【深入浅出 Yarn 架构与实现】3-3 Yarn Application Master 编写 - 大数据王小皮
source link: https://www.cnblogs.com/shuofxz/p/16904865.html
Go to the source link to view the article. You can view the picture content, updated content and better typesetting reading experience. If the link is broken, please click the button below to view the snapshot at that time.

本篇文章继续介绍 Yarn Application 中 ApplicationMaster 部分的编写方法。
一、Application Master 编写方法
上一节讲了 Client 提交任务给 RM 的全流程,RM 收到任务后,由 ApplicationsManager 向 NM 申请 Container,并根据 Client 提供的 ContainerLaunchContext 启动 ApplicationMaster。
本篇代码已上传 Github:
Github - MyApplicationMaster
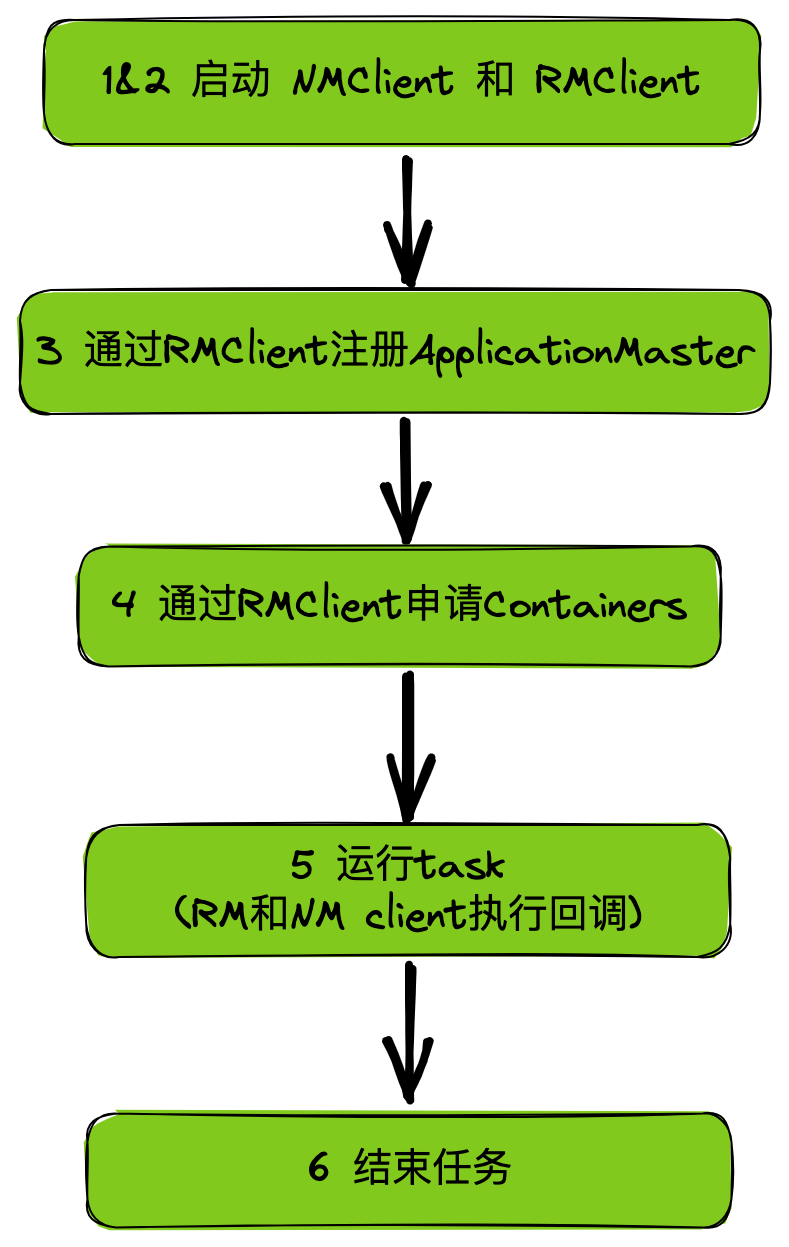
一)整体流程
1&2、启动 NMClient 和 RMClient
在 AM 中需要分别启动 NMClient 和 RMClient 进行通信。
两个客户端中都注册了我们自定义的 eventHandler,将会在后面进行介绍。
在 amRMClient 中会定义 AM 向 RM 定时发送心跳的间隔。(在 RM 中会有心跳容忍时间,注意不要超过 RM 配置的时间)
// logInformation();
Configuration conf = new Configuration();
// 1 create amRMClient
// 第一个参数是心跳时间 ms
amRMClient = AMRMClientAsync.createAMRMClientAsync(1000, new RMCallbackHandler());
amRMClient.init(conf);
amRMClient.start();
// 2 Create nmClientAsync
amNMClient = new NMClientAsyncImpl(new NMCallbackHandler());
amNMClient.init(conf);
amNMClient.start();
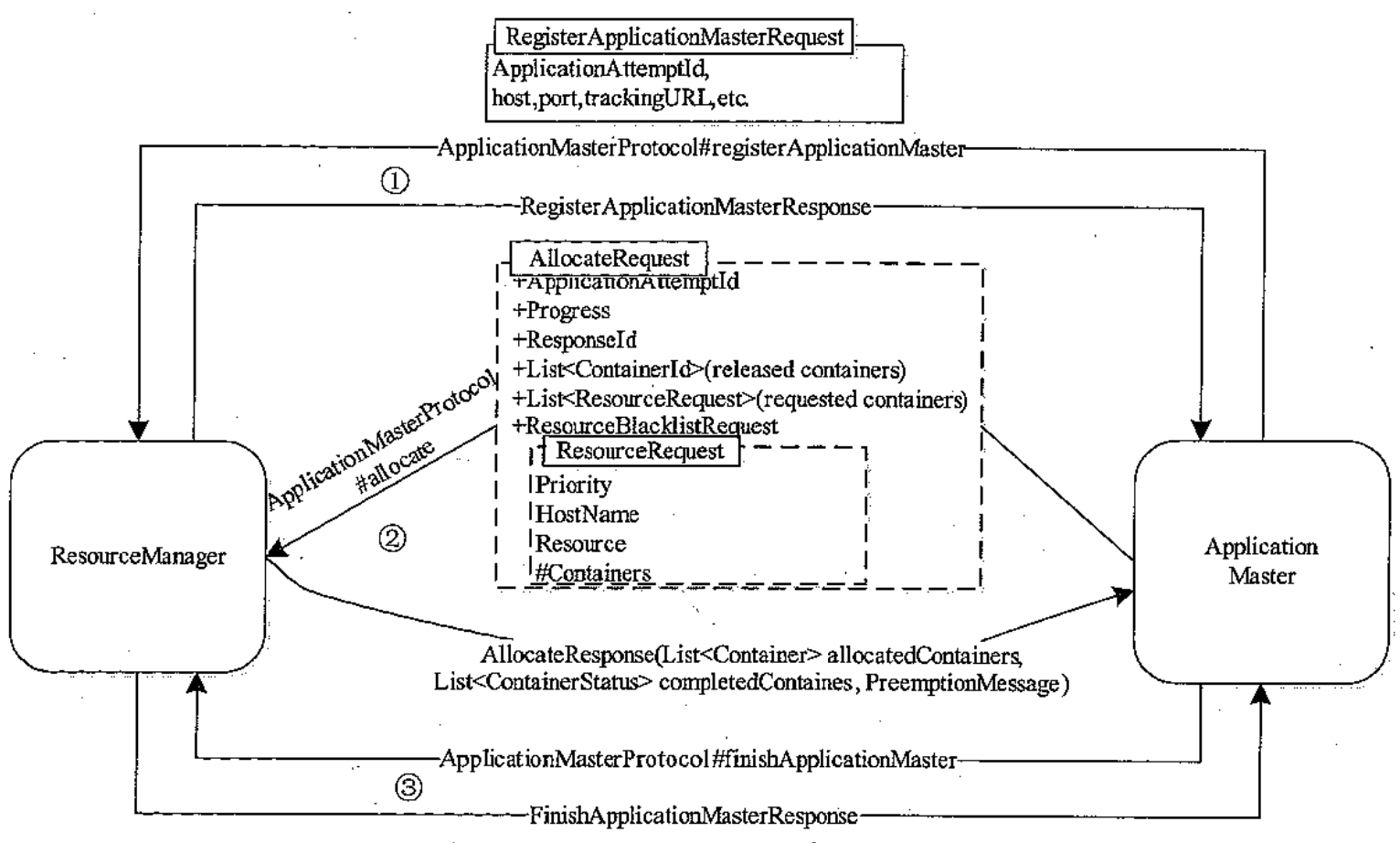
3、向 RM 注册 ApplicationMaster
// 3 register with RM and this will heart beating to RM
RegisterApplicationMasterResponse response = amRMClient
.registerApplicationMaster(NetUtils.getHostname(), -1, "");
4、申请 Containers
首先需要从 response 中确认资源池剩余资源,然后再根据需求申请 container
// 4 Request containers
response.getContainersFromPreviousAttempts();
// 4.1 check resource
long maxMem = response.getMaximumResourceCapability().getMemorySize();
int maxVCores = response.getMaximumResourceCapability().getVirtualCores();
// 4.2 request containers base on avail resource
for (int i = 0; i < numTotalContainers.get(); i++) {
ContainerRequest containerAsk = new ContainerRequest(
//100*10M + 1vcpu
Resource.newInstance(100, 1), null, null,
Priority.newInstance(0));
amRMClient.addContainerRequest(containerAsk);
}
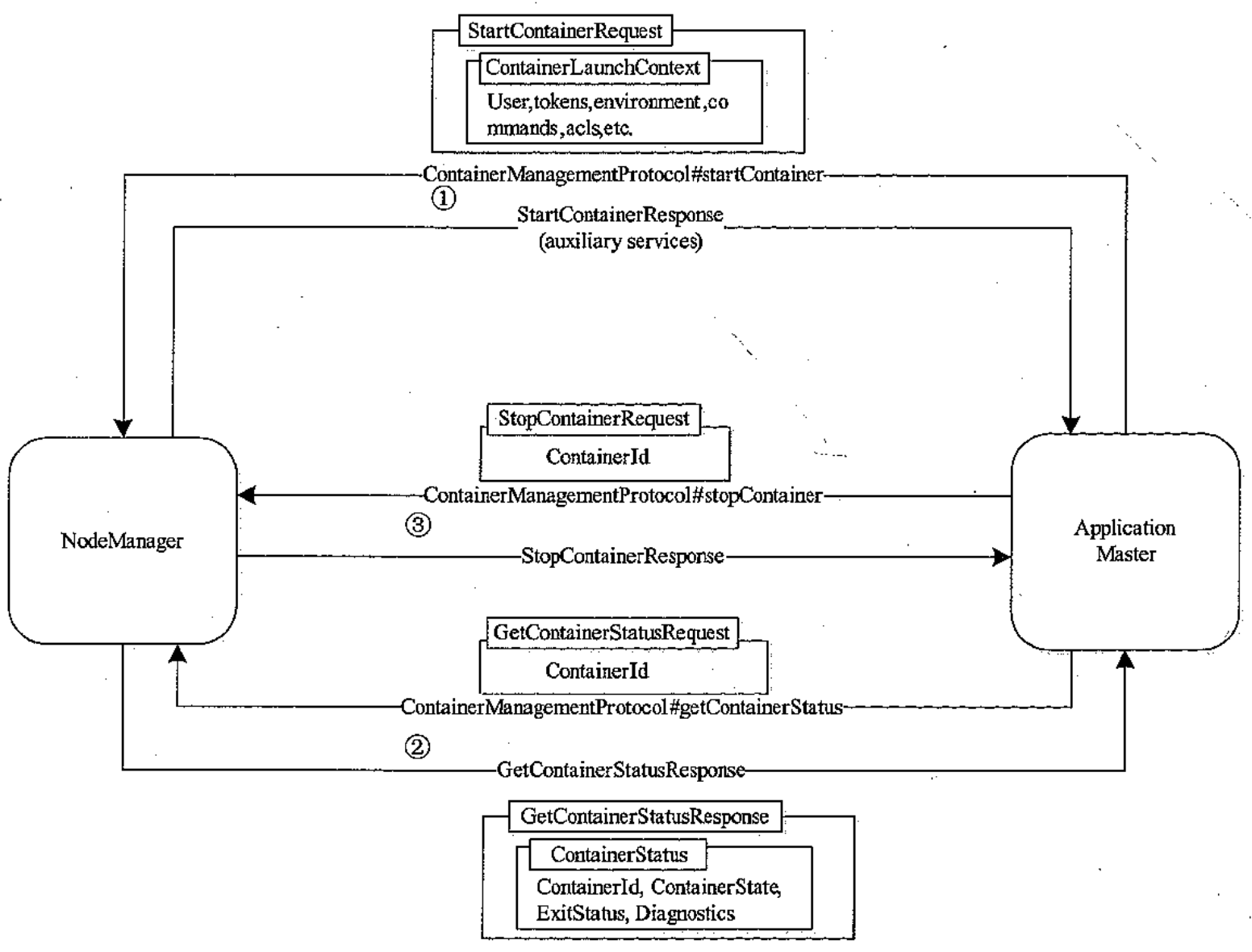
5、运行任务
将在 RMCallbackHandler 中的 onContainersAllocated 回调函数中处理,并在其中调用 NMCallbackHandler 的方法,执行对应的 task。
(RMCallbackHandler、NMCallbackHandler将在后面进行详细介绍。)
// RMCallbackHandler
public void onContainersAllocated(List<Container> containers) {
for (Container c : containers) {
log.info("Container Allocated, id = " + c.getId() + ", containerNode = " + c.getNodeId());
// LaunchContainerTask 实现在下面
exeService.submit(new LaunchContainerTask(c));
}
}
private class LaunchContainerTask implements Runnable {
@Override
public void run() {
// ……
// 发送事件交给 nm 处理
amNMClient.startContainerAsync(container, ctx);
}
}
6、结束任务
当全部子任务完成后,需要做收尾工作,将 amNMClient 和 amRMClient 停止。
while(numTotalContainers.get() != numCompletedContainers.get()){
try{
Thread.sleep(1000);
log.info("waitComplete" +
", numTotalContainers=" + numTotalContainers.get() +
", numCompletedConatiners=" + numCompletedContainers.get());
} catch (InterruptedException ex){}
}
log.info("ShutDown exeService Start");
exeService.shutdown();
log.info("ShutDown exeService Complete");
amNMClient.stop();
log.info("amNMClient stop Complete");
amRMClient.unregisterApplicationMaster(FinalApplicationStatus.SUCCEEDED, "dummy Message", null);
log.info("unregisterApplicationMaster Complete");
amRMClient.stop();
log.info("amRMClient stop Complete");
二)NMClient 和 RMClient Callback Handler 编写
1、RMCallbackHandler
本质是个 eventHandler,对事件库不熟悉的同学可以翻之前的文章「2-3 Yarn 基础库 - 服务库与事件库」进行学习。
其会处理 Container 启动、停止、更新等事件。
收到不同的事件时,会执行相应的回调函数。这里仅给出两个函数的实现。
💡 思考:之前版本中(2.6之前)还是实现 CallbackHandler 接口,为何后面改为了抽象类?
A:对原接口有了扩展增加了方法 onContainersUpdated。推测是因为避免使用接口继承。
private class RMCallbackHandler extends AMRMClientAsync.AbstractCallbackHandler {
@Override
public void onContainersCompleted(List<ContainerStatus> statuses) {
for (ContainerStatus status : statuses) {
log.info("Container completed: " + status.getContainerId().toString()
+ " exitStatus=" + status.getExitStatus());
if (status.getExitStatus() != 0) {
log.error("Container return error status: " + status.getExitStatus());
log.warn("Need rerun container!");
// do something restart container
continue;
}
ContainerId containerId = status.getContainerId();
runningContainers.remove(containerId);
numCompletedContainers.addAndGet(1);
}
}
@Override
// 这里在 container 中启动相应的 task
public void onContainersAllocated(List<Container> containers) {
for (Container c : containers) {
log.info("Container Allocated, id = " + c.getId() + ", containerNode = " + c.getNodeId());
// LaunchContainerTask 实现在下面
exeService.submit(new LaunchContainerTask(c));
}
}
// 其他方法实现……
}
private class LaunchContainerTask implements Runnable {
Container container;
public LaunchContainerTask(Container container) {
this.container = container;
}
@Override
public void run() {
LinkedList<String> commands = new LinkedList<>();
commands.add("sleep " + sleepSeconds.addAndGet(1));
ContainerLaunchContext ctx = ContainerLaunchContext.newInstance(null, null, commands, null, null, null);
// 这里去执行 amNMClient 的回调
amNMClient.startContainerAsync(container, ctx);
}
}
2、NMCallbackHandler
定义 nm container 需要执行的各种事件处理。
private class NMCallbackHandler extends NMClientAsync.AbstractCallbackHandler {
@Override
public void onContainerStarted(ContainerId containerId, Map<String, ByteBuffer> allServiceResponse) {
log.info("Container Stared " + containerId.toString());
}
// ……
三)涉及的通信协议
至此我们学习了编写 Yarn Application 的整体流程和实现方法,相信各位同学对其有了更深的认识。之后可以从 hadoop 提供的 DistributedShell 入手,再到其他框架(Hive、Flink)等探究工业级框架是如何提交 Application 的。
参考文章:
Hadoop Doc: Writing an ApplicationMaster (AM)
《Hadoop 技术内幕 - 深入解析 Yarn 结构设计与实现原理》第四章
__EOF__
Recommend
-
 2
2
了解 Yarn 基础库是后面阅读 Yarn 源码的基础,本节对 Yarn 基础库做总体的介绍。并对其中使用的第三方库 Protocol Buffers 和 Avro 是什么、怎么用做简要的介绍。 一、主要使用的库 Protocol Buffers
-
 3
3
RPC(Remote Procedure Call) 是 Hadoop 服务通信的关键库,支撑上层分布式环境下复杂的进程间(Inter-Process Communication, IPC)通信逻辑,是分布式系统的基础。允许运行于一台计算机上的程序像调用本地方法一样,调用另一台计算机的子程序。由于 RPC 服...
-
 6
6
一个庞大的分布式系统,各个组件间是如何协调工作的?组件是如何解耦的?线程运行如何更高效,减少阻塞带来的低效问题?本节将对 Yarn 的服务库和事件库进行介绍,看看 Yarn 是如何解决这些问题的。 一、服务库 对于生命周期较长的对...
-
 3
3
当一个服务拥有太多处理逻辑时,会导致代码结构异常的混乱,很难分辨一段逻辑是在哪个阶段发挥作用的。 这时就可以引入状态机模型,帮助代码结构变得清晰。 一、状态机库概述 状态机由一组状态组成: 【初始状态 -...
-
 2
2
【深入浅出 Yarn 架构与实现】3-1 Yarn Application 流程与编写方法 本篇学习 Yarn Application 编写方法,将带你更清楚的了解一个任务是如何提交到 Ya...
-
 9
9
前面几篇文章对 Yarn 基本架构、程序基础库、应用设计方法等进行了介绍。之后几篇将开始对 Yarn 核心组件进行剖析。 ResourceManager(RM)是 Yarn 的核心管理服务,负责集群管理、任务调度、状态机管理等,本篇将对 RM 总体架构进行介绍。
-
 13
13
本篇继续对 RM 中管理 NodeManager 的部分进行深入的讲解。主要有三个部分:检查 NM 是否存活;管理 NM 的黑白名单;响应 NM RPC 请求。 一、简介
-
 10
10
在 YARN 中,Application 是指应用程序,它可能启动多个运行实例,每个运行实例由 —个 ApplicationMaster 与一组该 ApplicationMaster 启动的任务组成,它拥有名称、队列、优先级等属性,是一个比较宽泛的概念,可以是一个 MepReduce 作业、一个 DAG 应用程序等。YAR...
-
 7
7
本节开始将对 Yarn 中的 NodeManager 服务进行剖析。 NodeManager 需要在每个计算节点上运行,与 ResourceManager 和 ApplicationMaster 进行交互。管理节点的计算资源以及调度容器。后续将对 NM 的功能职责、状态机、容器生命周期和资源隔离等方面进行讲解。...
-
 2
2
一、简介# NodeManager(NM)中的状态机分为三类:Application、Container 和 LocalizedResource,它们均直接或者间接参与维护一...
About Joyk
Aggregate valuable and interesting links.
Joyk means Joy of geeK