
4

PaddleOCR-EAST - 就是个飞舞
source link: https://www.cnblogs.com/tonyma/p/16819052.html
Go to the source link to view the article. You can view the picture content, updated content and better typesetting reading experience. If the link is broken, please click the button below to view the snapshot at that time.
写在前面:基于PaddleOCR代码库对其中所涉及到的算法进行代码简读,如果有必要可能会先研读一下原论文。
Abstract
- 论文链接:arxiv
- 应用场景:文本检测
- 代码配置文件:configs/det/det_r50_vd_east.yml
Train
PreProcess
class EASTProcessTrain(object):
def __init__(self,
image_shape=[512, 512],
background_ratio=0.125,
min_crop_side_ratio=0.1,
min_text_size=10,
**kwargs):
self.input_size = image_shape[1]
self.random_scale = np.array([0.5, 1, 2.0, 3.0])
self.background_ratio = background_ratio
self.min_crop_side_ratio = min_crop_side_ratio
self.min_text_size = min_text_size
...
def __call__(self, data):
im = data['image']
text_polys = data['polys']
text_tags = data['ignore_tags']
if im is None:
return None
if text_polys.shape[0] == 0:
return None
#add rotate cases
if np.random.rand() < 0.5:
# 旋转图片和文本框(90,180,270)
im, text_polys = self.rotate_im_poly(im, text_polys)
h, w, _ = im.shape
# 限制文本框坐标到有效范围内、检查文本框的有效性(基于文本框的面积)、以及点的顺序是否是顺时针
text_polys, text_tags = self.check_and_validate_polys(text_polys,
text_tags, h, w)
if text_polys.shape[0] == 0:
return None
# 随机缩放图片以及文本框
rd_scale = np.random.choice(self.random_scale)
im = cv2.resize(im, dsize=None, fx=rd_scale, fy=rd_scale)
text_polys *= rd_scale
if np.random.rand() < self.background_ratio:
# 只切纯背景图,如果有文本框会返回None
outs = self.crop_background_infor(im, text_polys, text_tags)
else:
"""
随机切图并以及crop图所包含的文本框,并基于缩小的文本框生成了几个label map:
- score_map: shape=[h,w],得分图,有文本的地方是1,其余地方为0
- geo_map: shape=[h,w,9]。前8个通道为缩小文本框内的像素到真实文本框的水平以及垂直距离,
最后一个通道用来做loss归一化,其值为每个框最短边长的倒数
- training_mask: shape=[h,w],使无效文本框不参与训练,有效的地方为1,无效的地方为0
"""
outs = self.crop_foreground_infor(im, text_polys, text_tags)
if outs is None:
return None
im, score_map, geo_map, training_mask = outs
# 产生最终降采样的score map,shape=[1,h//4,w//4]
score_map = score_map[np.newaxis, ::4, ::4].astype(np.float32)
# 产生最终降采样的gep map, shape=[9,h//4,w//4]
geo_map = np.swapaxes(geo_map, 1, 2)
geo_map = np.swapaxes(geo_map, 1, 0)
geo_map = geo_map[:, ::4, ::4].astype(np.float32)
# 产生最终降采样的training mask,shape=[1,h//4,w//4]
training_mask = training_mask[np.newaxis, ::4, ::4]
training_mask = training_mask.astype(np.float32)
data['image'] = im[0]
data['score_map'] = score_map
data['geo_map'] = geo_map
data['training_mask'] = training_mask
return data
Architecture
Backbone
采用resnet50_vd,得到1/4、1/8、1/16以及1/32倍共计4张降采样特征图。
基于Unect decoder架构,完成自底向上的特征融合过程,从1/32特征图逐步融合到1/4的特征图,最终得到一张带有多尺度信息的1/4特征图。
def forward(self, x):
# x是存储4张从backbone获取的特征图
f = x[::-1] # 此时特征图从小到大排列
h = f[0] # [b,512,h/32,w/32]
g = self.g0_deconv(h) # [b,128,h/16,w/16]
h = paddle.concat([g, f[1]], axis=1) # [b,128+256,h/16,w/16]
h = self.h1_conv(h) # [b,128,h/16,w/16]
g = self.g1_deconv(h) # [b,128,h/8,w/8]
h = paddle.concat([g, f[2]], axis=1) # [b,128+128,h/8,w/8]
h = self.h2_conv(h) # [b,128,h/8,w/8]
g = self.g2_deconv(h) # [b,128,h/4,w/4]
h = paddle.concat([g, f[3]], axis=1) # [b,128+64,h/4,w/4]
h = self.h3_conv(h) # [b,128,h/4,w/4]
g = self.g3_conv(h) # [b,128,h/4,w/4]
return g
输出分类头和回归头(quad),部分参数共享。
def forward(self, x, targets=None):
# x是融合后的1/4特征图,det_conv1和det_conv2用于进一步加强特征抽取
f_det = self.det_conv1(x) # [b,128,h/4,w/4]
f_det = self.det_conv2(f_det) # [b,64,h/4,w/4]
# # [b,1,h/4,w/4] 用于前、背景分类,注意kernel_size=1
f_score = self.score_conv(f_det)
f_score = F.sigmoid(f_score) # 获取相应得分
# # [b,8,h/4,w/4],8的意义:dx1,dy1,dx2,dy2,dx3,dy3,dx4,dy4
f_geo = self.geo_conv(f_det)
# 回归的range变为:[-800,800],那么最终获取的文本框的最大边长不会超过1600
f_geo = (F.sigmoid(f_geo) - 0.5) * 2 * 800
pred = {'f_score': f_score, 'f_geo': f_geo}
return pred
分类采用dice_loss,回归采用smooth_l1_loss。
class EASTLoss(nn.Layer):
def __init__(self,
eps=1e-6,
**kwargs):
super(EASTLoss, self).__init__()
self.dice_loss = DiceLoss(eps=eps)
def forward(self, predicts, labels):
"""
Params:
predicts: {'f_score': 前景得分图,'f_geo': 回归图}
labels: [imgs, l_score, l_geo, l_mask]
"""
l_score, l_geo, l_mask = labels[1:]
f_score = predicts['f_score']
f_geo = predicts['f_geo']
# 分类loss
dice_loss = self.dice_loss(f_score, l_score, l_mask)
channels = 8
# channels+1的原因是最后一个图对应了短边的归一化系数(后面会讲),前8个代表相对偏移的label
# [[b,1,h/4,w/4], ...]共9个
l_geo_split = paddle.split(
l_geo, num_or_sections=channels + 1, axis=1)
# [[b,1,h/4,w/4], ...]共8个
f_geo_split = paddle.split(f_geo, num_or_sections=channels, axis=1)
smooth_l1 = 0
for i in range(0, channels):
geo_diff = l_geo_split[i] - f_geo_split[i] # diff=label-pred
abs_geo_diff = paddle.abs(geo_diff) # abs_diff
# 计算abs_diff中小于1的且有文本的部分
smooth_l1_sign = paddle.less_than(abs_geo_diff, l_score)
smooth_l1_sign = paddle.cast(smooth_l1_sign, dtype='float32')
# smoothl1 loss,大于1和小于1的两个部分对应loss相加,只不过这里<1的部分没乘0.5,问题不大
in_loss = abs_geo_diff * abs_geo_diff * smooth_l1_sign + \
(abs_geo_diff - 0.5) * (1.0 - smooth_l1_sign)
# 用短边*8做归一化
out_loss = l_geo_split[-1] / channels * in_loss * l_score
smooth_l1 += out_loss
# paddle.mean(smooth_l1)就可以了,前面都乘过了l_score,这里再乘没卵用
smooth_l1_loss = paddle.mean(smooth_l1 * l_score)
# dice_loss权重为0.01,smooth_l1_loss权重为1
dice_loss = dice_loss * 0.01
total_loss = dice_loss + smooth_l1_loss
losses = {"loss":total_loss, \
"dice_loss":dice_loss,\
"smooth_l1_loss":smooth_l1_loss}
return losses
Dice Loss
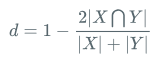
class DiceLoss(nn.Layer):
def __init__(self, eps=1e-6):
super(DiceLoss, self).__init__()
self.eps = eps
def forward(self, pred, gt, mask, weights=None):
# mask代表了有效文本的mask,有文本的地方是1,否则为0
assert pred.shape == gt.shape
assert pred.shape == mask.shape
if weights is not None:
assert weights.shape == mask.shape
mask = weights * mask
intersection = paddle.sum(pred * gt * mask) # 交集
union = paddle.sum(pred * mask) + paddle.sum(gt * mask) + self.eps # 并集
loss = 1 - 2.0 * intersection / union
assert loss <= 1
return loss
SmoothL1 Loss
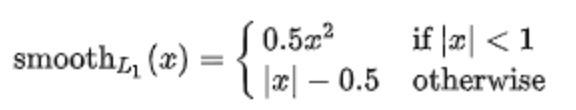
Infer
PostProcess
class EASTPostProcess(object):
def __init__(self,
score_thresh=0.8,
cover_thresh=0.1,
nms_thresh=0.2,
**kwargs):
self.score_thresh = score_thresh
self.cover_thresh = cover_thresh
self.nms_thresh = nms_thresh
...
def __call__(self, outs_dict, shape_list):
score_list = outs_dict['f_score'] # shape=[b,1,h//4,w//4]
geo_list = outs_dict['f_geo'] # shape=[b,8,h//4,w//4]
if isinstance(score_list, paddle.Tensor):
score_list = score_list.numpy()
geo_list = geo_list.numpy()
img_num = len(shape_list)
dt_boxes_list = []
for ino in range(img_num):
score = score_list[ino]
geo = geo_list[ino]
# 根据score、geo以及一些预设阈值和locality_nms操作拿到检测框
boxes = self.detect(
score_map=score,
geo_map=geo,
score_thresh=self.score_thresh,
cover_thresh=self.cover_thresh,
nms_thresh=self.nms_thresh)
boxes_norm = []
if len(boxes) > 0:
h, w = score.shape[1:]
src_h, src_w, ratio_h, ratio_w = shape_list[ino]
boxes = boxes[:, :8].reshape((-1, 4, 2))
# 文本框坐标根于缩放系数映射回输入图像上
boxes[:, :, 0] /= ratio_w
boxes[:, :, 1] /= ratio_h
for i_box, box in enumerate(boxes):
# 根据宽度比高度大这一先验,将坐标调整为以“左上角”点为起始点的顺时针4点框
box = self.sort_poly(box.astype(np.int32))
# 边长小于5的再进行一次过滤,拿到最终的检测结果
if np.linalg.norm(box[0] - box[1]) < 5 \
or np.linalg.norm(box[3] - box[0]) < 5:
continue
boxes_norm.append(box)
dt_boxes_list.append({'points': np.array(boxes_norm)})
return dt_boxes_list
def detect(self,
score_map,
geo_map,
score_thresh=0.8,
cover_thresh=0.1,
nms_thresh=0.2):
score_map = score_map[0] # shape=[h//4,w//4]
geo_map = np.swapaxes(geo_map, 1, 0)
geo_map = np.swapaxes(geo_map, 1, 2) # shape=[h//4,w//4,8]
# 获取score_map上得分大于阈值的点的坐标,shape=[n,2]
xy_text = np.argwhere(score_map > score_thresh)
if len(xy_text) == 0:
return []
# 按y轴从小到大的顺序对这些点进行排序
xy_text = xy_text[np.argsort(xy_text[:, 0])]
# 恢复成基于原图的文本框坐标
text_box_restored = self.restore_rectangle_quad(
xy_text[:, ::-1] * 4, geo_map[xy_text[:, 0], xy_text[:, 1], :])
# shape=[n,9] 前8个通道代表x1,y1,x2,y2的坐标,最后一个通道代表每个框的得分
boxes = np.zeros((text_box_restored.shape[0], 9), dtype=np.float32)
boxes[:, :8] = text_box_restored.reshape((-1, 8))
boxes[:, 8] = score_map[xy_text[:, 0], xy_text[:, 1]]
try:
import lanms
boxes = lanms.merge_quadrangle_n9(boxes, nms_thresh)
except:
print(
'you should install lanms by pip3 install lanms-nova to speed up nms_locality'
)
# locality nms,比传统nms要快,因为进入nms中的文本框的数量要比之前少很多。前面按y轴排序其实是在为该步骤做铺垫
boxes = nms_locality(boxes.astype(np.float64), nms_thresh)
if boxes.shape[0] == 0:
return []
# 最终还会根据框预测出的文本框内的像素在score_map上的得分再做一次过滤,感觉有一些不合理,因为score_map
# 上预测的是shrink_mask,会导致框内有很多背景像素,拉低平均得分,可能会让一些原本有效的文本框变得无效
# 当然这里的cover_thresh取的比较低,可能影响就比较小
for i, box in enumerate(boxes):
mask = np.zeros_like(score_map, dtype=np.uint8)
cv2.fillPoly(mask, box[:8].reshape(
(-1, 4, 2)).astype(np.int32) // 4, 1)
boxes[i, 8] = cv2.mean(score_map, mask)[0]
boxes = boxes[boxes[:, 8] > cover_thresh]
return boxes
def nms_locality(polys, thres=0.3):
def weighted_merge(g, p):
"""
框间merge的逻辑:坐标变为coor1*score1+coor2*score2,得分变为score1+score2
"""
g[:8] = (g[8] * g[:8] + p[8] * p[:8]) / (g[8] + p[8])
g[8] = (g[8] + p[8])
return g
S = []
p = None
for g in polys:
# 由于是按y轴排了序,所以循环遍历就可以了
if p is not None and intersection(g, p) > thres:
# 交集大于阈值那么就merge
p = weighted_merge(g, p)
else:
# 不能再merge的时候该框临近区域已无其他框,那么其加入进S
if p is not None:
S.append(p)
p = g
if p is not None:
S.append(p)
if len(S) == 0:
return np.array([])
# 将S保留下的文本框进行标准nms,略
return standard_nms(np.array(S), thres)
Recommend
About Joyk
Aggregate valuable and interesting links.
Joyk means Joy of geeK