

Spring系列20:注解详解和Spring注解增强(基础内功) - kongxubihai
source link: https://www.cnblogs.com/kongbubihai/p/15989937.html
Go to the source link to view the article. You can view the picture content, updated content and better typesetting reading experience. If the link is broken, please click the button below to view the snapshot at that time.

有部分小伙伴反馈说前面基于注解的Spring中大量使用注解,由于对Java的注解不熟悉,有点难受。建议总结一篇的Java注解的基础知识,那么,它来了!
- 什么是注解?
- 如何定义注解
- 如何使用注解
- 如何获取注解信息
- Spring 中对注解做了什么增强?
什么是注解?
什么是代码中写的注释?那是给开发者看的,但是编译之后的字节码文件中是没有注释信息的,也就是说注释对于java编译器和JVM来说是没有意义的,看不到!
类比注释是给人看的,注解则是给java编译器和JVM看的一些标识,编译器和虚拟机在运行的过程中可以获取注解信息来做一些处理。
如何定义注解
注解定义的语法如下:
public @interface 注解类名{
参数类型 参数名称1() [default 参数默认值];
参数类型 参数名称2() [default 参数默认值];
}
参数名称可以没有,也可以定义多个,定义细节如下:
- 参数类型只能是基本类型、String、Class、枚举类型、注解类型以及对应的一维数组
- 如果注解参数只有1个,建议定义名称为value,方便使用时缺省参数名
- default 可以指定默认值,如果没有默认值使用注解时必须给定参数值
定义注解时候需要考虑2个主要问题:
- 注解可以使用在哪里也就是使用范围?
- 注解保留到什么阶段,源码阶段,还是运行阶段?
java提供了一部分的元注解来解决上面的问题。
@Target指定注解的使用范围
来看下源码,主要是指定了可以应用注释类型的元素种类的数组参数。
@Documented
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Target(ElementType.ANNOTATION_TYPE)
public @interface Target {
// 返回可以应用注释类型的元素种类的数组
ElementType[] value();
}
/*注解的使用范围*/
public enum ElementType {
/*类、接口、枚举、注解上面*/
TYPE,
/*字段上*/
FIELD,
/*方法上*/
METHOD,
/*方法的参数上*/
PARAMETER,
/*构造函数上*/
CONSTRUCTOR,
/*本地变量上*/
LOCAL_VARIABLE,
/*注解上*/
ANNOTATION_TYPE,
/*包上*/
PACKAGE,
/*类型参数上 1.8之后*/
TYPE_PARAMETER,
/*类型名称上 1.8之后*/
TYPE_USE
}
@Retention指定注解的保留策略
指示要保留带注释类型的注释多长时间。如果注释类型声明中不存在保留注释,则保留策略默认为 RetentionPolicy.CLASS
@Documented
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Target(ElementType.ANNOTATION_TYPE)
public @interface Retention {
RetentionPolicy value();
}
public enum RetentionPolicy {
// 源码阶段,注解被编译器丢弃。
SOURCE,
// 注释将由编译器记录在类文件中,但不需要在运行时由 VM 保留。这是默认行为。
CLASS,
// 注释将由编译器记录在类文件中,并在运行时由 VM 保留,因此可以反射性地读取它们。
RUNTIME
}
综合上面2个注解,自定义一个保留到运行期的仅用在方法上的注解如下。
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Target(ElementType.METHOD)
public @interface DemoAnnotation {
String name() default "";
Class targetClazz();
}
如何使用注解
@注解类(参数1=值1,参数2=值2,参数3=值3,参数n=值n)
目标对象
使用前一节的注解来个简单的案例
public class MyBean {
@DemoAnnotation(name = "xxx", targetClazz = MyBean.class)
public void m() {
}
}
来一个综合案例,注解位置包括类上、方法上、构造函数上、方法参数上、字段上、本地变量上、泛型类型参数和类型名称上。
/**
* 综合案例
* @author zfd
* @version v1.0
* @date 2022/1/24 13:31
* @关于我 请关注公众号 螃蟹的Java笔记 获取更多技术系列
*/
@StrongAnnotation(value = "用在类上", elementType = ElementType.TYPE)
public class UseStrongAnnotation<@StrongAnnotation(value = "用在类型参数上T0", elementType = ElementType.TYPE_PARAMETER) T0,
@StrongAnnotation(value = "用在类型名称上T1", elementType = ElementType.TYPE_USE) T1> {
@StrongAnnotation(value = "用在字段上", elementType = ElementType.FIELD)
private String field;
@StrongAnnotation(value = "构造方法上", elementType = ElementType.CONSTRUCTOR)
public UseStrongAnnotation(@StrongAnnotation(value = "用在方法参数上", elementType = ElementType.PARAMETER) String field) {
this.field = field;
}
@StrongAnnotation(value = "用在普通方法上", elementType = ElementType.METHOD)
public void m(@StrongAnnotation(value = "方法参数上", elementType = ElementType.PARAMETER) String name) {
@StrongAnnotation(value = "用在本地变量上", elementType = ElementType.LOCAL_VARIABLE)
String prefix = "hello ";
System.out.println(prefix + name);
}
public <@StrongAnnotation(value = "方法的类型参数T2上", elementType = ElementType.TYPE_PARAMETER) T2> void m1() {
}
public <@StrongAnnotation(value = "方法的类型名称T3上", elementType = ElementType.TYPE_USE) T3> void m2() {
}
private Map<@StrongAnnotation(value = "Map后面的尖括号也是类型名称", elementType = ElementType.TYPE_USE) String ,
@StrongAnnotation(value = "Map后面的尖括号也是类型名称", elementType = ElementType.TYPE_PARAMETER)Object> map;
}
如何获取注解信息
java.lang.reflect.AnnotatedElement接口表示当前在此 VM 中运行的程序的注解元素。 该接口允许以反射方式读取注解。 此接口中方法返回的所有注解都是不可变的和可序列化的。 该接口的方法返回的数组可以被调用者修改,而不影响返回给其他调用者的数组。其获取注解的主要方法如下,见名知意。
主要的实现类或接口图如下
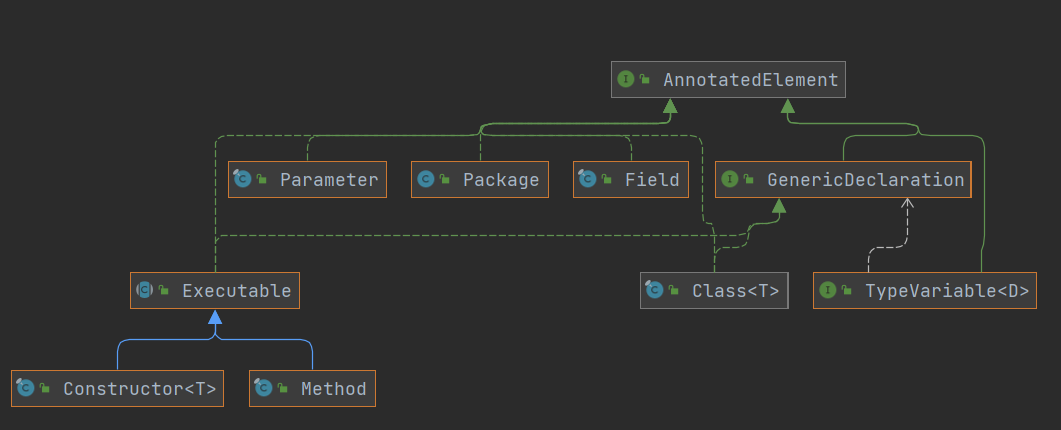
对应的实现的含义也很明确:
- Package:用来表示包的信息
- Class:用来表示类的信息
- Constructor:用来表示构造方法信息
- Field:用来表示类中属性信息
- Method:用来表示方法信息
- Parameter:用来表示方法参数信息
- TypeVariable:用来表示类型变量信息,如:类上定义的泛型类型变量,方法上面定义的泛型类型变量
来一个综合案例来解析上一节的注解使用UseStrongAnnotation。测试用例和结果如下,建议多实战敲敲代码。
package com.crab.spring.ioc.demo17;
import com.sun.xml.internal.bind.v2.model.core.ID;
import org.junit.Test;
import java.lang.annotation.Annotation;
import java.lang.reflect.*;
import java.util.Arrays;
import static org.junit.Assert.*;
/**
* @author zfd
* @version v1.0
* @date 2022/1/24 13:52
* @关于我 请关注公众号 螃蟹的Java笔记 获取更多技术系列
*/
public class UseStrongAnnotationTest {
@Test
public void test_annotated_class() {
System.out.println("解析类上注解:");
Arrays.stream(UseStrongAnnotation.class.getAnnotations())
.forEach(System.out::println);
}
// 解析类上注解:
// @com.crab.spring.ioc.demo17.StrongAnnotation(value=用在类上, elementType=TYPE)
@Test
public void test_annotated_class_type_parameter() {
TypeVariable<Class<UseStrongAnnotation>>[] typeParameters = UseStrongAnnotation.class.getTypeParameters();
for (TypeVariable<Class<UseStrongAnnotation>> typeParameter : typeParameters) {
System.out.println(typeParameter.getName() + " 1.8变量参数或变量名称注解信息:");
Annotation[] annotations = typeParameter.getAnnotations();
Arrays.stream(annotations).forEach(System.out::println);
}
}
// T0 1.8变量参数或变量名称注解信息:
// @com.crab.spring.ioc.demo17.StrongAnnotation(value=用在类型参数上T0, elementType=TYPE_PARAMETER)
// T1 1.8变量参数或变量名称注解信息:
// @com.crab.spring.ioc.demo17.StrongAnnotation(value=用在类型名称上T1, elementType=TYPE_USE)
@Test
public void test_annotated_field() throws NoSuchFieldException {
Field field = UseStrongAnnotation.class.getDeclaredField("field");
Arrays.stream(field.getAnnotations()).forEach(System.out::println);
}
// @com.crab.spring.ioc.demo17.StrongAnnotation(value=用在字段上, elementType=FIELD)
@Test
public void test_annotated_constructor() {
Constructor<?> constructor = UseStrongAnnotation.class.getDeclaredConstructors()[0];
for (Annotation annotation : constructor.getAnnotations()) {
System.out.println(annotation);
}
}
// @com.crab.spring.ioc.demo17.StrongAnnotation(value=构造方法上, elementType=CONSTRUCTO
@Test
public void test_annotated_normal_method() throws NoSuchMethodException {
Method method = UseStrongAnnotation.class.getDeclaredMethod("m", String.class);
System.out.println("方法注解:");
for (Annotation annotation : method.getAnnotations()) {
System.out.println(annotation);
}
System.out.println("方法参数注解:");
Parameter[] parameters = method.getParameters();
for (Parameter parameter : parameters) {
System.out.println(parameter.getName() + " 参数注解:");
for (Annotation annotation : parameter.getAnnotations()) {
System.out.println(annotation);
}
}
}
// 方法注解:
// @com.crab.spring.ioc.demo17.StrongAnnotation(value=用在普通方法上, elementType=METHOD)
// 方法参数注解:
// name 参数注解:
// @com.crab.spring.ioc.demo17.StrongAnnotation(value=方法参数上, elementType=PARAMETER)
@Test
public void test_annotated_map_type() throws NoSuchFieldException {
Field field = UseStrongAnnotation.class.getDeclaredField("map");
// 返回一个 Type 对象,该对象表示此 Field 对象表示的字段的声明类型。
// 如果 Type 是参数化类型,则返回的 Type 对象必须准确反映源代码中使用的实际类型参数。
Type genericType = field.getGenericType();
// 获取返回表示此类型的实际类型参数的 Type 对象数组
Type[] actualTypeArguments = ((ParameterizedType) genericType).getActualTypeArguments();
// 返回一个 AnnotatedType 对象,该对象表示使用一个类型来指定此 Field 表示的字段的声明类型。
AnnotatedType annotatedType = field.getAnnotatedType();
// 获取此参数化类型的可能带注释的实际类型参数数组
AnnotatedType[] annotatedActualTypeArguments =
((AnnotatedParameterizedType) annotatedType).getAnnotatedActualTypeArguments();
int index = 0;
for (AnnotatedType annotatedActualTypeArgument : annotatedActualTypeArguments) {
Type actualTypeArgument = actualTypeArguments[index++];
System.out.println(annotatedActualTypeArgument.getType());
System.out.println(actualTypeArgument.getTypeName() + " 类型上的注解:");
for (Annotation annotation : annotatedActualTypeArgument.getAnnotations()) {
System.out.println(annotation);
}
}
}
// T0 1.8变量参数或变量名称注解信息:
// @com.crab.spring.ioc.demo17.StrongAnnotation(value=用在类型参数上T0, elementType=TYPE_PARAMETER)
// T1 1.8变量参数或变量名称注解信息:
// @com.crab.spring.ioc.demo17.StrongAnnotation(value=用在类型名称上T1, elementType=TYPE_USE)
}
@Inherited实现子类继承父类的注解
@Inherited指示注解类型是自动继承的。注意针对的父类的注解,接口是无效的
@Documented
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Target(ElementType.ANNOTATION_TYPE)
public @interface Inherited {
}
来看一个案例,父类和接口上都有可继承的注解,观察下子类的上的注解情况。
/**
* 测试父类注解的继承
* 注意:是类,不是接口,接口无效
* @author zfd
* @version v1.0
* @date 2022/1/24 17:15
* @关于我 请关注公众号 螃蟹的Java笔记 获取更多技术系列
*/
public class TestInherited {
@Target(ElementType.TYPE)
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Inherited
@interface Annotation1{}
@Target(ElementType.TYPE)
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Inherited
@interface Annotation2{}
@Annotation1
interface Interface1{}
@Annotation2
static class SupperClass{}
// 继承 SupperClass 实现 Interface1,观察其注解继承情况
static class SubClass extends SupperClass implements Interface1{}
public static void main(String[] args) {
for (Annotation annotation : SubClass.class.getAnnotations()) {
System.out.println(annotation);
}
}
// 输出
// @com.crab.spring.ioc.demo17.TestInherited$Annotation2()
// 只继承了父类注解 无法继承接口上的注解
}
@Repeatable重复注解
常规情况下同一个目标上是无法使用同一个注解多个重复标记的。如果自定义注解需要实现可重复注解,则在定义的时候可以使用 @Repeatable来声明的注解类型是可重复的。
@Documented
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Target(ElementType.ANNOTATION_TYPE)
public @interface Repeatable {
// 指定容器注解类型
Class<? extends Annotation> value();
}
模拟 @ComponentScan @ComponentScans来提供一个案例。
/**
* 测试 @Repeatable 注解重复使用
* @author zfd
* @version v1.0
* @date 2022/1/24 17:30
* @关于我 请关注公众号 螃蟹的Java笔记 获取更多技术系列
*/
public class TestRepeatable {
@Target(ElementType.TYPE)
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Repeatable(ComponentScans.class)
@interface ComponentScan{}
@Target(ElementType.TYPE)
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@interface ComponentScans{
// 注意: 必须定义value参数,其类型是子重复注解的数组类型
ComponentScan[] value();
}
// 重复注解方式1
@ComponentScan
@ComponentScan
static class MyComponent{}
// 重复注解方式2
@ComponentScans({@ComponentScan, @ComponentScan})
static class MyComponentB{}
public static void main(String[] args) {
for (Annotation annotation : MyComponent.class.getAnnotations()) {
System.out.println(annotation);
}
for (Annotation annotation : MyComponentB.class.getAnnotations()) {
System.out.println(annotation);
}
}
// 输出
// @com.crab.spring.ioc.demo17.TestRepeatable$ComponentScans(value=[@com.crab.spring.ioc.demo17
// .TestRepeatable$ComponentScan(), @com.crab.spring.ioc.demo17.TestRepeatable$ComponentScan()])
// @com.crab.spring.ioc.demo17.TestRepeatable$ComponentScans(value=[@com.crab.spring.ioc.demo17
// .TestRepeatable$ComponentScan(), @com.crab.spring.ioc.demo17.TestRepeatable$ComponentScan()])
}
Spring 中@AliasFor对注解的增强
注解的定义参数是不能继承,如注解A上面有注解B,但是实际在使用B注解在目标类C的过程中想要设置A的参数是做不到的。
@Target(ElementType.TYPE)
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
public @interface AnnotationA {
String name() default "";
int value() default -1;
}
@Target(ElementType.TYPE)
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@AnnotationA
public @interface AnnotationB {
String name() default "";
int value() default 1;
String aliasForName() default "";
}
@AnnotationB(name = "xxx", value = 1) // 无法设置AnnotiaonA的参数值
public class ClassC {
}
Spring 中 提供了@AliasFor 元注解,用于声明注解属性的别名,主要的使用场景:
- 注解中的显式别名:在单个注解中, @AliasFor可以在一对属性上声明,以表明它们是彼此可互换的别名
- 元注解中属性的显式别名:如果@AliasFor的annotation属性设置为与声明它的注解不同的注解,则该attribute被解释为元注解中属性的别名(即显式元注解属性覆盖)。 这可以精确控制注解层次结构中覆盖的属性。
- 注解中的隐式别名:如果注解中的一个或多个属性被声明为相同元注解属性的属性覆盖(直接或传递),则这些属性将被视为彼此的一组隐式别名,从而导致类似于注解中显式别名的行为。
源码简单过一下
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Target(ElementType.METHOD)
@Documented
public @interface AliasFor {
@AliasFor("attribute")
String value() default "";
@AliasFor("value")
String attribute() default "";
// 声明别名属性的注解类型。默认为 Annotation,这意味着别名属性在与此属性相同的注解中声明。
Class<? extends Annotation> annotation() default Annotation.class;
}
来使用@AliasFor 改造下 AnnotationB。
@Target(ElementType.TYPE)
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@AnnotationA
public @interface AnnotationB {
// 注解AnnotationB内部显式别名
@AliasFor(value = "aliasForName")
String name() default "";
int value() default 1;
// 注解AnnotationB内部显式别名
@AliasFor(annotation = AnnotationB.class, attribute = "name")
String aliasForName() default "";
// 元注解AnnotationA属性name显式别名
@AliasFor(annotation = AnnotationA.class, value = "name")
String aliasForAnnotationAName() default "";
// 元注解AnnotationA属性name显式别名2
@AliasFor(annotation = AnnotationA.class, value = "name")
String aliasForAnnotationAName2() default "";
// 元注解AnnotationA属性value显式别名
@AliasFor(annotation = AnnotationA.class, value = "value")
int aliasForAnnotationAValue() default -1;
}
使用AnnotationB 注解,注意:互为别名的属性设置时只能设置其中一个,否则设置多个会报错。
@AnnotationB(value = 100,
name = "xx",
aliasForAnnotationAName = "a1",
aliasForAnnotationAValue = -100
)
public class ClassC2 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//spring提供一个查找注解的工具类AnnotatedElementUtils
System.out.println(AnnotatedElementUtils.getMergedAnnotation(ClassC2.class, AnnotationB.class));
System.out.println(AnnotatedElementUtils.getMergedAnnotation(ClassC2.class, AnnotationA.class));
}
}
输出结果显示AnnotationB 通过别名设置AnnotationA中属性成功。
@com.crab.spring.ioc.demo17.AnnotationB(aliasForAnnotationAName=a1, aliasForAnnotationAName2=a1, aliasForAnnotationAValue=-100, aliasForName=xx, name=xx, value=100)
@com.crab.spring.ioc.demo17.AnnotationA(name=a1, value=-100)
本文详解了注解的概念,如何定义注解、使用注解、获取注解;并介绍了元注解@Target、@Retention、@Inherited、@Repeatable 的使用;重点讲解了Spring 中 @AliasFor 注解来为元注解属性设置别名的增强处理。
本篇源码地址: https://github.com/kongxubihai/pdf-spring-series/tree/main/spring-series-ioc/src/main/java/com/crab/spring/ioc/demo17
知识分享,转载请注明出处。学无先后,达者为先!
Recommend
-
 33
33
【Spring Data 系列学习】Spring Data JPA @Query 注解查询 前面的章节讲述了 Spring Data Jpa 通过声明式对数据库进行操作,上手速度快简单易操作。但同时 JPA 还提供通过注解的方式实现,通过将 @Query 注解在...
-
 12
12
¶ Java 基础 - 注解机制详解 注解是JDK1.5版本开始引入的一个特性,用于对代码进行说明,可以对包、类、接口、字段、方法参数、局部变量等进行注解。...
-
 10
10
前言 本系列全部基于 Spring 5.2.2.BUILD-SNAPSHOT 版本。因为 Spring 整个体系太过于庞大,所以只会进行关键部分的源码解析。 什么是公共注解?公共注解就是常见的Java注解,特别是JSR-250中的注解。...
-
 31
31
Hi ! 我是小小,开始本周的第一篇,本周第一篇内容是关于Spring Boot 最核心的三个注解,将会对这三个注解进行详细解释。 前言 Spring Boot 最大的特点是无需 XML 配置文件,能够实现自动装配,并进行全自动化的jar包...
-
 14
14
在之前的《使用Sentinel实现接口限流》一文中,我们仅依靠引入Spring Cloud Alibaba对Sentinel的整合封装spring-cloud-starter-alibaba-sentinel,就完成了对所有Sprin...
-
 6
6
【基础系列】接口上注解AOP拦截不到场景兼容 ...
-
 4
4
-
 7
7
研究一下自定义注解实现。新建Spring Boot项目1. pom.xml引入相关依赖<dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot...
-
 5
5
【基础系列】SpringBoot应用篇@Value注解支持配置自动刷新能力扩展 ...
-
 4
4
今天给大家介绍@Lazy懒加载注解用法,希望对大家能有所帮助!
About Joyk
Aggregate valuable and interesting links.
Joyk means Joy of geeK