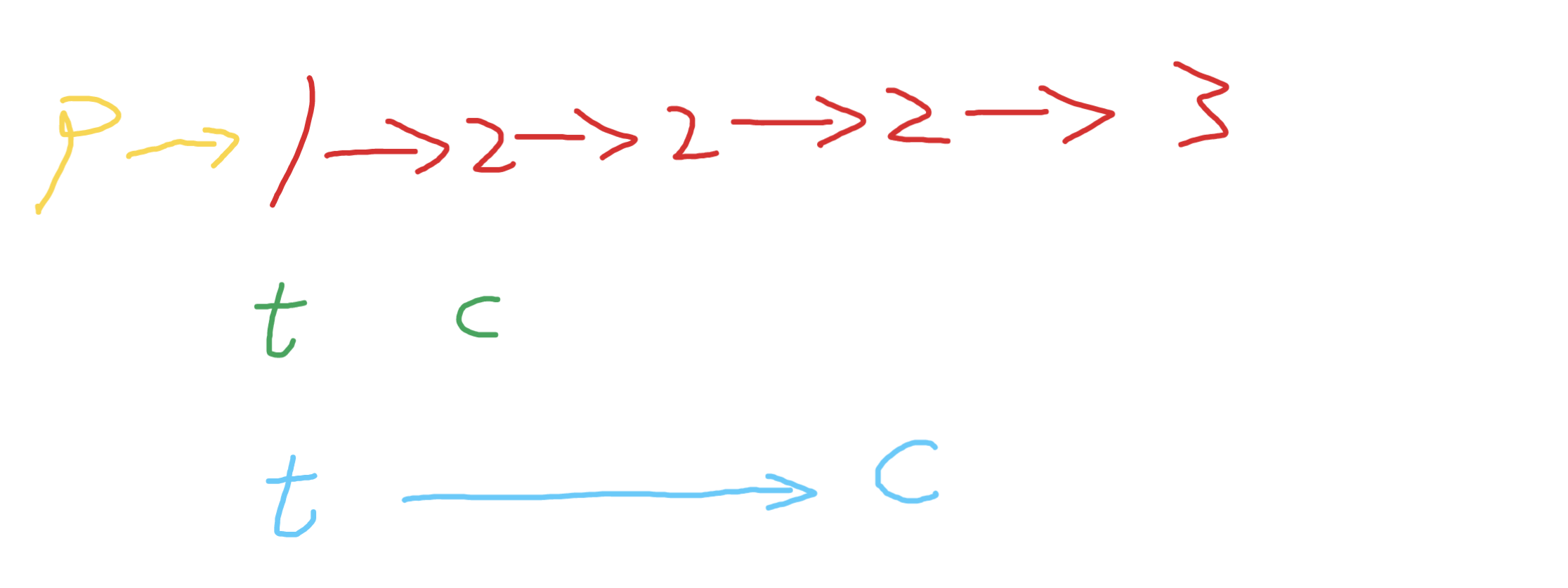
首先这是一个排序链表,这意味着相同值的节点是相邻的。
初始化一个哑节点p,和新链表的尾巴节点t,c表示当前遍历的节点
如果c和下一个节点值不同 那么c可以保留,串到t后,更新到绿色位置,遇到重复的节点,就让c走到最后一个重复的节点,然后让t指向c,后更新t和c继续遍历
代码:#
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* public class ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode next;
* ListNode() {}
* ListNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* ListNode(int val, ListNode next) { this.val = val; this.next = next; }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public ListNode deleteDuplicates(ListNode head) {
if(head == null || head.next == null){
return head;
}
//哑节点
ListNode preHead = new ListNode(-1,head);
//尾巴节点
ListNode tail = preHead;
//当前遍历的节点
ListNode cur = head;
while(cur != null){
//如果下一个节点为空 或者 下一个节点和当前节点值不为空
//那么当前节点保留,让tail的下一个指向当前节点
if(cur.next == null || cur.val != cur.next.val){
tail.next = cur;
tail = cur;
cur = cur.next;
continue;
}
//到此说明重复了 记录下重复的值
int duplicateValue = cur.val;
//下一个节点
ListNode nextNode = cur.next;
//一直到下一个节点为空 或者值不重复了
while(nextNode != null && nextNode.val == duplicateValue){
nextNode = nextNode.next;
}
//到这就是不重复的 删除这其中的重复的节点
cur.next = nextNode;
//连接
tail.next = cur;
//刷新进入下一轮循环
tail = cur;
cur = cur.next;
}
return preHead.next;
}
}
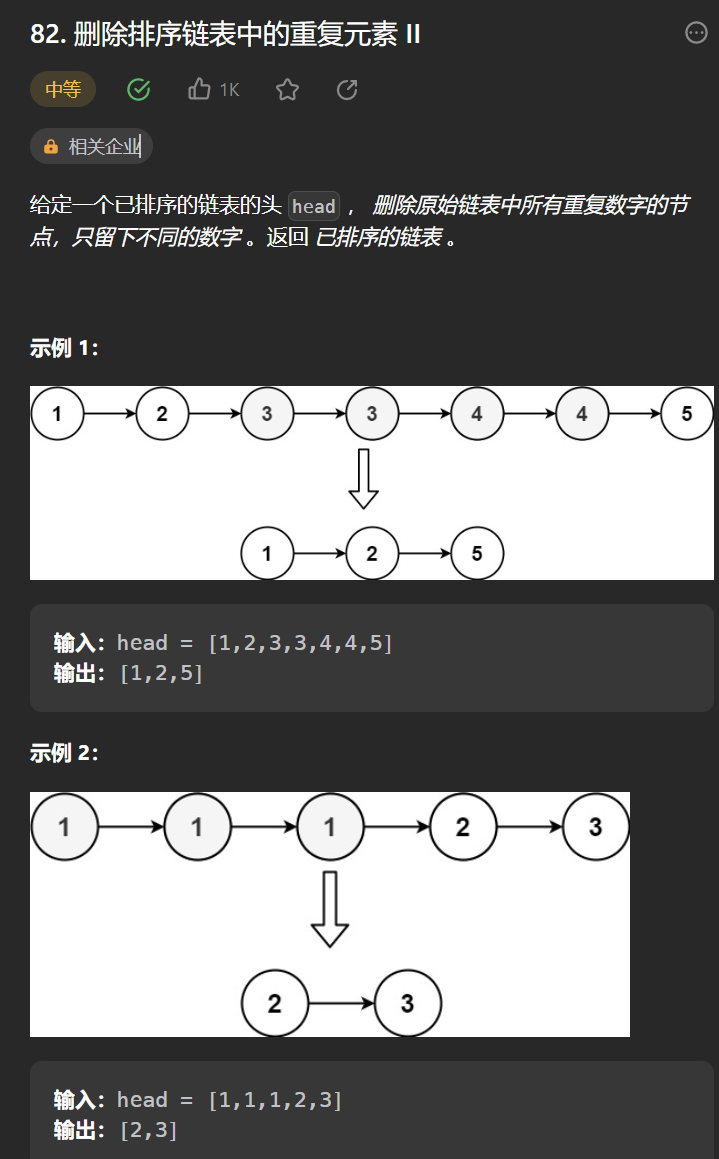
十丶[删除排序链表中的重复元素 II](82. 删除排序链表中的重复元素 II - 力扣(Leetcode))#
思路:#
思路和第九题差不多,唯一的差别是重复节点不能保留,所以发生重复的时候需要把tail的下一个节点置为null
代码:#
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* public class ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode next;
* ListNode() {}
* ListNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* ListNode(int val, ListNode next) { this.val = val; this.next = next; }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public ListNode deleteDuplicates(ListNode head) {
if(head == null || head.next == null){
return head;
}
//哑节点
ListNode preHead = new ListNode(-1,head);
//新链表尾节点
ListNode tail = preHead;
//当前变遍历到的节点
ListNode cur = head;
while(cur != null){
//如果下一个节点为null 那么必然不会与下一个节点值相同
//或者下一个节点和当前节点 值不同
//那么说明当前节点可以假如到新链表中
//让尾巴的下一个指向当前节点
if(cur.next == null || cur.val != cur.next.val){
tail.next = cur;
tail = cur;
}
//如果相同 那么一直到最后一个值相等的节点
while(cur.next != null && cur.val == cur.next.val){
//说明这部分重复了,我们首先让新链表不要和这部分连接到一起
tail.next = null;
cur = cur.next;
}
//cur向下 就必然是不相同的节点
cur = cur.next;
}
return preHead.next;
}
}
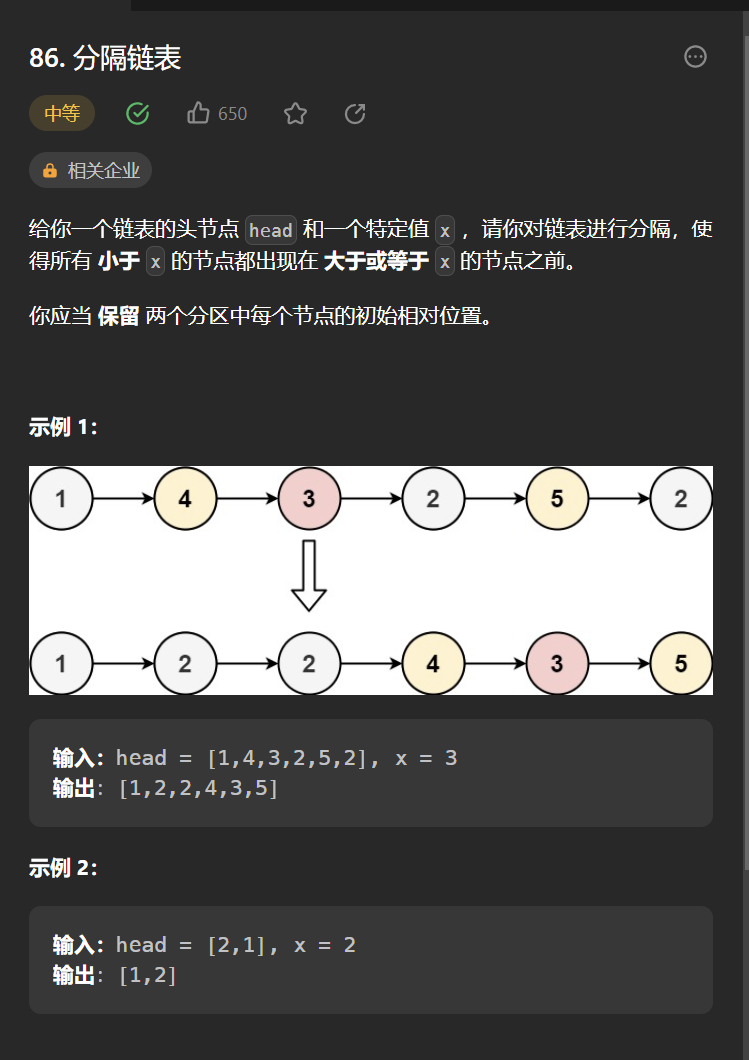
十一丶[分隔链表](86. 分隔链表 - 力扣(Leetcode))#
思路:#
题目乍一看可能没思路,纠结于怎么保持相对顺序不变,其实只需要使用两个哑节点,一个记录大于等于x,一个小于x的节点,最后把这两个哑节点代表的链表的进行串联即可
代码:#
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* public class ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode next;
* ListNode() {}
* ListNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* ListNode(int val, ListNode next) { this.val = val; this.next = next; }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public ListNode partition(ListNode head, int x) {
if(head == null || head.next == null){
return head;
}
//小于x的哑节点 和尾节点
ListNode lessPreHead = new ListNode();
ListNode lessTail = lessPreHead;
//大于等于x的哑节点 和尾节点
ListNode betterEqualHead = new ListNode();
ListNode betterEqualTail = betterEqualHead;
ListNode cur = head;
//遍历
while(cur != null){
ListNode curNext = cur.next;
//如果小于 那么连接到 小于链表上
if(cur.val < x){
lessTail.next = cur;
lessTail = lessTail.next;
cur.next = null;
}else{
//反之连接到大于等于链表
betterEqualTail.next = cur;
betterEqualTail = betterEqualTail.next;
cur.next = null;
}
cur = curNext;
}
lessPreHead = lessPreHead.next;
betterEqualHead = betterEqualHead.next;
//没有大于等于x的节点 那么返回小于头
if(betterEqualHead == null){
return lessPreHead;
}
//没用小于x的节点 返回大于等于头
if(lessPreHead == null){
return betterEqualHead;
}
//连接起来
lessTail.next = betterEqualHead;
return lessPreHead;
}
}
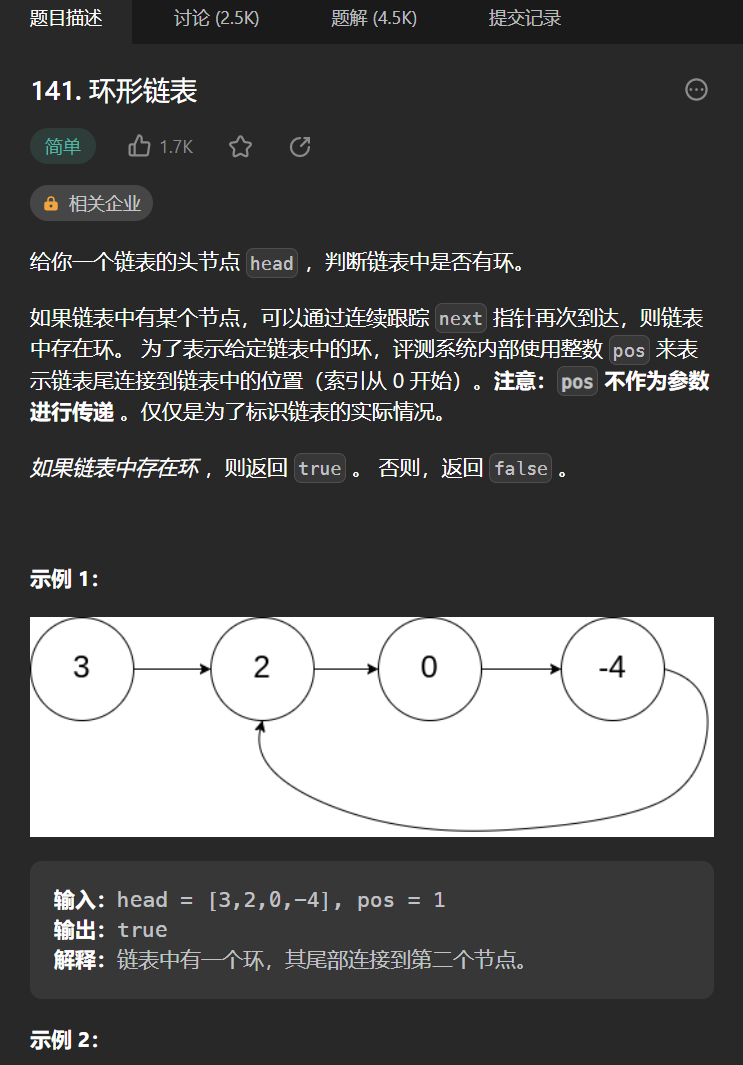
十二丶[环形链表](141. 环形链表 - 力扣(Leetcode))#
思路:#
如果可以使用set缓存所有的节点,然后遍历的时候发现next存在于set中那么可以判断其有环,但是这样空间复杂度为n,所以我们需要记住一个结论,快慢指针都从头开始出发,快指针一次走两步,慢指针一次一步,如果二者相遇说明有环,如果慢指针为null了还没相遇那么说明无环(「乌龟」和「兔子」在链表上移动,「兔子」跑得快,「乌龟」跑得慢。当「乌龟」和「兔子」从链表上的同一个节点开始移动时,如果该链表中没有环,那么「兔子」将一直处于「乌龟」的前方;如果该链表中有环,那么「兔子」会先于「乌龟」进入环,并且一直在环内移动。等到「乌龟」进入环时,由于「兔子」的速度快,它一定会在某个时刻与乌龟相遇,即套了「乌龟」若干圈。)
代码:#
public class Solution {
public boolean hasCycle(ListNode head) {
if(head == null || head.next == null){
return false;
}
ListNode fast = head;
ListNode slow = head;
do{
if(fast == null||fast.next==null){
return false;
}
fast = fast.next.next;
slow = slow.next;
if(fast == slow){
return true;
}
}while(slow != null);
return false;
}
}
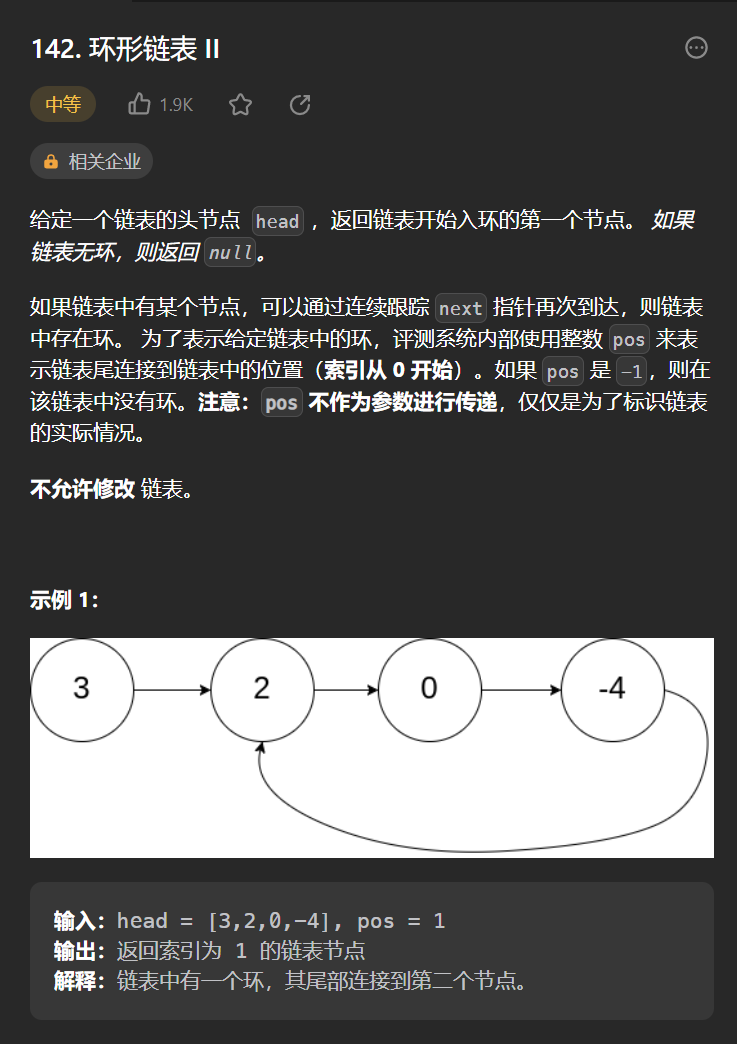
十三丶[环形链表 II](142. 环形链表 II - 力扣(Leetcode))#
思路:#
需要记住一个结论,快慢指针同时出发,快一次两步,慢一次一步,相遇的时候就是链表存在环,之后快指针从头开始,慢指针继续运动,二者都一次走一步,相等的时候就是入环节点的位置
代码:#
public class Solution {
public ListNode detectCycle(ListNode head) {
if(head == null || head.next == null){
return null;
}
ListNode fast = head;
ListNode slow = head;
do{
if(fast == null || fast.next==null){
return null;
}
fast = fast.next.next;
slow = slow.next;
if(fast == slow){
break;
}
}while(slow != null);
fast = head;
while(fast != slow){
fast =fast.next;
slow = slow.next;
}
return fast;
}
}
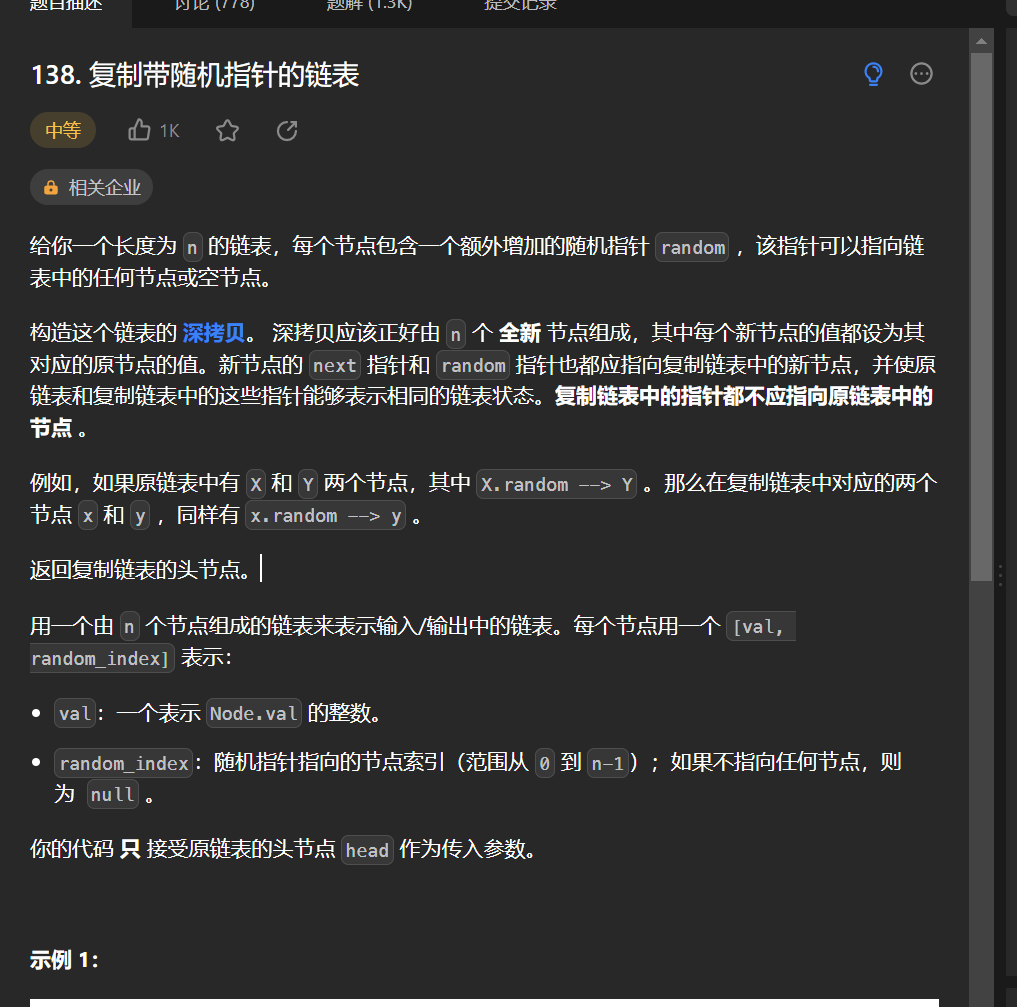
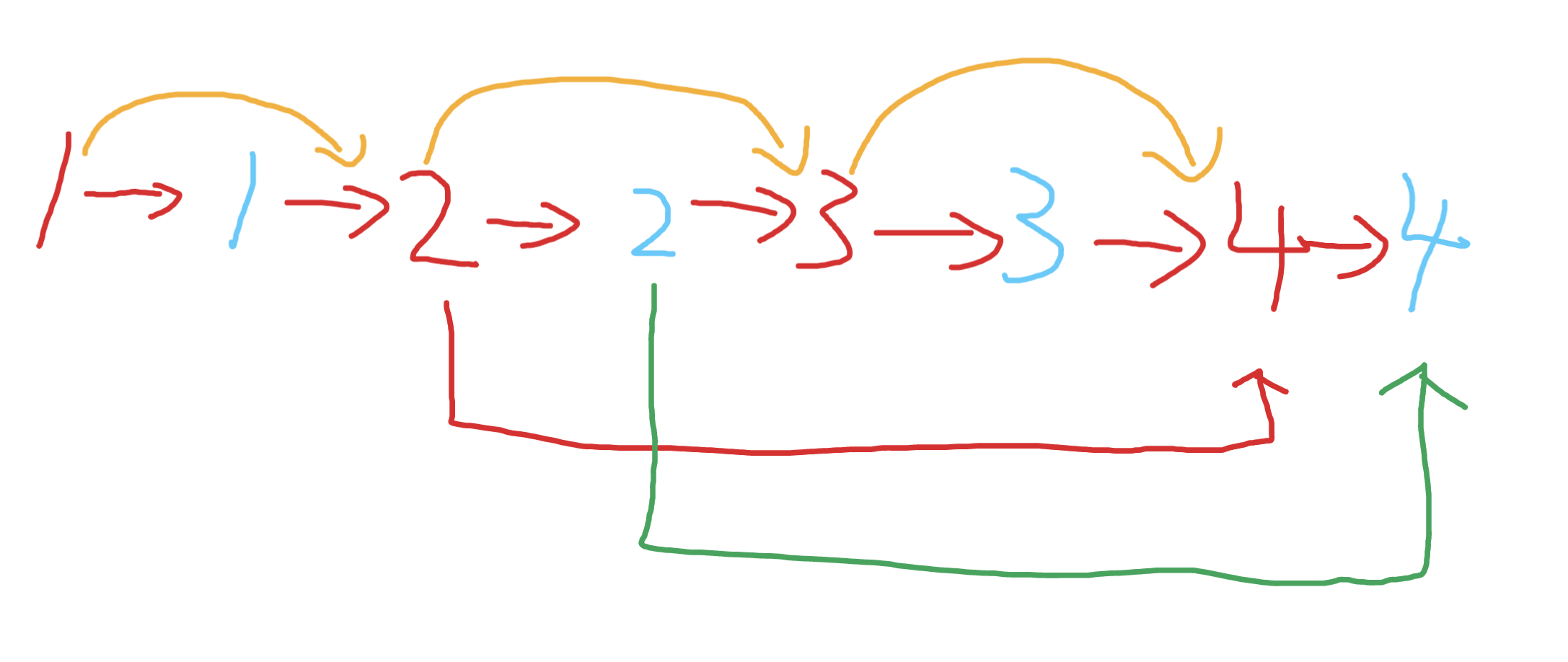
十四丶[复制带随机指针的链表](138. 复制带随机指针的链表 - 力扣(Leetcode))#
思路:#
如果可以使用map存储每一个节点的下一个节点, 和random指针节点,那么这个题就没什么难度,但是如果追求极致的空间不使用额外空间的话,还是有点巧妙的
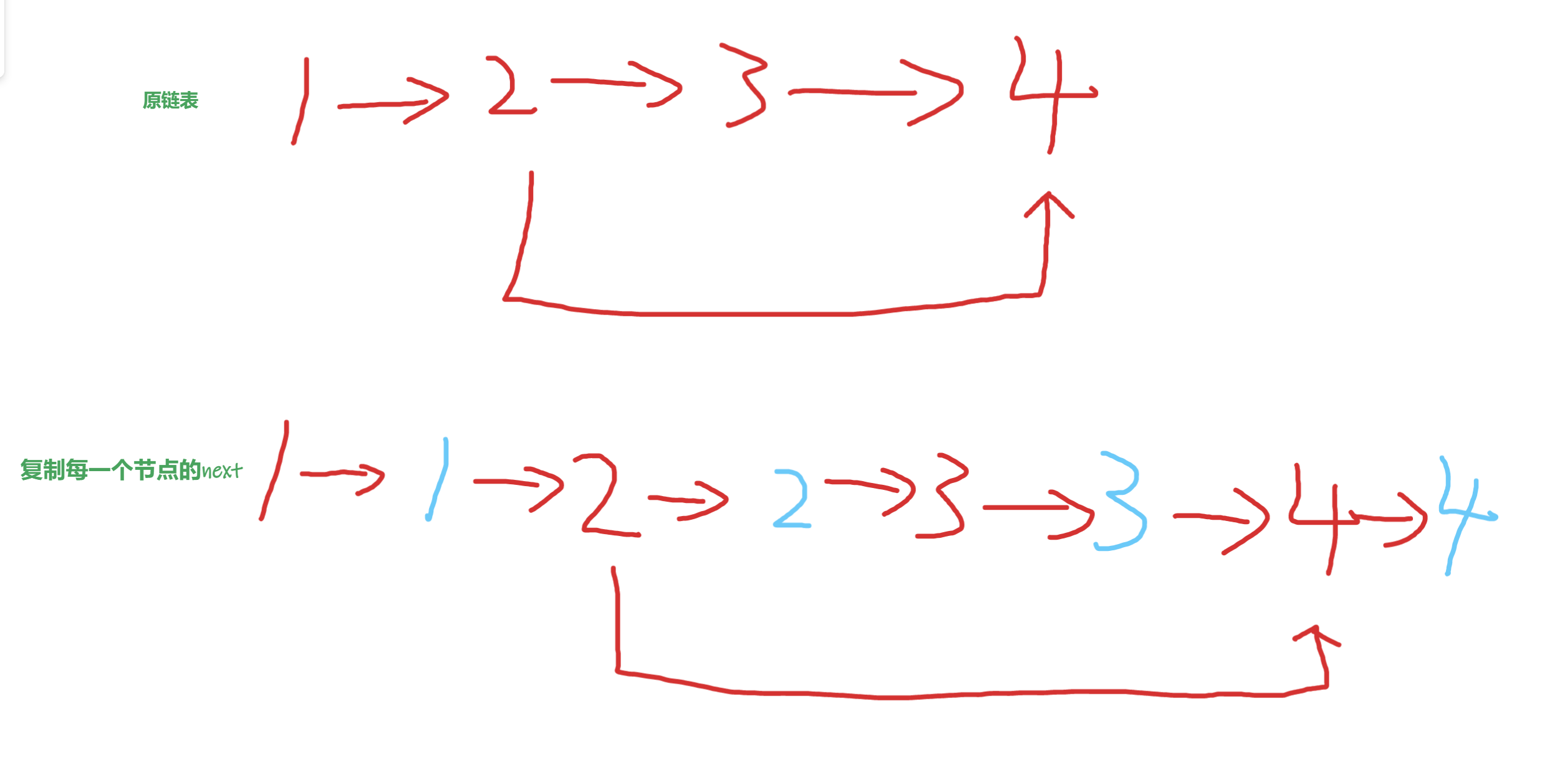
-
复制每一个节点的next,并且让复制节点和原节点使用next串联起来,做到如下效果
蓝色是复制的节点,红色是原节点
这时我们其实可以很快的得到蓝色2的random指针指向的是蓝色的4,也就是红色4的next
-
接下来我们要把两个链表拆开,并且复制random指针
我们遍历到红色2的时候发现,其具备random指向了公司的4,那么蓝色2的指向就是红色4的下一个
代码:#
/*
// Definition for a Node.
class Node {
int val;
Node next;
Node random;
public Node(int val) {
this.val = val;
this.next = null;
this.random = null;
}
}
*/
class Solution {
public Node copyRandomList(Node head) {
if(head == null ){
return null;
}
Node cur = head;
//深拷贝
while(cur != null){
Node copy = new Node(cur.val);
Node next = cur.next;
cur.next = copy;
copy.next = next;
cur = next;
}
//拷贝后的头
Node copyHead = head.next;
//接下来需要复制random指向
cur = head;
while(cur != null){
Node copy = cur.next;
//拷贝random
if(cur.random != null){
copy.random = cur.random.next;
}
cur = copy.next;
}
//拆分
cur = head;
while(cur != null){
Node copy = cur.next;
Node sourceNext = copy.next;
cur.next = sourceNext;
if(sourceNext != null){
copy.next = sourceNext.next;
}
cur =sourceNext;
}
return copyHead;
}
}
十五丶[LRU 缓存](146. LRU 缓存 - 力扣(Leetcode))#
思路:#
LRU 最近最少使用,如果看过linkedHashMap源码,我们可以知道,让linkedHashMap按照访问顺序排序然后复写removeEldestEntry让容量大于最大容量的时候删除节点即可实现lru淘汰策略(mybatis源码中的LRU缓存便是如此实现的)。原理便是最近被访问(put 或者get)的内容,放在链表的头部,这样链表的尾部便是最近最少访问的缓存内容,所以我们只要使用链表来维护这个顺序,使用hashMap实现查找即可
代码:#
class LRUCache {
//双向链表
static class Node {
Node pre;
Node next;
int key ;
int val;
}
//最大容量
int maxSize;
//当前容量
int size=0;
//头 哑节点
Node head;
//尾 哑节点
Node tail;
//缓存内容
Map<Integer,Node> map = new HashMap<>();
//初始化
public LRUCache(int capacity) {
maxSize = capacity;
head = new Node();
tail = new Node();
head.next = tail;
tail.pre = head;
}
public int get(int key) {
Node n = map.get(key);
//缓存中没 返回-1
if(n == null){
return -1;
}
//缓存中存在,说明最近被使用到 那么调整到队列头部
adjustToHead(n);
return n.val;
}
public void put(int key, int value) {
Node n = map.get(key);
//缓存中最开始没用 那么需要 new 一个节点存到map中
if(n == null){
n = new Node();
n.val = value;
n.key = key;
map.put(key,n);
size++;
}else{
//缓存中有 那么改变值
n.val = value;
}
//调整到队列头部
adjustToHead(n);
}
//将节点移动到头部 如果容量超过需要删除尾部节点
void adjustToHead(Node n){
if(n == head.next){
//判断是否需要删除最近最少使用的内容
removeTailIfNeed();
return;
}
//调整到头部
Node sourceFirst = head.next;
if(n.pre != null){
n.pre.next = n.next;
n.next.pre = n.pre;
}
n.next = sourceFirst;
sourceFirst.pre = n;
n.pre = head;
head.next = n;
//判断是否需要删除最近最少使用的内容
removeTailIfNeed();
}
//删除最近最少使用的内容
void removeTailIfNeed(){
if(size > maxSize){
map.remove(tail.pre.key);
size -- ;
Node needRemove = tail.pre;
needRemove.pre.next = tail;
tail.pre = needRemove.pre;
}
}
}
十六丶[回文链表](234. 回文链表 - 力扣(Leetcode))#
思路:#
如果可以使用额外数据结构保存链表中的值,那么这个问题非常简单,但是如果不允许使用额外空间,这个问题就有点巧妙了
首先我们要找到链表的重点(1->2->3找到2,1->2->3->4 找到2)然后将中点右侧部分进行反转,返回再比较中点左半部分 和 右半部分是否相同的数值,最后还需要把右半部分翻转回来,复原链表
代码:#
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* public class ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode next;
* ListNode() {}
* ListNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* ListNode(int val, ListNode next) { this.val = val; this.next = next; }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public boolean isPalindrome(ListNode head) {
//0个节点, 一个节点 直接true
if(head == null || head.next == null){
return true;
}
//两个节点 看两个节点值是否相同
if(head.next.next == null){
return head.val == head.next.val;
}
//找中点
ListNode slow = head;
ListNode fast = head;
while(fast.next!=null&&fast.next.next!=null){
slow = slow.next;
fast = fast.next.next;
}
//中点
ListNode half = slow;
//需要翻转的右半部分
ListNode needReverseHead = half.next;
//翻转 数组第1个是头 第二个是翻转后的尾
ListNode[]rArray = reverseList(needReverseHead);
ListNode halfHead = rArray[0];
//标记是否 回文
boolean flag = true;
//比较是否回文
while(halfHead!=null){
flag = halfHead.val==head.val;
if(!flag){
break;
}
halfHead = halfHead.next;
head = head.next;
}
//翻转回去
ListNode[] recovery = reverseList(rArray[0]);
//复原链表
slow.next = recovery[0];
return flag;
}
//翻转 并返回 头和尾
private ListNode[] reverseList(ListNode head) {
if(head==null){
return null;
}
if(head.next == null){
return new ListNode[]{head,null};
}
//哑节点
ListNode preHead = new ListNode(-1,head);
//当前需要操作的节点
ListNode cur = head.next;
//下一个节点
ListNode next = cur.next;
//尾巴
ListNode tail = preHead.next;
while(cur != null){
//翻转
cur.next = preHead.next;
tail.next = next;
preHead.next = cur;
//更新
cur = next;
if(next == null){
return new ListNode[]{preHead.next,tail};
}
next = next.next;
}
return new ListNode[]{preHead.next,tail};
}
}
Recommend
About Joyk
Aggregate valuable and interesting links.
Joyk means Joy of geeK