

Math.abs JIT Optimization Bug in JSC
source link: https://paper.seebug.org/1917/
Go to the source link to view the article. You can view the picture content, updated content and better typesetting reading experience. If the link is broken, please click the button below to view the snapshot at that time.
作者:360漏洞研究院 戴建军
原文链接:https://vul.360.net/archives/397
2021年天府杯我们成功完成iPhone 13 pro RCE的目标,这篇文章将会详细介绍其中使用到的Safari JavaScriptCore(JSC) 漏洞,漏洞编号为CVE-2021-30953。
ArithNegate
在JSC的JIT FTL优化过程中,对于 -n 的表达式会生成ArithNegate opcode,且ArithNegate会伴随相应的ArithMode,ArithMode有如下几种定义:
enum Mode {
NotSet, // Arithmetic mode is either not relevant because we're using doubles anyway or we are at a phase in compilation where we don't know what we're doing, yet. Should never see this after FixupPhase except for nodes that take doubles as inputs already.
Unchecked, // Don't check anything and just do the direct hardware operation.
CheckOverflow, // Check for overflow but don't bother with negative zero.
CheckOverflowAndNegativeZero, // Check for both overflow and negative zero.
DoOverflow // Up-convert to the smallest type that soundly represents all possible results after input type speculation.
};相信从注释中大家也能明白他们的含义,这里我们主要关注Unchecked和CheckOverflow,顾名思义Unchecked表示不需要对ArithNegate操作做任何检查,CheckOverflow则需要检查是否产生溢出。那么 -n 操作为什么需要检查溢出呢?什么数据能导致 -n 操作产生溢出呢?
我们都知道在INT32类型中,有一个INT_MIN,它的实际值是-2147483648,在JSC中,-(-2147483648)的结果会是什么呢?我们来看一个例子:
n = -2147483648 (INT_MIN)
let y = -n; // 2147483648 in 64bit value
let z = -n; // -2147483648 in 32 bit value, but overflow check normally在JSC中,所有Number类型均采用64位浮点数表达,但是如果在JIT过程中n的类型是32位,则编译器会认为ArithNegate操作产生的结果也是32位的,且会附加上CheckOverflow的检查,所以当n=-2147483648时,-n的结果也会是-2147483648,如果此时ArithMode为CheckOverflow,则会发生bailout,如若ArithMode为Unchecked,则不会bailout。
我们来看看ArithNegate的JIT编译函数:
void compileArithNegate()
{
switch (m_node->child1().useKind()) {
case Int32Use: {
LValue value = lowInt32(m_node->child1());
LValue result;
if (!shouldCheckOverflow(m_node->arithMode()))
result = m_out.neg(value);
else if (!shouldCheckNegativeZero(m_node->arithMode())) {
CheckValue* check = m_out.speculateSub(m_out.int32Zero, value);
blessSpeculation(check, Overflow, noValue(), nullptr, m_origin);
result = check;
} else {
speculate(Overflow, noValue(), nullptr, m_out.testIsZero32(value, m_out.constInt32(0x7fffffff)));
result = m_out.neg(value);
}
setInt32(result);
break;
}从代码中也能看出,CheckOverflow会产生溢出检查的汇编代码,Unchecked则直接产生 neg 汇编指令。
CheckInBounds
JSC中针对数组的访问,FTL SSALowering优化阶段会引入一个index范围检查的opcode: CheckInBounds,相应的代码如下:
case GetByVal: {
lowerBoundsCheck(m_graph.varArgChild(m_node, 0), m_graph.varArgChild(m_node, 1), m_graph.varArgChild(m_node, 2));
break;
}
case PutByVal:
case PutByValDirect: {
Edge base = m_graph.varArgChild(m_node, 0);
Edge index = m_graph.varArgChild(m_node, 1);
Edge storage = m_graph.varArgChild(m_node, 3);
if (lowerBoundsCheck(base, index, storage))
break;
...
Node* length = m_insertionSet.insertNode(
m_nodeIndex, SpecInt32Only, op, m_node->origin,
OpInfo(m_node->arrayMode().asWord()), Edge(base.node(), KnownCellUse), storage);
checkInBounds = m_insertionSet.insertNode(
m_nodeIndex, SpecInt32Only, CheckInBounds, m_node->origin,
index, Edge(length, KnownInt32Use)); 编译 CheckInBounds 的函数如下:
void compileCheckInBounds()
{
speculate(
OutOfBounds, noValue(), nullptr,
m_out.aboveOrEqual(lowInt32(m_node->child1()), lowInt32(m_node->child2())));从代码中也可以看出,CheckInBounds实际就是检查 index>= 0 && index < array.length。
DFGIntegerRangeOptimization
JSC FTL优化的 DFGIntegerRangeOptimization阶段,会删除一些它认为冗余的溢出和范围检查,例如下面的代码:
for (var i = 0; i < array.length; ++i) array[i];运行到该阶段之前,循环体内相应的主要opcode如下:
CheckInBounds
GetByVal很显然从JS代码中可以看出,i 的范围是[0, array.length),所以DFGIntegerRangeOptimization认为CheckInBounds是可以删除掉的,经该阶段优化之后,循环体内的opcode只剩GetByVal。
GetByValDFGIntegerRangeOptimization通过for (var i = 0; i < array.length; ++i)建立两个关系:Relationship(i >=0)和Relationship(i < array.length),而这两个关系刚好满足优化CheckInBounds的条件,相关代码如下:
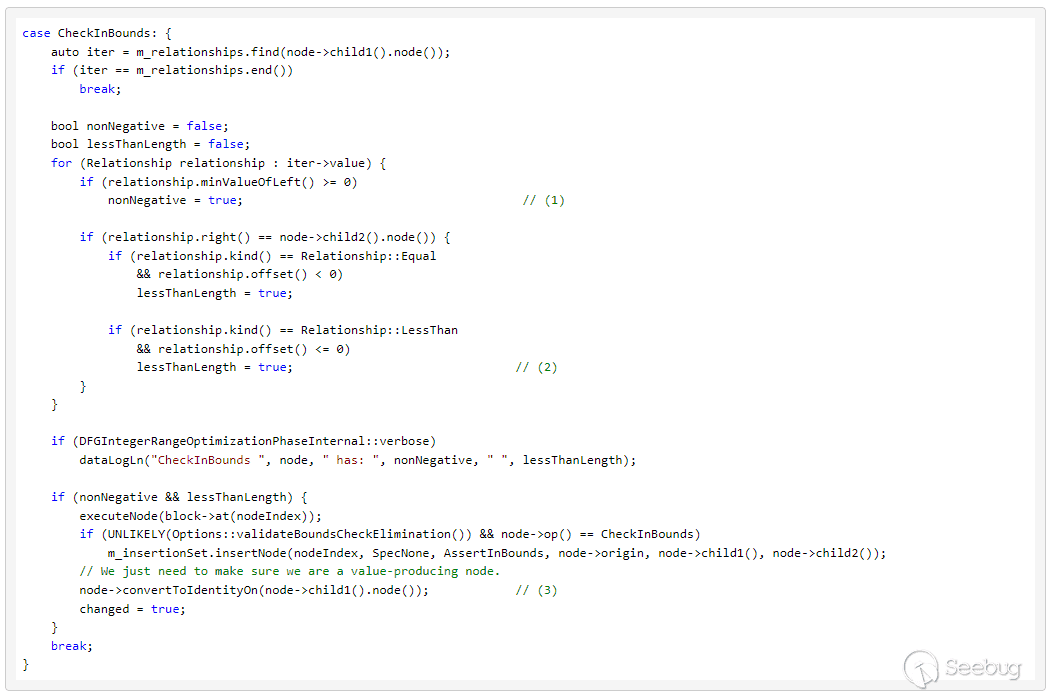
根据 (1) && (2) 优化CheckInBounds(3)。从上述代码中可以总结出这样一个结论:要想优化CheckInBounds,必须建立两个Relationships:index >=0 和 index < array.length。
The Bug
DFGIntegerRangeOptimization会通过如下代码给 i = ArithAbs(n) 建立 i >= 0的关系:
case ArithAbs: {
if (node->child1().useKind() != Int32Use)
break;
setRelationship(Relationship(node, m_zero, Relationship::GreaterThan, -1));
break;当 n < 0 且 Math.abs(n) 不会产生溢出的时候,DFGIntegerRangeOptimization会将 Math.abs(n)转化成 ArithNegate(n),且 ArithMode 为 Unchecked,相关代码如下:
case ArithAbs: {
if (node->child1().useKind() != Int32Use)
break;
...
executeNode(block->at(nodeIndex));
if (minValue >= 0) {
node->convertToIdentityOn(node->child1().node());
changed = true;
break;
}
bool absIsUnchecked = !shouldCheckOverflow(node->arithMode()); // (1)
if (maxValue < 0 || (absIsUnchecked && maxValue <= 0)) {
node->convertToArithNegate(); // (2)
if (absIsUnchecked || minValue > std::numeric_limits<int>::min())
node->setArithMode(Arith::Unchecked); // (3)
changed = true;
break;
}结合上述两段代码,如下实例代码会产生关系 i >= 0,且 Math.abs(n) 转换成 -n,但此时 ArithMode 为 CheckOverflow。
if(n < -1){
let i = Math.abs(n); // => (-n), CheckOverflow, i>=0;
}那么关键问题就在于:要想 -int_min 操作不会被检查CheckOverflow,即 ArithNegate 的 ArithMode被设置成Arith::Unchecked(3),则 ArithAbs 的 ArithMode也必须为 Arith::Unchecked。
此时问题转化成如何将 ArithAbs 的 ArithMode 设置成 Arith::Unchecked。
在Fixup阶段会设置 ArithAbs 的 ArithMode:
case ArithAbs: {
if (node->child1()->shouldSpeculateInt32OrBoolean()
&& node->canSpeculateInt32(FixupPass)) {
fixIntOrBooleanEdge(node->child1());
if (bytecodeCanTruncateInteger(node->arithNodeFlags())) // (1)
node->setArithMode(Arith::Unchecked);
else
node->setArithMode(Arith::CheckOverflow);
node->clearFlags(NodeMustGenerate);
node->setResult(NodeResultInt32);
break;
}如果满足条件(1),则会将 ArithMode 设置成 Unchecked。bytecodeCanTruncateInteger函数代码如下:
static inline bool bytecodeUsesAsNumber(NodeFlags flags)
{
return !!(flags & NodeBytecodeUsesAsNumber);
}
static inline bool bytecodeCanTruncateInteger(NodeFlags flags)
{
return !bytecodeUsesAsNumber(flags);
}此时问题转化成如何将 ArithAbs 的 NodeFlags设置成 ~NodeBytecodeUsesAsNumber。
而 NodeFlags 的设置操作发生在 BackwardsPropagation阶段:
case ArithBitOr: //(1)
case ArithBitXor:
case ValueBitAnd:
case ValueBitOr:
case ValueBitXor:
case ValueBitLShift:
case ArithBitLShift:
case ArithBitRShift:
case ValueBitRShift:
case BitURShift:
case ArithIMul: {
flags |= NodeBytecodeUsesAsInt;
flags &= ~(NodeBytecodeUsesAsNumber | NodeBytecodeNeedsNegZero | NodeBytecodeUsesAsOther);
flags &= ~NodeBytecodeUsesAsArrayIndex;
node->child1()->mergeFlags(flags); // (2)
node->child2()->mergeFlags(flags);
break;
}ArithBitOr 的操作会将 ArithBitOr->child1->flags 设置成 ~NodeBytecodeUsesAsNumber。
结合BackwardsPropagation阶段的代码来看看如下实例:
if(n < -1){
let i = Math.abs(n) | 0;
}此时 ArithBitOr->child1() 即是 ArithAbs(n),那么ArithAbs(n)->flags 会 merge( ~NodeBytecodeUsesAsNumber),将 ArithAbs 的 NodeFlags设置成 ~NodeBytecodeUsesAsNumber。然而 DFGIntegerRangeOptimization 阶段并没有 ArithBitOr 的优化处理,则 Math.abs(n)>= 0 的关系并不会传递到 i 。
此时问题转化成如何将 Math.abs(n) | 0 转换成 Math.abs(n)。
StrengthReduction 阶段解决了该问题:
case ArithBitOr:
handleCommutativity();
if (m_node->child1().useKind() != UntypedUse && m_node->child2()->isInt32Constant() && !m_node->child2()->asInt32()) {
convertToIdentityOverChild1(); // (1)
break;
}
break;当 ArithBitOr->child2() 等于0时,ArithBitOr 被转换成 child1(),从而 Math.abs(n) | 0 转换成 Math.abs(n)。
把上述涉及到的几个优化阶段串联起来:
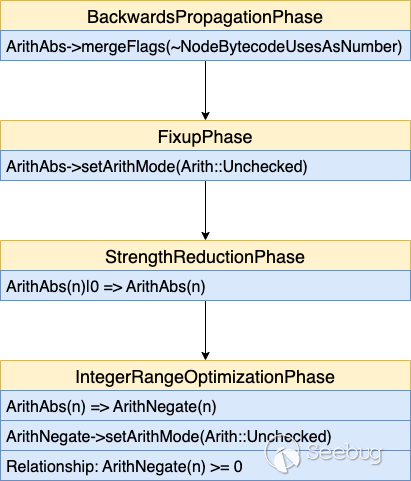
结合上述的优化流程,如下实例代码则成功优化 CheckInBounds:
function jit(arr, n) {
// Force n to be a 32bit integer
n |= 0;
if (n < -1) {
let i = Math.abs(n)|0; // (1) i >= 0, Unchecked
if (i < arr.length) { // (2) i < array.length
arr[i] = 1.04380972981885e-310; // (3) remove CheckInBounds
}
}
}代码(1)建立关系 i >= 0;代码(2)建立关系 i < arr.length,则代码(3)处的 CheckInBounds会被优化。
再结合文章开始分析的,当 n = -2147483648 时,i = -n = -2147483648,整数溢出不会被检查,而此时 arr[i] 也没有CheckInBounds检查,则发生越界写。
Exploit
漏洞利用采用比较常规的方法,通过越界写完成addrOf 和 fakeObj 两个原语,再结合 Samuel Gro?介绍的方法完成任意地址读写。JSC公开的利用方法有很多,在这里就不详细介绍了。
Patch
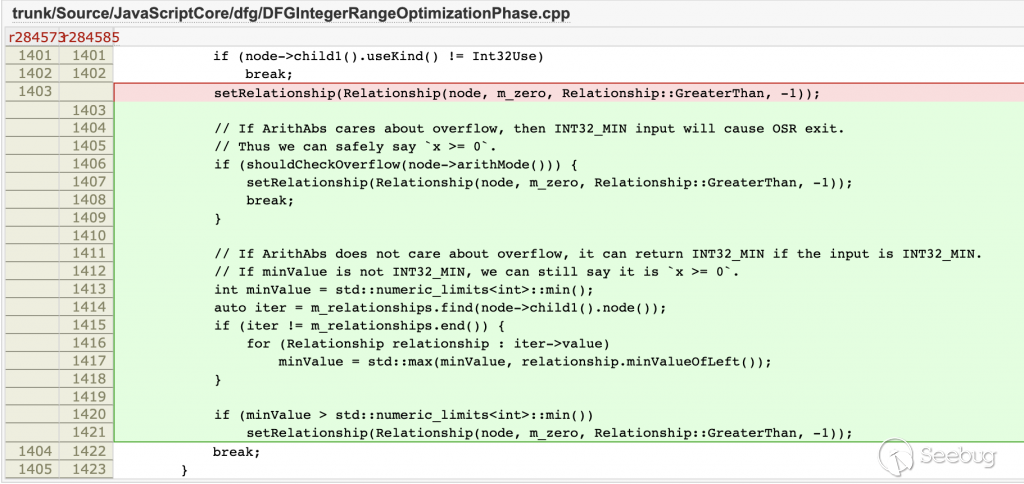
DFGIntegerRangeOptimization 在创建 ArithAbs >= 0关系时,增加了对 ArithMode 和最小值的检查。
Conclusion
本文对CVE-2021-30953的成因进行了分析,详细介绍了漏洞涉及到的全部优化过程,文章最后简单介绍了漏洞利用方法和漏洞修复方法。
 本文由 Seebug Paper 发布,如需转载请注明来源。本文地址:https://paper.seebug.org/1917/
本文由 Seebug Paper 发布,如需转载请注明来源。本文地址:https://paper.seebug.org/1917/
Recommend
About Joyk
Aggregate valuable and interesting links.
Joyk means Joy of geeK