
0

数据结构与算法回顾(四):环形内存缓冲区 ringbuffer(TODO FIX)
source link: https://pandaychen.github.io/2022/04/05/A-LINIX-C-BASED-RING-BUFFER-ANALYSIS/
Go to the source link to view the article. You can view the picture content, updated content and better typesetting reading experience. If the link is broken, please click the button below to view the snapshot at that time.
0x00 前言
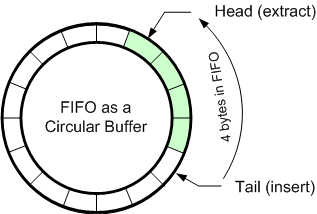
环形队列是一种 FIFO 数据结构,适合内存 / 共享内存的存储场景,是项目中解耦模块间(进程间)通信的可用手段之一。通常也称为 Ring Buffer、Circular Buffer。下图描绘了一个 A 24-byte keyboard circular buffer:
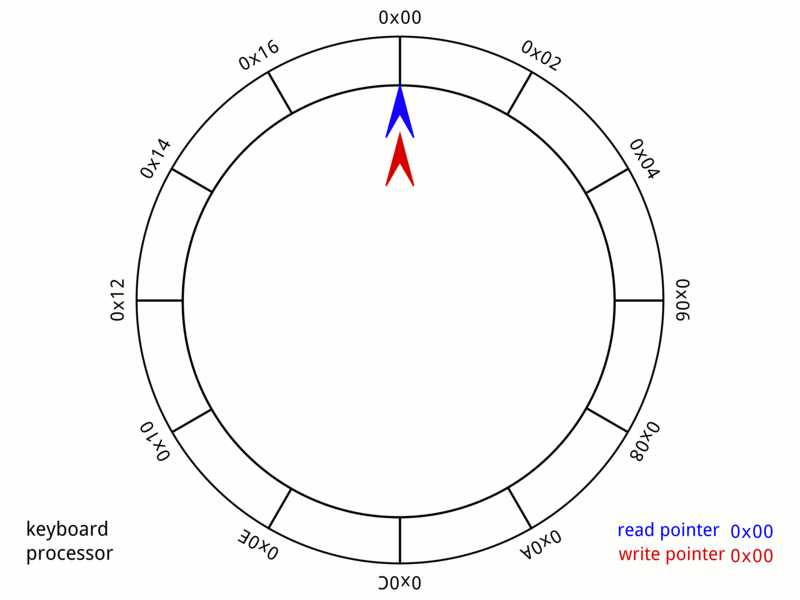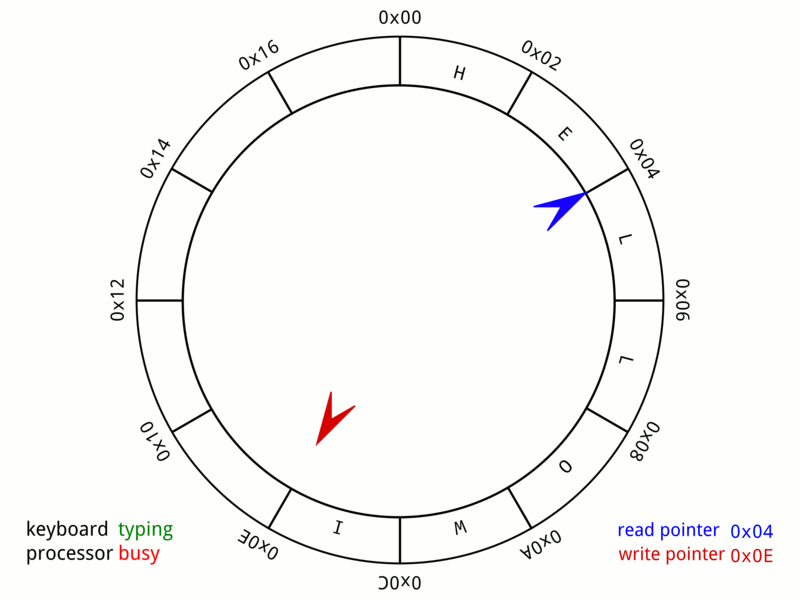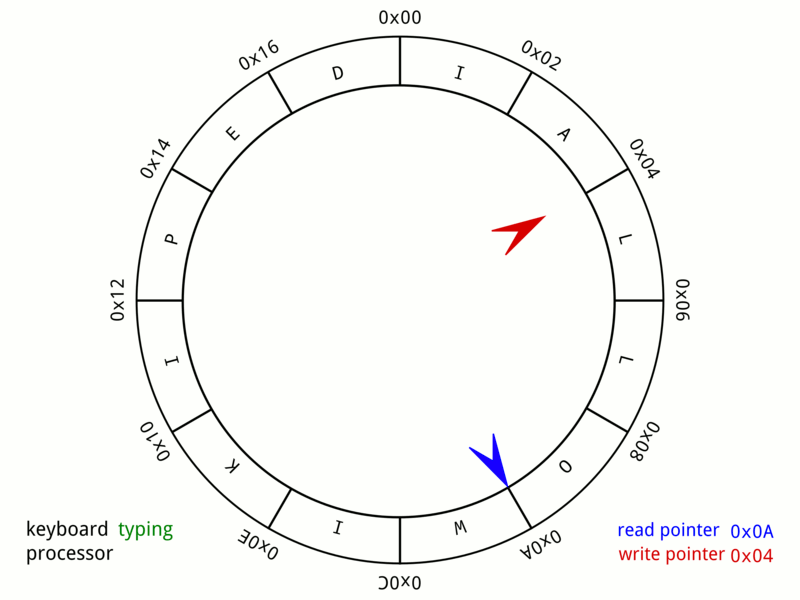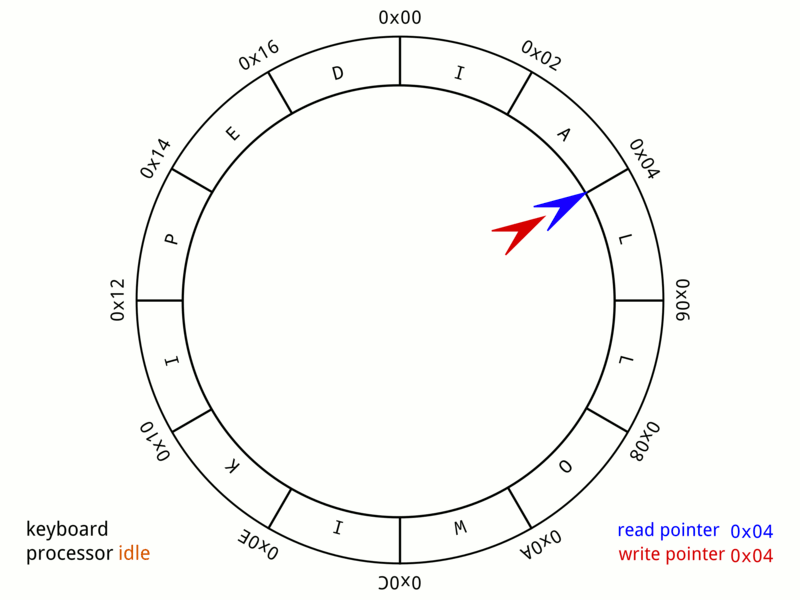
0x01 实现
ringbuffer 的实现主要依赖于读写指针的移动(head-ReadIndex/tail-WriteIndex):
- 初始化一块定长的内存(或共享内存)作为存储空间,长度即为
m_size - 通过
mod m_size得出 ReadIndex/WriteIndex 的相对位置,进而实现 “环形” 的机制 - 写入 / 读取操作时需要考虑边界情况,写入需要移动
tail指针,读取需要移动head指针
0x02 现网应用
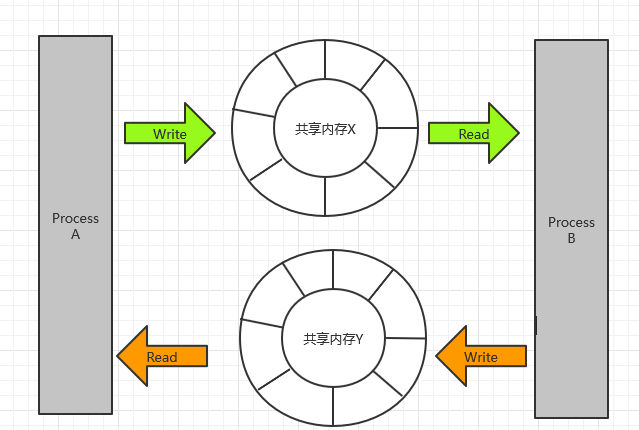
基于 ringbuffer 可以实现无锁的通信,在现网项目中,会遇到进程间通信的场景,及两个进程(进程 A 和进程 B)需要进行双向数据通信,如何无锁化实现呢?这就可以借用 ringbuffer,实现思路如下:
- 创建两块固定大小的共享内存(共享内存
X和共享内存Y),每个共享存储单元的数据头信息结构为DataHead,数据体信息为DataUnit - 当进程
A想传送数据体信息给进程B时,进程A向共享内存X写入数据体信息,变更共享内存 A 中的DataHead中的tail信息,进程B从共享内存X读出数据体信息,变更共享内存X中的DataHead中的head信息 - 同样的方式,当进程
B想传送数据体信息给进程A时,进程B向共享内存Y写入数据体信息,变更共享内存Y中的DataHead中的tail信息,进程A从共享内存Y读出数据体信息,变更共享内存Y中的DataHead中的head信息 - 整个交互过程中,进程
A与进程B无缝的通过 ringbuffer 进行通信,实现了进程间通信效率的最大化
流程图如下:
0x03 代码实现
整个存储结构如下:
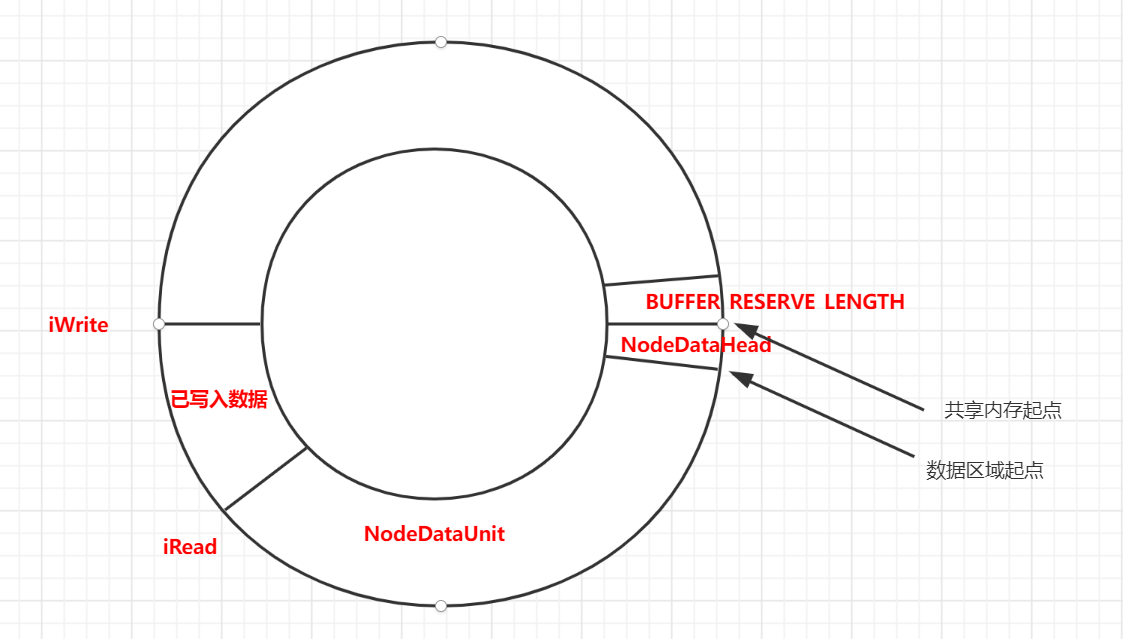
数据结构定义
每个存储在内存中的数据都包括如下两个结构 DataHead 和 DataUnit:
DataHead:内存数据头结构DataUnit:内存数据体结构(变长)
struct NodeDataHead
{
int iSize;
int iTail; // 写入数据更新位置
int iHead; // 读取数据更新位置
int iOffset;
};
struct NodeDataUnit
{
int iLen; // 可变长
char *pData;
};
0x04 总结
代码实现在此
0x05 参考
Related Issues not found
Please contact @pandaychen to initialize the comment
Recommend
About Joyk
Aggregate valuable and interesting links.
Joyk means Joy of geeK