

熊喵君的博客
source link: https://pandaychen.github.io/2022/06/10/2022-06-02-A-GOLANG-LRUCACHE-ANALYSIS-2/
Go to the source link to view the article. You can view the picture content, updated content and better typesetting reading experience. If the link is broken, please click the button below to view the snapshot at that time.
0x00 开篇
本文分析下 go-zero 框架的 LRU-cache 组件 实现,此库有如下特性:
- 缓存增删改,自动失效,可以指定过期时间(基于 TimeWheel 策略实现了 TTL 的机制);缓存大小限制,可以指定缓存个数
- LRU 支持
- 缓存命中率统计
- 并发安全,解决缓存击穿问题
- 解决缓存击穿问题(
syncx.SharedCalls,类似 singleflight 机制)
实际存储是最基础的锁 + map 机制,没啥好说的。
1、基础操作
// 参数:key 统一的过期时间 / cache 设置选项(key 数量上限)
cache, err = collection.NewCache(time.Minute, collection.WithLimit(10))
if err != nil {
log.Fatal(err)
}
// 1. add/update 增加 / 更新
cache.Set("key", "first element")
// 2. get 获取 key 下的 value
value, ok := cache.Get("key")
// 3. del 删除一个 key
cache.Del("key")
2、Set And Fetch:在 key 对于的 value 不存在时,执行传入的 fetch 方法,将具体读取逻辑交给开发者实现,并自动将结果放入缓存
cache.Take("key", func() (interface{}, error) {
// 模拟逻辑写入 local cache
time.Sleep(time.Millisecond * 100)
return "first element", nil
})
0x01 代码分析:基础接口
着重从以下几个方面分析 Cache 的实现:
- 有限容量(超过需要考虑如何淘汰)
- TTL 机制
- LRU 机制
- 热点数据统计
- 多线程存取,并发安全(高效)
type (
CacheOption func(cache *Cache)
Cache struct {
name string // 缓存名称
lock sync.Mutex
data map[string]interface{} // 缓存存储,最最基础的实现
expire time.Duration // 过期时间
timingWheel *TimingWheel // 框架封装的定时器
lruCache lru //LRU 组件
barrier syncx.SharedCalls// 缓存并发安全组件,可以解决缓存击穿的问题
unstableExpiry mathx.Unstable // 生成随机数的插件
stats *cacheStat // 统计命中率模块
}
)
其中 lru 可以由用户自行实现,go-zero 也基于 container/list 实现了一个版本 keyLru 供开发者 使用;
type lru interface {
add(key string)
remove(key string)
}
CRUD 操作
1、初始化缓存
- 初始化缓存命中统计模块
-
初始化时间轮,用于设置 key 自动过期的定时器 ```golang func NewCache(expire time.Duration, opts …CacheOption) (*Cache, error) { cache := &Cache{ data: make(map[string]interface{}), expire: expire, lruCache: emptyLruCache, // 默认是一个空的 LRU 结构,可以通过 opts 来控制 barrier: syncx.NewSharedCalls(),// 解决缓存击穿的核心方法 unstableExpiry: mathx.NewUnstable(expiryDeviation),// 框架自己做的一个并发安全的随机数 }
for _, opt := range opts { opt(cache) // 应用配置 }
// 缓存命中统计模块,初始化
cache.stats = newCacheStat(cache.name, cache.size)
// 定时器 - 时间轮模块,初始化
timingWheel, err := NewTimingWheel(time.Second, slots, func(k, v interface{}) {
key, ok := k.(string)
if !ok {
return
}
cache.Del(key)
})
//...
return cache, nil } ```
2、Get 操作
- 调用
doGet查询,查询命中,更新 LRU - 统计缓存命中率
// Get returns the item with the given key from c.
func (c *Cache) Get(key string) (interface{}, bool) {
value, ok := c.doGet(key)
if ok {
// 统计命中率
c.stats.IncrementHit()
} else {
// 统计 miss 率
c.stats.IncrementMiss()
}
return value, ok
}
func (c *Cache) doGet(key string) (interface{}, bool) {
c.lock.Lock()
defer c.lock.Unlock()
value, ok := c.data[key]
if ok {
//lru 操作
c.lruCache.add(key)
}
return value, ok
}
3、Set 操作
注意 Set 操作时,如果 key 已经存在,那么 c.timingWheel.MoveTimer 更新时间轮的定时器;否则调用 c.timingWheel.SetTimer 初始化定时器。
// Set sets value into c with key.
func (c *Cache) Set(key string, value interface{}) {
c.SetWithExpire(key, value, c.expire)
}
// SetWithExpire sets value into c with key and expire with the given value.
func (c *Cache) SetWithExpire(key string, value interface{}, expire time.Duration) {
c.lock.Lock()
_, ok := c.data[key]
c.data[key] = value
c.lruCache.add(key)
c.lock.Unlock()
expiry := c.unstableExpiry.AroundDuration(expire)
if ok {
c.timingWheel.MoveTimer(key, expiry)
} else {
c.timingWheel.SetTimer(key, value, expiry)
}
}
4、Del 操作
- 删除 key
- 删除 LRU 链中的 key
- 并且从时间轮中移除该 key(异步的)
// Del deletes the item with the given key from c. func (c *Cache) Del(key string) { c.lock.Lock() delete(c.data, key) c.lruCache.remove(key) c.lock.Unlock() c.timingWheel.RemoveTimer(key) }
0x02 最基础的 LRU 算法
go-zero 提供了 lru 的实现接口及一个内置的 keyLru 实现,开发者可以自己实现对应的 LRU 逻辑:
type lru interface {
add(key string) // 调用 LRU 的方法操作一个 key
remove(key string)
}
LRU 核心思路
一般采用链表方式实现 LRU 链,因为插入和删除的时间复杂度都是 O(1):
Set插入方法:直接将新数据插入到 LRU 链表头部Get查询方法:每当缓存命中(即缓存数据被访问),则将数据移到链表头部- 容量超过上限的解决方法:当链表满的时候,直接将链表尾部的数据丢弃
Del删除方法:直接删除链表中对应的节点即可
KeyLRU 的实现
PS:golang 标准库的 container/list 默认不是并发安全的,所以这里针对的 LRU 的操作必须要加锁(go-zero 中 LRU 的操作和 map 操作共用一把锁)
type keyLru struct {
limit int // 总长度
evicts *list.List // cache中LRU的链
elements map[string]*list.Element// 存放的是元素在链表中的地址。利用 MAP 查询,不用遍历链表即可找到需要的元素的地址
onEvict func(key string) // 删除的回调方法
}
这里的小技巧是通过 elements 这个 map 把链表元素的指针存储下来,减小链表查询的耗时,典型的空间换时间策略。
1、add 操作
- 当元素已经存在(依靠
elements),直接移动到最前 - 不存在直接添加在最前
-
当LRU超过容量限制时,删掉末尾的(同时还需要删除缓存中的该元素) ```golang func (klru *keyLru) add(key string) { if elem, ok := klru.elements[key]; ok { klru.evicts.MoveToFront(elem)// 如果新增元素已存在,就直接移到最前面 return }
elem := klru.evicts.PushFront(key)// 在链表最前面增加一个元素 klru.elements[key] = elem // 记录这个元素的地址
if klru.evicts.Len()> klru.limit { klru.removeOldest()// 如果链表的最大长度超过配置,移除最老的元素 } }
func (klru *keyLru) removeOldest() { elem := klru.evicts.Back()// 取链表最后一个元素 if elem != nil { klru.removeElement(elem) // 移除元素 } }
2、`remove` 操作<br>
删除数据时,还需要删除LRU链
```golang
func (klru *keyLru) remove(key string) {
if elem, ok := klru.elements[key]; ok {
klru.removeElement(elem)
}
}
func (klru *keyLru) removeElement(e *list.Element) {
klru.evicts.Remove(e)// 移除链表中的元素
key := e.Value.(string)// 获取 Key
delete(klru.elements, key)// 移除 MAP 中的元素
klru.onEvict(key) // 执行删除的后置操作
}
0x03 解决缓存击穿
0x04 缓存的命中统计
type cacheStat struct {
name string // 名称,最后打印日志记录是要用到
hit uint64 // 命中缓存次数
miss uint64 // 未命中次数
sizeCallback func() int // 自定义回调函数,会在打印结果的时候用到
}
func (cs *cacheStat) IncrementHit() {
atomic.AddUint64(&cs.hit, 1) // 记录命中次数
}
func (cs *cacheStat) IncrementMiss() {
atomic.AddUint64(&cs.miss, 1)
}
0x05 总结
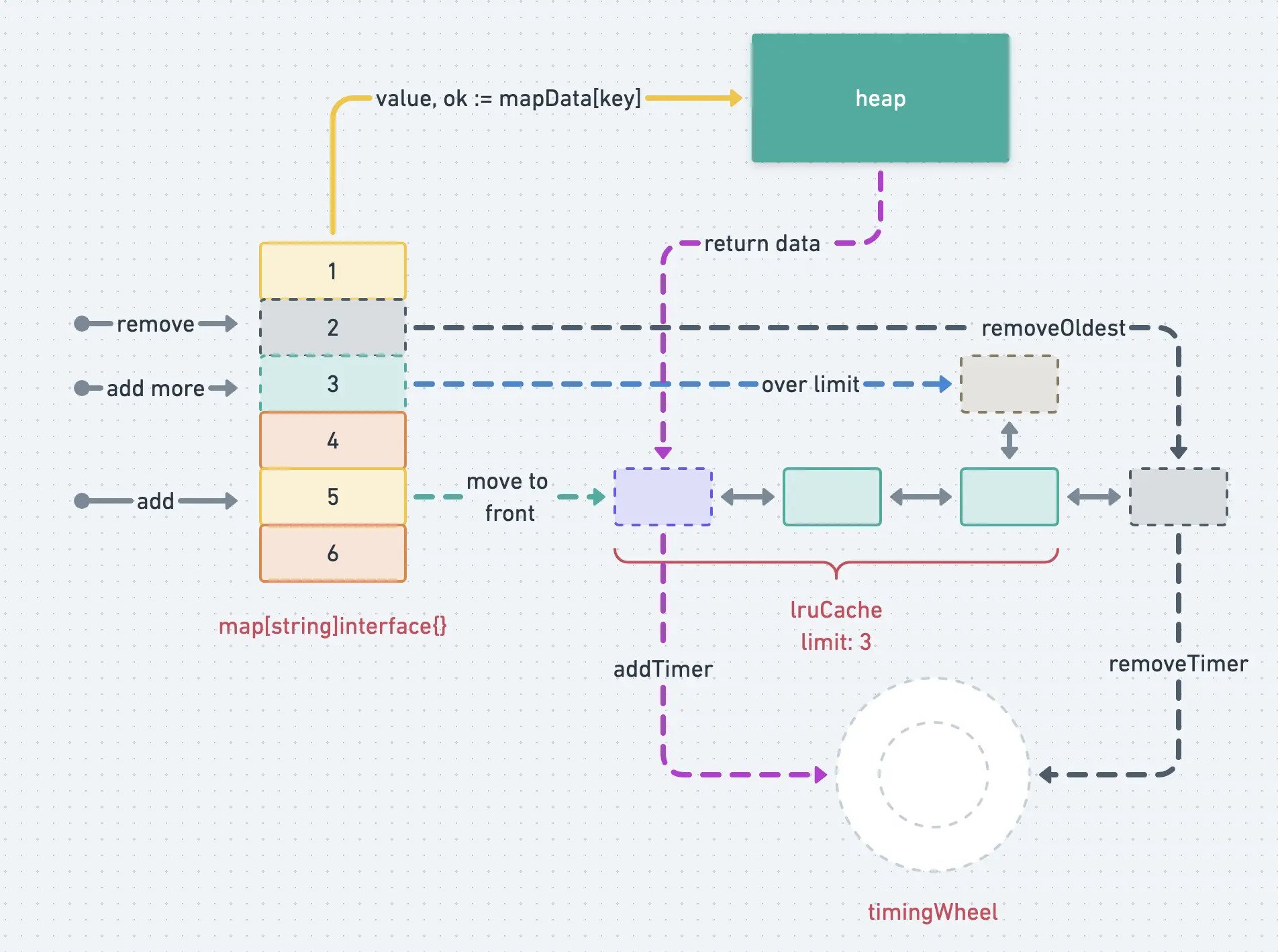
官网文件给的结构体很直观了:
0x06 参考
Related Issues not found
Please contact @pandaychen to initialize the comment
Recommend
About Joyk
Aggregate valuable and interesting links.
Joyk means Joy of geeK