

JDK自带javap命令反编译class文件和Jad反编译class文件(推荐使用jad) - 小王写博客
source link: https://www.cnblogs.com/wang1221/p/16698918.html
Go to the source link to view the article. You can view the picture content, updated content and better typesetting reading experience. If the link is broken, please click the button below to view the snapshot at that time.

我们在日常学习中,对一个java代码有问题,不知道jvm内部怎么进行解析的时候;有个伟大壮举就是反编译,这样就可以看到jvm内部怎么进行对这个java文件解析的!我们可以使用JDK自带的javap命令来进行反编译,反编译出来的如果看不太明白,可以使用Jad工具来配合使用。还有就是把jar包完全反编译为我们写的代码的是GD-GUI,有兴趣可以去官网看一下哈,小编这里不做进一步说明。
我们今天以String string = new String("wang") + new String("zhen");,这条语句在底层是怎么创建的来深入理解jvm底层,同时也对反编译有进一步的了解哈!!话不多说,跟着小编一起学习吧。
二、编写java文件
public class JavaPTest {
String string = new String("学") + new String("Java");
}
三、科补代码理解
上面代码可是创建了5个对象哈,我们一步步的说哈!
首先,会先判断字符串常量池中是否存在"学"字符串对象,如果不存在则在字符串常量池中创建一个对象。当执行到new关键字在堆中创建一个"学"字符串对象。后面的new String("Java"),也是这样。
然后,当右边完成时,会在堆中创建一个"学Java"字符串对象。并把栈中的变量"str6"指向堆中的对象。
总结:一句代码创建了5个对象,但是有两个在堆中是没有引用的,按照垃圾回收的可达性分析,他们是垃圾就是"学"、"Java"这俩垃圾。
内存图如下:
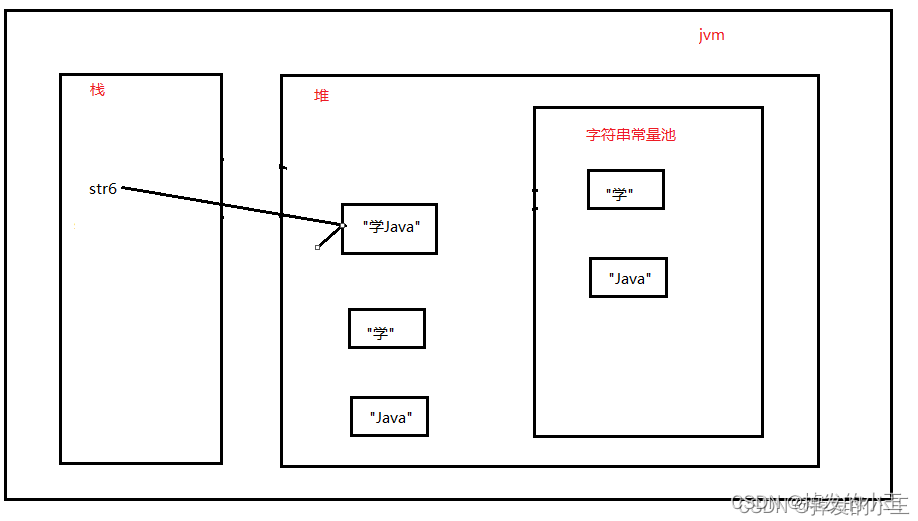
小编刚刚开始也是有疑问,为什么是五个呢?下面我们进一步探究!!
四、javap命令
不知道有什么命令的小伙伴,直接win+R输入cmd 打开的窗口输入javap即可看到一下内容
C:\Users\Administrator>javap
用法: javap <options> <classes>
其中, 可能的选项包括:
-help --help -? 输出此用法消息
-version 版本信息
-v -verbose 输出附加信息
-l 输出行号和本地变量表
-public 仅显示公共类和成员
-protected 显示受保护的/公共类和成员
-package 显示程序包/受保护的/公共类
和成员 (默认)
-p -private 显示所有类和成员
-c 对代码进行反汇编
-s 输出内部类型签名
-sysinfo 显示正在处理的类的
系统信息 (路径, 大小, 日期, MD5 散列)
-constants 显示最终常量
-classpath <path> 指定查找用户类文件的位置
-cp <path> 指定查找用户类文件的位置
心得:常用的就是javap -c -v class名字.class
例子:javap -c -v JavaPTest.class
五、执行javap命令
在IDEA的java类中按快捷键ctrl + f9编译成class文件,为反编译做准备;
找到class文件的位置
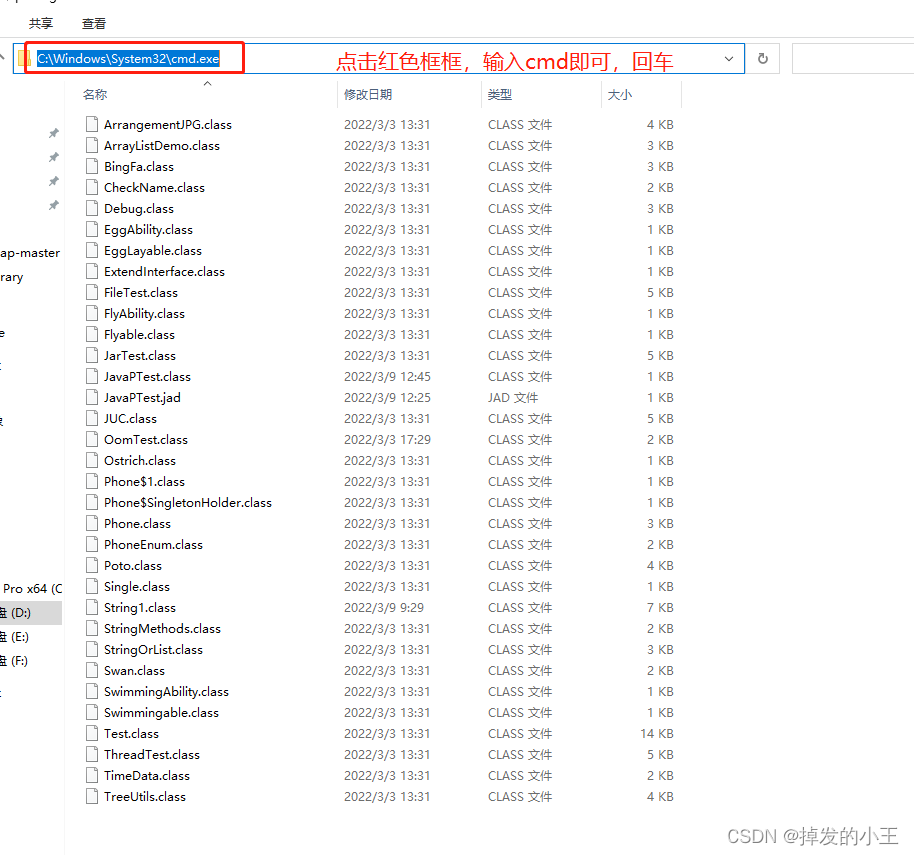
来到此目录下,不用cd切换到这个目录了哈
输入javap -c -v JavaPTest.class,有反编译后的可见,创建了5个对象。

六、下载Jad包
1. 网址下载
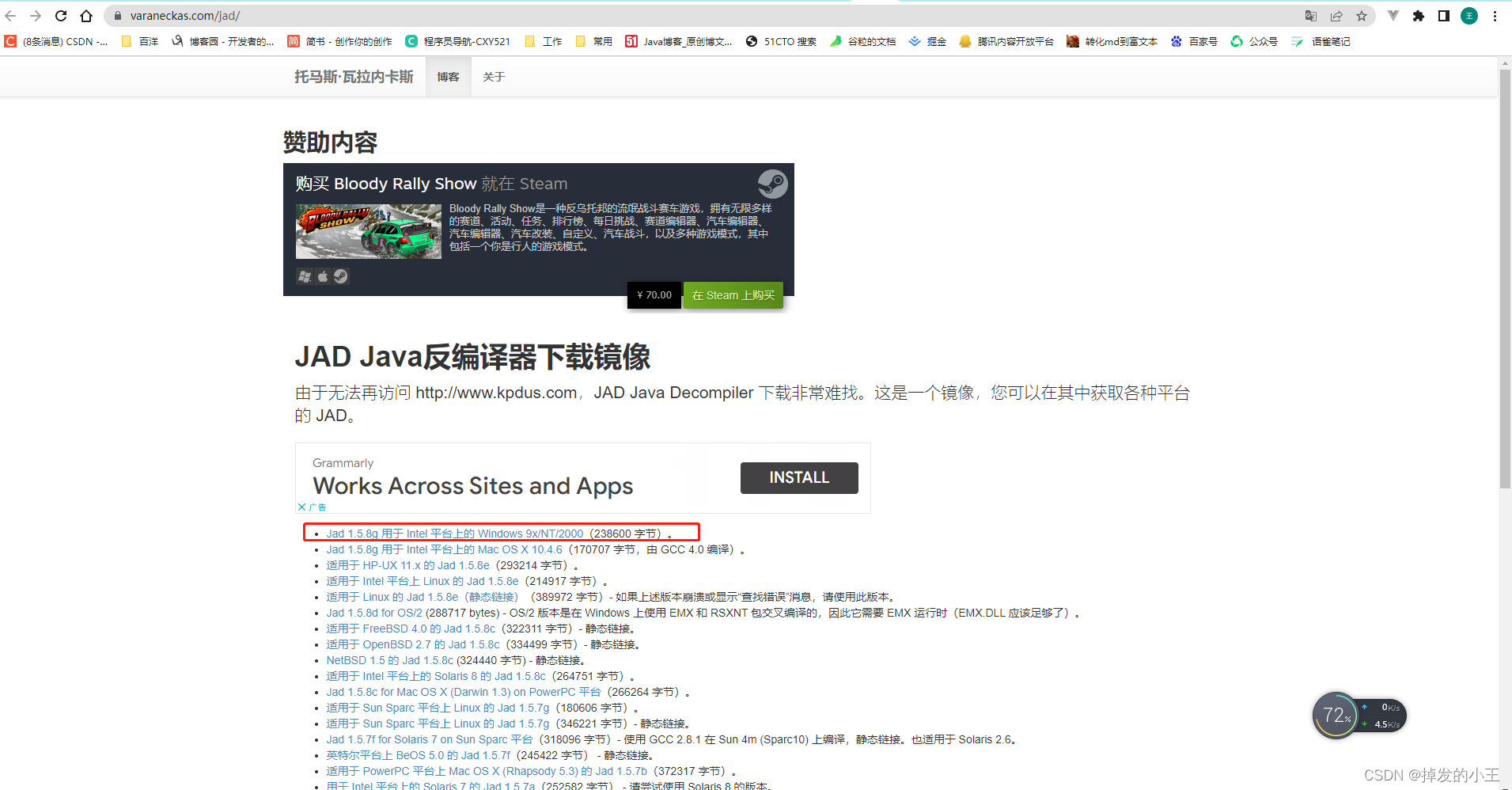
2. 解压到指定目录

3. 配置环境变量
为什么还要配置环境变量?
这样在任何地方我们都可以使用cmd命令来进行反编译,也是为了方便哈!!
PS:大家jdk都知道配置路径,这里小编就不带大家一步步找到配置地方了,直接进行添加环境变量
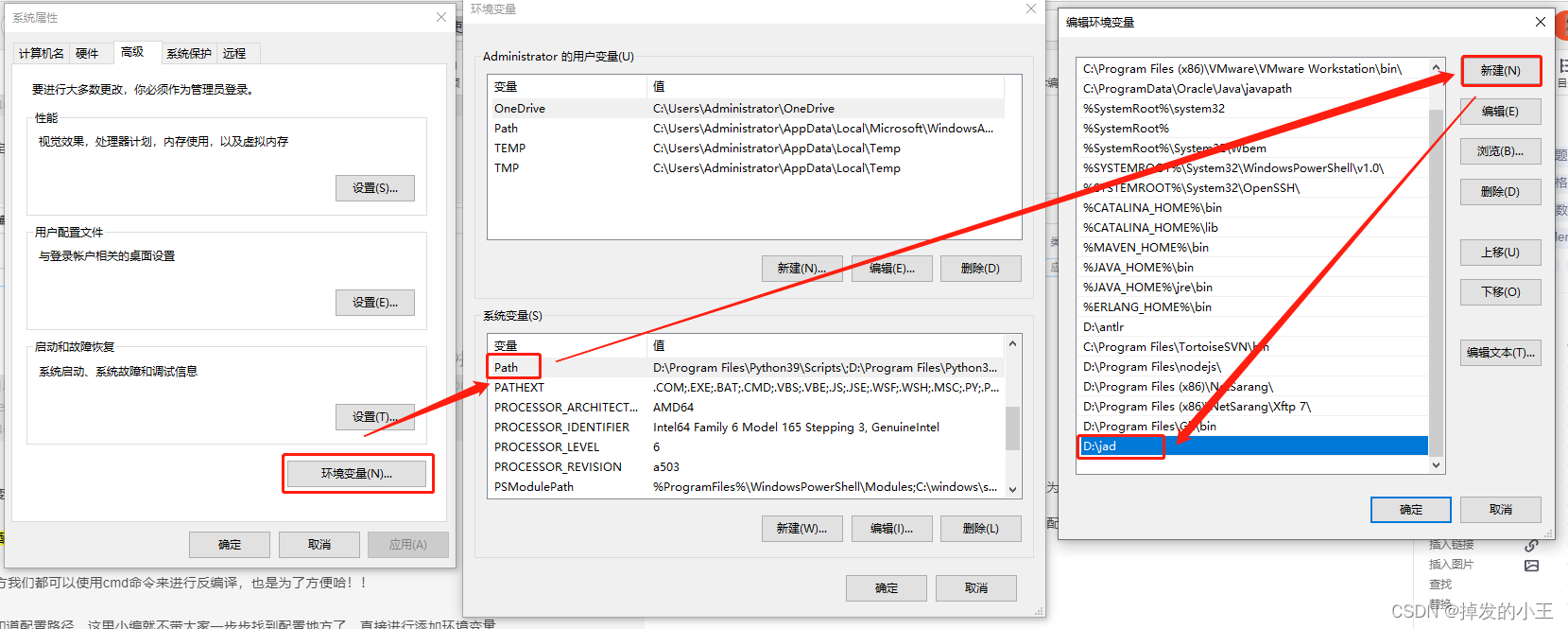
4. 常用命令查看
不知道有什么命令的小伙伴,直接win+R输入cmd 打开的窗口输入jad即可看到一下内容
C:\Users\Administrator>jad
Jad v1.5.8g. Copyright 2001 Pavel Kouznetsov ([email protected]).
Usage: jad [option(s)] <filename(s)>
Options: -a - generate JVM instructions as comments (annotate)
-af - output fully qualified names when annotating
-b - generate redundant braces (braces)
-clear - clear all prefixes, including the default ones
-d <dir> - directory for output files
-dead - try to decompile dead parts of code (if there are any)
-dis - disassembler only (disassembler)
-f - generate fully qualified names (fullnames)
-ff - output fields before methods (fieldsfirst)
-i - print default initializers for fields (definits)
-l<num> - split strings into pieces of max <num> chars (splitstr)
-lnc - output original line numbers as comments (lnc)
-lradix<num>- display long integers using the specified radix
-nl - split strings on newline characters (splitstr)
-noconv - don't convert Java identifiers into valid ones (noconv)
-nocast - don't generate auxiliary casts
-noclass - don't convert .class operators
-nocode - don't generate the source code for methods
-noctor - suppress the empty constructors
-nodos - turn off check for class files written in DOS mode
-nofd - don't disambiguate fields with the same names (nofldis)
-noinner - turn off the support of inner classes
-nolvt - ignore Local Variable Table entries (nolvt)
-nonlb - don't insert a newline before opening brace (nonlb)
-o - overwrite output files without confirmation
-p - send all output to STDOUT (for piping)
-pa <pfx>- prefix for all packages in generated source files
-pc <pfx>- prefix for classes with numerical names (default: _cls)
-pe <pfx>- prefix for unused exception names (default: _ex)
-pf <pfx>- prefix for fields with numerical names (default: _fld)
-pi<num> - pack imports into one line using .* (packimports)
-pl <pfx>- prefix for locals with numerical names (default: _lcl)
-pm <pfx>- prefix for methods with numerical names (default: _mth)
-pp <pfx>- prefix for method parms with numerical names (default:_prm)
-pv<num> - pack fields with the same types into one line (packfields)
-r - restore package directory structure
-radix<num>- display integers using the specified radix (8, 10, or 16)
-s <ext> - output file extension (default: .jad)
-safe - generate additional casts to disambiguate methods/fields
-space - output space between keyword (if, while, etc) and expression
-stat - show the total number of processed classes/methods/fields
-t<num> - use <num> spaces for indentation (default: 4)
-t - use tabs instead of spaces for indentation
-v - show method names while decompiling
-8 - convert Unicode strings into ANSI strings (ansi)
-& - redirect STDERR to STDOUT
小编这里就翻译了哈,常用的就是jad -o -p class文件名称
-o:无需确认直接覆盖输出
-p: 直接反编译代码到输出到命令下(直接在界面显示)
5.实践命令
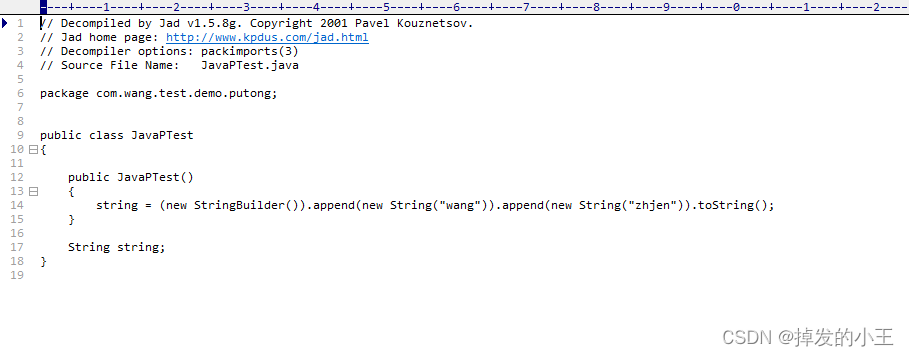
输入:jad -o JavaPTest,会在class文件所在同一级命令生成.jad文件,看的也比较清晰,我们使用工具打开:
// Decompiled by Jad v1.5.8g. Copyright 2001 Pavel Kouznetsov.
// Jad home page: http://www.kpdus.com/jad.html
// Decompiler options: packimports(3)
// Source File Name: JavaPTest.java
package com.wang.test.demo.putong;
public class JavaPTest
{
public JavaPTest()
{
string = (new StringBuilder()).append(new String("wang"))
.append(new String("zhjen")).toString();
}
String string;
}
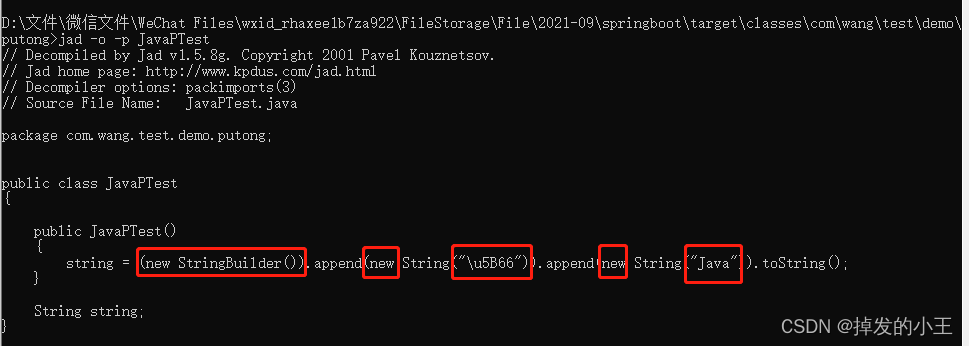
输入:jad -o -p JavaPTest,也是五个对象更加简单版的,不需要向上面一样要打开文件才可以看
这样我们就完成了class文件反编译了,两种方法有利有弊,大家根据实际情况来进行反编译。总而言之,这两种方法都是要必须掌握的!
看到这里了,还不给小编三连一波哈!!谢谢大家喽!!
有缘人才可以看得到的哦!!!
欢迎关注小编的微信公众号:

Recommend
About Joyk
Aggregate valuable and interesting links.
Joyk means Joy of geeK