DBaaS - Percona Monitoring and Management
source link: https://docs.percona.com/percona-monitoring-and-management/using/dbaas.html
Go to the source link to view the article. You can view the picture content, updated content and better typesetting reading experience. If the link is broken, please click the button below to view the snapshot at that time.
DBaaS¶
Caution
DBaaS functionality is currently in technical preview and is subject to change.
The DBaaS dashboard is where you add, remove, and operate on Kubernetes and database clusters.
Activate DBaaS¶
The DBaaS feature is turned off by default. To turn it on:
-
Go to Configuration → Settings → Advanced Settings.
-
Click the toggle in the Technical preview features section of the page.
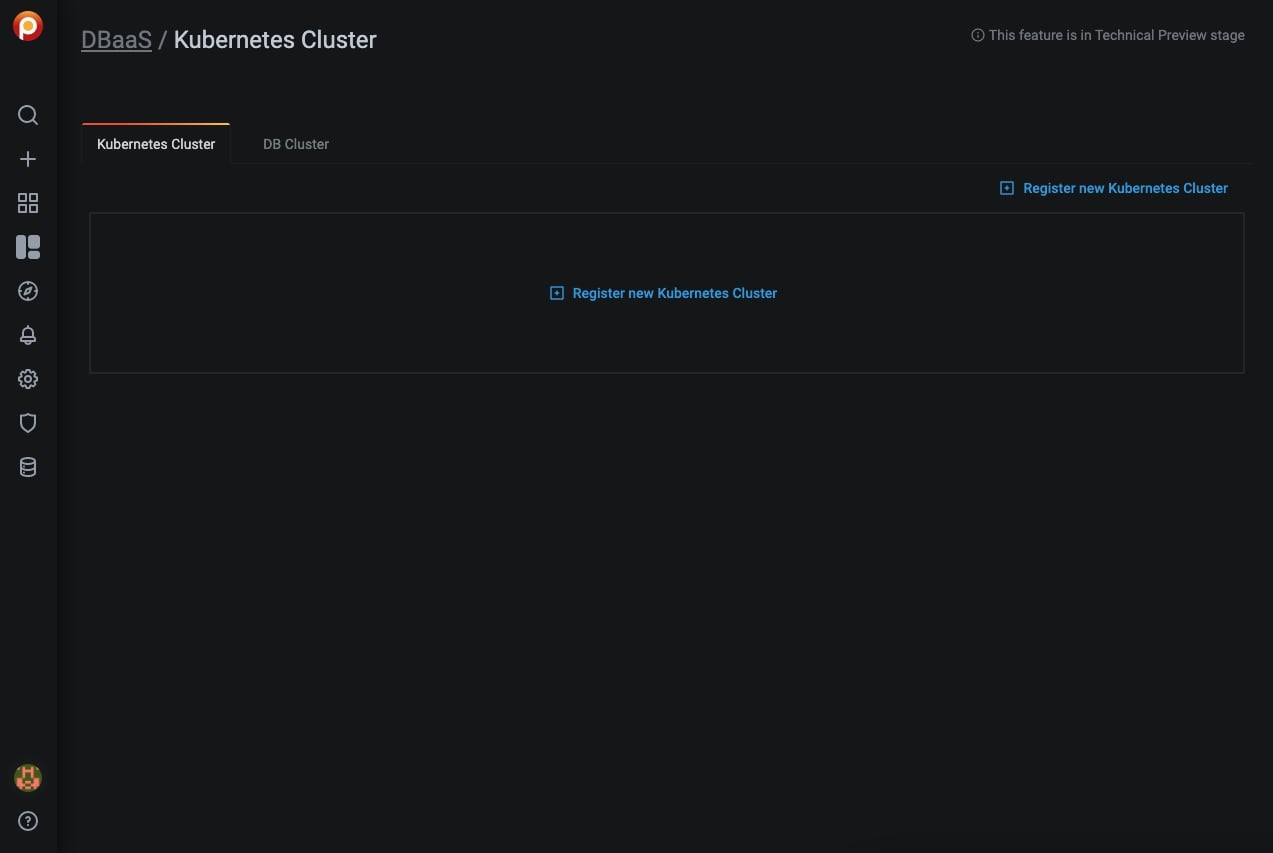
Open the DBaaS dashboard¶
From the left menu, select DBaaS.
Kubernetes clusters¶
Add a Kubernetes cluster¶
Caution
Ensure that you set PMM Public Address under Configuration → Settings → Advanced Settings before creating a Kubernetes cluster. Otherwise, PMM would not monitor the Kubernetes cluster along with the associated database clusters.
PXC and PSMDB operators are installed as part of the Kubernetes cluster registration process. It enables you to deploy database clusters into the Kubernetes cluster.
If a public address is set VM Operator is also installed as part of the Kubernetes cluster registration process. It lets you monitor a kubernetes cluster via PMM.
-
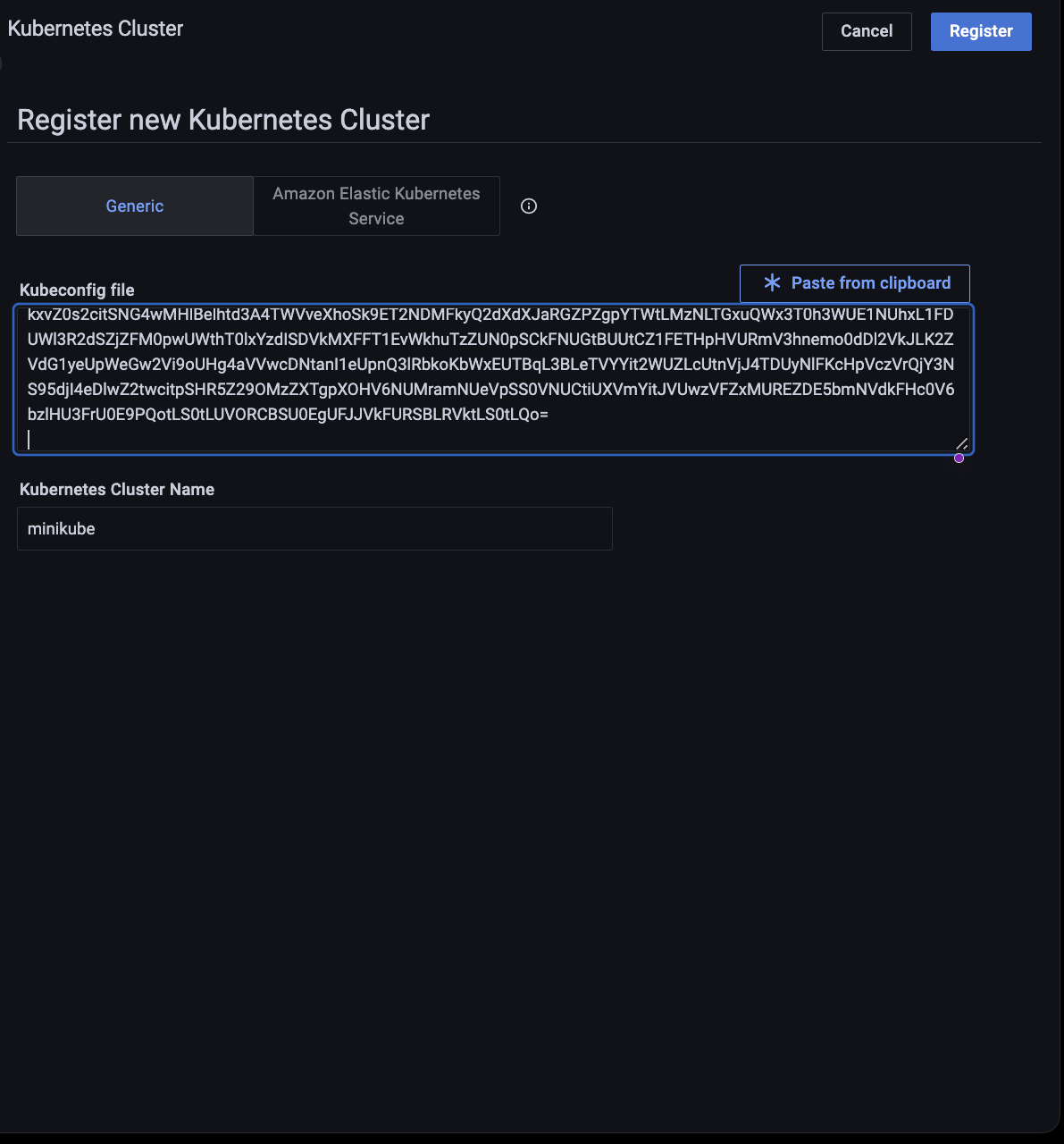
Click Register new Kubernetes Cluster.
-
Enter values for the Kubernetes Cluster Name and Kubeconfig file in the corresponding fields.
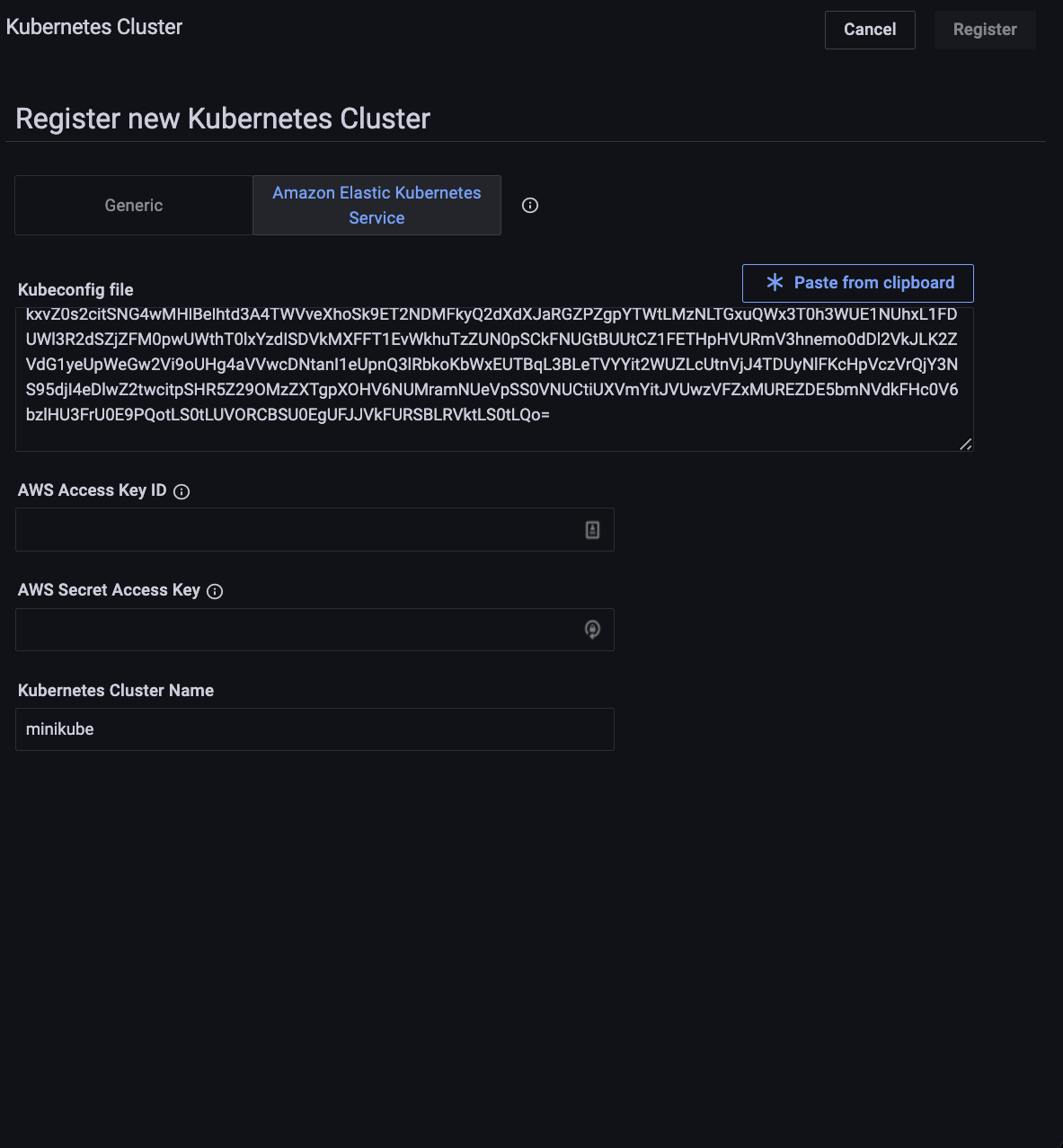
For a Kubernetes cluster, when using Amazon Elastic Kubernetes Service (EKS) and the kubeconfig file does not contain the AWS access key ID and AWS secret access key. Select the Using Amazon Elastic Kubernetes Service (EKS) checkbox and enter the access key ID and secret access key in the respective fields. For information on obtaining these, see the AWS documentation.
-
Click Register.
-
A message will momentarily display telling you whether the registration was successful or not.
Unregister a Kubernetes cluster¶
Important
You can’t unregister a Kubernetes cluster if there DB clusters associated with it.
-
Click Unregister.
-
Confirm the action by clicking Proceed, or abandon by clicking Cancel.
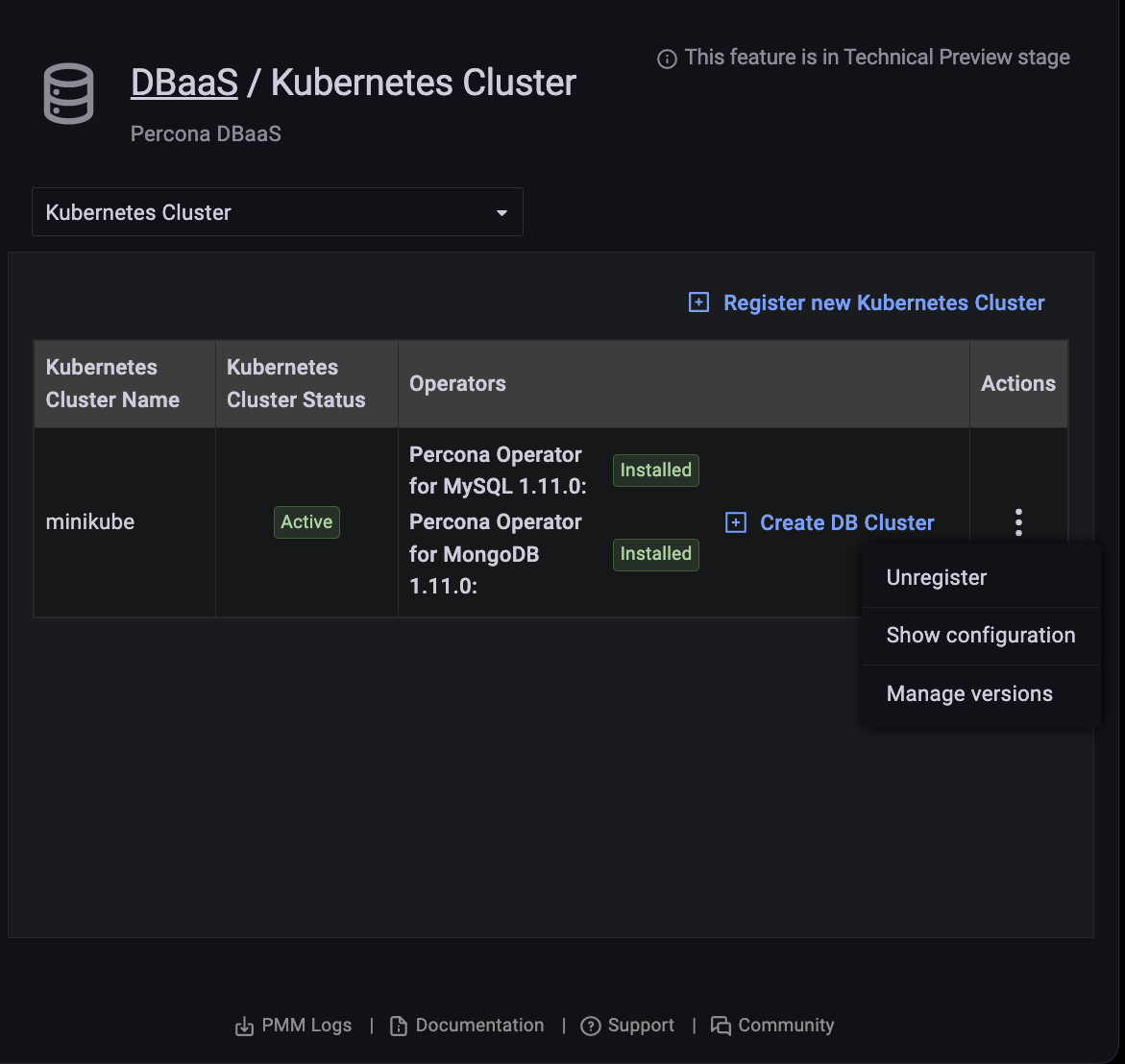
View a Kubernetes cluster’s configuration¶
-
Find the row with the Kubernetes cluster you want to see.
-
In the Actions column, open the menu and click Show configuration.
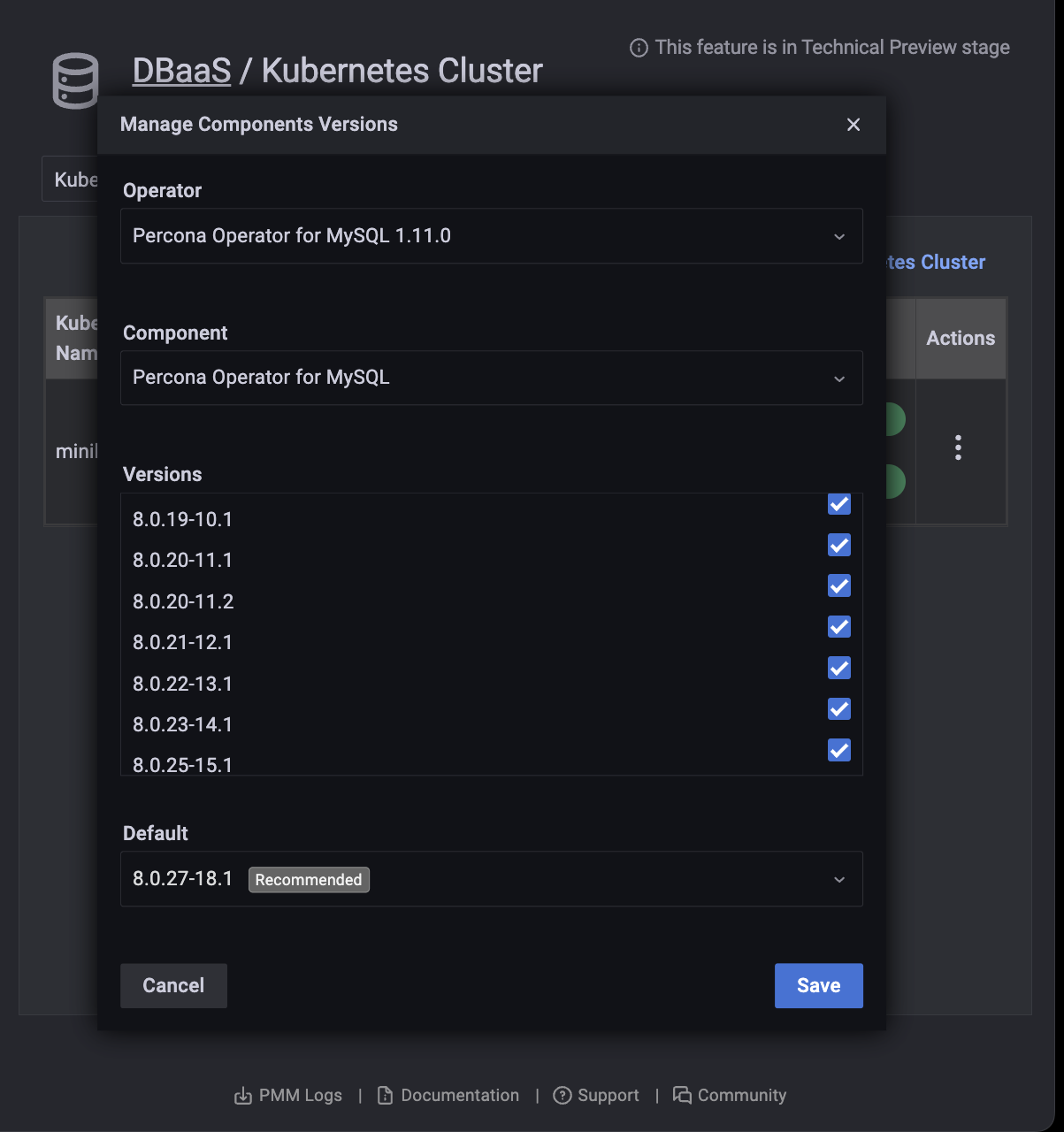
Manage allowed component versions¶
Administrators can select allowed and default versions of components versions for each cluster.
-
Find the row with the Kubernetes cluster you want to manage.
-
In the Actions column, open the menu and click Manage versions.
-
Select an Operator and Component from the drop-down menus.
-
Activate or deactivate allowed versions, and select a default in the Default menu.
-
Click Save.
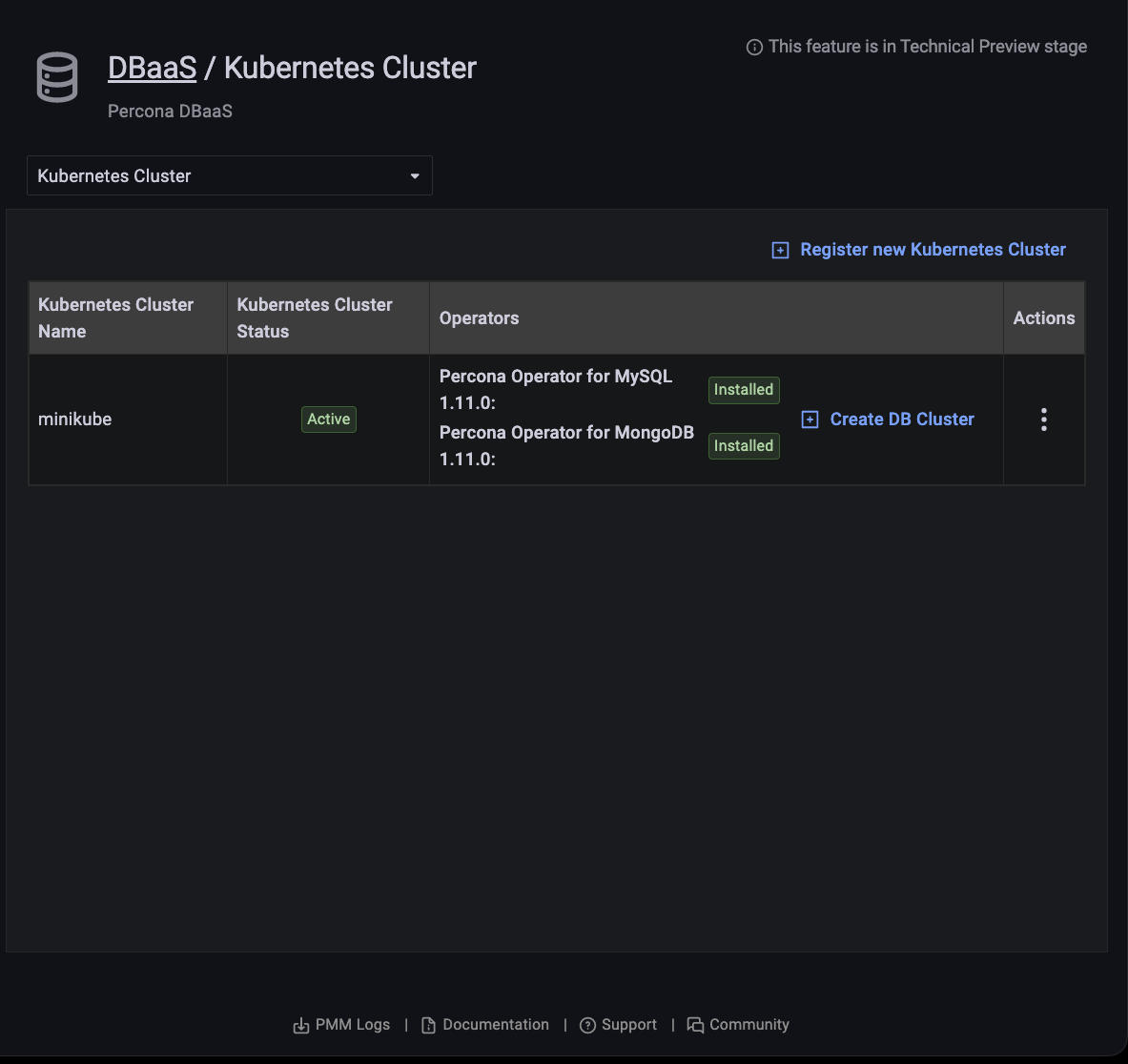
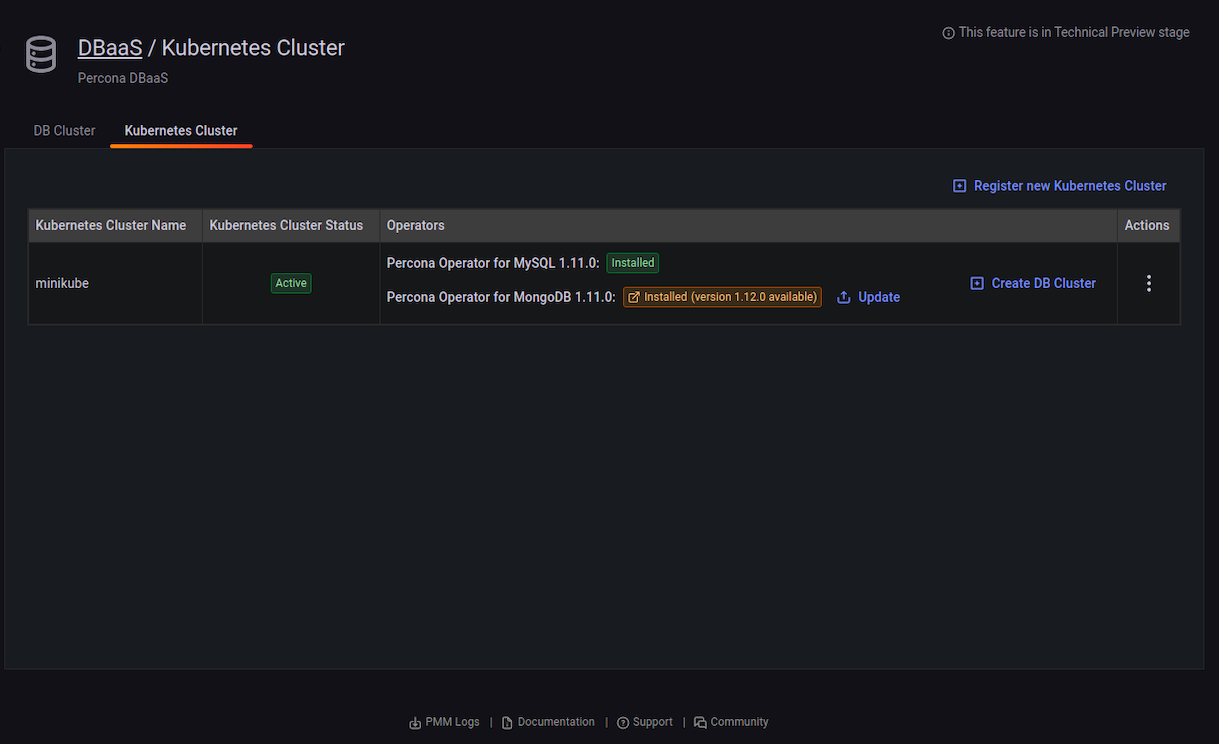
Kubernetes operator status¶
The Kubernetes Cluster tab shows the status of operators.
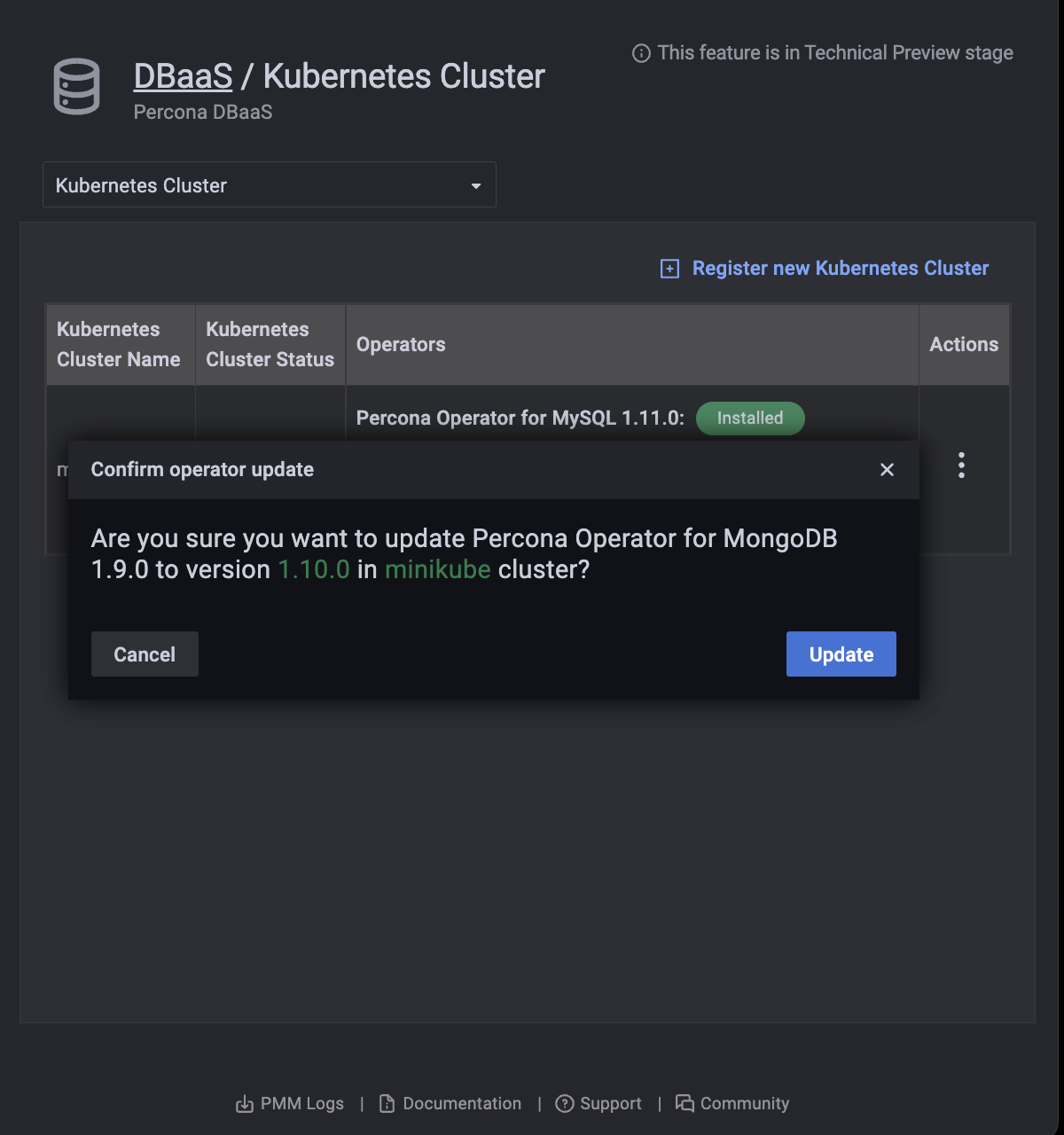
Kubernetes operator update¶
When a new version of the operator is available the Operators column shows a message with this information. Click the message to go to the operator release notes to find out more about the update.
To update the cluster:
-
Find the row with the operator you want to update.
-
Click the Update button in front of the operator.
-
Confirm the action by clicking Update, or abandon by clicking Cancel.
DB clusters¶
Add a DB Cluster¶
You must create at least one Kubernetes cluster to create a DB cluster.
To monitor a DB cluster, set up a public address for PMM Server first.
-
Select the DB Cluster tab.
-
Click Create DB Cluster.
-
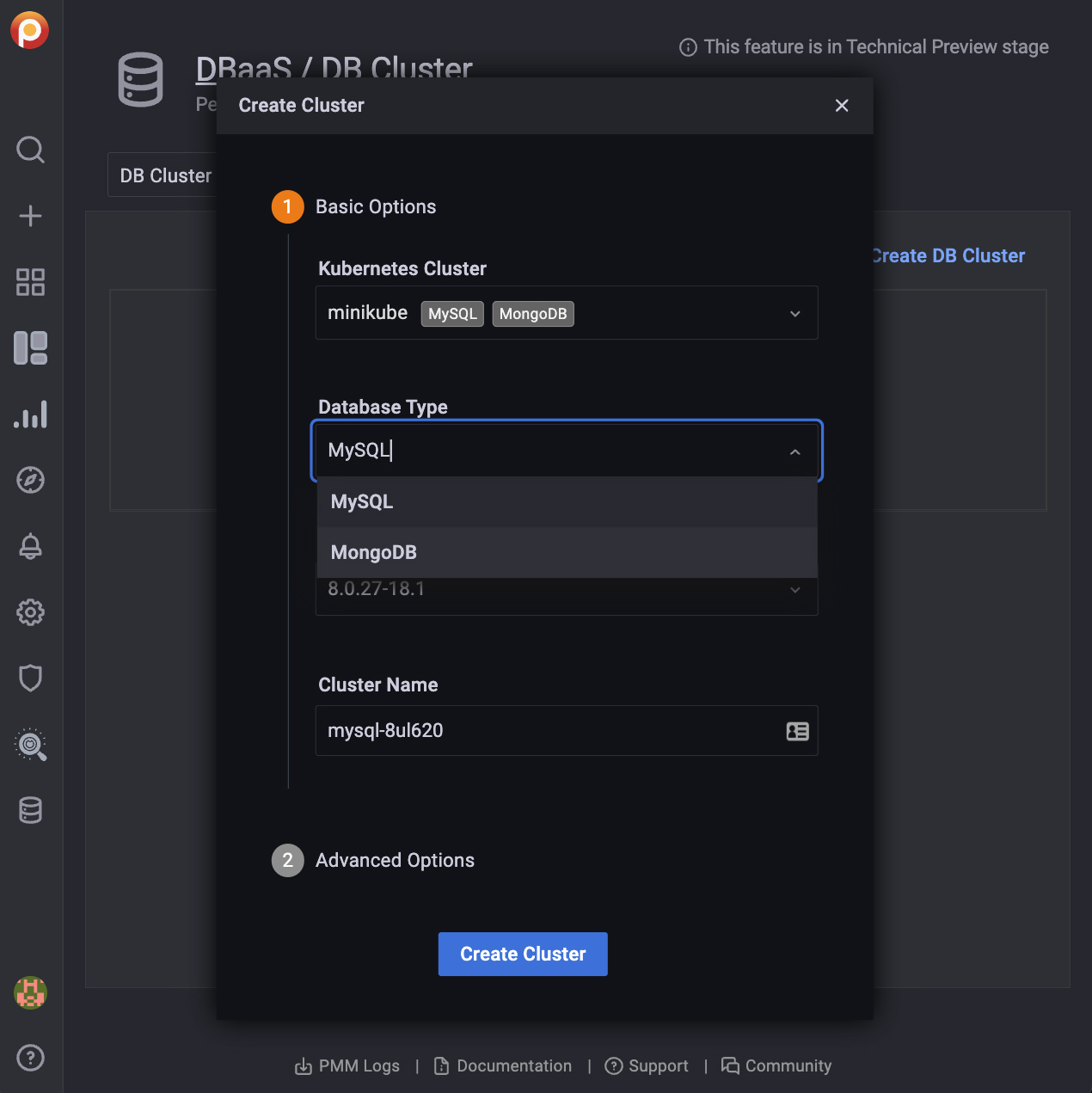
In section 1, Basic Options:
-
Enter a value for Cluster name. A cluster name:
- must begin with a lowercase letter;
- can comprise lowercase letters, numbers and dashes;
- must end with an alphanumeric character.
-
Select a cluster from the Kubernetes Cluster menu.
-
Select a database type from the Database Type menu.
-
-
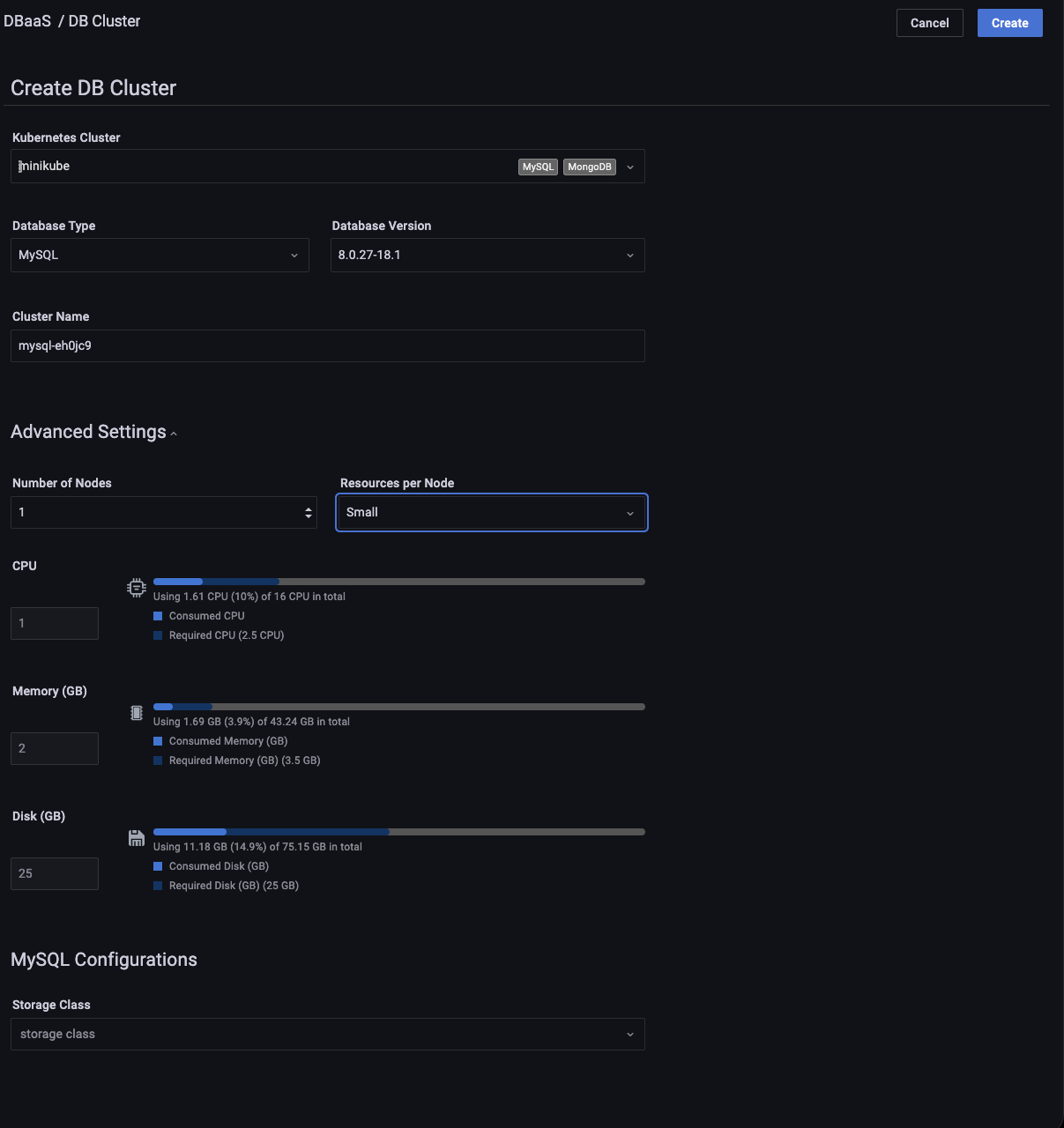
Expand section 2, Advanced Options.
-
Select Topology, either Cluster or Single Node.
-
Select the number of nodes. (The lower limit is 3.)
-
Select External Access if you want to make your DB cluster available outside of Kubernetes cluster.
By default, only internal access is provided.
External Access can’t be granted for local Kubernetes clusters (e.g. minikube).
-
Select a preset for Resources per Node.
Small, Medium and Large are fixed preset values for Memory, CPU, and Disk.
Values for the Custom preset can be edited.
Beside each resource type is an estimate of the required and available resources represented numerically in absolute and percentage values, and graphically as a colored, segmented bar showing the projected ratio of used to available resources. A red warning triangle is shown if the requested resources exceed those available.
-
-
When both Basic Options and Advanced Options section icons are green, the Create Cluster button becomes active. (If inactive, check the values for fields in sections whose icon is red.)
Click Create Cluster to create your cluster.
-
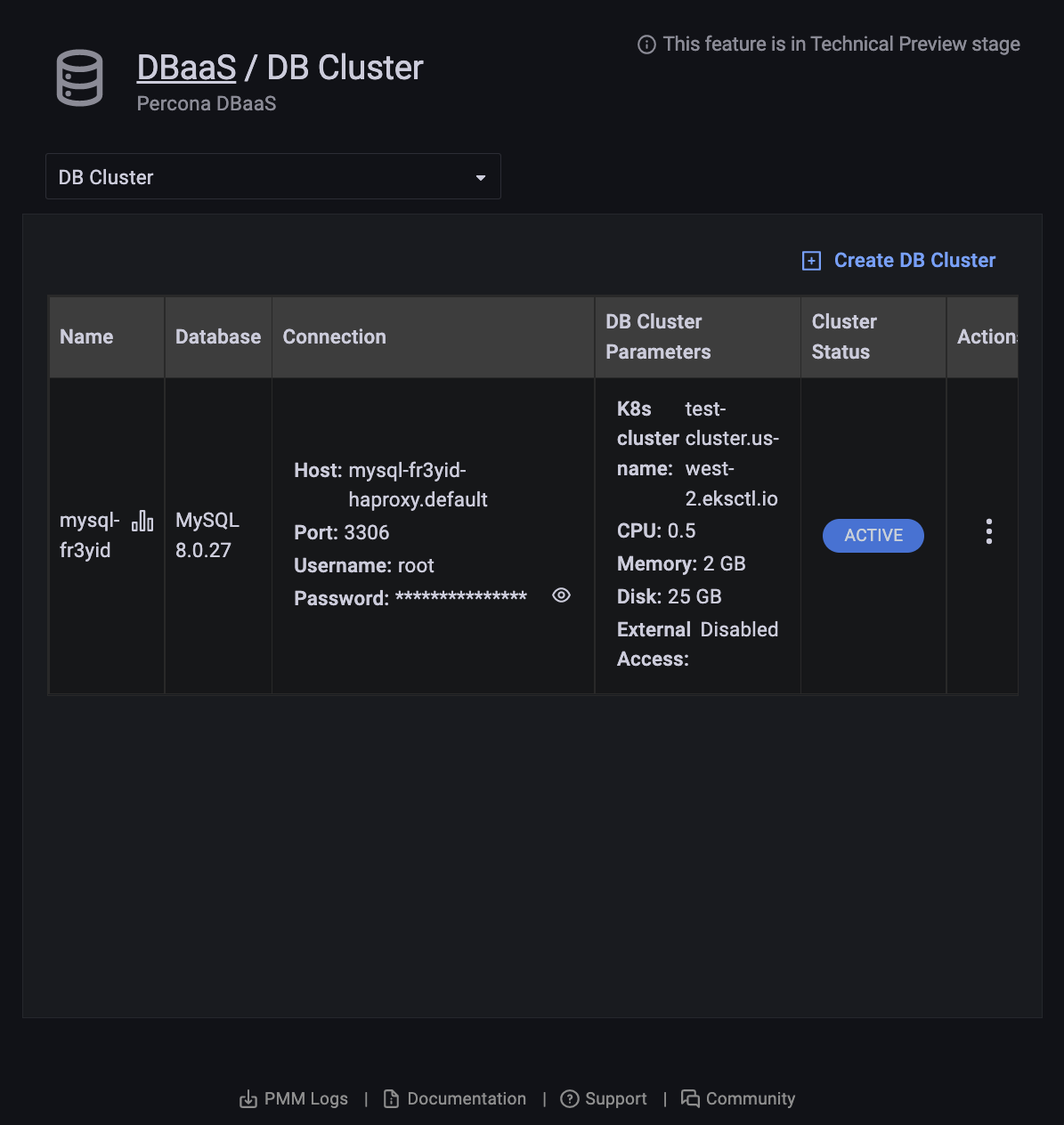
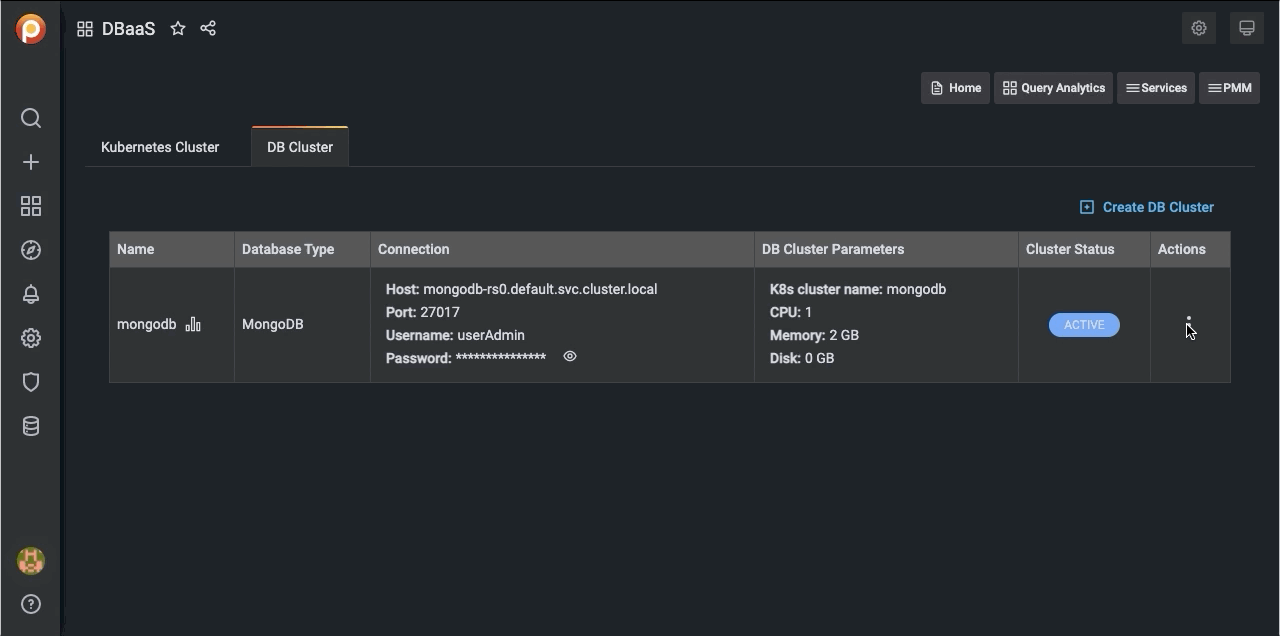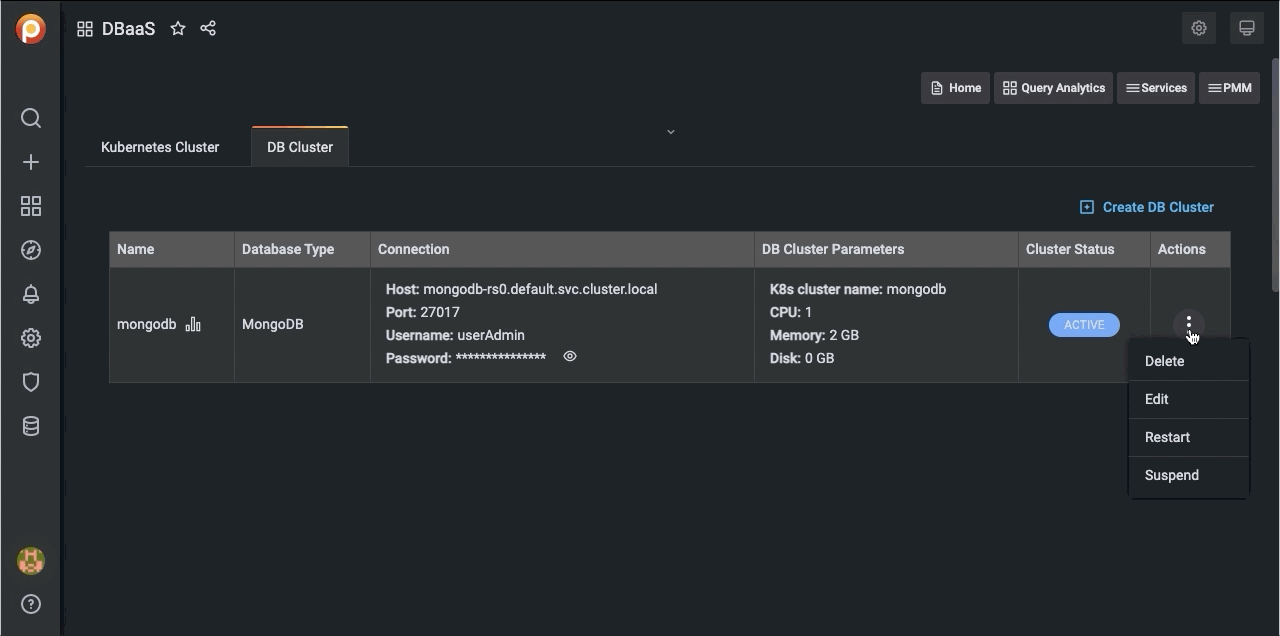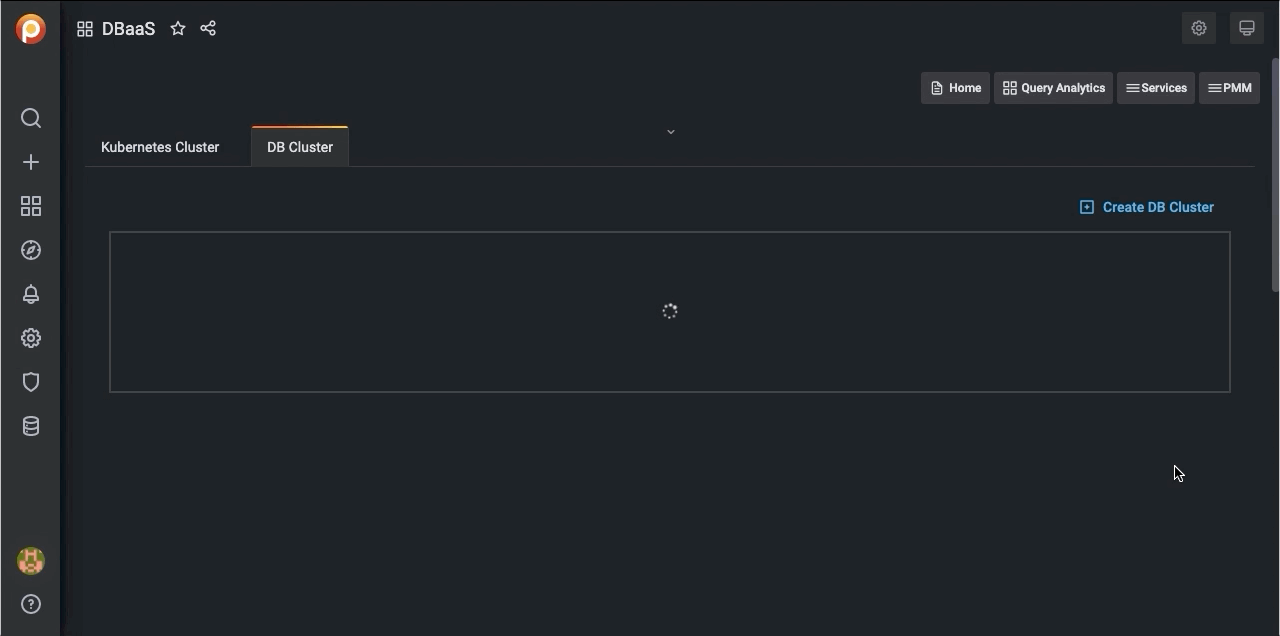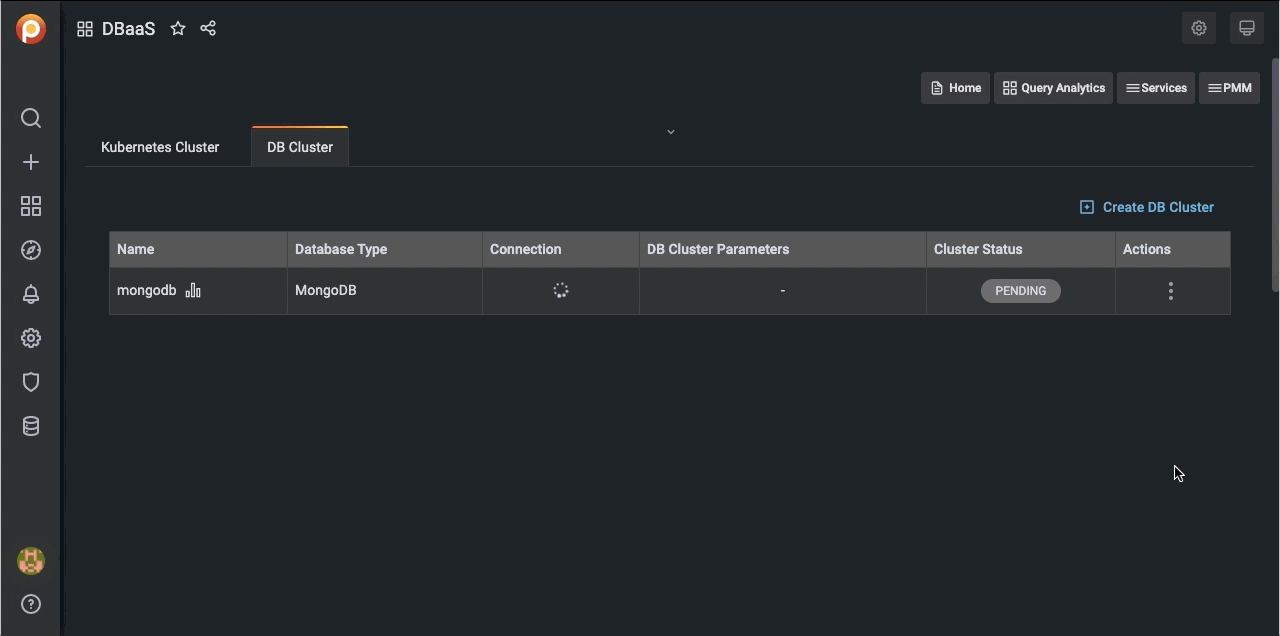
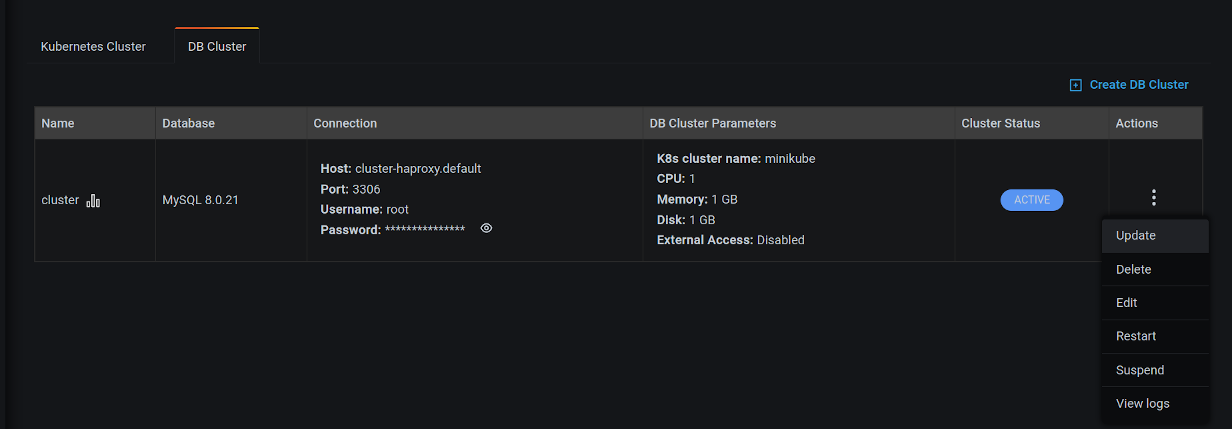
A row appears with information on your cluster:
- Name: The cluster name.
- Database: The cluster database type and version.
- Connection:
- Host: The hostname.
- Port: The port number.
- Username: The connection username.
- Password: The connection password (click the eye icon to reveal).
- DB Cluster Parameters:
- K8s cluster name: The Kubernetes cluster name.
- CPU: The number of CPUs allocated to the cluster.
- Memory: The amount of memory allocated to the cluster.
- Disk: The amount of disk space allocated to the cluster.
- Cluster Status:
- PENDING: The cluster is being created.
- ACTIVE: The cluster is active.
- FAILED: The cluster could not be created.
- DELETING: The cluster is being deleted.
- UPDATING: The cluster is being updated.
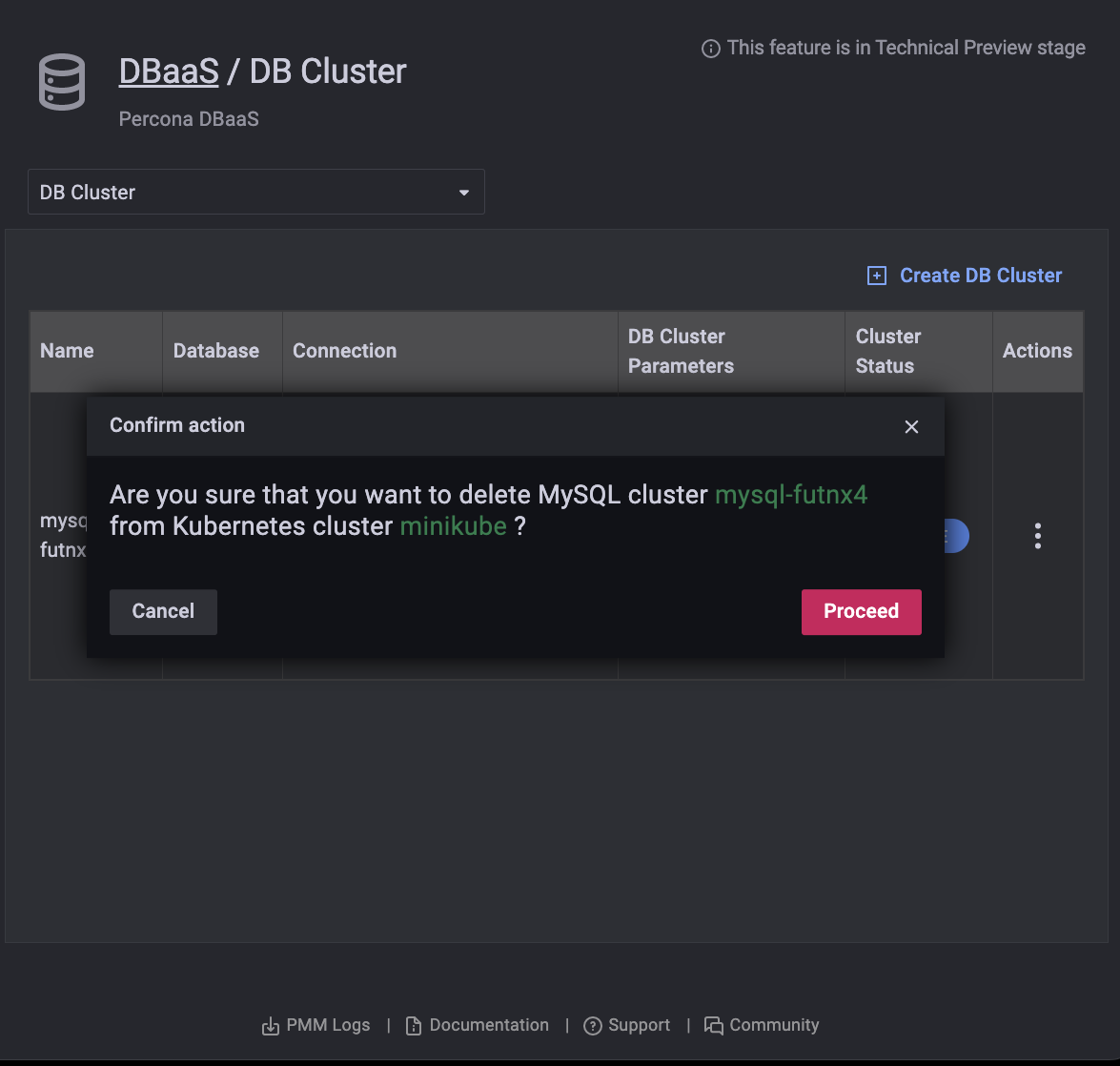
Delete a DB Cluster¶
-
Find the row with the database cluster you want to delete.
-
In the Actions column, open the menu and click Delete.
-
Confirm the action by clicking Proceed, or abandon by clicking Cancel.
Danger
Deleting a cluster in this way also deletes any attached volumes.
Edit a DB Cluster¶
-
Select the DB Cluster tab.
-
Find the row with the database cluster you want to change.
-
In the Actions column, open the menu and click Edit.
A paused cluster can’t be edited.
Restart a DB Cluster¶
-
Select the DB Cluster tab.
-
Identify the database cluster to be changed.
-
In the Actions column, open the menu and click Restart.
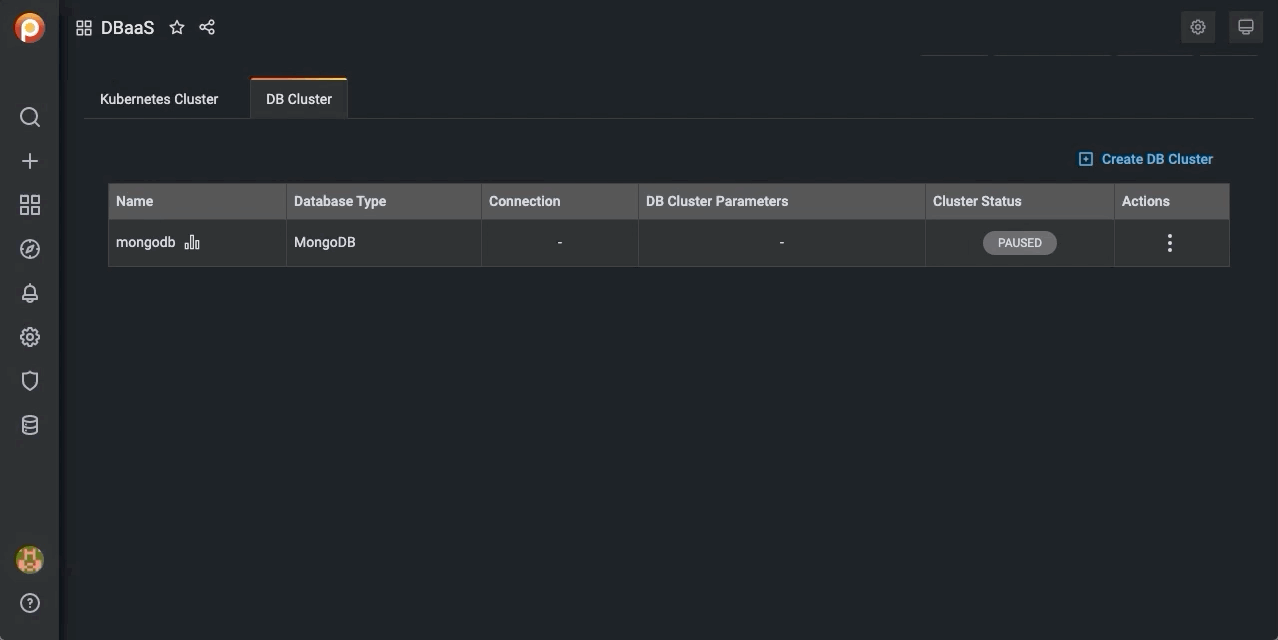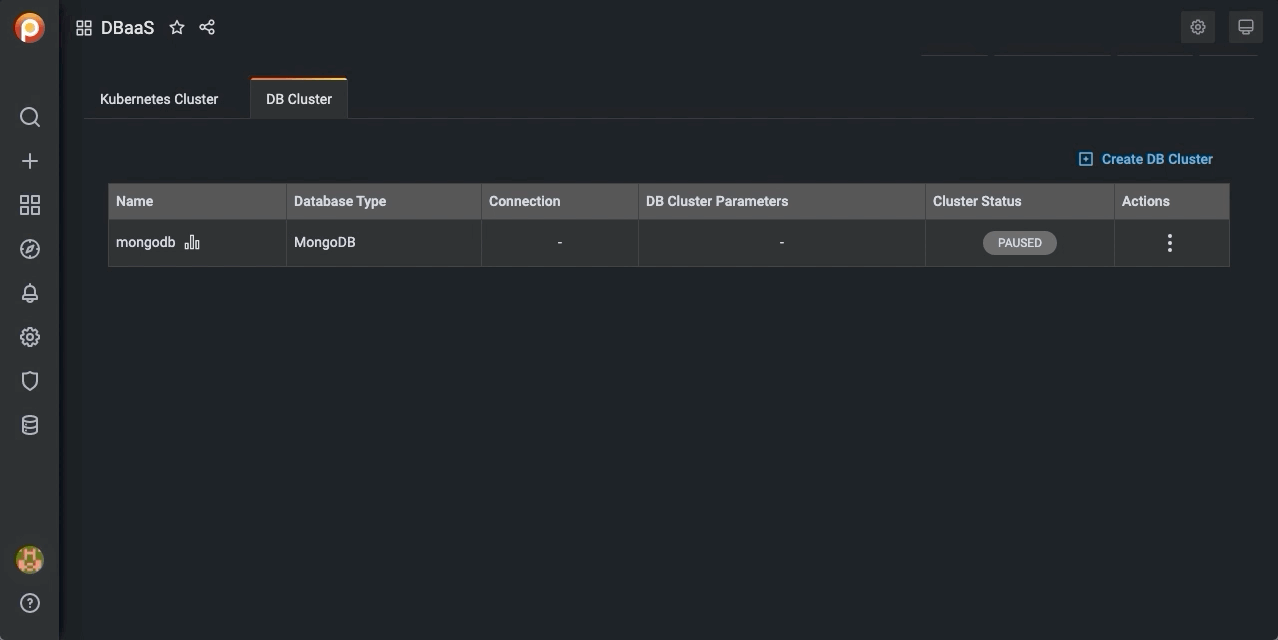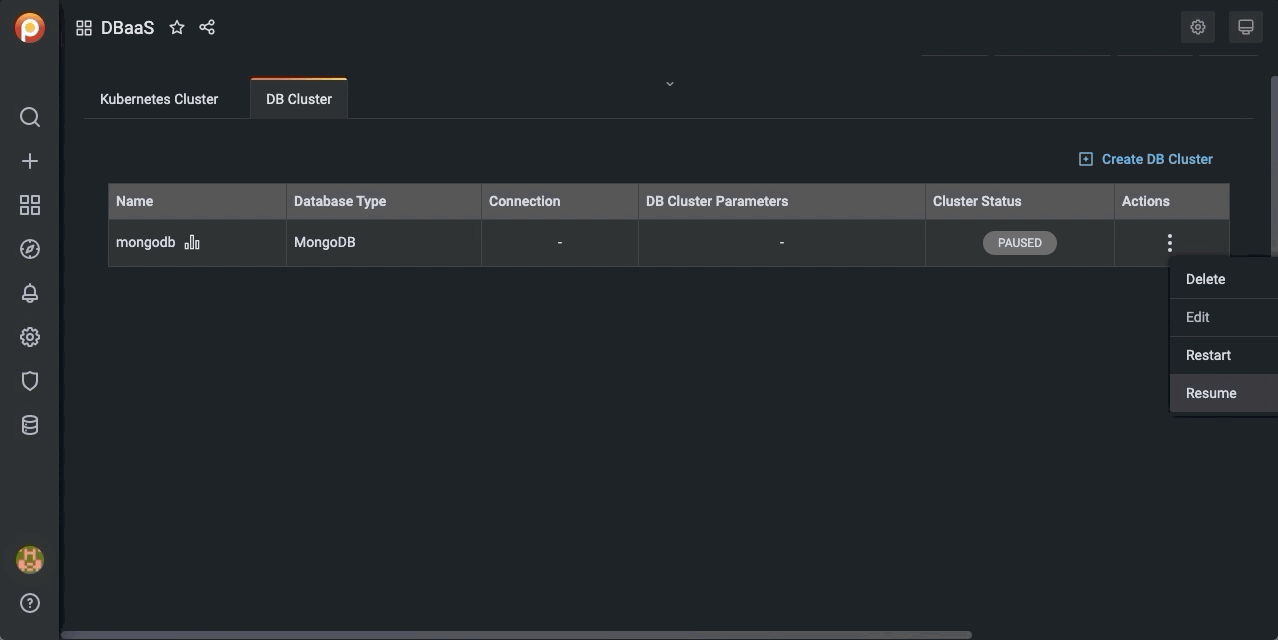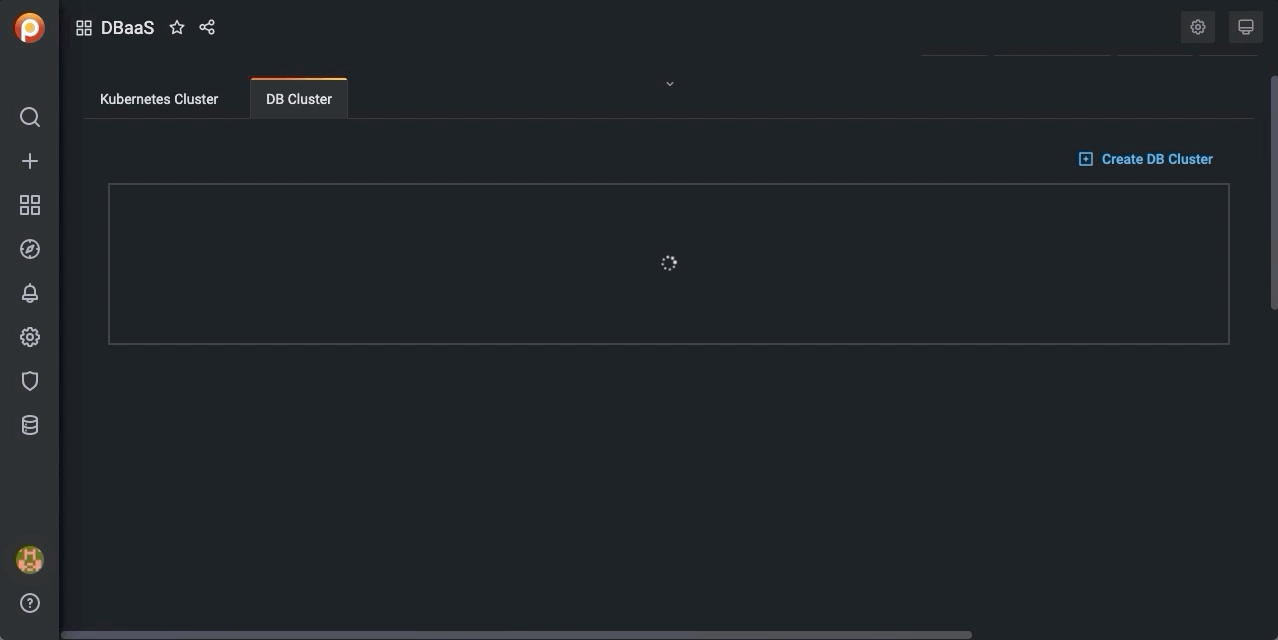
Suspend or resume a DB Cluster¶
-
Select the DB Cluster tab.
-
Identify the DB cluster to suspend or resume.
-
In the Actions column, open the menu and click the required action:
-
For active clusters, click Suspend.
-
For paused clusters, click Resume.
-
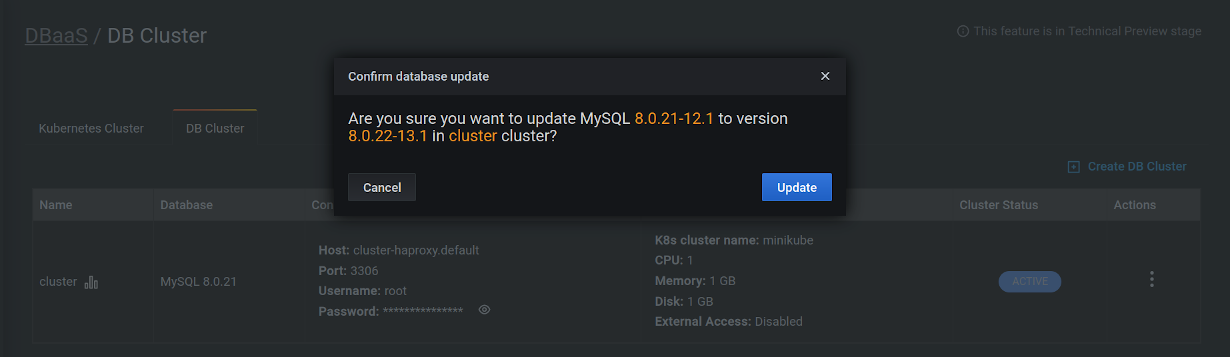
Update a DB Cluster¶
-
Select the DB Cluster tab.
-
Identify the DB cluster to update.
-
In the Actions column, open the menu and click Update:
-
Confirm the update by clicking on Update, or abandon by clicking Cancel.
Recommend
About Joyk
Aggregate valuable and interesting links.
Joyk means Joy of geeK