

Eesen中的CTC实现
source link: http://placebokkk.github.io/asr/2020/01/13/asr-ctc-eesen.html
Go to the source link to view the article. You can view the picture content, updated content and better typesetting reading experience. If the link is broken, please click the button below to view the snapshot at that time.
Eesen的CTC框架
- 准备输入feature:利用kaldi的工具提取
- 准备输出label数据
- phone text根据字典变为phone序列
- charactor/grapheme 单词拆分成,增加space
- 利用kaldi nnet1框架,实现CTC损失函数,直接训练神经网络的声学模型
- extract_net_output得到feature通过网络的输出
- 构建 TLG解码图,T可以是phone或者char
- 利用lattice decoder解码输出,kaldi中HCLG fst的input是transition-id,eesen中是token-id.
其中第3步和第4步也可以使用其他框架实现, 我实现了一个pytorch版本,可以复现eesen中的wsj数据集上的结果。
Eesen中CTC的训练
Eesen中CTC的实现和原始论文的推导很接近,没做什么优化,很适合用来学习理解CTC。 但是Eesen的CTC实现在梯度的计算上,没有直接使用论文中最后得到softmax前的a值的导数公式,而是先求出softmax后的y值的导数,再求出a值的导数,因此和原论文的公式并不相同。 本文主要对此进行解释。
src/net/ctc-loss.cc文件中Ctc::Eval和Ctc::EvalParallel都是计算CTC损失对softmax前的a值的导数,区别是前者计算单个样本,后者计算一组(Batch)样本。
下面仅对Ctc::Eval进行说明
CTC的前向后向计算
在首尾和字符间插入blank,(l变为l'),如abbc变为-a-b-b-c-,长度n变为L=2n+1
diff->Resize(net_out.NumRows(), net_out.NumCols());
int32 num_frames = net_out.NumRows();
int32 num_classes = net_out.NumCols();
// label expansion by inserting blank (indexed by 0) at the beginning and end,
// and between every pair of labels
int32 len_labels = label.size();
int32 exp_len_labels = 2*len_labels + 1;
label_expand_.resize(0);
label_expand_.resize(exp_len_labels, 0);
for (int l = 0; l < len_labels; l++) {
label_expand_[2*l+1] = label[l];
}前后向算法是在log域上进行计算的,对NN的softmax输出值取log
// compute in log scale
CuMatrix<BaseFloat> log_nnet_out(net_out);
log_nnet_out.ApplyLog();计算前向alpha和后向beta值
alpha_.Resize(num_frames, exp_len_labels, kSetZero);
beta_.Resize(num_frames, exp_len_labels, kSetZero);
for (int t = 0; t < num_frames; t++) {
alpha_.ComputeCtcAlpha(log_nnet_out, t, label_expand_, false);
}
for (int t = (num_frames - 1); t >= 0; t--) {
beta_.ComputeCtcBeta(log_nnet_out, t, label_expand_, false);
}ComputeCtcAlpha和ComputeCtcBeta分别计算前向和后向值,算法类似,本文只讨论前者。ComputeCtcAlpha会调用_compute_ctc_alpha_one_sequence(位于/src/gpucompute/cuda-kernels.cu)完成实际计算。
template<typename Real>
__global__
static void _compute_ctc_alpha_one_sequence(Real* mat_alpha, int row, MatrixDim dim_alpha, const Real* mat_prob, MatrixDim dim_prob, const int32_cuda* labels) {
...
if (row == 0) {
if (i < 2) mat_alpha[index_alpha] = mat_prob[index_prob];
else mat_alpha[index_alpha] = NumericLimits<Real>::log_zero_;
} else {
if (i > 1) {
if (i % 2 == 0 || labels[i-2] == labels[i]) {
mat_alpha[index_alpha] = AddAB(mat_prob[index_prob], LogAPlusB(mat_alpha[index_alpha_rm1_im1], mat_alpha[index_alpha_rm1_i]));
} else {
Real tmp = LogAPlusB(mat_alpha[index_alpha_rm1_im1], mat_alpha[index_alpha_rm1_i]);
mat_alpha[index_alpha] = AddAB(mat_prob[index_prob], LogAPlusB(mat_alpha[index_alpha_rm1_im2], tmp));
}
} else if (i == 1) {
mat_alpha[index_alpha] = AddAB(mat_prob[index_prob], LogAPlusB(mat_alpha[index_alpha_rm1_im1], mat_alpha[index_alpha_rm1_i]));
} else {
mat_alpha[index_alpha] = AddAB(mat_prob[index_prob], mat_alpha[index_alpha_rm1_i]);
}
}
}参考论文公式
αt(s)={ˉαt(s)yt1′s if l′s=b or l′s−2=l′s(ˉαt(s)+αt−1(s−2))yt1′s otherwise
ˉαt(s) def =αt−1(s)+αt−1(s−1)
很容易理解上述代码逻辑。 这里涉及CTC里针对CTC前向计算的cuda kernel的设计,但是和CTC的算法本身无关,这里先跳过,本文后面章节会介绍cuda相关的知识
计算条件似然函数
接着根据公式 Z=p(l|x)=α(T,L)+α(T,L−1) 计算当前模型下条件似然的值
// compute the log-likelihood of the label sequence given the inputs logP(z|x)
BaseFloat tmp1 = alpha_(num_frames-1, exp_len_labels-1);
BaseFloat tmp2 = alpha_(num_frames-1, exp_len_labels-2);
BaseFloat pzx = tmp1 + log(1 + ExpA(tmp2 - tmp1));这里alpha和beta都是log域的量.已知log(a)和log(b),求log(a+b) log(a+b)=log(a)+log(1+exp(log(b)−log(a))),if b<a=log(b)+log(1+exp(log(a)−log(b))),if a<b
所以pzx = tmp1 + log(1 + ExpA(tmp2 - tmp1)) 等价于log(exp(tmp1)+exp(tmp2)).
CTC的反向传播导数
t时刻的输出softmax函数为
p(ytk)=exp(atk)∑Kk′expatk′
原始论文中公式(16)直接有a值的导数公式:
∂−lnp(l|x)∂atk=ytk−1ytkp(l|x)∑s∈lab(z,k)ˆαt(s)ˆβt(s)
但是eesen中没有使用该公式,而是先计算y值(softmax之后)的导数,再计算a值(softmax之前)的导数.
softmax后y值的导数
梯度法求的是极小值,因此最大化似然等价于最小化似然的负数,从而目标是求-p(l|x)对a的导数。整体代码如下:
// gradients from CTC
ctc_err_.Resize(num_frames, num_classes, kSetZero);
ctc_err_.ComputeCtcErrorMSeq(alpha_, beta_, net_out, label_expand_, frame_num_utt, pzx); // here should use the original ??
// back-propagate the errors through the softmax layer
ctc_err_.MulElements(net_out);
CuVector<BaseFloat> row_sum(num_frames, kSetZero);
row_sum.AddColSumMat(1.0, ctc_err_, 0.0);
CuMatrix<BaseFloat> net_out_tmp(net_out);
net_out_tmp.MulRowsVec(row_sum);
diff->CopyFromMat(ctc_err_);
diff->AddMat(-1.0, net_out_tmp);一步步看,先看
ctc_err_.ComputeCtcError(alpha_, beta_, net_out, label_expand_, pzx); 首先计算softmax后y值的导数,保存在ctc_err_中。ctc_err_是一个T行K列的矩阵, T是序列长度,K是output个数, 则ctc_err_矩阵中第t行k列的值为
Etk=∂−ln(p(l|x))∂ytk=−1p(l|x)∂p(l|x)∂ytk
已知论文中的公式
∂p(l|x)∂ytk=1(ytk)2∑s∈lab(1,k)αt(s)βt(s)
Etk=−1p(l|x)1(ytk)2∑s∈lab(1,k)αt(s)βt(s)=−exp{log{∑s∈lab(1,k)αt(s)βt(s))}−logp(l|x)−2logytk}
ComputeCtcError会调用_compute_ctc_error_one_sequence(位于/src/gpucompute/cuda-kernels.cu),其计算过程和上式最后一行完全一致。
// mat_prob are in probability scale.
template<typename Real>
__global__
static void _compute_ctc_error_one_sequence(Real* mat_error, MatrixDim dim_error, const Real* mat_alpha, const Real* mat_beta, MatrixDim dim_alpha, const Real* mat_prob, const int32_cuda* labels, Real pzx) {
int32_cuda i = blockIdx.x * blockDim.x + threadIdx.x; // row index
int32_cuda j = blockIdx.y * blockDim.y + threadIdx.y; // column index
if (i < dim_error.rows && j < dim_error.cols) {
Real err = NumericLimits<Real>::log_zero_;
int32_cuda index_error = i * dim_error.stride + j;
for(int s = 0; s < dim_alpha.cols; s++) {
if (labels[s] == j) { //
int32_cuda index_alpha = i * dim_alpha.stride + s;
err = LogAPlusB(err, AddAB(mat_alpha[index_alpha], mat_beta[index_alpha]));
}
}
Real val = ExpA(SubAB(err, AddAB(pzx, mat_prob[index_error] == 0? NumericLimits<Real>::log_zero_ : 2*log(mat_prob[index_error]))));
mat_error[index_error] = -1.0 * val;
}
}softmax前a值的导数
接着计算softmax之前a值的导数。我们先推导出计算公式:
∂−lnp(l|x)∂atk=K∑k′∂−lnp(l|x)∂ytk′∂ytk′∂atk=K∑k′Etk′⋅∂ytk′∂atk
其中softmax的输入y对输出a的导数
∂ytk′∂atk=ytk′∂lnytk′∂atk=ytk′(δkk′−ytk)
∂−lnp(l|x)∂atk=K∑k′Etk′ytk′⋅(δkk′−ytk)=K∑k′Etk′ytk′δkk′−K∑k′Etk′ytk′ytk=Etkytk−K∑k′Etk′ytk′ytk=Etkytk−(K∑k′Etk′ytk′)ytk
// back-propagate the errors through the softmax layer
ctc_err_.MulElements(net_out);
CuVector<BaseFloat> row_sum(num_frames, kSetZero);
row_sum.AddColSumMat(1.0, ctc_err_, 0.0);ctc_err_.MulElements(net_out);对两个相同大小的矩阵做elementwise乘法,得到一个矩阵,其第t行第k列的值是 Etkytk
row_sum.AddColSumMat(1.0, ctc_err_, 0.0);将上述的矩阵的列相加,得到一个T*1 的矩阵(后者叫T维列向量),其第t行的值是 ∑Kk′Etk′ytk′
CuMatrix<BaseFloat> net_out_tmp(net_out);
net_out_tmp.MulRowsVec(row_sum);MulRowsVec对net_out_tmp 中的第n行里的每个值,都乘上row_sum的第n维值。从而net_out_tmp计算后得到了一个矩阵,其第t行k列的值是 (∑Kk′Etk′ytk′)ytk
diff->CopyFromMat(ctc_err_);
diff->AddMat(-1.0, net_out_tmp);diff是一个T*K的矩阵,其第t行k列的值为,即
Etkytk−(K∑k′Etk′ytk′)ytk
关于Cuda计算的介绍
Cuda的计算架构里有Grid/Block/Thread概念。
- 一个Grid里有多个Block。
- 一个Block里有多个Thread。
- 每个Cuda Kernel在一个Thread上计算。Thread之间是并行的。
- Grid和Block的布局可以是1,2,3维的。
设计一个算法的cuda版本,需要考虑如何把算法分配到Thread上并行计算。
Eesen里的CTC里的Alpha
//eesen/src/net/ctc-loss.cc
void Ctc::Eval(...){
...
alpha_.Resize(num_frames, exp_len_labels, kSetZero);
for (int t = 0; t < num_frames; t++) {
alpha_.ComputeCtcAlpha(log_nnet_out, t, label_expand_, false);
}
...
}- exp_len_labels是在标注序列的首尾及各字符之间插入blank扩展后的序列。原序列长度
n,则新序列长度为L=2n+1 - alpha_是一个num_frames行,exp_len_labels列的矩阵。每一行对应一个时间帧t。
ComputeCtcAlpha里的cuda
//eesen/src/gpucompute/cuda-matrix.cc
template<typename Real>
void CuMatrixBase<Real>::ComputeCtcAlpha(const CuMatrixBase<Real> &prob,
int32 row_idx,
const std::vector<MatrixIndexT> &labels,
bool rescale) {
MatrixIndexT prob_cols = prob.NumCols();
CuArray<MatrixIndexT> cuda_labels(labels);
int dimBlock(CU1DBLOCK);
int dimGrid(n_blocks(num_cols_,CU1DBLOCK));
cuda_compute_ctc_alpha(dimGrid, dimBlock, data_, row_idx, Dim(), prob.data_, prob.Dim(), cuda_labels.Data());
}
inline void cuda_compute_ctc_alpha(dim3 Gr, dim3 Bl, float *alpha, int row_idx, MatrixDim dim_alpha, const float *prob, MatrixDim dim_prob, const int *labels) {
cudaF_compute_ctc_alpha(Gr, Bl, alpha, row_idx, dim_alpha, prob, dim_prob, labels);
}
void cudaF_compute_ctc_alpha(dim3 Gr, dim3 Bl, float *alpha, int row_idx, MatrixDim dim_alpha, const float *prob, MatrixDim dim_prob, const int *labels) {
_compute_ctc_alpha_one_sequence<<<Gr, Bl>>>(alpha, row_idx, dim_alpha, prob, dim_prob, labels);
}其中CU1DBLOCK定义为256
eesen/src/gpucompute/cuda-matrixdim.h
// The size of a CUDA 1-d block, e.g. for vector operations..
#define CU1DBLOCK 256n_blocks用于确定一个Grid里Block的个数
//eesen/src/gpucompute/cuda-common.h
inline int32 n_blocks(int32 size, int32 block_size) {
return size / block_size + ((size % block_size == 0)? 0 : 1);
}假设exp_len_labels的长度为L,则n_blocks=L/256.
所以cuda_compute_ctc_alpha的一个Grid里有L/256个Block, 一个Block里有256个Thread
现在再看最终调用的_compute_ctc_alpha_one_sequence«<Gr, Bl»>()的完整代码。
template<typename Real>
__global__
static void _compute_ctc_alpha_one_sequence(Real* mat_alpha, int row, MatrixDim dim_alpha, const Real* mat_prob, MatrixDim dim_prob, const int32_cuda* labels) {
int32_cuda i = blockIdx.x * blockDim.x + threadIdx.x;
int32_cuda dim = dim_alpha.cols;
if (i < dim) {
int32_cuda index_alpha = i + row * dim_alpha.stride;
int32_cuda class_idx = labels[i];
int32_cuda index_prob = class_idx + row * dim_prob.stride;
int32_cuda index_alpha_rm1_i = i + (row - 1) * dim_alpha.stride;
int32_cuda index_alpha_rm1_im1 = (i - 1) + (row - 1) * dim_alpha.stride;
int32_cuda index_alpha_rm1_im2 = (i - 2) + (row - 1) * dim_alpha.stride;
if (row == 0) {
if (i < 2) mat_alpha[index_alpha] = mat_prob[index_prob];
else mat_alpha[index_alpha] = NumericLimits<Real>::log_zero_;
} else {
if (i > 1) {
if (i % 2 == 0 || labels[i-2] == labels[i]) {
mat_alpha[index_alpha] = AddAB(mat_prob[index_prob], LogAPlusB(mat_alpha[index_alpha_rm1_im1], mat_alpha[index_alpha_rm1_i]));
} else {
Real tmp = LogAPlusB(mat_alpha[index_alpha_rm1_im1], mat_alpha[index_alpha_rm1_i]);
mat_alpha[index_alpha] = AddAB(mat_prob[index_prob], LogAPlusB(mat_alpha[index_alpha_rm1_im2], tmp));
}
} else if (i == 1) {
mat_alpha[index_alpha] = AddAB(mat_prob[index_prob], LogAPlusB(mat_alpha[index_alpha_rm1_im1], mat_alpha[index_alpha_rm1_i]));
} else {
mat_alpha[index_alpha] = AddAB(mat_prob[index_prob], mat_alpha[index_alpha_rm1_i]);
}
}
}
}Cuda里计算t时刻CTC Alpha的划分如下图,代码中的i对应图中纵坐标(从上往下),row(即t)对应横坐标。每个block对应图中的一个框,其中有256个thread。每个thread计算一个圆圈上的统计量。
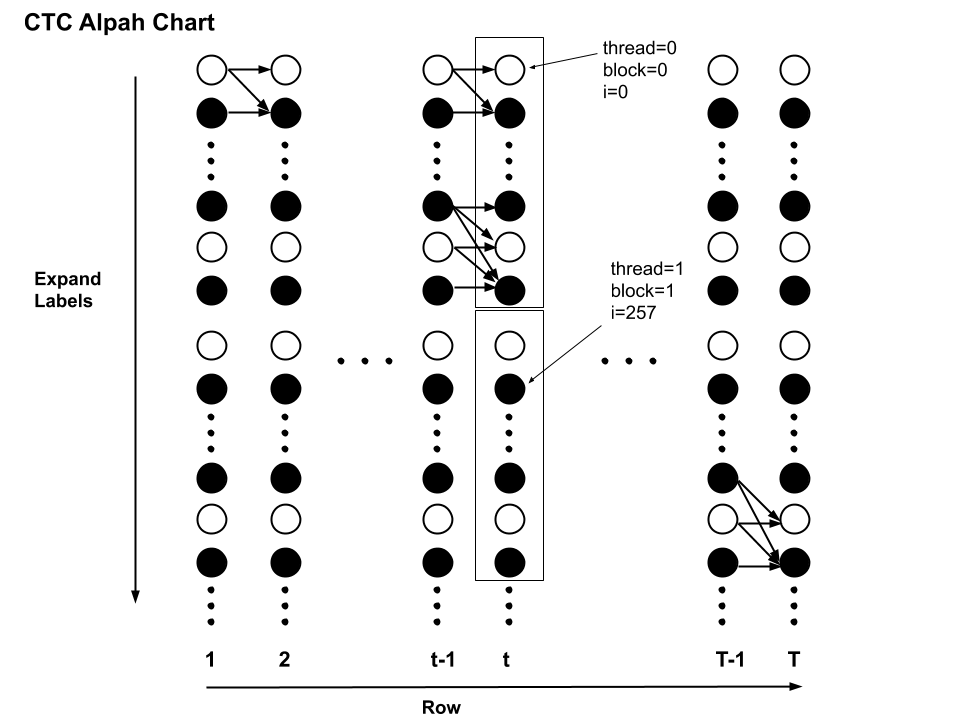
结合图看代码:
- index_alpha_*记录前向统计量矩阵中的index,比如index_alpha_rm1_im1表示,r是row的意思,也就是时间帧t,其中m是minus的意思,即(t-1,i-1)对应的alpha矩阵中的index
- index_prob记录当前thread(t时刻,expand-label第i个位置)的label在网络输出的prob矩阵中的index
if (i < dim): 这里dim即label的长度L,因为L不一定是Blocksize(256)的整数倍,所以最后一个block里的i可能会大于L,因此if (i < dim)是必要的。
另外,因为CTC本身的性质,t时刻只能计算到t*2位置的label的alpha值,所以这里if (i < dim)可以改为 if (i < 2*row + 1 && i < dim),减小一些的计算量。不过因为一般T都远大于L,所以减少的计算量也不多。
Eesen中的CTC的解码[待更新]
解码图构建
Recommend
About Joyk
Aggregate valuable and interesting links.
Joyk means Joy of geeK