

day38-IO流05 - 一刀一个小西瓜
source link: https://www.cnblogs.com/liyuelian/p/16690969.html
Go to the source link to view the article. You can view the picture content, updated content and better typesetting reading experience. If the link is broken, please click the button below to view the snapshot at that time.

JavaIO流05
4.常用的类04
4.4节点流和处理流03
4.4.8打印流-PrintStream和PrintWriter
打印流只有输出流,没有输入流
1.简单介绍及应用
- PrintStream是字节打印流
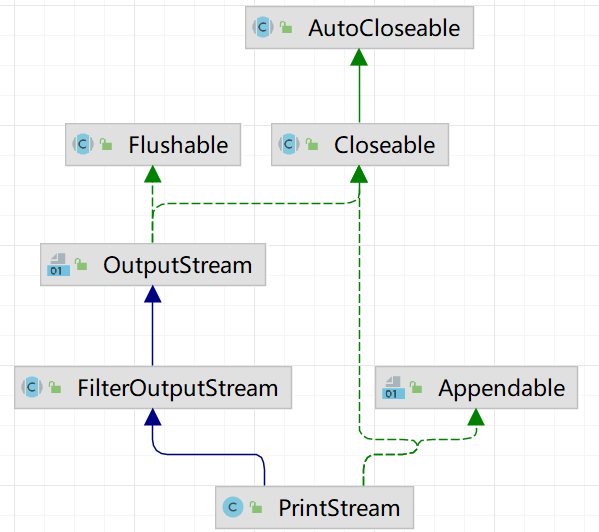
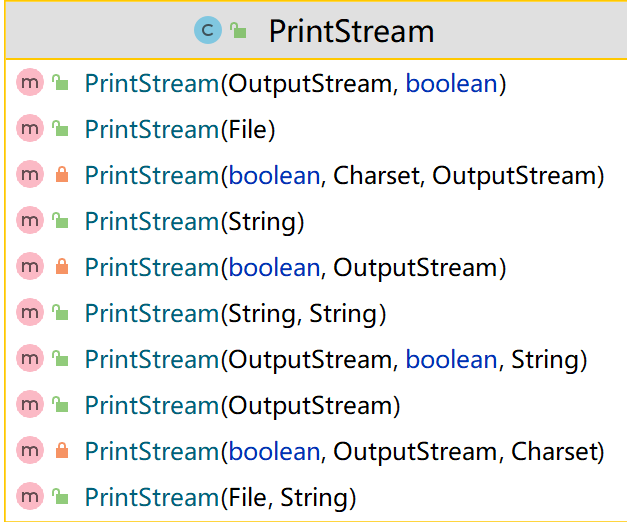
例子1:演示PrintStream(字节打印流/输出流)
package li.io.printstream; import java.io.IOException;import java.io.PrintStream; /** * 演示PrintStream(字节打印流/输出流) */public class PrintStream_ { public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException { PrintStream out = System.out; //在默认情况下,PrintStream 输出数据的位置是 标准输出,即显示器 out.print("jack,hello"); /** * public void print(String s) { * if (s == null) { * s = "null"; * } * write(s); * } */ //因为print底层使用的是write,所以我们可以直接调用write进行打印/输出 out.write("Hello北京".getBytes()); out.close(); //我们可以去修改打印流输出的位置/设备 // 1.修改为打印到d:\f1.txt // 2."落霞与孤鹜齐飞,秋水共长天一色" 这句话就会打印到d:\f1.txt里 // 3.System.setOut底层: /** * public static void setOut(PrintStream out) { * checkIO(); * setOut0(out);//native方法 ,修改了 out * } */ System.setOut(new PrintStream("d:\\f1.txt")); System.out.println("落霞与孤鹜齐飞,秋水共长天一色");//打印到d:\f1.txt }}
运行结果:
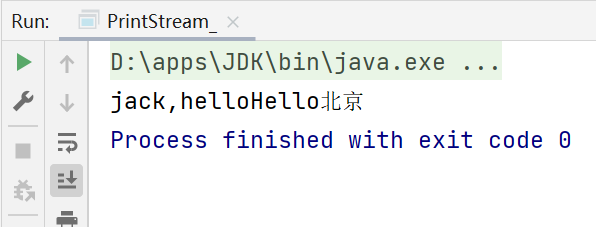

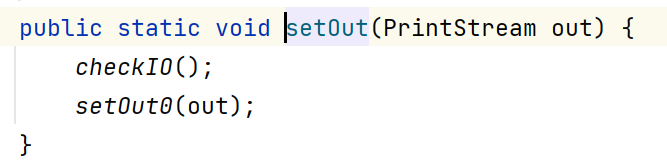
如上所示:在修改了打印流 输出的位置/设备之后,再调用System.out.println方法,打印/输出的地方就变为指定的文件路径,点击System.setOut方法,可以看到底层是调用了setOut0方法,该方法是本地方法(native)。它会去修改out,即修改输出数据的位置:

- PrintWriter是字符打印流
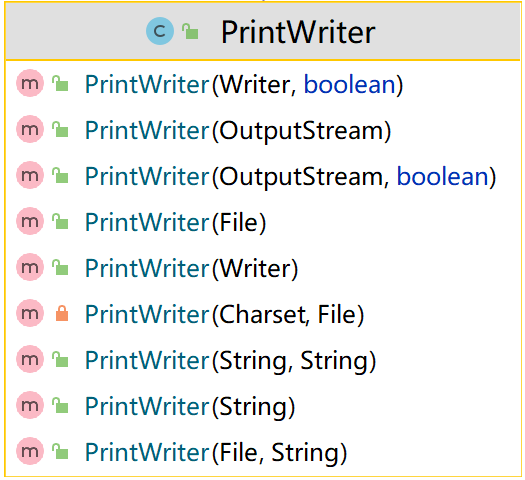
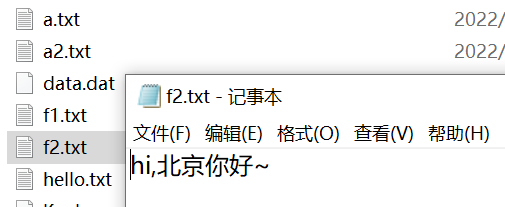
package li.io.printstream; import java.io.FileWriter;import java.io.IOException;import java.io.PrintWriter; /** * 演示PrintWriter的使用方式 */public class PrintWriter_ { public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException { //PrintWriter printWriter = new PrintWriter(System.out); //向PrintWriter构造器中传入一个FileWriter对象 PrintWriter printWriter = new PrintWriter(new FileWriter("d:\\f2.txt")); printWriter.print("hi,北京你好~"); printWriter.close();//flush()+关闭流,才会将数据写入到文件中 }}
4.5Properties类
- 看一个需求:
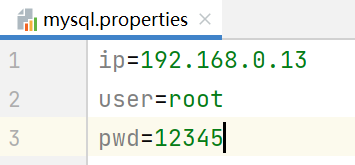
如下一个配置文件 mysql.properties:
ip=192.168.0.13user=rootpwd=12345
问编程读取ip、user、pwd的值是多少要怎么做?
- 传统的方法
- 使用Properties类可以方便实现
例子:传统方法
在scr文件夹下创建一个mysql.properties文件,内容为
package li.io.properties_; import java.io.BufferedReader;import java.io.FileReader;import java.io.IOException; public class Properties01 { public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException { //读取mysql.properties文件,并得到ip,user,pwd //创建 BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new FileReader("src\\mysql.properties")); String line = ""; //读取 while ((line = br.readLine()) != null) {//循环读取 String[] split = line.split("="); System.out.println(split[0] + "值是: " + split[1]); } //关闭 br.close(); }}
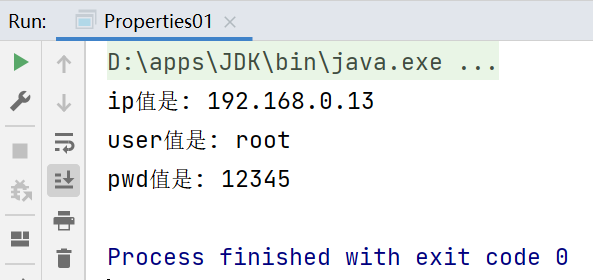
如上所示,如果mysql.properties的参数很多,并且要求读取修改其中一项或者n项参数,那么使用传统的读取方法,就需要我们对读取的参数进行条件判断,一旦要读取的参数过多,代码就会变得非常繁琐。这时候就需要使用到Properties类。
4.5.1基本介绍
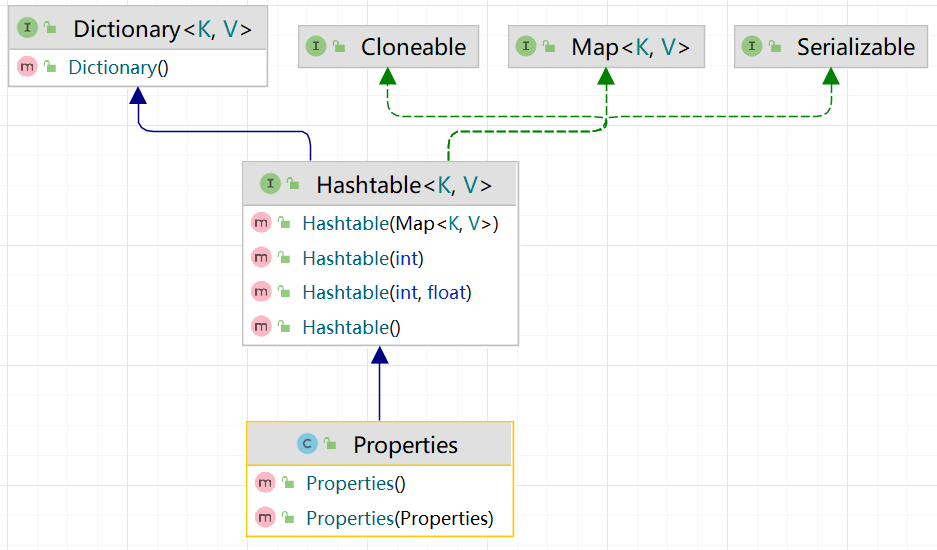
Properties是Hashtable的子类,是专门用于读写配置文件的集合类:
1)配置文件的格式:
键=值键=值
2)注意:键值对之间不需要有空格,值不需要用引号括起来。默认的类型是String
3)Properties的常见方法:
- load:加载配置文件的键值对到Properties对象
- list:将数据显示到指定设备/流对象
- getProperty(Key):根据键获取值
- setProperty(Key,Value):设置键值对到Properties对象
- store:将Properties中的键值对存储到配置文件中,在idea中,保存信息到配置文件,如果含有中文,会存储为unicode码
应用案例1:使用Properties类完成对mysql.properties 的读取
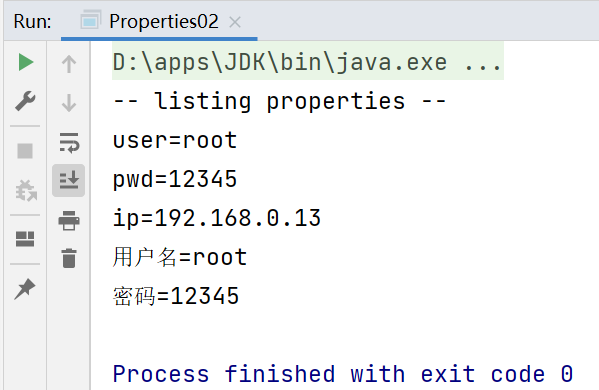
package li.io.properties_; import java.io.IOException;import java.io.FileReader;import java.util.Properties; public class Properties02 { public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException { //使用Properties类来读取 mysql.properties 文件 // 1.创建Properties对象 Properties properties = new Properties(); // 2.加载指定的配置文件 properties.load(new FileReader("src\\mysql.properties")); // 3.将 k-v 显示到控制台 properties.list(System.out); // 4.根据key获取对应的值 String user = properties.getProperty("user"); String pwd = properties.getProperty("pwd"); System.out.println("用户名=" + user); System.out.println("密码=" + pwd); }}
应用案例2:使用Properties类添加 key-value 到新文件 mysql2.properties 中,并修改某个 key-value
package li.io.properties_; import java.io.FileOutputStream;import java.io.IOException;import java.util.Properties; public class Properties03 { public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException { //使用Properties类添加 key-value 到新文件 mysql2.properties 中 //创建对象 Properties properties = new Properties(); //创建 //如果该文件没有key,就是创建 //如果该文件有key,就是修改/替换 /** * Properties类的父类就是 Hashtable ,底层就是 Hashtable的核心方法 * public synchronized V put(K key, V value) { * // Make sure the value is not null * if (value == null) { * throw new NullPointerException(); * } * * // Makes sure the key is not already in the hashtable. * Entry<?,?> tab[] = table; * int hash = key.hashCode(); * int index = (hash & 0x7FFFFFFF) % tab.length; * @SuppressWarnings("unchecked") * Entry<K, V> entry = (Entry<K,V>)tab[index]; * for(; entry != null ; entry = entry.next) { * if ((entry.hash == hash) && entry.key.equals(key)) { * V old = entry.value;//如果key存在,就替换 * entry.value = value; * return old; * } * } * * addEntry(hash, key, value, index);//如果是新的key,就添加新 key * return null; * } */ properties.setProperty("charset", "utf-8"); properties.setProperty("user", "汤姆");//注意:保存的是中文的Unicode码值 properties.setProperty("pwd", "abcd123"); properties.setProperty("pwd", "1111");//替换 //将k-v存储到文件中即可 properties.store(new FileOutputStream("src\\mysql2.properties"), null);//第二个参数是添加注释 System.out.println("保存配置文件成功~"); }}
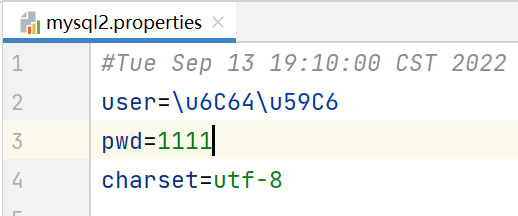
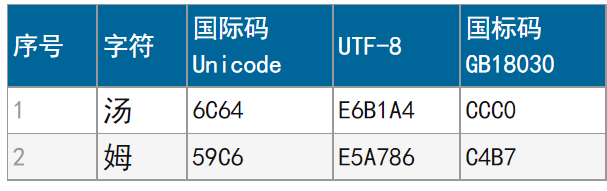
查询发现 \u6C64\u59C6 对应的中文就是 汤姆
5.IO习题
5.1Homework01
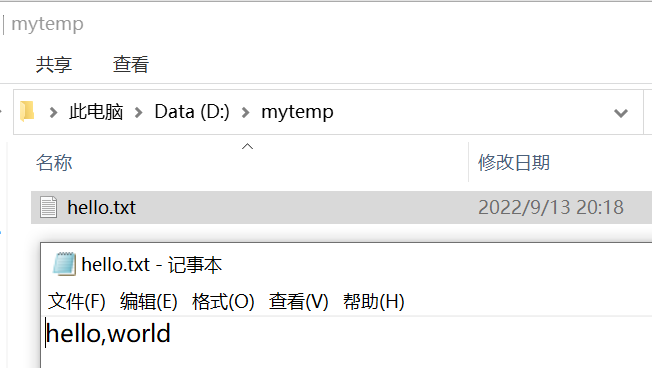
(1)判断d盘下是否有文件夹mytemp,如果没有就创建mytemp
(2)在d:\mytemp目录下,创建文件hello.txt
(3)如果hello.txt已经存在,就提示该文件已经存在,就不要重复创建了
(4)并在hello.txt文件中写入内容"hello,world".
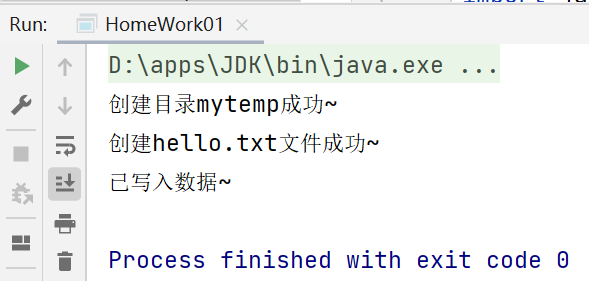
package li.io.homework; import java.io.File;import java.io.FileOutputStream;import java.io.IOException; public class HomeWork01 { public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException { String filePath = "d:\\mytemp\\hello.txt"; String dictionaryPath = "d:\\mytemp"; //创建对象 File file = new File(dictionaryPath);//目录 File file2 = new File(filePath);//文件 FileOutputStream fileOutputStream = null; if (!file.exists()) {//如果目录不存在 if (file.mkdir()) {//创建目录 System.out.println("创建目录mytemp成功~"); } } else { System.out.println("目录mytemp已存在"); } if (file2.exists()) { System.out.println("hello.txt文件已存在"); //如果文件存在,就写入数据 fileOutputStream = new FileOutputStream(filePath); fileOutputStream.write("hello,world".getBytes()); System.out.println("已写入数据~"); } else { if (file2.createNewFile()) { System.out.println("创建hello.txt文件成功~"); //如果文件存在,就写入数据 fileOutputStream = new FileOutputStream(filePath); fileOutputStream.write("hello,world".getBytes()); System.out.println("已写入数据~"); } } //关闭流 fileOutputStream.close(); }}
5.2Homework02
编程题:要求:使用BufferedReader读取一个文本文件,为每行加上行号,再连同内容一并输出到屏幕上。
package li.io.homework; import java.io.BufferedReader;import java.io.FileReader;import java.io.IOException; public class HomeWork02 { public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException { String filePath = "d:\\story.txt"; String line = ""; int i = 0;//行号 //创建对象 BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new FileReader(filePath)); //读取 while ((line = br.readLine()) != null) { System.out.println((++i) + "\t" + line); } //关闭流 br.close(); }}

要求2:如果将文本的编码改为GBK,怎么将其输出到控制台上而不使其乱码?
使用转换流,FileInputStream-->InputStreamReader(指定编码)-->BufferedReader
package li.io.homework; import java.io.*; public class HomeWork02 { public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException { String filePath = "d:\\story.txt"; String line = ""; int i = 0;//行号 //创建对象 BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(new FileInputStream(filePath),"GBK"));//使用转换流,选择编码为“GBK” //读取 while ((line = br.readLine()) != null) {//循环读取 System.out.println((++i) + "\t" + line); } //关闭流 br.close(); }}
5.3Homework03
-
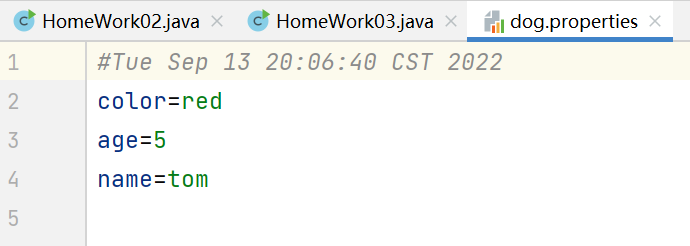
要编写一个dog.properties
name=tomage=5color=red -
编写Dog类(name,age,color)创建一个dog对象,读取dog.properties 用相应的内容完成初始化,并输出
-
将创建的Dog对象,序列化到 文件 dog.dat文件
-
再反序列化dog对象
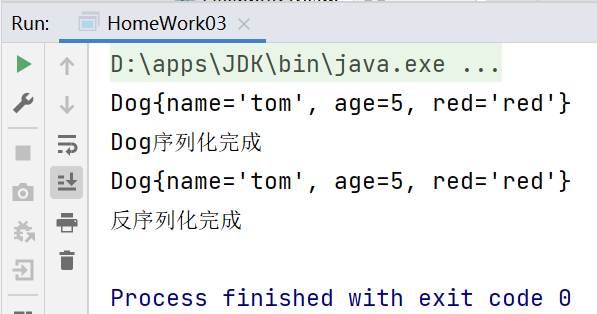
package li.io.homework; import java.io.*;import java.util.Properties; public class HomeWork03 { public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException, ClassNotFoundException { //1.编写dog.properties //创建Properties对象 Properties properties = new Properties(); //在properties对象中添加k-v properties.setProperty("name", "tom"); properties.setProperty("age", "5"); properties.setProperty("color", "red"); //将properties对象的k-v存储到文件中 properties.store(new FileOutputStream("src\\dog.properties"), null); //2.读取dog.properties完成Dog对象 的初始化 int age = Integer.parseInt(properties.getProperty("age")); Dog dog = new Dog(properties.getProperty("name"), age, properties.getProperty("color")); System.out.println(dog); //3.将创建的Dog对象,序列化到 dog.dat文件 String filePath = "d:\\dog.dat"; ObjectOutputStream oos = new ObjectOutputStream(new FileOutputStream(filePath)); oos.writeObject(dog); //关闭流 oos.close(); System.out.println("Dog序列化完成"); //4.反序列化dog对象 ObjectInputStream ois = new ObjectInputStream(new FileInputStream(filePath)); Dog dog1 = (Dog) ois.readObject(); System.out.println(dog1); //关闭流 ois.close(); System.out.println("反序列化完成"); }} //序列化的类要实现Serializable接口class Dog implements Serializable { private String name; private int age; private String red; public Dog(String name, int age, String red) { this.name = name; this.age = age; this.red = red; } @Override public String toString() { return "Dog{" + "name='" + name + '\'' + ", age=" + age + ", red='" + red + '\'' + '}'; }}
Recommend
-
 9
9
Java注解 1.注解的理解 注解(Annotation)也被称为元数据(Metadata),用于修饰解释 包、类、方法、属性、构造器、局部变量等数据信息 和注释一样,注解不影响程序逻辑,但注解可以被编译或者运...
-
 5
5
线程基础01 1.程序 进程 线程 程序(program):是为完成的特定任务,用某种语言编写的一组指令的集合。简单来说,就是我们写的代码。
-
 6
6
JavaOI流02 4.常用的类 4.1文件字节流输入流-FileInputStream InputStream抽象类是所有类字节输入流的超类 InputStream常用的...
-
 8
8
JavaIO流03 4.常用的类02 4.4节点流和处理流
-
 6
6
多用户即时通讯系统05 4.编码实现04(拓展) 拓展功能: 实现离线留言,如果某个用户不在线 ,当登陆后,可以接收离线的消息 实现离线发文件,如果某个功能没有在线,当登...
-
 6
6
MySQL基础知识02 4.CRUD 数据库CRUD语句:增(create)、删(delete)、改(update)、查(Retrieve) Insert 语句 (添加数据) Update 语句(更新数据) Delete 语句(删除数据)...
-
 8
8
JDBC和连接池05 11.BasicDAO 先来分析一个问题 前面我们使用了Apache-DBUtils和Druid简化了JDBC开发,但仍存在以下不足: SQL语句是固定的,不能通过参数传入,通用性不好...
-
 5
5
正则表达式01 5.1正则表达式的作用 正则表达式的便利 在一篇文章中,想要提取相应的字符,比如提取文章中的所有英文单词,提取文章中的所有数字等。 ...
-
 13
13
引入课程和Maven 1.Maven maven中央仓库:Maven Repository: Search/Browse/Explore (mvnrepository.com) maven仓库是国外的一...
-
 8
8
WEB开发会话技术02 6.Cookie的生命周期 默认情况下,Cookie只在浏览器的内存中存活,也就是说,当你关闭浏览器后,Cookie就会消失。但是也可以通过方法设置cookie的生存时间。 cookie的生命...
About Joyk
Aggregate valuable and interesting links.
Joyk means Joy of geeK