

畸变矫正、透视变换加速(OpenCV C++) - 湾仔码农
source link: https://www.cnblogs.com/Fish0403/p/16801563.html
Go to the source link to view the article. You can view the picture content, updated content and better typesetting reading experience. If the link is broken, please click the button below to view the snapshot at that time.

前两周,同事和我说检测时间超时,其中对图像做畸变矫正和投影变换就要花费25ms(3000×3000的图)。而此时我们已经用上了文章opencv图像畸变矫正加速、透视变换加速方法总结中的方法。突然我想到了我去年笔记OpenCV笔记(10) 相机模型与标定中的一个函数cv::undistortPoints(),对感兴趣点进行畸变矫正。在应用之前,需要测试下两种方法计算出来的点的差值,即remap和undistortPoints的不同。结论:对全图进行畸变矫正,再找点 VS 找点后,对点进行畸变矫正,两者的差值小于0.1个像素,可行!同样的方法可以运用在投影变换上。在尺寸测量方面,这样可以节省掉畸变矫正和投影变换的时间。
1 只对感兴趣的点进行畸变矫正
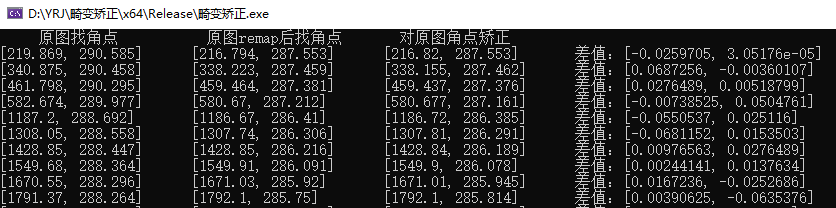
// 读取相机参数文件FileStorage fs("D:/distortionLens.xml", FileStorage::READ);Mat intrinsic_matrix = Mat(3, 3, CV_32FC1, Scalar::all(0));Mat distortion_coeffs = Mat(1, 5, CV_32FC1, Scalar::all(0));fs["intrinsic_matrix"] >> intrinsic_matrix;fs["distortion_coeffs"] >> distortion_coeffs;Mat mapx = Mat(s, CV_32FC1);Mat mapy = Mat(s, CV_32FC1);// 根据内参和畸变系数,建立查找表//intrinsic_matrix = getOptimalNewCameraMatrix(intrinsic_matrix, distortion_coeffs, s, 1, s, 0);initUndistortRectifyMap(intrinsic_matrix, distortion_coeffs, Mat(),intrinsic_matrix, s, CV_32FC1, mapx, mapy);// 方法1:畸变矫正后找角点Mat distortionMat;remap(src, distortionMat, mapx, mapy, INTER_CUBIC);vector<Point2f> distortPoints;findChessboardCornersSB(src, Size(21, 21), distortPoints, 64);// 方法2:找角点后畸变矫正vector<Point2f> oriPoints, sparsePoints;findChessboardCornersSB(src, Size(21, 21), oriPoints, 64);undistortPoints(oriPoints, sparsePoints, intrinsic_matrix, distortion_coeffs, Mat(), intrinsic_matrix);// 打印比较cout << " 原图找角点 " << "\t" << " 原图remap后找角点 " << "\t" << " 对原图角点矫正 " << endl;for (int i = 0; i < sparsePoints.size(); i++) {cout << oriPoints[i] << "\t" << distortPoints[i] << "\t" << sparsePoints[i] << "\t" << "差值:" << distortPoints[i] - sparsePoints[i] << endl;} |
部分数据如下所示,可以看出,两者差值小于0.1个像素,加速10ms完成,接下来再对投影变换加速一下。
2 只对感兴趣的点进行投影变换
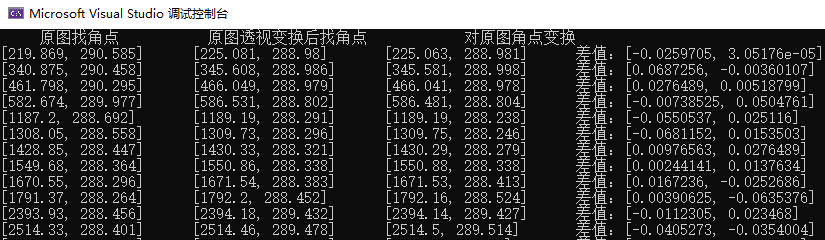
// 读取变换矩阵fs = FileStorage("D:/transMat.txt", FileStorage::READ);Mat transMat = Mat(3, 3, CV_32FC1, Scalar::all(0));fs["transMat"] >> transMat;// 方法1:进行透视变换后找角点Mat warpMat;warpPerspective(src, warpMat, transMat, s, INTER_LINEAR, BORDER_CONSTANT, Scalar(255));vector<Point2f> warpPoints;findChessboardCornersSB(warpMat,Size(21, 21), warpPoints, 64);// 方法2:找角点后进行透视变换vector<Point2f> outPoints;for (int i = 0; i < oriPoints.size(); i++) {Mat_<double> oriPoint(3, 1);oriPoint(0, 0) = oriPoints[i].x;oriPoint(1, 0) = oriPoints[i].y;oriPoint(2, 0) = 1;Mat dstPoints = transMat * oriPoint;double a1 = dstPoints.at<double>(0, 0);double a2 = dstPoints.at<double>(1, 0);double a3 = dstPoints.at<double>(2, 0);outPoints.push_back(Point2f(a1 * 1.0 / a3, a2 * 1.0 / a3));}<br>//打印cout << " 原图找角点 " << "\t" << " 原图透视变换后找角点 " << "\t" << " 对原图角点变换 " << endl;for (int i = 0; i < sparsePoints.size(); i++) {cout << oriPoints[i] << "\t" << warpPoints[i] << "\t" << outPoints[i] << "\t" << "差值:" << distortPoints[i] - sparsePoints[i] << endl;} |
3.1 读取文件
void GetMap(){FileStorage fs(path+"distortionLens.xml", FileStorage::READ);if (fs.isOpened()){intrinsic_matrix = Mat(3, 3, CV_64FC1, Scalar::all(0));distortion_coeffs = Mat(1, 5, CV_64FC1, Scalar::all(0));fs["intrinsic_matrix"] >> intrinsic_matrix;fs["distortion_coeffs"] >> distortion_coeffs;}fs = FileStorage(path+"transMat.txt", FileStorage::READ);if (fs.isOpened()){transMat = Mat(3, 3, CV_64FC1, Scalar::all(0));fs["transMat"] >> transMat;}} |
3.2 变换感兴趣点
void remapPoints(vector<Point2f>& points) {for (int i = 0; i < points.size(); i++) {Mat_<double> oriPoint(3, 1);oriPoint(0, 0) = points[i].x;oriPoint(1, 0) = points[i].y;oriPoint(2, 0) = 1;Mat dstPoint = transMat * oriPoint;double a1 = dstPoint.at<double>(0, 0);double a2 = dstPoint.at<double>(1, 0);double a3 = dstPoint.at<double>(2, 0);points[i] = Point2f(a1 * 1.0 / a3, a2 * 1.0 / a3);}undistortPoints(points, points, intrinsic_matrix, distortion_coeffs, Mat(), intrinsic_matrix);} |
Recommend
About Joyk
Aggregate valuable and interesting links.
Joyk means Joy of geeK