

Spring核心原理之IoC容器初体验(2)
source link: https://my.oschina.net/gupaoedutom/blog/5378243
Go to the source link to view the article. You can view the picture content, updated content and better typesetting reading experience. If the link is broken, please click the button below to view the snapshot at that time.

本文节选自《Spring 5核心原理》
1 IoC与DI基本概念
IoC(Inversion of Control,控制反转)就是把原来代码里需要实现的对象创建、依赖,反转给容器来帮忙实现。我们需要创建一个容器,同时需要一种描述来让容器知道要创建的对象与对象的关系。这个描述最具体的表现就是我们所看到的配置文件。
DI(Dependency Injection,依赖注入)就是指对象被动接受依赖类而不自己主动去找,换句话说,就是指对象不是从容器中查找它依赖的类,而是在容器实例化对象时主动将它依赖的类注入给它。 我们先从自己设计的视角来考虑。 (1)对象与对象的关系怎么表示? 可以用XML、properties等语义化配置文件表示。 (2)描述对象关系的文件存放在哪里? 可能是classpath、filesystem或者URL网络资源、servletContext等。 (3)不同的配置文件对对象的描述不一样,如标准的、自定义声明式的,如何统一? 在内部需要有一个统一的关于对象的定义,所有外部的描述都必须转化成统一的描述定义。 (4)如何对不同的配置文件进行解析? 需要对不同的配置文件语法采用不同的解析器。
2 Spring核心容器类图
2.1. BeanFactory
Spring中Bean的创建是典型的工厂模式,这一系列的Bean工厂,即IoC容器,为开发者管理对象之间的依赖关系提供了很多便利和基础服务,在Spring中有许多IoC容器的实现供用户选择,其相互关系如下图所示。

其中,BeanFactory作为最顶层的一个接口类,定义了IoC容器的基本功能规范,BeanFactory有三个重要的子类:ListableBeanFactory、HierarchicalBeanFactory和AutowireCapableBeanFactory。但是从类图中我们可以发现最终的默认实现类是DefaultListableBeanFactory,它实现了所有的接口。那么为何要定义这么多层次的接口呢?查阅这些接口的源码和说明发现,每个接口都有它的使用场合,主要是为了区分在Spring内部操作过程中对象的传递和转化,对对象的数据访问所做的限制。例如,ListableBeanFactory接口表示这些Bean可列表化,而HierarchicalBeanFactory表示这些Bean是有继承关系的,也就是每个Bean可能有父Bean。AutowireCapableBeanFactory接口定义Bean的自动装配规则。这三个接口共同定义了Bean的集合、Bean之间的关系及Bean行为。最基本的IoC容器接口是BeanFactory,来看一下它的源码:
public interface BeanFactory {
//对FactoryBean的转义定义,因为如果使用Bean的名字检索FactoryBean得到的对象是工厂生成的对象
//如果需要得到工厂本身,需要转义
String FACTORY_BEAN_PREFIX = "&";
//根据Bean的名字,获取在IoC容器中得到的Bean实例
Object getBean(String name) throws BeansException;
//根据Bean的名字和Class类型来得到Bean实例,增加了类型安全验证机制
<T> T getBean(String name, @Nullable Class<T> requiredType) throws BeansException;
Object getBean(String name, Object... args) throws BeansException;
<T> T getBean(Class<T> requiredType) throws BeansException;
<T> T getBean(Class<T> requiredType, Object... args) throws BeansException;
//提供对Bean的检索,看看在IoC容器中是否有这个名字的Bean
boolean containsBean(String name);
//根据Bean的名字得到Bean实例,同时判断这个Bean是不是单例
boolean isSingleton(String name) throws NoSuchBeanDefinitionException;
boolean isPrototype(String name) throws NoSuchBeanDefinitionException;
boolean isTypeMatch(String name, ResolvableType typeToMatch) throws
NoSuchBeanDefinitionException;
boolean isTypeMatch(String name, @Nullable Class<?> typeToMatch) throws
NoSuchBeanDefinitionException;
//得到Bean实例的Class类型
@Nullable
Class<?> getType(String name) throws NoSuchBeanDefinitionException;
//得到Bean的别名,如果根据别名检索,那么其原名也会被检索出来
String[] getAliases(String name);
}
在BeanFactory里只对IoC容器的基本行为做了定义,根本不关心你的Bean是如何定义及怎样加载的。正如我们只关心能从工厂里得到什么产品,不关心工厂是怎么生产这些产品的。 要知道工厂是如何产生对象的,我们需要看具体的IoC容器实现,Spring提供了许多IoC容器实现,比如GenericApplicationContext、ClasspathXmlApplicationContext等。 ApplicationContext是Spring提供的一个高级的IoC容器,它除了能够提供IoC容器的基本功能,还为用户提供了以下附加服务。
(1)支持信息源,可以实现国际化(实现MessageSource接口)。 (2)访问资源(实现ResourcePatternResolver接口,后面章节会讲到)。 (3)支持应用事件(实现ApplicationEventPublisher接口)。
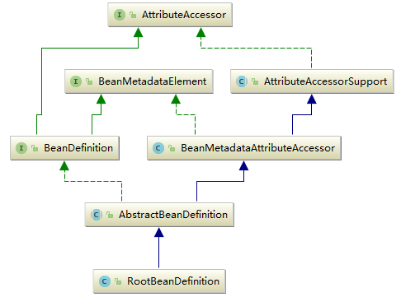
2.2. BeanDefinition
BeanDefinition 用于保存 Bean 的相关信息,包括属性、构造方法参数、依赖的 Bean 名称及是否单例、延迟加载等,它相当于实例化 Bean 的原材料,Spring 就是根据 BeanDefinition 中的信息实例化 Bean。,其继承体系如下图所示。
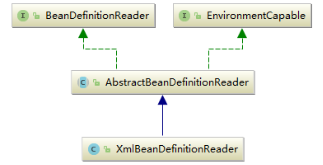
2.3. BeanDefinitionReader
Bean的解析过程非常复杂,功能被分得很细,因为这里需要被扩展的地方很多,必须保证足够的灵活性,以应对可能的变化。Bean的解析主要就是对Spring配置文件的解析。这个解析过程主要通过BeanDefinitionReader来完成,看看Spring中BeanDefinitionReader的类结构图,如下图所示。
通过前面的分析,我们对Spring框架体系有了一个基本的宏观了解,希望“小伙伴们”好好理解,最好在脑海中形成画面,为以后的学习打下良好的基础。
3 基于Web的IoC容器初体验
我们还是从大家最熟悉的DispatcherServlet开始,最先想到的应该是DispatcherServlet的init()方法。我们在DispatherServlet中并没有找到init()方法,经过探索,在其父类HttpServletBean中找到了,代码如下:
@Override
public final void init() throws ServletException {
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Initializing servlet '" + getServletName() + "'");
}
PropertyValues pvs = new ServletConfigPropertyValues(getServletConfig(),
this.requiredProperties);
if (!pvs.isEmpty()) {
try {
//定位资源
BeanWrapper bw = PropertyAccessorFactory.forBeanPropertyAccess(this);
//加载配置信息
ResourceLoader resourceLoader = new ServletContextResourceLoader(getServletContext());
bw.registerCustomEditor(Resource.class, new ResourceEditor(resourceLoader,
getEnvironment()));
initBeanWrapper(bw);
bw.setPropertyValues(pvs, true);
}
catch (BeansException ex) {
if (logger.isErrorEnabled()) {
logger.error("Failed to set bean properties on servlet '" + getServletName() + "'", ex);
}
throw ex;
}
}
initServletBean();
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Servlet '" + getServletName() + "' configured successfully");
}
}
在init()方法中,真正完成初始化容器动作的代码其实在initServletBean()方法中,我们继续跟进:
@Override
protected final void initServletBean() throws ServletException {
getServletContext().log("Initializing Spring FrameworkServlet '" + getServletName() + "'");
if (this.logger.isInfoEnabled()) {
this.logger.info("FrameworkServlet '" + getServletName() + "': initialization started");
}
long startTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
try {
this.webApplicationContext = initWebApplicationContext();
initFrameworkServlet();
}
catch (ServletException ex) {
this.logger.error("Context initialization failed", ex);
throw ex;
}
catch (RuntimeException ex) {
this.logger.error("Context initialization failed", ex);
throw ex;
}
if (this.logger.isInfoEnabled()) {
long elapsedTime = System.currentTimeMillis() - startTime;
this.logger.info("FrameworkServlet '" + getServletName() + "': initialization completed
in " + elapsedTime + " ms");
}
}
在上面的代码中终于看到了似曾相识的代码initWebApplicationContext(),继续跟进:
protected WebApplicationContext initWebApplicationContext() {
//先从ServletContext中获得父容器WebApplicationContext
WebApplicationContext rootContext =
WebApplicationContextUtils.getWebApplicationContext(getServletContext());
//声明子容器
WebApplicationContext wac = null;
//建立父、子容器之间的关联关系
if (this.webApplicationContext != null) {
wac = this.webApplicationContext;
if (wac instanceof ConfigurableWebApplicationContext) {
ConfigurableWebApplicationContext cwac = (ConfigurableWebApplicationContext) wac;
if (!cwac.isActive()) {
if (cwac.getParent() == null) {
cwac.setParent(rootContext);
}
configureAndRefreshWebApplicationContext(cwac);
}
}
}
//先去ServletContext中查找Web容器的引用是否存在,并创建好默认的空IoC容器
if (wac == null) {
wac = findWebApplicationContext();
}
//给上一步创建好的IoC容器赋值
if (wac == null) {
wac = createWebApplicationContext(rootContext);
}
//触发onRefresh()方法
if (!this.refreshEventReceived) {
onRefresh(wac);
}
if (this.publishContext) {
String attrName = getServletContextAttributeName();
getServletContext().setAttribute(attrName, wac);
if (this.logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
this.logger.debug("Published WebApplicationContext of servlet '" + getServletName() +
"' as ServletContext attribute with name [" + attrName + "]");
}
}
return wac;
}
@Nullable
protected WebApplicationContext findWebApplicationContext() {
String attrName = getContextAttribute();
if (attrName == null) {
return null;
}
WebApplicationContext wac =
WebApplicationContextUtils.getWebApplicationContext(getServletContext(), attrName);
if (wac == null) {
throw new IllegalStateException("No WebApplicationContext found: initializer not registered?");
}
return wac;
}
protected WebApplicationContext createWebApplicationContext(@Nullable ApplicationContext parent) {
Class<?> contextClass = getContextClass();
if (this.logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
this.logger.debug("Servlet with name '" + getServletName() +
"' will try to create custom WebApplicationContext context of class '" +
contextClass.getName() + "'" + ", using parent context [" + parent + "]");
}
if (!ConfigurableWebApplicationContext.class.isAssignableFrom(contextClass)) {
throw new ApplicationContextException(
"Fatal initialization error in servlet with name '" + getServletName() +
"': custom WebApplicationContext class [" + contextClass.getName() +
"] is not of type ConfigurableWebApplicationContext");
}
ConfigurableWebApplicationContext wac =
(ConfigurableWebApplicationContext) BeanUtils.instantiateClass(contextClass);
wac.setEnvironment(getEnvironment());
wac.setParent(parent);
String configLocation = getContextConfigLocation();
if (configLocation != null) {
wac.setConfigLocation(configLocation);
}
configureAndRefreshWebApplicationContext(wac);
return wac;
}
protected void configureAndRefreshWebApplicationContext(ConfigurableWebApplicationContext wac) {
if (ObjectUtils.identityToString(wac).equals(wac.getId())) {
if (this.contextId != null) {
wac.setId(this.contextId);
}
else {
wac.setId(ConfigurableWebApplicationContext.APPLICATION_CONTEXT_ID_PREFIX +
ObjectUtils.getDisplayString(getServletContext().getContextPath()) + '/' + getServletName());
}
}
wac.setServletContext(getServletContext());
wac.setServletConfig(getServletConfig());
wac.setNamespace(getNamespace());
wac.addApplicationListener(new SourceFilteringListener(wac, new ContextRefreshListener()));
ConfigurableEnvironment env = wac.getEnvironment();
if (env instanceof ConfigurableWebEnvironment) {
((ConfigurableWebEnvironment) env).initPropertySources(getServletContext(),
getServletConfig());
}
postProcessWebApplicationContext(wac);
applyInitializers(wac);
wac.refresh();
}
从上面的代码可以看出,在configAndRefreshWebApplicationContext()方法中调用了refresh()方法,这是真正启动IoC容器的入口,后面会详细介绍。IoC容器初始化以后,调用了DispatcherServlet的onRefresh()方法,在onRefresh()方法中又直接调用initStrategies()方法初始化Spring MVC的九大组件:
@Override
protected void onRefresh(ApplicationContext context) {
initStrategies(context);
}
//初始化策略
protected void initStrategies(ApplicationContext context) {
//多文件上传的组件
initMultipartResolver(context);
//初始化本地语言环境
initLocaleResolver(context);
//初始化模板处理器
initThemeResolver(context);
//初始化handlerMapping
initHandlerMappings(context);
//初始化参数适配器
initHandlerAdapters(context);
//初始化异常拦截器
initHandlerExceptionResolvers(context);
//初始化视图预处理器
initRequestToViewNameTranslator(context);
//初始化视图转换器
initViewResolvers(context);
//初始化Flashmap管理器
initFlashMapManager(context);
}
关注微信公众号『 Tom弹架构 』回复“Spring”可获取完整源码。

本文为“Tom弹架构”原创,转载请注明出处。技术在于分享,我分享我快乐!
如果本文对您有帮助,欢迎关注和点赞;如果您有任何建议也可留言评论或私信,您的支持是我坚持创作的动力。关注微信公众号『 Tom弹架构 』可获取更多技术干货!
原创不易,坚持很酷,都看到这里了,小伙伴记得点赞、收藏、在看,一键三连加关注!如果你觉得内容太干,可以分享转发给朋友滋润滋润!
Recommend
-
 14
14
说到spring不得不提其两大特性IOC、AOP,本文主要介绍结合代码看下spring Ioc相关原理,阅读源码如果只是为了看源码效率就会很低,还是要有一定的目的性,我们结合着以下的问题去源码中找答案。本篇文章为《图灵学院》...
-
 15
15
在本文中,我们将通过用C#重构一个非常简单的代码示例来解释依赖注入和IoC容器。 简介: 依赖注入和IoC乍一看可能相当复杂,但它们非常容易学习和理解。 在本文中,我们将通过在C#中重构一个非常简单的代码示...
-
 13
13
概述 对于 Java 后端开发而言,Spring 框架的重要性不言而喻。而 Spring 中最核心的无非就是 IoC 和 AOP。 相关的概念不再赘述,网上可以找到很多对它们的介绍。 这里想说的是,IoC 只是一种设计思想,它...
-
 9
9
概述 上篇文章「Spring 中的 IoC 容器」从整体介绍了 Spring IoC 容器的相关概念和大致实现流程,本文要进入源码来一探究竟了。 这里仍以前文的代码为例进行分析,测试代码如下: public...
-
 7
7
前情回顾 前文「 Spring IoC 容器初始化 」...
-
 4
4
Spring 最重要的方法refresh方法 根据上一篇文章 https://www.cnblogs.com/redwinter/p/16141285.html Spring Bean IOC 的创建流程继续解读Spring源码,...
-
 8
8
本文最后更新于 268 天前,文中所描述的信息可能已发生改变差不多该写写该系列文章了,咕了好几天 ?。在 XK-PHP 中 IoC 容器是框架的核心,其掌管着框架中实例的存储和初始化,并提供自动依赖注入...
-
 11
11
控制反转与大家熟知的依赖注入同理, 这是通过依赖注入对象的过程. 创建 Bean 后, 依赖的对象由控制反转容器通过构造参数 工厂方法参数或者属性注入. 创建过程相对于普通创建对象的过程是反向, 称之为控制反转 (IoC). Tomcat...
-
 6
6
IoC容器的实现学习——02 前面学习了 IoC 模式的核心概念,使用场景,以及 Spring 对 IoC 具体实现的两种系列:BeanFactory 和 ApplicationContext 通过两种系列的具体 IoC 容器来...
-
 7
7
欢迎来到本篇文章!通过上一篇什么是 Spring?为什么学它?的学习,我们知道了 Spring 的基本概念,知道什么是 Spring,以及为什么学习 Spring。今天,这篇就来说说...
About Joyk
Aggregate valuable and interesting links.
Joyk means Joy of geeK