ReentrantLock 公平锁源码 第1篇 - Jame!
source link: https://www.cnblogs.com/sunankang/p/16458795.html
Go to the source link to view the article. You can view the picture content, updated content and better typesetting reading experience. If the link is broken, please click the button below to view the snapshot at that time.

ReentrantLock 1
这篇还是接着ReentrantLock的公平锁,没看过第0篇的可以先去看上一篇https://www.cnblogs.com/sunankang/p/16456342.html
这篇就以问题为导向,先提出问题,然后根据问题去看代码
确保能唤醒排队的线程?
A,B两线程,A线程执行完业务释放锁过程中B线程添加进了链表,如何保证B线程能正常醒来
现在假设A线程走完tryAcuqire后获取到锁,执行业务代码,最后unlock() tryAcquire代码就不进去看了,上篇讲过了 现在只需关注两个点
lock方法中的acquireQueued 用来park
unlock方法中的release用来unpark
首先来看park的条件是啥
public final void acquire(int arg) {
if (!tryAcquire(arg) && acquireQueued(addWaiter(Node.EXCLUSIVE), arg))
selfInterrupt();
}
进入acquireQueued方法
final boolean acquireQueued(final Node node, int arg) {
boolean failed = true;
try {
boolean interrupted = false;
for (;;) {
final Node p = node.predecessor();
if (p == head && tryAcquire(arg)) {
setHead(node);
p.next = null; // help GC
failed = false;
return interrupted;
}
if (shouldParkAfterFailedAcquire(p, node) &&
parkAndCheckInterrupt()) //在这里进行的park
interrupted = true;
}
} finally {
if (failed)
cancelAcquire(node);
}
}
也就是shouldParkAfterFailedAcquire 如果这个方法返回true,才会去park
private static boolean shouldParkAfterFailedAcquire(Node pred, Node node) {
int ws = pred.waitStatus;
if (ws == Node.SIGNAL)
return true;
if (ws > 0) {
do {
node.prev = pred = pred.prev;
} while (pred.waitStatus > 0);
pred.next = node;
} else {
compareAndSetWaitStatus(pred, ws, Node.SIGNAL);
}
return false;
}
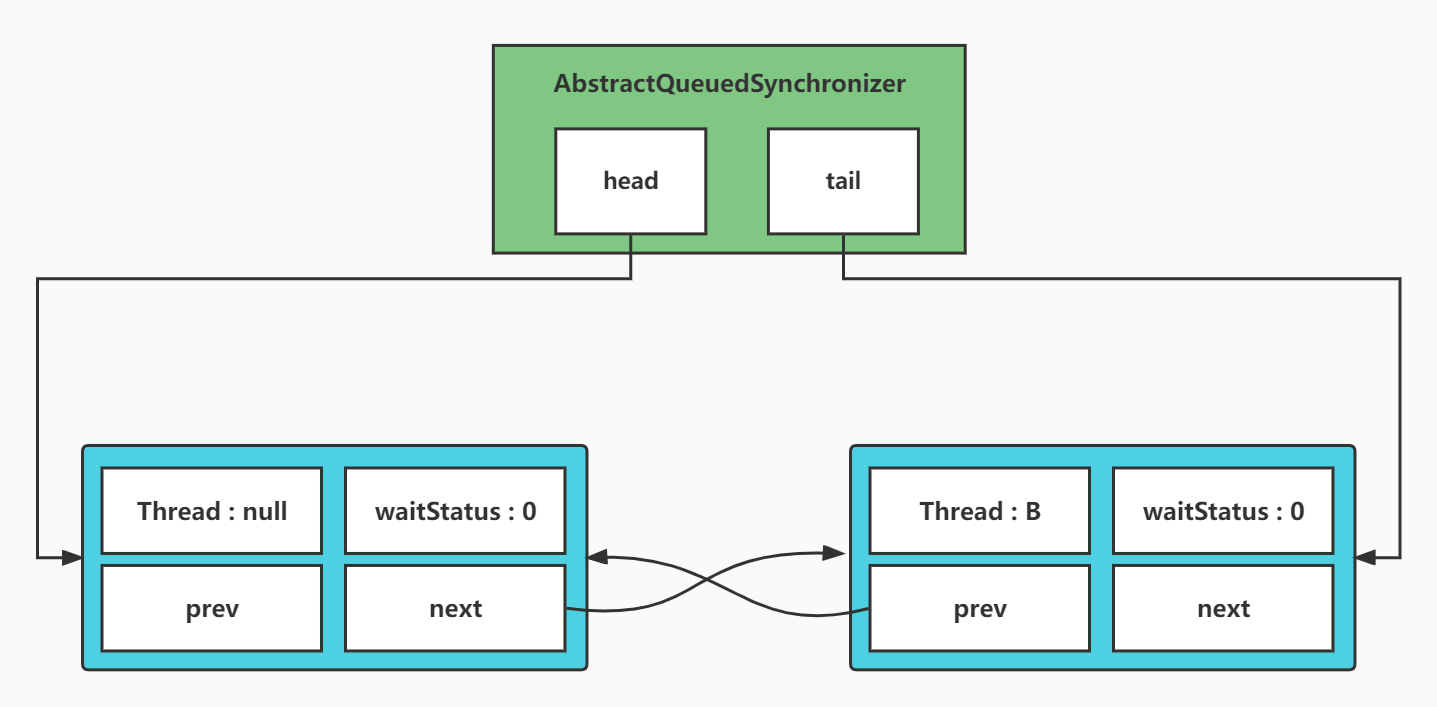
现在假设第一种情况,首次进入这个shouldParkAfterFailedAcquire方法的时候,A线程就进入unlock方法了 那么此时节点状态如下图
public final boolean release(int arg) {
if (tryRelease(arg)) {
Node h = head;
//主要看这段代码
if (h != null && h.waitStatus != 0)
unparkSuccessor(h);
return true;
}
return false;
}
那么h!=null进入,但是头节点的waitStatus还是0,所以不走unpark,A线程结束
A线程结束了谁来唤醒B线程呢? 回到acquireQueued方法
final boolean acquireQueued(final Node node, int arg) {
boolean failed = true;
try {
boolean interrupted = false;
for (;;) {
final Node p = node.predecessor();
if (p == head && tryAcquire(arg)) {
setHead(node);
p.next = null; // help GC
failed = false;
return interrupted;
}
if (shouldParkAfterFailedAcquire(p, node) &&
parkAndCheckInterrupt())
interrupted = true;
}
} finally {
if (failed)
cancelAcquire(node);
}
}
因为第一次进入shouldParkAfterFailedAcquire方法中,最后走到else代码块,我们假设没有发生冲突,修改成功
A线程执行完了unlock,而此时锁的状态值为0,没有被持有的状态,最外层的for(;;)让代码又重新跑了一遍
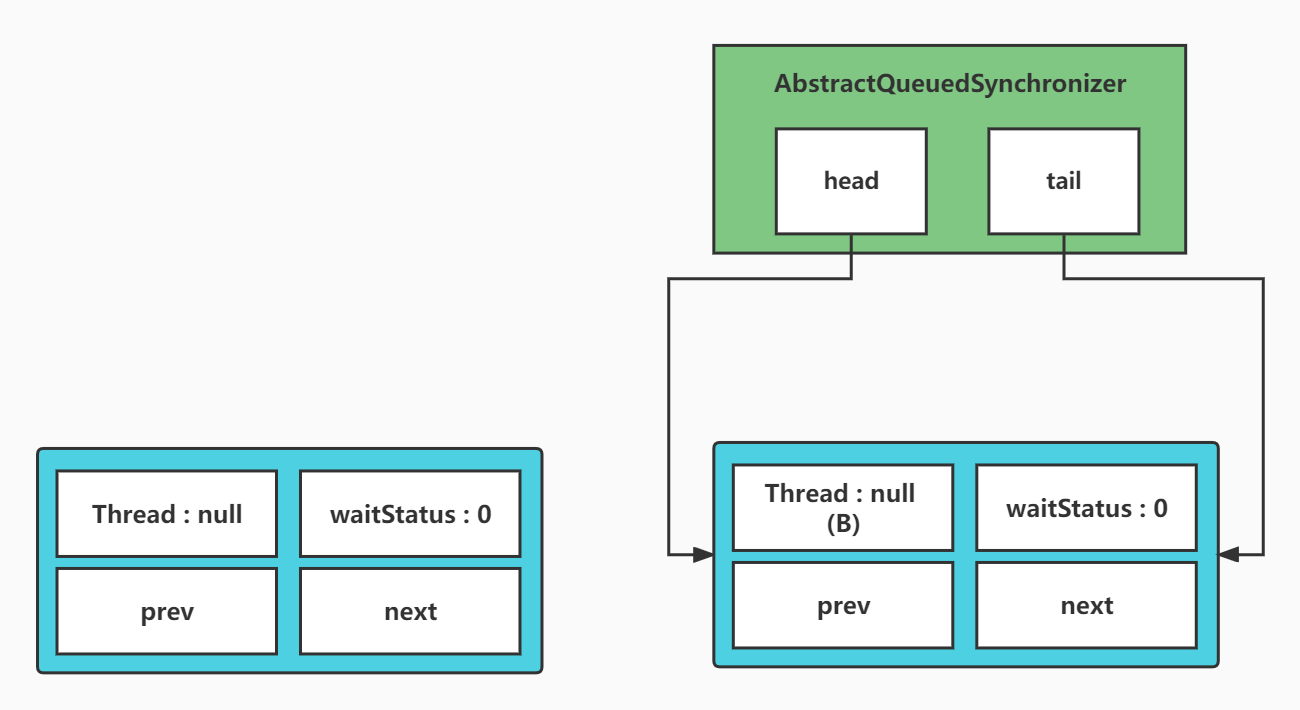
第二次的时候if (p == head && tryAcquire(arg)) 这个if就会进入,因为现在已经没有其他线程在持有锁了,所以tryAcquire尝试获取锁成功,返回ture
private void setHead(Node node) {
head = node;
node.thread = null;
node.prev = null;
}
在setHead方法中将当前节点,咱们这个例子中也就是B节点,设置为head,之后清空上个引用和当前引用的线程
最后清除上个节点对B节点的引用,此时节点关系如下
而原来的头节点没有任何引用,等待GC即可,也可以看到在代码p.next = null; // help GC 这段旁边写的注释 帮助GC
之后将失败状态设置为false,返回是否被打断的变量,lock方法结束,
现在来假设在shouldParkAfterFailedAcquire方法中修改成功,但此时的A线程还没有走到unlock,当B线程马上要开始走parkAndCheckInterrupt方法开始park的时候,时间片用完的情况
final boolean acquireQueued(final Node node, int arg) {
boolean failed = true;
try {
boolean interrupted = false;
for (;;) {
final Node p = node.predecessor();
if (p == head && tryAcquire(arg)) {
setHead(node);
p.next = null; // help GC
failed = false;
return interrupted;
}
if (shouldParkAfterFailedAcquire(p, node) &&
//====假设此时B线程在这里=====
parkAndCheckInterrupt())
interrupted = true;
}
} finally {
if (failed)
cancelAcquire(node);
}
}
此时节点关系如下
A线程的unlock就可以进入unparkSuccessor
public final boolean release(int arg) {
if (tryRelease(arg)) {
Node h = head;
if (h != null && h.waitStatus != 0)
unparkSuccessor(h);
return true;
}
return false;
}
private void unparkSuccessor(Node node) {
int ws = node.waitStatus;
if (ws < 0)
compareAndSetWaitStatus(node, ws, 0);
Node s = node.next;
if (s == null || s.waitStatus > 0) {
s = null;
for (Node t = tail; t != null && t != node; t = t.prev)
if (t.waitStatus <= 0)
s = t;
}
if (s != null)
LockSupport.unpark(s.thread);
}
第一个if判断为true,尝试修改状态为0 (这里没看懂为什么是尝试修改)
if (s == null || s.waitStatus > 0) 这个判断我们是不进入的,注意unparkSuccessor这个方法的node参数是head节点,而不是我们的B节点,所以继续执行下面的if判断
s就是B节点,在B线程park前唤醒,B线程再走到park的时候是不会再进行park的,直接返回,方法结束
真的公平吗?
A线程在运行,B线程初始化链表中的过程中,A线程运行完成,释放锁,C线程进入
我们只需要看线程B初始化链表的情况即可
addWaiter中enq方法
private Node enq(final Node node) {
for (;;) {
Node t = tail;
if (t == null) { // Must initialize
if (compareAndSetHead(new Node()))
//假设线程B走到这里时间片用完,还没来得及设置tail
tail = head;
} else {
node.prev = t;
if (compareAndSetTail(t, node)) {
t.next = node;
return t;
}
}
}
}
那么此时线程A解锁了,线程C调用lock方法
protected final boolean tryAcquire(int acquires) {
final Thread current = Thread.currentThread();
int c = getState();
if (c == 0) {
if (!hasQueuedPredecessors() &&
compareAndSetState(0, acquires)) {
setExclusiveOwnerThread(current);
return true;
}
}
else if (current == getExclusiveOwnerThread()) {
int nextc = c + acquires;
if (nextc < 0)
throw new Error("Maximum lock count exceeded");
setState(nextc);
return true;
}
return false;
}
在tryAcquire方法的hasQueuedPredecessors方法中
public final boolean hasQueuedPredecessors() {
Node t = tail;
Node h = head;
Node s;
return h != t &&
((s = h.next) == null || s.thread != Thread.currentThread());
}
此时tail还是null,而head已经被线程B设置了一个空Node,h!=t为true,h也只是一个空Node,所以(s = h.next) == null为true,整体返回true,外层取反为false,退出tryAcquire方法去入队列
那么入队列会破坏队列的初始化或者C线程变成第一个排队的节点吗?,注意咱们现在假设的线程B还没有获取到cpu的调用,还是停在 tail = head;代码执行前
线程C执行addWaiter方法
private Node addWaiter(Node mode) {
Node node = new Node(Thread.currentThread(), mode);
// Try the fast path of enq; backup to full enq on failure
Node pred = tail;
if (pred != null) {
node.prev = pred;
if (compareAndSetTail(pred, node)) {
pred.next = node;
return node;
}
}
enq(node);
return node;
}
这个时候tail还是空,进入enq方法
private Node enq(final Node node) {
for (;;) {
Node t = tail;
if (t == null) { // Must initialize
if (compareAndSetHead(new Node()))
tail = head;
} else {
node.prev = t;
if (compareAndSetTail(t, node)) {
t.next = node;
return t;
}
}
}
}
首先第一个判断是会进入的,这个时候tail还是空,但是if (compareAndSetHead(new Node()))方法不会成功,来看看代码
private final boolean compareAndSetHead(Node update) {
//注意第三个参数 null
return unsafe.compareAndSwapObject(this, headOffset, null, update);
}
判断的是head为null的时候才会进行修改,所以线程C没有修改成功,那么会一直在for(;;)中循环,直到线程B初始化完空的头节点,也就是执行tail = head;这段代码
如果线程B走完了 tail = head;没来得及进行第二次循环添加B节点的时候,线程A解锁了,线程C进来了呢
还是在tryAcquire方法的hasQueuedPredecessors中
public final boolean hasQueuedPredecessors() {
Node t = tail;
Node h = head;
Node s;
return h != t &&
((s = h.next) == null || s.thread != Thread.currentThread());
}
这个时候第一个h!=t就是false,因为B线程已经将head和tail的引用指向同一个空节点了,返回false
protected final boolean tryAcquire(int acquires) {
final Thread current = Thread.currentThread();
int c = getState();
if (c == 0) {
//因为返回false,取反则进行获取锁的操作
if (!hasQueuedPredecessors() &&
compareAndSetState(0, acquires)) {
setExclusiveOwnerThread(current);
return true;
}
}
else if (current == getExclusiveOwnerThread()) {
int nextc = c + acquires;
if (nextc < 0)
throw new Error("Maximum lock count exceeded");
setState(nextc);
return true;
}
return false;
}
C线程直接获取锁去运行代码了,所以ReentrantLock的公平锁其实并不是绝对的公平
__EOF__
Recommend
-
 27
27
一、ReentrantLock简介ReentrantLock重入锁,顾名思义,就是支持重入的锁,它表示能够支持一个线程对资源的重复加锁;我们之前学习过Synchronized锁,它也是支持重入的一种锁,参考我的另一篇Synchronized锁的实现原理与应用,Synchronized支持隐式的重入锁,比如...
-
 10
10
1篇文章怎么有效的多平台分发? 15天0基础极速入门数据分析,掌握一套数据分析流程和方法,学完就能写一份数据报告!了解一下>>...
-
 14
14
深圳某小公司面试题:AQS是什么?公平锁和非公平锁?ReentrantLock?
-
 14
14
第1篇-关于Java虚拟机HotSpot,开篇说的简单点 | HeapDump性能社区文章>第1篇-关于Java虚拟机HotSpot,开篇说的简单点第1篇-关于Java虚拟机HotSpot,开篇说的简单点
-
 5
5
2022 Global Game Jame 深圳站报名开启 发表于13小时前 评论0
-
 3
3
编辑导语:如今,中国的老龄化现象越来越严重,但是却有许多老年人不能适应这个数字化的社会,本篇文章作者分享了有关适老化设计的内容,感兴趣的一起来看一下吧。
-
 3
3
mysql拆分字符串作为查询条件 有个群友问一个问题
-
 4
4
Reentrant 2 前两篇写完了后我自己研究了下,还有有很多疑惑和问题,这篇就继续以自问自答的方式写 如果没看过第1篇的可以先看看那个https://www.cnblogs.com/sunankang/p/16458795.html
-
 6
6
图解ReentrantLock底层公平锁和非公平锁实现原理
-
 6
6
选品(第1篇)——Regan选品心路历程Regan跨境推送行业新闻,分享行业干货。四年亚马逊跨境电商人,喜欢结交朋友,分享经验。持续关注,我相信会是你...
About Joyk
Aggregate valuable and interesting links.
Joyk means Joy of geeK