

简单入门Fetch API
source link: https://www.clzczh.top/2022/06/18/fetchAPI/
Go to the source link to view the article. You can view the picture content, updated content and better typesetting reading experience. If the link is broken, please click the button below to view the snapshot at that time.

简单入门Fetch API
Fetch API是使用 JavaScript请求资源的优秀工具。虽然我们开发时可能是经常使用axios,但是实际上Fetch API也能做很多一样的事。并且使用Fetch API不需要安装axios,所以我们做一些小案例,但是需要调接口的话,Fetch API便是很好的选择,不需要安装axios,也不需要像XMLHttpRequest 对象那样子需要较多步骤。
接口有需要可以到最后自取(express接口)
只需要使用fetch()方法即可,传参为获取资源的URL。该方法返回一个Promise对象。(和axios使用非常像)
const r = fetch('http://localhost:8088/getInfo')
console.log(r)
r.then(res => {
console.log(res)
})
上面我们已经把响应结果打印出来了,但是并没有得到真正的响应体的数据。
这时候可以使用text()方法,这个方法会返回一个Promise对象,这个对象会resolve为读取资源的完整内容。
fetch('http://localhost:8088/getInfo?name=clz')
.then(async (res) => {
const data = await res.text()
console.log(data)
console.log(typeof data)
})
从结果来看,发现这时候得到的数据是string类型的,之后还需要通过JSON.parse()来操作。很显然不太好,这个时候只需要不是使用text()方法,而是使用json()方法即可。(使用方式和text()方法一样)
请求失败的时候还是会正常执行then方法里的处理函数。(这里的失败是指服务器返回了响应,但是不是成功的请求。)
fetch('http://localhost:8088/getBadRequest')
.then(async (res) => {
const data = await res.json()
console.log(data)
})
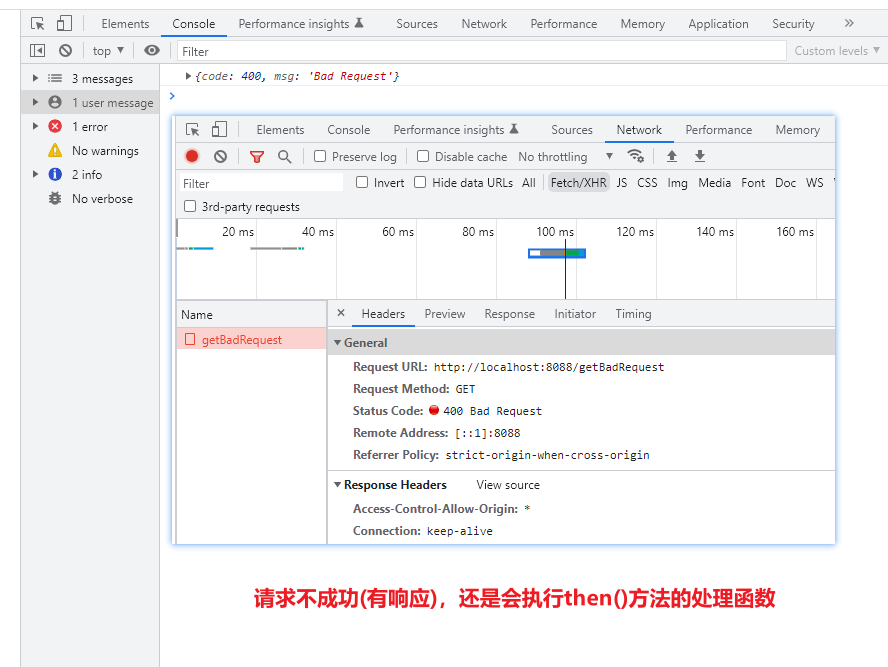
如果服务器没有响应导致浏览器超时的话,这时候就不会再执行then()方法的处理函数,而是执行catch()方法的,因为这时候的Promise不再是resolved状态,而是rejected状态。(比如跨域时候)
后端接口注释掉app.use(cors()),不再处理跨域
fetch('http://localhost:8088/getBadRequest')
.then(async (res) => {
const data = await res.json()
console.log(data)
})
.catch(reason => {
console.log('catch()方法里的处理函数')
console.log(reason)
})
POST方法
上面我们直接使用fetch()方法就是GET请求,那么假如我们想要使用POST方法来进行新增数据之类的操作呢?
fetch方法的第二个参数就是自定义选项,通过自定义选项就能实现GET请求之外的请求。比如使用POST方法的时候,自定义选项就需要method来确定请求方法,以及body来确定请求体的数据。
const data = {
name: 'clz',
age: 21
}
fetch('http://localhost:8088/postInfo', {
method: 'POST',
body: JSON.stringify(data)
})
.then(async (res) => {
const data = await res.json()
console.log(data)
})
结果发现:请求得到的响应的状态码是400,提示信息是需要姓名和年龄,但是我们明明已经把姓名和年龄传过去了。这种时候,有可能是后端处理的问题,也有可能是前端传出去的格式的问题(即请求头的Content-Type)
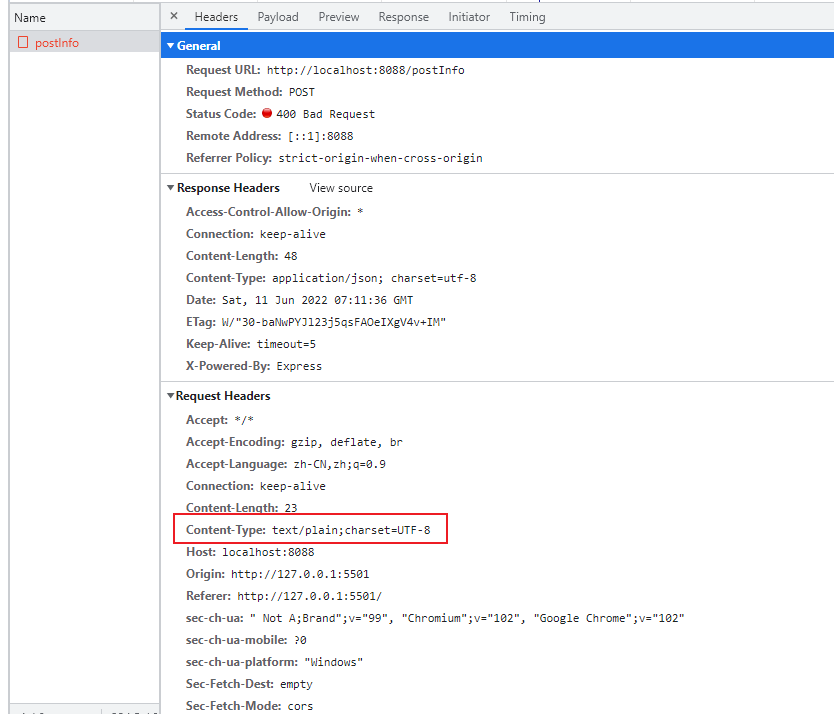
果不其然,我们传的数据是json形式的,但是Content-Type却不是json,所以我们的自定义选项还需要添加一个headers选项来设置选项的请求头。
const data = {
name: 'clz',
age: 21
}
const headers = new Headers({
'Content-Type': 'application/json; charset=utf-8'
})
fetch('http://localhost:8088/postInfo', {
method: 'POST',
body: JSON.stringify(data),
headers
})
.then(async (res) => {
const data = await res.json()
console.log(data)
})
express接口
const express = require('express')
const cors = require('cors')
const app = express()
// 解决跨域
app.use(cors())
// 解析请求体的中间件(json格式)
app.use(express.json())
// GET请求
app.get('/getInfo', (req, res) => {
res.json({
code: 200,
data: {
name: '赤蓝紫',
age: 21
},
msg: '获取信息成功',
})
})
// 响应状态码为400
app.get('/getBadRequest', (req, res) => {
res.status(400).json({
code: 400,
msg: 'Bad Request',
})
})
// POST请求
app.post('/postInfo', (req, res) => {
if (req.body.name === undefined || req.body.age === undefined) {
res.status(400).json({
code: 400,
msg: '必须要有姓名、年龄'
})
} else {
res.json({
code: 200,
data: req.body
})
}
})
const port = 8088
app.listen(port, () => {
console.log(`http://localhost:${port}`)
})
Recommend
About Joyk
Aggregate valuable and interesting links.
Joyk means Joy of geeK