全新升级的AOP框架Dora.Interception[3]: 基于特性标注的拦截器注册方式 - Artech
source link: https://www.cnblogs.com/artech/p/dora-aop-3.html
Go to the source link to view the article. You can view the picture content, updated content and better typesetting reading experience. If the link is broken, please click the button below to view the snapshot at that time.

在Dora.Interception(github地址,觉得不错不妨给一颗星)中按照约定方式定义的拦截器可以采用多种方式注册到目标方法上。本篇文章介绍最常用的基于“特性标注”的拦截器注册方式,下一篇会介绍另一种基于(Lambda)表达式的注册方式。如果原生定义的这两种注册方式不能满足要求,利用框架提供的扩展,我们可以完成任何你想要的拦截器注册手段。(拙著《ASP.NET Core 6框架揭秘》于日前上市,加入读者群享6折优惠)
目录
一、InterceptorAttribute 特性
二、指定构造拦截器的参数列表
三、将拦截器类型定义成特性
四、合法性检验
五、针对类型、属性的标注
六、拦截的屏蔽
一、InterceptorAttribute 特性
拦截器类型可以利用如下这个InterceptorAttribute特性应用到标注的类型、属性和方法上。除了通过Interceptor属性指定拦截器类型之外,我们还可以利用Order属性控制拦截器的执行顺序,该属性默认值为0。该特性的Arguments用来提供构造拦截器对象的参数。
[AttributeUsage(AttributeTargets.Class | AttributeTargets.Method | AttributeTargets.Property, AllowMultiple = true, Inherited = false)]
public class InterceptorAttribute : Attribute
{
public Type Interceptor { get; }
public object[] Arguments { get; }
public int Order { get; set; }
public InterceptorAttribute(params object[] arguments) :
public InterceptorAttribute(Type? interceptor, params object[] arguments);
}二、指定构造拦截器的参数列表
拦截器对象是通过依赖注入容器提供的,容器能够自动提供注入到构造函数中对象。如果构造函数包含额外的参数,对应的参数值就需要利用InterceptorAttribute 特性的Arguments属性来提供,此属性由构造函数的arguments参数提供。
public class FoobarInterceptor
{
public string Name { get; }
public FoobarInterceptor(string name, IFoobar foobar)
{
Name = name;
Debug.Assert(foobar is not null);
}
public ValueTask InvokeAsync(InvocationContext invocationContext)
{
Console.WriteLine($"FoobarInterceptor '{Name}' is invoked.");
return invocationContext.ProceedAsync();
}
}
public interface IFoobar { }
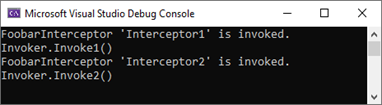
public class Foobar : IFoobar { }对于如上这个拦截器类型FoobarInterceptor,其构造函数定义了一个字符串的参数name用来指定拦截器的名称,当我利用InterceptorAttribute 特性将此拦截器应用到Invoker类型的Invoke1和Invoke2方法上是,就需要按照如下的方式指定具体的名称(Interceptor1和Interceptor2)。
public class Invoker
{
[FoobarInterceptor("Interceptor1")]
public virtual void Invoke1() => Console.WriteLine("Invoker.Invoke1()");
[FoobarInterceptor("Interceptor2")]
public virtual void Invoke2() => Console.WriteLine("Invoker.Invoke2()");
}我们按照如下的方式调用Invoker对象的Invoke1和Invoke2方法。
var invoker = new ServiceCollection()
.AddSingleton<Invoker>()
.AddSingleton<IFoobar, Foobar>()
.BuildInterceptableServiceProvider()
.GetRequiredService<Invoker>();
invoker.Invoke1();
invoker.Invoke2();程序执行后,拦截器会以如下的形式将自身的名称输出到控制台上(源代码)。
三、将拦截器类型定义成特性
其实我们可以让定义的拦截器类型派生于InterceptorAttribute 特性,这样就可以直接将它标注到目标类型、属性和方法上。比如上面这个FoobarInterceptor类型可以改写成如下的形式。
public class FoobarInterceptorAttribute: InterceptorAttribute
{
public string Name { get; }
public FoobarInterceptorAttribute(string name) => Name = name;
public ValueTask InvokeAsync(InvocationContext invocationContext)
{
Console.WriteLine($"FoobarInterceptor '{Name}' is invoked.");
return invocationContext.ProceedAsync();
}
}那么它就可以按照如下的方式标注到Invoker类型的两个方法上(源代码)。
public class Invoker
{
[FoobarInterceptor("Interceptor1")]
public virtual void Invoke1() => Console.WriteLine("Invoker.Invoke1()");
[FoobarInterceptor("Interceptor2")]
public virtual void Invoke2() => Console.WriteLine("Invoker.Invoke2()");
}四、合法性检验
只有接口方法和虚方法才能被拦截,Dora.Interception针对拦截器的应用提供了如下的验证逻辑:
- 标注到方法上(函数属性的Get/Set方法):如果目标方法均不能被拦截,抛出异常;
- 标注到属性上:表示将拦截器应用到该属性可以被拦截的Get/Set方法上。如果Get和Set方法均不能被拦截,抛出异常;
- 标注到类型上:表示将拦截器应用到目标类型可以来拦截的方法(含属性方法)上,如果类型的所有方法均不能被拦截,此时不会抛出异常。
public class Foo
{
[FoobarInterceptor]
public void M() { }
}
public class Bar
{
[FoobarInterceptor]
public object? P { get; set; }
}
[FoobarInterceptor]
public class Baz
{
public void M() { }
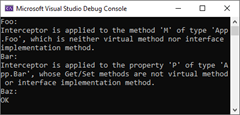
}对于上面定义的三个类型,Foo的M方法和Bar的P属性均是无法被拦截,Baz类型并没有可以被拦截的方法。我们采用如下的程序测试上述的检验逻辑。
GetService<Foo>();
GetService<Bar>();
GetService<Baz>();
static void GetService<T>() where T:class
{
try
{
Console.WriteLine($"{typeof(T).Name}:");
_ = new ServiceCollection()
.AddSingleton<T>()
.BuildInterceptableServiceProvider()
.GetRequiredService<T>();
Console.WriteLine("OK");
}
catch (Exception ex)
{
Console.WriteLine(ex.Message);
}
}程序运行后会在控制台上输出如下的结果,可以看出只有将拦截器应用到不合法的方法和属性上才会抛出异常(源代码)。
五、针对类型、属性的标注
我们利用如下这个拦截器类型FoobarInterceptorAttribute 来演示将拦截器应用到类型和属性上。该拦截器类型派生于InterceptorAttribute特性,并在执行的时候输出当前的方法。
public class FoobarInterceptorAttribute : InterceptorAttribute
{
public ValueTask InvokeAsync(InvocationContext invocationContext)
{
var method = invocationContext.MethodInfo;
Console.WriteLine($"{method.DeclaringType!.Name}.{method.Name} is intercepted.");
return invocationContext.ProceedAsync();
}
}我们将FoobarInterceptorAttribute 特性标注到Foo类型上,后者定义的M1方法和P1属性是可以被拦截的,但是M2方法和P2属性则不能。FoobarInterceptorAttribute 特性还被应用到Bar类型的P1属性以及P2属性的Set方法上。
[FoobarInterceptor]
public class Foo
{
public virtual void M1() { }
public void M2() { }
public virtual object? P1 { get; set; }
public object? P2 { get; set; }
}
public class Bar
{
[FoobarInterceptor]
public virtual object? P1 { get; set; }
public virtual object? P2 { get; [FoobarInterceptor] set; }
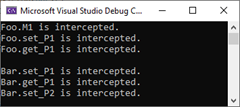
}我们利用如下的程序来检验针对Foo和Bar对象所有方法和属性的调用,那么被拦截器拦截下来。
var provider = new ServiceCollection()
.AddSingleton<Foo>()
.AddSingleton<Bar>()
.BuildInterceptableServiceProvider();
var foo = provider.GetRequiredService<Foo>();
var bar = provider.GetRequiredService<Bar>();
foo.M1();
foo.M2();
foo.P1 = null;
_ = foo.P1;
foo.P2 = null;
_ = foo.P2;
Console.WriteLine();
bar.P1 = null;
_ = bar.P1;
bar.P2 = null;
_ = bar.P2;程序运行之后会在控制台上输出如下的结果(源代码)。
六、拦截的屏蔽
如果某个拦截器需要被应用大某个类型的绝大部分成员,我们可以选择“排除法”:将拦截器应用到该类型上,将某些非目标成员屏蔽掉。还有一种情况下,如果我们确定某些类型或者方法不能被拦截(比如会在一个循环中频繁调用),又担心一些“模糊”的拦截器注册方法将它们与某些拦截器错误地关联在一起,此时我们可以选择将其拦截功能显式屏蔽掉。
针对拦截的屏蔽可以通过在类型、属性、方法设置程序集上标注NonInterceptableAttribute特性。由于屏蔽功能具有最高优先级,一旦将此特性应用到某个类型上,该类型上的所有成员均不会被拦截。如果被标注到属性上,其Get和Set方法也不会被拦截。具有如下定义的Foo和Bar类型的所有方法和属性都不会被拦截(源代码)。
[FoobarInterceptor]
public class Foo
{
[NonInterceptable]
public virtual void M() { }
[NonInterceptable]
public virtual object? P1 { get; set; }
public virtual object? P2 { [NonInterceptable] get; set; }
}
[NonInterceptable]
public class Bar
{
[FoobarInterceptor]
public virtual void M() { }
[FoobarInterceptor]
public virtual object? P { get; set; }
}全新升级的AOP框架Dora.Interception[1]: 编程体验
全新升级的AOP框架Dora.Interception[2]: 基于约定的拦截器定义方式
全新升级的AOP框架Dora.Interception[3]: 基于“特性标注”的拦截器注册方式
全新升级的AOP框架Dora.Interception[4]: 基于“Lambda表达式”的拦截器注册方式
全新升级的AOP框架Dora.Interception[5]: 实现任意的拦截器注册方式
全新升级的AOP框架Dora.Interception[6]: 框架设计和实现原理
Recommend
-
 25
25
Dora.Interception最初的定位就是专门针对.NET Core的AOP框架,所以在整个迭代过程中我大部分是在做减法。对于.NET Core程序开发来说,依赖注入已经成为无处不在并且“深入骨髓”的东西,不论是在进行业务应用的开发,还是进行基础组件的开...
-
 47
47
和所有的AOP框架一样,我们必须将正常的方法调用进行拦截,才能将应用到当前方法上的所有拦截器纳入当前调用链。Dora.Interception采用 IL Eimit 的方式实现对方法调用的拦截,接下来我们就来聊聊大致的实现原理。 ...
-
 34
34
对于所有的AOP框架来说,多个拦截器最终会应用到某个方法上。这些拦截器按照指定的顺序构成一个管道,管道的另一端就是针对目标方法的调用。从设计角度来将,拦截器和中间件本质是一样的,那么我们可以按照类似的模式来设计拦截器。
-
 7
7
Dora.Interception(github地址,觉得不错不妨给一颗星)有别于其他AOP框架的最大的一个特点就是采用针对“约定”的拦截器定义方式。如果我们为拦截器定义了一个接口或者基类,那么拦截方法将失去...
-
 6
6
全新升级的AOP框架Dora.Interception[1]: 编程体验 ...
-
 5
5
如果拦截器应用的目标类型是由自己定义的,Dora.Interception(github地址,觉得不错不妨给一颗星)可以在其类型或成员上标注InterceptorAttribute特性来应用对应的拦截器。如果对那个的程序集是...
-
 10
10
Dora.Interception提供了两种拦截器注册方式,一种是利用标注在目标类型、属性和方法上的InterceptorAttribute特性,另一种采用基于目标方法或者属性的调用表达式。通过提供的扩展点,我们可以任何我们希望的拦截器注册方式。(拙著《ASP.NET Core 6框架揭秘》
-
 7
7
本系列前面的五篇文章主要介绍Dora.Interception(github地址,觉得不错不妨给一颗星)的编程模式以及对它的扩展定制,现在我们来聊聊它的设计和实现原理。(拙著《ASP.NET Core 6框架揭秘》
-
 9
9
多年之前利用IL Emit写了一个名为Dora.Interception(github地址,觉得不错不妨给一颗星)的AOP框架。前几天利用Roslyn的Source Generator对自己为公司写的一个GraphQL框架进行改造,性能得到显...
-
 11
11
无需人工标注,自生成指令框架打破ChatGPT等LLM的成本瓶颈 作者:机器之心 2022-12-29 08:17:57 人工智能 当前,大型语言模型的性能已经达到...
About Joyk
Aggregate valuable and interesting links.
Joyk means Joy of geeK