

一文搞懂 | Linux 时钟子系统
source link: https://os.51cto.com/article/706272.html
Go to the source link to view the article. You can view the picture content, updated content and better typesetting reading experience. If the link is broken, please click the button below to view the snapshot at that time.


不同的clock设置,需要从某个或某几个时钟源头而来,最终开枝散叶,形成一颗时钟树。可通过 cat /sys/kernel/debug/clk/clk_summary 查看这棵时钟树。
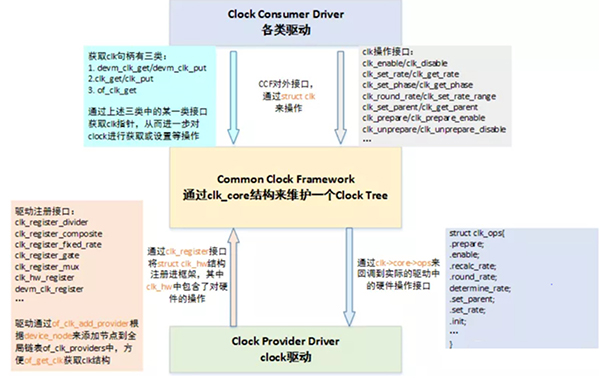
内核中用 CCF 框架来管理 clock,如下所示,右边是 clock 提供者,即 Clock Provider;中间是 CCF;左边是设备驱动的 clock 使用者,即 Clock Consumer。
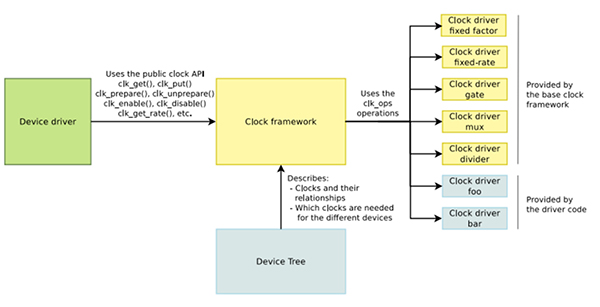
Clock Provider
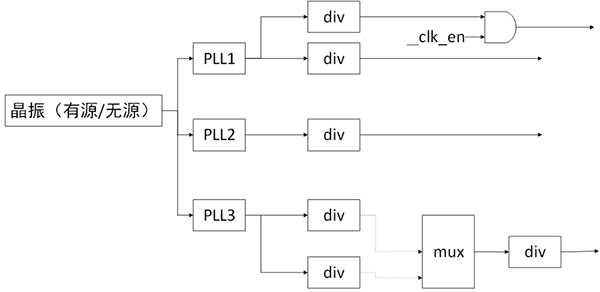
- 根节点一般是 Oscillator(有源振荡器)或者 Crystal(无源振荡器)。
- 中间节点有很多种,包括 PLL(锁相环,用于提升频率的),Divider(分频器,用于降频的),Mux(从多个clock path中选择一个),Gate(用来控制ON/OFF的)。
- 叶节点是使用 clock 做为输入的、有具体功能的 HW block。
根据 clock 的特点,clock framework 将 clock 分为 fixed rate、gate、devider、mux、fixed factor、composite 六类。
上面六类本质上都属于clock device,内核把这些 clock HW block 的特性抽取出来,用 struct clk_hw 来表示,具体如下:
struct clk_hw {
//指向CCF模块中对应 clock device 实例
struct clk_core *core;
//clk是访问clk_core的实例。每当consumer通过clk_get对CCF中的clock device(也就是clk_core)发起访问的时候都需要获取一个句柄,也就是clk
struct clk *clk;
//clock provider driver初始化时的数据,数据被用来初始化clk_hw对应的clk_core数据结构。
const struct clk_init_data *init;
};
struct clk_init_data {
//该clock设备的名字
const char *name;
//clock provider driver进行具体的 HW 操作
const struct clk_ops *ops;
//描述该clk_hw的拓扑结构
const char * const *parent_names;
const struct clk_parent_data *parent_data;
const struct clk_hw **parent_hws;
u8 num_parents;
unsigned long flags;
};
以固定频率的振动器 fixed rate 为例,它的数据结构是:
struct clk_fixed_rate {
//下面是fixed rate这种clock device特有的成员
struct clk_hw hw;
//基类
unsigned long fixed_rate;
unsigned long fixed_accuracy;
u8 flags;
};
其他的特定的clock device大概都是如此,这里就不赘述了。
这里用一张图描述这些数据结构之间的关系:
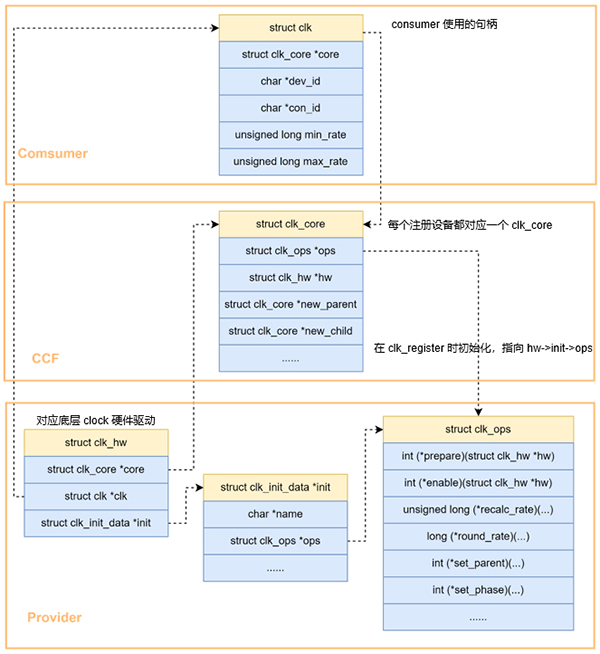
理解了数据结构,我们再看下每类 clock device 的注册方式。
1. fixed rate clock
这一类clock具有固定的频率,不能开关、不能调整频率、不能选择parent,是最简单的一类clock。可以直接通过 DTS 配置的方式支持。也可以通过接口,可以直接注册 fixed rate clock,如下:
CLK_OF_DECLARE(fixed_clk, "fixed-clock", of_fixed_clk_setup);
struct clk *clk_register_fixed_rate(struct device *dev, const char *name,
const char *parent_name, unsigned long flags,
unsigned long fixed_rate);
2. gate clock
这一类clock只可开关(会提供.enable/.disable回调),可使用下面接口注册:
struct clk *clk_register_gate(struct device *dev, const char *name,
const char *parent_name, unsigned long flags,
void __iomem *reg, u8 bit_idx,
u8 clk_gate_flags, spinlock_t *lock);
3. divider clock
这一类clock可以设置分频值(因而会提供.recalc_rate/.set_rate/.round_rate回调),可通过下面两个接口注册:
struct clk *clk_register_divider(struct device *dev, const char *name,
const char *parent_name, unsigned long flags,
void __iomem *reg, u8 shift, u8 width,
u8 clk_divider_flags, spinlock_t *lock);
struct clk *clk_register_divider_table(struct device *dev, const char *name,
const char *parent_name, unsigned long flags,
void __iomem *reg, u8 shift, u8 width,
u8 clk_divider_flags, const struct clk_div_table *table,
spinlock_t *lock);
4. mux clock
这一类clock可以选择多个parent,因为会实现.get_parent/.set_parent/.recalc_rate回调,可通过下面两个接口注册:
struct clk *clk_register_mux(struct device *dev, const char *name,
const char **parent_names, u8 num_parents, unsigned long flags,
void __iomem *reg, u8 shift, u8 width,
u8 clk_mux_flags, spinlock_t *lock);
struct clk *clk_register_mux_table(struct device *dev, const char *name,
const char **parent_names, u8 num_parents, unsigned long flags,
void __iomem *reg, u8 shift, u32 mask,
u8 clk_mux_flags, u32 *table, spinlock_t *lock);
5. fixed factor clock
这一类clock具有固定的factor(即multiplier和divider),clock的频率是由parent clock的频率,乘以mul,除以div,多用于一些具有固定分频系数的clock。由于parent clock的频率可以改变,因而fix factor clock也可该改变频率,因此也会提供.recalc_rate/.set_rate/.round_rate等回调。可通过下面接口注册:
struct clk *clk_register_fixed_factor(struct device *dev, const char *name,
const char *parent_name, unsigned long flags,
unsigned int mult, unsigned int div);
6. composite clock
顾名思义,就是mux、divider、gate等clock的组合,可通过下面接口注册:
struct clk *clk_register_composite(struct device *dev, const char *name,
const char **parent_names, int num_parents,
struct clk_hw *mux_hw, const struct clk_ops *mux_ops,
struct clk_hw *rate_hw, const struct clk_ops *rate_ops,
struct clk_hw *gate_hw, const struct clk_ops *gate_ops,
unsigned long flags);
这些注册函数最终都会通过函数 clk_register 注册到 Common Clock Framework 中,返回为 struct clk 指针。如下所示:
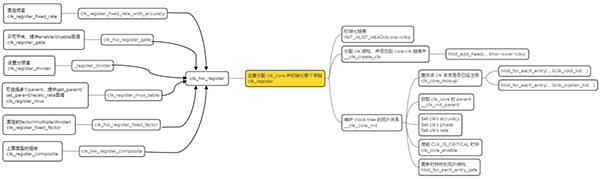
然后将返回的 struct clk 指针,保存在一个数组中,并调用 of_clk_add_provider 接口,告知 Common Clock Framework。
Clock Consumer
获取 clock
即通过 clock 名称获取 struct clk 指针的过程,由 clk_get、devm_clk_get、clk_get_sys、of_clk_get、of_clk_get_by_name、of_clk_get_from_provider 等接口负责实现,这里以 clk_get 为例,分析其实现过程:
struct clk *clk_get(struct device *dev, const char *con_id)
{
const char *dev_id = dev ? dev_name(dev) : NULL;
struct clk *clk;
if (dev) {
//通过扫描所有“clock-names”中的值,和传入的name比较,如果相同,获得它的index(即“clock-names”中的第几个),调用of_clk_get,取得clock指针。
clk = __of_clk_get_by_name(dev->of_node, dev_id, con_id);
if (!IS_ERR(clk) || PTR_ERR(clk) == -EPROBE_DEFER)
return clk;
}
return clk_get_sys(dev_id, con_id);
}
struct clk *of_clk_get(struct device_node *np, int index)
{
struct of_phandle_args clkspec;
struct clk *clk;
int rc;
if (index < 0)
return ERR_PTR(-EINVAL);
rc = of_parse_phandle_with_args(np, "clocks", "#clock-cells", index,
&clkspec);
if (rc)
return ERR_PTR(rc);
//获取clock指针
clk = of_clk_get_from_provider(&clkspec);
of_node_put(clkspec.np);
return clk;
}
of_clk_get_from_provider 通过便利 of_clk_providers 链表,并调用每一个 provider 的 get 回调函数,获取 clock 指针。如下:
struct clk *of_clk_get_from_provider(struct of_phandle_args *clkspec)
{
struct of_clk_provider *provider;
struct clk *clk = ERR_PTR(-ENOENT);
/* Check if we have such a provider in our array */
mutex_lock(&of_clk_lock);
list_for_each_entry(provider, &of_clk_providers, link) {
if (provider->node == clkspec->np)
clk = provider->get(clkspec, provider->data);
if (!IS_ERR(clk))
break;
}
mutex_unlock(&of_clk_lock);
return clk;
}
至此,Consumer 与 Provider 里讲的 of_clk_add_provider 对应起来了。
操作 clock
//启动clock前的准备工作/停止clock后的善后工作。可能会睡眠。
int clk_prepare(struct clk *clk)
void clk_unprepare(struct clk *clk)
//启动/停止clock。不会睡眠。
static inline int clk_enable(struct clk *clk)
static inline void clk_disable(struct clk *clk)
//clock频率的获取和设置
static inline unsigned long clk_get_rate(struct clk *clk)
static inline int clk_set_rate(struct clk *clk, unsigned long rate)
static inline long clk_round_rate(struct clk *clk, unsigned long rate)
//获取/选择clock的parent clock
static inline int clk_set_parent(struct clk *clk, struct clk *parent)
static inline struct clk *clk_get_parent(struct clk *clk)
//将clk_prepare和clk_enable组合起来,一起调用。将clk_disable和clk_unprepare组合起来,一起调用
static inline int clk_prepare_enable(struct clk *clk)
static inline void clk_disable_unprepare(struct clk *clk)
Recommend
-
 25
25
-
 38
38
一、前言 在用户空间接口函数文档中,我们描述了和POSIX timer相关的操作,主要包括创建一个timer、设定timer、获取timer的状态、获取timer overrun的信息、删除timer。本文将沿着这些用户空间的接口定义来看看内核态的实现。虽...
-
 11
11
配置Linux的时钟同步 2020-09-22 19:25:26 +08 字数:573 标签: Linux Ubuntu系统默认的时钟同步服务器是
-
 10
10
通过 Linux 子系统在 Windows 10 上安装 Ubuntu¶
-
 12
12
Linux时间子系统之八:动态时钟框架(CONFIG_NO_HZ、tickless) 2017-07-23 18:19:00 http://blog.csdn.net/DroidPhone/article/details/8112948
-
 18
18
Linux时间子系统之四:定时器的引擎:clock_event_device 2017-07-23 14:04:00 http://blog.csdn.net/DroidPhone/article/details/8017604
-
 13
13
Linux时间子系统之一:clock source(时钟源) 2017-07-23 12:54:00 http://blog.csdn.net/droidphone/article/details/7975694 clo...
-
 9
9
Documentation/rtc.txt http://blog.csdn.net/yaozhenguo2006/article/details/6820218 ...
-
 7
7
linux系统时间和硬件时钟问题(date和hwclock) 2016-01-06 10:48:00 http://rpf413.blog.163.com/blog/static/455637602012283144467...
-
 6
6
一文搞懂Linux系统内核的重要性 2023-03-27 09:08:11 今天我要跟大家分享一下Linux内核的重要性。内核就像Linux系统运行的大心脏,对系统的运行起到了至关重要的作用。那么Linux内核到底难不难学呢?
About Joyk
Aggregate valuable and interesting links.
Joyk means Joy of geeK