

iOS刨根问底-深入理解GCD
source link: https://www.cnblogs.com/kenshincui/p/13272517.html
Go to the source link to view the article. You can view the picture content, updated content and better typesetting reading experience. If the link is broken, please click the button below to view the snapshot at that time.

做过iOS开发的同学相信对于GCD(Grand Central Dispatch)并不陌生,因为在平时多线程开发过程中GCD应该是使用最多的技术甚至它要比它的上层封装NSOperation还要常用,其中最主要的原因是简单易用功能强大。本文将从GCD的原理和使用两个层面分析GCD的内容,本文会结合源码和实例分析使用GCD的注意事项,源码解读部分主要通过注释源码的方式方便进行源码分析,具体到细节通过在源码解释说明。
开源的libdispatch
和前面一篇文章深入了解Runloop一样GCD的代码是开源的(也可以直接从苹果官网下载),这样要弄清GCD的很多实现原理就有了可能,所以文中不涉及的很多细节大家可以通过源代码进行了解。下面让我们看一下关于常见的几个类型的源码:
队列类型 dispatch_queue_t
dispatch_queue_t应该是平时接触最多的一个GCD类型,比如说创建一个队列,它返回的就是一个dispatch_queue_t类型:
dispatch_queue_t serialDispatch = dispatch_queue_create("com.cmjstudio.dispatch", nil);
通过查看源码可以看到dispatch_queue_t的定义:
// 首先可以看到dispatch_queue_t本身只是dispatch_queue_s这个结构体指针
typedef struct dispatch_queue_s *dispatch_queue_t;
// 继续查看dispatch_queue_s定义,可以看到一个
DISPATCH_QUEUE_CLASS_HEADER的宏定义
struct dispatch_queue_s {
DISPATCH_QUEUE_CLASS_HEADER(queue, void *__dq_opaque1);
/* 32bit hole on LP64 */
} DISPATCH_ATOMIC64_ALIGN;
// 查看DISPATCH_QUEUE_CLASS_HEADER
#define DISPATCH_QUEUE_CLASS_HEADER(x, __pointer_sized_field__) \
_DISPATCH_QUEUE_CLASS_HEADER(x, __pointer_sized_field__); \
/* LP64 global queue cacheline boundary */ \
unsigned long dq_serialnum; \
const char *dq_label; \
DISPATCH_UNION_LE(uint32_t volatile dq_atomic_flags, \
const uint16_t dq_width, \
const uint16_t __dq_opaque2 \
); \
dispatch_priority_t dq_priority; \
union { \
struct dispatch_queue_specific_head_s *dq_specific_head; \
struct dispatch_source_refs_s *ds_refs; \
struct dispatch_timer_source_refs_s *ds_timer_refs; \
struct dispatch_mach_recv_refs_s *dm_recv_refs; \
}; \
int volatile dq_sref_cnt
// 展开_DISPATCH_QUEUE_CLASS_HEADER
#define _DISPATCH_QUEUE_CLASS_HEADER(x, __pointer_sized_field__) \
DISPATCH_OBJECT_HEADER(x); \
DISPATCH_UNION_LE(uint64_t volatile dq_state, \
dispatch_lock dq_state_lock, \
uint32_t dq_state_bits \
); \
__pointer_sized_field__
// 持续展开DISPATCH_OBJECT_HEADER
#define DISPATCH_OBJECT_HEADER(x) \
struct dispatch_object_s _as_do[0]; \
_DISPATCH_OBJECT_HEADER(x)
// 进一步查看 _DISPATCH_OBJECT_HEADER
#define _DISPATCH_OBJECT_HEADER(x) \
struct _os_object_s _as_os_obj[0]; \
OS_OBJECT_STRUCT_HEADER(dispatch_##x); \
struct dispatch_##x##_s *volatile do_next; \
struct dispatch_queue_s *do_targetq; \
void *do_ctxt; \
void *do_finalizer
// 再查看 OS_OBJECT_STRUCT_HEADER
#define OS_OBJECT_STRUCT_HEADER(x) \
_OS_OBJECT_HEADER(\
const void *_objc_isa, \
do_ref_cnt, \
do_xref_cnt); \
const struct x##_vtable_s *do_vtable
// 进一步查看 _OS_OBJECT_HEADER
#define _OS_OBJECT_HEADER(isa, ref_cnt, xref_cnt) \
isa; /* must be pointer-sized */ \
int volatile ref_cnt; \
int volatile xref_cnt
上面的源代码拆分过程尽管繁琐但是每一步都可以在源码中顺利的找到倒也不是太复杂。最终可以看到 dispatch_queue_t 本身存储了我们平时常见的label、priority、specific等,本身就是isa指针和引用计数器等一些信息。
需要说明的是 dispatch 版本众多,如果查看当前版本可以直接打印
DISPATCH_API_VERSION即可。
创建队列 dispatch_queue_create
dispatch_queue_create 用于创建一个队列,返回类型是上面分析过的dispatch_queue_t ,那么现在看一下如何创建一个队列:
dispatch_queue_t
dispatch_queue_create(const char *label, dispatch_queue_attr_t attr)
{
return _dispatch_lane_create_with_target(label, attr,
DISPATCH_TARGET_QUEUE_DEFAULT, true);
}
// 然后进一步查看 _dispatch_lane_create_with_target 的代码
static dispatch_queue_t
_dispatch_lane_create_with_target(const char *label, dispatch_queue_attr_t dqa,
dispatch_queue_t tq, bool legacy)
{
dispatch_queue_attr_info_t dqai = _dispatch_queue_attr_to_info(dqa);
//
// Step 1: Normalize arguments (qos, overcommit, tq)
//
dispatch_qos_t qos = dqai.dqai_qos;
#if !HAVE_PTHREAD_WORKQUEUE_QOS
if (qos == DISPATCH_QOS_USER_INTERACTIVE) {
dqai.dqai_qos = qos = DISPATCH_QOS_USER_INITIATED;
}
if (qos == DISPATCH_QOS_MAINTENANCE) {
dqai.dqai_qos = qos = DISPATCH_QOS_BACKGROUND;
}
#endif // !HAVE_PTHREAD_WORKQUEUE_QOS
_dispatch_queue_attr_overcommit_t overcommit = dqai.dqai_overcommit;
if (overcommit != _dispatch_queue_attr_overcommit_unspecified && tq) {
if (tq->do_targetq) {
DISPATCH_CLIENT_CRASH(tq, "Cannot specify both overcommit and "
"a non-global target queue");
}
}
if (tq && dx_type(tq) == DISPATCH_QUEUE_GLOBAL_ROOT_TYPE) {
// Handle discrepancies between attr and target queue, attributes win
if (overcommit == _dispatch_queue_attr_overcommit_unspecified) {
if (tq->dq_priority & DISPATCH_PRIORITY_FLAG_OVERCOMMIT) {
overcommit = _dispatch_queue_attr_overcommit_enabled;
} else {
overcommit = _dispatch_queue_attr_overcommit_disabled;
}
}
if (qos == DISPATCH_QOS_UNSPECIFIED) {
qos = _dispatch_priority_qos(tq->dq_priority);
}
tq = NULL;
} else if (tq && !tq->do_targetq) {
// target is a pthread or runloop root queue, setting QoS or overcommit
// is disallowed
if (overcommit != _dispatch_queue_attr_overcommit_unspecified) {
DISPATCH_CLIENT_CRASH(tq, "Cannot specify an overcommit attribute "
"and use this kind of target queue");
}
} else {
if (overcommit == _dispatch_queue_attr_overcommit_unspecified) {
// Serial queues default to overcommit!
overcommit = dqai.dqai_concurrent ?
_dispatch_queue_attr_overcommit_disabled :
_dispatch_queue_attr_overcommit_enabled;
}
}
if (!tq) {
tq = _dispatch_get_root_queue(
qos == DISPATCH_QOS_UNSPECIFIED ? DISPATCH_QOS_DEFAULT : qos,
overcommit == _dispatch_queue_attr_overcommit_enabled)->_as_dq;
if (unlikely(!tq)) {
DISPATCH_CLIENT_CRASH(qos, "Invalid queue attribute");
}
}
//
// Step 2: Initialize the queue
//
if (legacy) {
// if any of these attributes is specified, use non legacy classes
if (dqai.dqai_inactive || dqai.dqai_autorelease_frequency) {
legacy = false;
}
}
const void *vtable;
dispatch_queue_flags_t dqf = legacy ? DQF_MUTABLE : 0;
if (dqai.dqai_concurrent) {
vtable = DISPATCH_VTABLE(queue_concurrent);
} else {
vtable = DISPATCH_VTABLE(queue_serial);
}
switch (dqai.dqai_autorelease_frequency) {
case DISPATCH_AUTORELEASE_FREQUENCY_NEVER:
dqf |= DQF_AUTORELEASE_NEVER;
break;
case DISPATCH_AUTORELEASE_FREQUENCY_WORK_ITEM:
dqf |= DQF_AUTORELEASE_ALWAYS;
break;
}
if (label) {
const char *tmp = _dispatch_strdup_if_mutable(label);
if (tmp != label) {
dqf |= DQF_LABEL_NEEDS_FREE;
label = tmp;
}
}
dispatch_lane_t dq = _dispatch_object_alloc(vtable,
sizeof(struct dispatch_lane_s));
_dispatch_queue_init(dq, dqf, dqai.dqai_concurrent ?
DISPATCH_QUEUE_WIDTH_MAX : 1, DISPATCH_QUEUE_ROLE_INNER |
(dqai.dqai_inactive ? DISPATCH_QUEUE_INACTIVE : 0));
dq->dq_label = label;
dq->dq_priority = _dispatch_priority_make((dispatch_qos_t)dqai.dqai_qos,
dqai.dqai_relpri);
if (overcommit == _dispatch_queue_attr_overcommit_enabled) {
dq->dq_priority |= DISPATCH_PRIORITY_FLAG_OVERCOMMIT;
}
if (!dqai.dqai_inactive) {
_dispatch_queue_priority_inherit_from_target(dq, tq);
_dispatch_lane_inherit_wlh_from_target(dq, tq);
}
_dispatch_retain(tq);
dq->do_targetq = tq;
_dispatch_object_debug(dq, "%s", __func__);
return _dispatch_trace_queue_create(dq)._dq;
}
从源码注释也可以看出主要有两步操作,第一步是 Normalize arguments,第二部才是真正创建队列,忽略一些参数规范化操作。首先_dispatch_get_root_queue用于获取root队列,它有两个参数:一个是队列优先级(有6个:userInteractive>default>unspecified>userInitiated>utility>background),另一个是支持不支持过载overcommit(支持overcommit的队列在创建队列时无论系统是否有足够的资源都会重新开一个线程),所以总共就有12个root队列。对应的源代码如下(其实是从一个数组中获取):
DISPATCH_ALWAYS_INLINE DISPATCH_CONST
static inline dispatch_queue_global_t
_dispatch_get_root_queue(dispatch_qos_t qos, bool overcommit)
{
if (unlikely(qos < DISPATCH_QOS_MIN || qos > DISPATCH_QOS_MAX)) {
DISPATCH_CLIENT_CRASH(qos, "Corrupted priority");
}
return &_dispatch_root_queues[2 * (qos - 1) + overcommit];
}
至于12个root队列可以查看源代码:
struct dispatch_queue_global_s _dispatch_root_queues[] = {
#define _DISPATCH_ROOT_QUEUE_IDX(n, flags) \
((flags & DISPATCH_PRIORITY_FLAG_OVERCOMMIT) ? \
DISPATCH_ROOT_QUEUE_IDX_##n##_QOS_OVERCOMMIT : \
DISPATCH_ROOT_QUEUE_IDX_##n##_QOS)
#define _DISPATCH_ROOT_QUEUE_ENTRY(n, flags, ...) \
[_DISPATCH_ROOT_QUEUE_IDX(n, flags)] = { \
DISPATCH_GLOBAL_OBJECT_HEADER(queue_global), \
.dq_state = DISPATCH_ROOT_QUEUE_STATE_INIT_VALUE, \
.do_ctxt = _dispatch_root_queue_ctxt(_DISPATCH_ROOT_QUEUE_IDX(n, flags)), \
.dq_atomic_flags = DQF_WIDTH(DISPATCH_QUEUE_WIDTH_POOL), \
.dq_priority = flags | ((flags & DISPATCH_PRIORITY_FLAG_FALLBACK) ? \
_dispatch_priority_make_fallback(DISPATCH_QOS_##n) : \
_dispatch_priority_make(DISPATCH_QOS_##n, 0)), \
__VA_ARGS__ \
}
_DISPATCH_ROOT_QUEUE_ENTRY(MAINTENANCE, 0,
.dq_label = "com.apple.root.maintenance-qos",
.dq_serialnum = 4,
),
_DISPATCH_ROOT_QUEUE_ENTRY(MAINTENANCE, DISPATCH_PRIORITY_FLAG_OVERCOMMIT,
.dq_label = "com.apple.root.maintenance-qos.overcommit",
.dq_serialnum = 5,
),
_DISPATCH_ROOT_QUEUE_ENTRY(BACKGROUND, 0,
.dq_label = "com.apple.root.background-qos",
.dq_serialnum = 6,
),
_DISPATCH_ROOT_QUEUE_ENTRY(BACKGROUND, DISPATCH_PRIORITY_FLAG_OVERCOMMIT,
.dq_label = "com.apple.root.background-qos.overcommit",
.dq_serialnum = 7,
),
_DISPATCH_ROOT_QUEUE_ENTRY(UTILITY, 0,
.dq_label = "com.apple.root.utility-qos",
.dq_serialnum = 8,
),
_DISPATCH_ROOT_QUEUE_ENTRY(UTILITY, DISPATCH_PRIORITY_FLAG_OVERCOMMIT,
.dq_label = "com.apple.root.utility-qos.overcommit",
.dq_serialnum = 9,
),
_DISPATCH_ROOT_QUEUE_ENTRY(DEFAULT, DISPATCH_PRIORITY_FLAG_FALLBACK,
.dq_label = "com.apple.root.default-qos",
.dq_serialnum = 10,
),
_DISPATCH_ROOT_QUEUE_ENTRY(DEFAULT,
DISPATCH_PRIORITY_FLAG_FALLBACK | DISPATCH_PRIORITY_FLAG_OVERCOMMIT,
.dq_label = "com.apple.root.default-qos.overcommit",
.dq_serialnum = 11,
),
_DISPATCH_ROOT_QUEUE_ENTRY(USER_INITIATED, 0,
.dq_label = "com.apple.root.user-initiated-qos",
.dq_serialnum = 12,
),
_DISPATCH_ROOT_QUEUE_ENTRY(USER_INITIATED, DISPATCH_PRIORITY_FLAG_OVERCOMMIT,
.dq_label = "com.apple.root.user-initiated-qos.overcommit",
.dq_serialnum = 13,
),
_DISPATCH_ROOT_QUEUE_ENTRY(USER_INTERACTIVE, 0,
.dq_label = "com.apple.root.user-interactive-qos",
.dq_serialnum = 14,
),
_DISPATCH_ROOT_QUEUE_ENTRY(USER_INTERACTIVE, DISPATCH_PRIORITY_FLAG_OVERCOMMIT,
.dq_label = "com.apple.root.user-interactive-qos.overcommit",
.dq_serialnum = 15,
),
};
其实我们平时用到的全局队列也是其中一个root队列,这个只要查看dispatch_get_global_queue代码就可以了:
dispatch_queue_global_t
dispatch_get_global_queue(intptr_t priority, uintptr_t flags)
{
dispatch_assert(countof(_dispatch_root_queues) ==
DISPATCH_ROOT_QUEUE_COUNT);
if (flags & ~(unsigned long)DISPATCH_QUEUE_OVERCOMMIT) {
return DISPATCH_BAD_INPUT;
}
dispatch_qos_t qos = _dispatch_qos_from_queue_priority(priority);
#if !HAVE_PTHREAD_WORKQUEUE_QOS
if (qos == QOS_CLASS_MAINTENANCE) {
qos = DISPATCH_QOS_BACKGROUND;
} else if (qos == QOS_CLASS_USER_INTERACTIVE) {
qos = DISPATCH_QOS_USER_INITIATED;
}
#endif
if (qos == DISPATCH_QOS_UNSPECIFIED) {
return DISPATCH_BAD_INPUT;
}
return _dispatch_get_root_queue(qos, flags & DISPATCH_QUEUE_OVERCOMMIT);
}
可以很清楚的看到,dispatch_get_global_queue的本质就是调用_dispatch_get_root_queue,其中的flag只是一个苹果予保留字段,通常我们传0(你可以试试传1应该队列创建失败),而代入上面的数组当使用dispatch_get_global_queue(QOS_CLASS_DEFAULT, 0)。如果打印这个返回结果可以看到:
<OS_dispatch_queue_global: com.apple.root.default-qos[0x1063cbf00] = { xref = -2147483648, ref = -2147483648, sref = 1, target = [0x0], width = 0xfff, state = 0x0060000000000000, in-barrier}>
首先通过上面数组进行索引2 * (qos - 1) + overcommit = 2*(4-1)+0 = 6 ,可以索引得到 dq_serialnum=10的队列,刚好label=com.apple.root.default-qos。至于qos参数为什么是4呢?
DISPATCH_ALWAYS_INLINE
static inline dispatch_qos_t
_dispatch_qos_from_queue_priority(intptr_t priority)
{
switch (priority) {
case DISPATCH_QUEUE_PRIORITY_BACKGROUND: return DISPATCH_QOS_BACKGROUND;
case DISPATCH_QUEUE_PRIORITY_NON_INTERACTIVE: return DISPATCH_QOS_UTILITY;
case DISPATCH_QUEUE_PRIORITY_LOW: return DISPATCH_QOS_UTILITY;
case DISPATCH_QUEUE_PRIORITY_DEFAULT: return DISPATCH_QOS_DEFAULT;
case DISPATCH_QUEUE_PRIORITY_HIGH: return DISPATCH_QOS_USER_INITIATED;
default: return _dispatch_qos_from_qos_class((qos_class_t)priority);
}
#define DISPATCH_QOS_DEFAULT ((dispatch_qos_t)4)
}
然后我们分析一下dispatch_queue_create中的DISPATCH_VTABLE这个宏:
#define DISPATCH_VTABLE(name) DISPATCH_OBJC_CLASS(name)
// 查看DISPATCH_OBJC_CLASS
#define DISPATCH_OBJC_CLASS(name) (&DISPATCH_CLASS_SYMBOL(name))
// 进一步查看 DISPATCH_CLASS_SYMBOL
#define DISPATCH_CLASS_SYMBOL(name) OS_dispatch_##name##_class
解析之后就是按队列类型分别获取不同队列类型的类: OS_dispatch_queue_concurrent_class 和 OS_dispatch_queue_serial_class ,对比我们平时打印一个队列的信息(如下),可以看到 OS_dispatch_queue_serial 或者 OS_dispatch_queue_concurrent_class :
<OS_dispatch_queue_serial: com.cmjstudio.dispatch[0x6000026a5a00] = { xref = 1, ref = 1, sref = 1, target = com.apple.root.default-qos.overcommit[0x108a4bf80], width = 0x1, state = 0x001ffe2000000000, in-flight = 0}>
接着看_dispatch_object_alloc和_dispatch_queue_init,分别用于申请对应类型的内存和初始化。首先看前者的实现:
// 注意对于iOS并不满足 OS_OBJECT_HAVE_OBJC1
void *
_dispatch_object_alloc(const void *vtable, size_t size)
{
#if OS_OBJECT_HAVE_OBJC1
const struct dispatch_object_vtable_s *_vtable = vtable;
dispatch_object_t dou;
dou._os_obj = _os_object_alloc_realized(_vtable->_os_obj_objc_isa, size);
dou._do->do_vtable = vtable;
return dou._do;
#else
return _os_object_alloc_realized(vtable, size);
#endif
}
// 接着看 _os_object_alloc_realized
_os_object_t
_os_object_alloc_realized(const void *cls, size_t size)
{
dispatch_assert(size >= sizeof(struct _os_object_s));
return _os_objc_alloc(cls, size);
}
// 再看一下 _os_objc_alloc
static inline id
_os_objc_alloc(Class cls, size_t size)
{
id obj;
size -= sizeof(((struct _os_object_s *)NULL)->os_obj_isa);
while (unlikely(!(obj = class_createInstance(cls, size)))) {
_dispatch_temporary_resource_shortage();
}
return obj;
}
DISPATCH_NOINLINE
void
_dispatch_temporary_resource_shortage(void)
{
sleep(1);
__asm__ __volatile__(""); // prevent tailcall
}
然后看一下内存分配之后的初始化_dispatch_queue_init源码,也只是简单的进行了初始化工作,不过值得一提的是dqai.dqai_concurrent ? DISPATCH_QUEUE_WIDTH_MAX : 1这个参数,DISPATCH_QUEUE_WIDTH_MAX其实看一下源码就知道是0x1000ull-2就是0xffe,而如果是串行队列就是1,这也是为什么可以在上面打印中看到width = 0x1的原因,width本身就是并发数的个数,对于串行队列是1而对于并发队列是不限制的(回过头去看全局队列width为什么是0xfff呢,因为它的width是#define DISPATCH_QUEUE_WIDTH_POOL (DISPATCH_QUEUE_WIDTH_FULL - 1)
)=0x1000ull-1:
static inline dispatch_queue_class_t
_dispatch_queue_init(dispatch_queue_class_t dqu, dispatch_queue_flags_t dqf,
uint16_t width, uint64_t initial_state_bits)
{
uint64_t dq_state = DISPATCH_QUEUE_STATE_INIT_VALUE(width);
dispatch_queue_t dq = dqu._dq;
dispatch_assert((initial_state_bits & ~(DISPATCH_QUEUE_ROLE_MASK |
DISPATCH_QUEUE_INACTIVE)) == 0);
if (initial_state_bits & DISPATCH_QUEUE_INACTIVE) {
dq_state |= DISPATCH_QUEUE_INACTIVE + DISPATCH_QUEUE_NEEDS_ACTIVATION;
dq->do_ref_cnt += 2; // rdar://8181908 see _dispatch_lane_resume
if (dx_metatype(dq) == _DISPATCH_SOURCE_TYPE) {
dq->do_ref_cnt++; // released when DSF_DELETED is set
}
}
dq_state |= (initial_state_bits & DISPATCH_QUEUE_ROLE_MASK);
dq->do_next = DISPATCH_OBJECT_LISTLESS;
dqf |= DQF_WIDTH(width);
os_atomic_store2o(dq, dq_atomic_flags, dqf, relaxed);
dq->dq_state = dq_state;
dq->dq_serialnum =
os_atomic_inc_orig(&_dispatch_queue_serial_numbers, relaxed);
return dqu;
}
接着看dispatch_queue_create的dq->do_targetq = tq;这句话是什么意思呢?这个其实是当使用dispatch_queue_create创建的自定义队列(事实上包括主队列和管理队列,也就是非全局队列[可以看一下上面的源代码全局队列并没有设置do_targetq,但是事实上它本身就是root队列]),都需要压入到全局队列(这里指的是root队列)进行处理,这个目标队列的目的就是允许我们将一个队列放在另一个队列里执行任务。看一下上面创建自定义队列的源码不难发现,如果是自定义一个串行队列其实最终就是一个root队列。
为了验证上面关于主队列也是root队列的说法不放看一下主队列的源码:
DISPATCH_INLINE DISPATCH_ALWAYS_INLINE DISPATCH_CONST DISPATCH_NOTHROW
dispatch_queue_main_t
dispatch_get_main_queue(void)
{
return DISPATCH_GLOBAL_OBJECT(dispatch_queue_main_t, _dispatch_main_q);
}
// 进一步查看 DISPATCH_GLOBAL_OBJECT
#define DISPATCH_GLOBAL_OBJECT(type, object) ((OS_OBJECT_BRIDGE type)&(object))
// 先看一下类型 dispatch_queue_main_t
#if defined(__DISPATCH_BUILDING_DISPATCH__) && !defined(__OBJC__)
typedef struct dispatch_queue_static_s *dispatch_queue_main_t;
#else
DISPATCH_DECL_SUBCLASS(dispatch_queue_main, dispatch_queue_serial);
#endif
// 然后查看 _dispatch_main_q,可以看到真正的类型如下
struct dispatch_queue_static_s _dispatch_main_q = {
DISPATCH_GLOBAL_OBJECT_HEADER(queue_main),
#if !DISPATCH_USE_RESOLVERS
.do_targetq = _dispatch_get_default_queue(true),
#endif
.dq_state = DISPATCH_QUEUE_STATE_INIT_VALUE(1) |
DISPATCH_QUEUE_ROLE_BASE_ANON,
.dq_label = "com.apple.main-thread",
.dq_atomic_flags = DQF_THREAD_BOUND | DQF_WIDTH(1),
.dq_serialnum = 1,
};
// 查看 _dispatch_get_default_queue源码
#define _dispatch_get_default_queue(overcommit) \
_dispatch_root_queues[DISPATCH_ROOT_QUEUE_IDX_DEFAULT_QOS + \
!!(overcommit)]._as_dq
// 查看 DISPATCH_ROOT_QUEUE_IDX_DEFAULT_QOS
enum {
DISPATCH_ROOT_QUEUE_IDX_MAINTENANCE_QOS = 0,
DISPATCH_ROOT_QUEUE_IDX_MAINTENANCE_QOS_OVERCOMMIT,
DISPATCH_ROOT_QUEUE_IDX_BACKGROUND_QOS,
DISPATCH_ROOT_QUEUE_IDX_BACKGROUND_QOS_OVERCOMMIT,
DISPATCH_ROOT_QUEUE_IDX_UTILITY_QOS,
DISPATCH_ROOT_QUEUE_IDX_UTILITY_QOS_OVERCOMMIT,
DISPATCH_ROOT_QUEUE_IDX_DEFAULT_QOS,
DISPATCH_ROOT_QUEUE_IDX_DEFAULT_QOS_OVERCOMMIT,
DISPATCH_ROOT_QUEUE_IDX_USER_INITIATED_QOS,
DISPATCH_ROOT_QUEUE_IDX_USER_INITIATED_QOS_OVERCOMMIT,
DISPATCH_ROOT_QUEUE_IDX_USER_INTERACTIVE_QOS,
DISPATCH_ROOT_QUEUE_IDX_USER_INTERACTIVE_QOS_OVERCOMMIT,
_DISPATCH_ROOT_QUEUE_IDX_COUNT,
};
可以看到主队列do_targetq也是一个root队列(通过获取_dispatch_root_queues),DISPATCH_ROOT_QUEUE_IDX_DEFAULT_QOS =6 所以 _dispatch_root_queues[6+1] 就是com.apple.root.default-qos.overcommit,不妨打印一些主队列(如下),可以看到target正是com.apple.root.default-qos.overcommit,而且width=1,其次由于dispatch_queue_main_t是对dispatch_queue_serial的重写所以也是一个串行队列:
<OS_dispatch_queue_main: com.apple.main-thread[0x1092dfb00] = { xref = -2147483648, ref = -2147483648, sref = 1, target = com.apple.root.default-qos.overcommit[0x1092dff80], width = 0x1, state = 0x001ffe9000000300, dirty, in-flight = 0, thread = 0x303 }>
到了这里关于队列的创建我们已经基本介绍完了,可以看到不管是自定义队列、全局队列还是主队列最终都直接或者间接的依赖12个root队列来执行任务调度(尽管如此主队列有自己的label,如果按照label计算总共16个,除了上面的12个,就是com.apple.main-thread还有两个内部管理队列com.apple.libdispatch-manager和com.apple.root.libdispatch-manager以及runloop的运行队列)。下面看一下几个常用的队列任务的执行方法的源码,对于任务的执行GCD其实主要用两个方法dispatch_sync和dispatch_async。
队列和线程之间的关系
上面提到一个重要概念是overcommit,overcommit的队列在队列创建时会新建一个线程,非overcommit队列创建队列则未必创建线程。另外width=1意味着是串行队列,只有一个线程可用,width=0xffe则意味着并行队列,线程则是从线程池获取,可用线程数是64个。
可以看到全局队列是非overcommit的(flat保留字只能传0,如果默认优先级则是com.apple.root.default-qos,但是width=0xffe是并行队列);主队列是overcommit的com.apple.root.default-qos.overcommit,不过它是串行队列,width=1,并且运行的这个线程只能是主线程;自定义串行队列是overcommit的,默认优先级则是 com.apple.root.default-qos.overcommit,并行队列则是非overcommit的。
这里看一下为什么上面说并行队列最大线程数是64个,不妨结合几个例子来查看:
/**
串行队列只有一个线程,线程num > 2
**/
- (void)test1 {
dispatch_queue_t serialQueue = dispatch_queue_create("com.cmjstudio.dispatch", DISPATCH_QUEUE_SERIAL);
for (int i=0; i<1000; ++i) {
dispatch_async(serialQueue, ^{
NSLog(@"%@,%i",[NSThread currentThread],i); // only one thread(number = 3~66)
});
}
}
- (void)test2 {
dispatch_queue_attr_t attr = dispatch_queue_attr_make_with_qos_class(DISPATCH_QUEUE_SERIAL, QOS_CLASS_USER_INITIATED, -1);
dispatch_queue_t serialQueue = dispatch_queue_create("com.cmjstudio.dispatch", attr);
for (int i=0; i<1000; ++i) {
dispatch_async(serialQueue, ^{
NSLog(@"%@,%i",[NSThread currentThread],i); // only one thread
});
}
}
/**
不管优先级多高并行队列有最多有64个线程,线程num在3~66,在一次轮询中遇到高优先级的会先执行
**/
- (void)test3 {
dispatch_queue_t concurrentQueue = dispatch_queue_create("com.cmjstudio.dispatch", DISPATCH_QUEUE_CONCURRENT);
for (int i=0; i<1000; ++i) {
dispatch_async(concurrentQueue, ^{
NSLog(@"%@,%i",[NSThread currentThread],i); // 64 thread (num = 3~66)
});
}
}
// 全局队列是并行队列(下面的demo会先输出global然后是所有custom再是剩余的global,整体遵循高优先级先执行规则,个别低优先级先输出的原因是发送global期间还没有轮训到高优先级任务,一旦遇到就会先执行高优先级任务)
- (void)test4 {
dispatch_queue_t globalQueue = dispatch_get_global_queue(DISPATCH_QUEUE_PRIORITY_LOW, 0);
for (int i=0; i<100; ++i) {
dispatch_async(globalQueue, ^{
NSLog(@"global:%@,%i",[NSThread currentThread],i); // 64 thread (num = 3~66)
});
}
dispatch_queue_attr_t attr = dispatch_queue_attr_make_with_qos_class(DISPATCH_QUEUE_CONCURRENT, QOS_CLASS_USER_INITIATED, -1);
dispatch_queue_t concurrentQueue = dispatch_queue_create("com.cmjstudio.dispatch", attr);
for (int i=0; i<100; ++i) {
dispatch_async(concurrentQueue, ^{
NSLog(@"custom:%@,%i",[NSThread currentThread],i); // 64 thread (num = 3~66)
});
}
}
/**
串行队列和并行队列都存在线程数多了1个,number最大到了67,不过串行队列的任务不一定在67这个线程中而是会复用前面的任意一个线程。说明串行队列加入时一定会创建一个线程
**/
- (void)test5 {
dispatch_queue_attr_t attr = dispatch_queue_attr_make_with_qos_class(DISPATCH_QUEUE_CONCURRENT, QOS_CLASS_USER_INITIATED, -1);
dispatch_queue_t concurrentQueue = dispatch_queue_create("com.cmjstudio.dispatch", attr);
for (int i=0; i<100; ++i) {
dispatch_async(concurrentQueue, ^{
NSLog(@"concurrent:%@,%i",[NSThread currentThread],i);
});
}
dispatch_queue_t serialQueue = dispatch_queue_create("com.cmjstudio.dispatch", DISPATCH_QUEUE_SERIAL);
for (int i=0; i<100; ++i) {
dispatch_async(serialQueue, ^{
NSLog(@"serial:%@,%i",[NSThread currentThread],i);
});
}
}
/**
当一个串行队列依附于一个并行队列时(非overcommit,如果是overcommit队列则会新建一个线程),线程最多恢复到了64个,并不会再新建一个线程了
**/
- (void)test6 {
dispatch_queue_attr_t attr = dispatch_queue_attr_make_with_qos_class(DISPATCH_QUEUE_CONCURRENT, QOS_CLASS_USER_INITIATED, -1);
dispatch_queue_t concurrentQueue = dispatch_queue_create("com.cmjstudio.dispatch", attr);
for (int i=0; i<100; ++i) {
dispatch_async(concurrentQueue, ^{
NSLog(@"%@,%i",[NSThread currentThread],i);
});
}
dispatch_queue_t serialQueue = dispatch_queue_create("com.cmjstudio.dispatch", DISPATCH_QUEUE_SERIAL);
dispatch_set_target_queue(serialQueue, concurrentQueue);
for (int i=0; i<100; ++i) {
dispatch_async(serialQueue, ^{
NSLog(@"%@,%i",[NSThread currentThread],i);
});
}
}
可以看到对于 dispatch_asyn 的调用(同步操作线程都在主线程不再赘述)串行队列是overcommit的,创建队列会创建1个新的线程,并行队列是非overcommit的,不一定会新建线程,会从线程池中的64个线程中获取并使用。另外上面的dispatch_set_target_queue 操作和前面源码中的do_targetq是作用一样的。
这样以来反而串行队列是开发中应该注意的,因为一旦新建一个串行队列就会新建一个线程,避免在类似循环操作中新建串行队列,这个上限是多少是任意多吗?其实也不是最多新增512个(不算主线程,number从4开始到515)但是这明显已经是灾难性的了。另外对于多个同一优先级的自定义串行队列(比如:com.apple.root.default-qos.overcommit)对于 dispatch_asyn 调用又怎么保证调用顺序呢?尽管是overcommit可以创建多个线程,毕竟都在一个root队列中执行,优先级又是相同的。
先看一段代码:
-(void)test10{
dispatch_queue_t serialQueue1 = dispatch_queue_create("com.cmjstudio.dispatch1", DISPATCH_QUEUE_SERIAL);
dispatch_queue_t serialQueue2 = dispatch_queue_create("com.cmjstudio.dispatch2", DISPATCH_QUEUE_SERIAL);
dispatch_queue_t serialQueue3 = dispatch_queue_create("com.cmjstudio.dispatch3", DISPATCH_QUEUE_SERIAL);
dispatch_async(serialQueue1, ^{
NSLog(@"serialQueue1 async invoke:%@", [NSThread currentThread]);
});
dispatch_async(serialQueue2, ^{
NSLog(@"serialQueue2 async invoke:%@", [NSThread currentThread]);
});
dispatch_async(serialQueue3, ^{
NSLog(@"serialQueue3 async invoke:%@", [NSThread currentThread]);
});
}
三次执行顺序依次如下:
2020-07-07 19:26:57.951602+0800 GCDBasic[68448:3758078] serialQueue2 async invoke:<NSThread: 0x600000e06500>{number = 4, name = (null)}
2020-07-07 19:26:57.951633+0800 GCDBasic[68448:3758079] serialQueue1 async invoke:<NSThread: 0x600000e37f00>{number = 6, name = (null)}
2020-07-07 19:26:57.951651+0800 GCDBasic[68448:3758076] serialQueue3 async invoke:<NSThread: 0x600000e3cc80>{number = 7, name = (null)}
2020-07-07 19:27:08.292555+0800 GCDBasic[68448:3758077] serialQueue1 async invoke:<NSThread: 0x600000e06480>{number = 3, name = (null)}
2020-07-07 19:27:08.292651+0800 GCDBasic[68448:3758271] serialQueue3 async invoke:<NSThread: 0x600000e37e80>{number = 8, name = (null)}
2020-07-07 19:27:08.292659+0800 GCDBasic[68448:3758273] serialQueue2 async invoke:<NSThread: 0x600000e30340>{number = 9, name = (null)}
2020-07-07 19:27:12.261150+0800 GCDBasic[68448:3758077] serialQueue1 async invoke:<NSThread: 0x600000e06480>{number = 3, name = (null)}
2020-07-07 19:27:12.261157+0800 GCDBasic[68448:3758273] serialQueue2 async invoke:<NSThread: 0x600000e30340>{number = 9, name = (null)}
2020-07-07 19:27:12.261162+0800 GCDBasic[68448:3758271] serialQueue3 async invoke:<NSThread: 0x600000e37e80>{number = 8, name = (null)}
确实单次执行都创建了新的线程(和前面说的 overcommit 是相符的),但是执行任务的顺序可以说是随机的,这个和线程调度有关,那么如果有比较重的任务会不会造成影响呢?这个答案是如果都分别创建了队列(overcommit)一般不会有影响,除非创建超过了512个,因为尽管是同一个root队列但是会创建不同的线程,此时当前root队列仅仅控制任务FIFO,但是并不是只有第一个任务执行完第二个任务才能开始,也就是说FIFO控制的是开始的节奏,但是任务在不同的thread执行不会阻塞。当然一个串行队列中的多个异步task是相互有执行顺序的,比如下面的代码task2一定会被task1阻塞,但是都不会阻塞task3:
-(void)test11{
dispatch_queue_t serialQueue1 = dispatch_queue_create("com.cmjstudio.dispatch1", DISPATCH_QUEUE_SERIAL);
dispatch_async(serialQueue1, ^{
NSLog(@"task1 in");
[NSThread sleepForTimeInterval:5];
NSLog(@"serialQueue1-task1 async invoke:%@", [NSThread currentThread]);
});
dispatch_async(serialQueue1, ^{
NSLog(@"task2 in");
[NSThread sleepForTimeInterval:5];
NSLog(@"serialQueue1-task2 async invoke:%@", [NSThread currentThread]);
});
dispatch_queue_t serialQueue2 = dispatch_queue_create("com.cmjstudio.dispatch2", DISPATCH_QUEUE_SERIAL);
dispatch_async(serialQueue2, ^{
NSLog(@"task3 in");
NSLog(@"serialQueue2-task3 async invoke:%@", [NSThread currentThread]);
});
}
同步执行 dispatch_sync
DISPATCH_NOINLINE
void
dispatch_sync(dispatch_queue_t dq, dispatch_block_t work)
{
uintptr_t dc_flags = DC_FLAG_BLOCK;
if (unlikely(_dispatch_block_has_private_data(work))) {
return _dispatch_sync_block_with_privdata(dq, work, dc_flags);
}
_dispatch_sync_f(dq, work, _dispatch_Block_invoke(work), dc_flags);
}
// 进一步查看 _dispatch_sync_f
DISPATCH_NOINLINE
static void
_dispatch_sync_f(dispatch_queue_t dq, void *ctxt, dispatch_function_t func,
uintptr_t dc_flags)
{
_dispatch_sync_f_inline(dq, ctxt, func, dc_flags);
}
// 查看 _dispatch_sync_f_inline
DISPATCH_ALWAYS_INLINE
static inline void
_dispatch_sync_f_inline(dispatch_queue_t dq, void *ctxt,
dispatch_function_t func, uintptr_t dc_flags)
{
if (likely(dq->dq_width == 1)) {
return _dispatch_barrier_sync_f(dq, ctxt, func, dc_flags);
}
if (unlikely(dx_metatype(dq) != _DISPATCH_LANE_TYPE)) {
DISPATCH_CLIENT_CRASH(0, "Queue type doesn't support dispatch_sync");
}
dispatch_lane_t dl = upcast(dq)._dl;
// Global concurrent queues and queues bound to non-dispatch threads
// always fall into the slow case, see DISPATCH_ROOT_QUEUE_STATE_INIT_VALUE
if (unlikely(!_dispatch_queue_try_reserve_sync_width(dl))) {
return _dispatch_sync_f_slow(dl, ctxt, func, 0, dl, dc_flags);
}
if (unlikely(dq->do_targetq->do_targetq)) {
return _dispatch_sync_recurse(dl, ctxt, func, dc_flags);
}
_dispatch_introspection_sync_begin(dl);
_dispatch_sync_invoke_and_complete(dl, ctxt, func DISPATCH_TRACE_ARG(
_dispatch_trace_item_sync_push_pop(dq, ctxt, func, dc_flags)));
}
可以看到首先通过width判定是串行队列还是并发队列,如果是并发队列则调用_dispatch_sync_invoke_and_complete,串行队列则调用_dispatch_barrier_sync_f。先展开看一下串行队列的同步执行源代码:
DISPATCH_NOINLINE
static void
_dispatch_barrier_sync_f(dispatch_queue_t dq, void *ctxt,
dispatch_function_t func, uintptr_t dc_flags)
{
_dispatch_barrier_sync_f_inline(dq, ctxt, func, dc_flags);
}
// 看一下 _dispatch_barrier_sync_f_inline
DISPATCH_ALWAYS_INLINE
static inline void
_dispatch_barrier_sync_f_inline(dispatch_queue_t dq, void *ctxt,
dispatch_function_t func, uintptr_t dc_flags)
{
dispatch_tid tid = _dispatch_tid_self();
if (unlikely(dx_metatype(dq) != _DISPATCH_LANE_TYPE)) {
DISPATCH_CLIENT_CRASH(0, "Queue type doesn't support dispatch_sync");
}
dispatch_lane_t dl = upcast(dq)._dl;
// The more correct thing to do would be to merge the qos of the thread
// that just acquired the barrier lock into the queue state.
//
// However this is too expensive for the fast path, so skip doing it.
// The chosen tradeoff is that if an enqueue on a lower priority thread
// contends with this fast path, this thread may receive a useless override.
//
// Global concurrent queues and queues bound to non-dispatch threads
// always fall into the slow case, see DISPATCH_ROOT_QUEUE_STATE_INIT_VALUE
if (unlikely(!_dispatch_queue_try_acquire_barrier_sync(dl, tid))) {
return _dispatch_sync_f_slow(dl, ctxt, func, DC_FLAG_BARRIER, dl,
DC_FLAG_BARRIER | dc_flags);
}
if (unlikely(dl->do_targetq->do_targetq)) {
return _dispatch_sync_recurse(dl, ctxt, func,
DC_FLAG_BARRIER | dc_flags);
}
_dispatch_introspection_sync_begin(dl);
_dispatch_lane_barrier_sync_invoke_and_complete(dl, ctxt, func
DISPATCH_TRACE_ARG(_dispatch_trace_item_sync_push_pop(
dq, ctxt, func, dc_flags | DC_FLAG_BARRIER)));
}
首先获取线程id,然后处理死锁的情况,因此这里先看一下死锁的情况:
DISPATCH_NOINLINE
static void
_dispatch_sync_f_slow(dispatch_queue_class_t top_dqu, void *ctxt,
dispatch_function_t func, uintptr_t top_dc_flags,
dispatch_queue_class_t dqu, uintptr_t dc_flags)
{
dispatch_queue_t top_dq = top_dqu._dq;
dispatch_queue_t dq = dqu._dq;
if (unlikely(!dq->do_targetq)) {
return _dispatch_sync_function_invoke(dq, ctxt, func);
}
pthread_priority_t pp = _dispatch_get_priority();
struct dispatch_sync_context_s dsc = {
.dc_flags = DC_FLAG_SYNC_WAITER | dc_flags,
.dc_func = _dispatch_async_and_wait_invoke,
.dc_ctxt = &dsc,
.dc_other = top_dq,
.dc_priority = pp | _PTHREAD_PRIORITY_ENFORCE_FLAG,
.dc_voucher = _voucher_get(),
.dsc_func = func,
.dsc_ctxt = ctxt,
.dsc_waiter = _dispatch_tid_self(),
};
_dispatch_trace_item_push(top_dq, &dsc);
__DISPATCH_WAIT_FOR_QUEUE__(&dsc, dq);
if (dsc.dsc_func == NULL) {
dispatch_queue_t stop_dq = dsc.dc_other;
return _dispatch_sync_complete_recurse(top_dq, stop_dq, top_dc_flags);
}
_dispatch_introspection_sync_begin(top_dq);
_dispatch_trace_item_pop(top_dq, &dsc);
_dispatch_sync_invoke_and_complete_recurse(top_dq, ctxt, func,top_dc_flags
DISPATCH_TRACE_ARG(&dsc));
}
// 看一下 __DISPATCH_WAIT_FOR_QUEUE__
DISPATCH_NOINLINE
static void
__DISPATCH_WAIT_FOR_QUEUE__(dispatch_sync_context_t dsc, dispatch_queue_t dq)
{
uint64_t dq_state = _dispatch_wait_prepare(dq);
if (unlikely(_dq_state_drain_locked_by(dq_state, dsc->dsc_waiter))) {
DISPATCH_CLIENT_CRASH((uintptr_t)dq_state,
"dispatch_sync called on queue "
"already owned by current thread");
}
// Blocks submitted to the main thread MUST run on the main thread, and
// dispatch_async_and_wait also executes on the remote context rather than
// the current thread.
//
// For both these cases we need to save the frame linkage for the sake of
// _dispatch_async_and_wait_invoke
_dispatch_thread_frame_save_state(&dsc->dsc_dtf);
if (_dq_state_is_suspended(dq_state) ||
_dq_state_is_base_anon(dq_state)) {
dsc->dc_data = DISPATCH_WLH_ANON;
} else if (_dq_state_is_base_wlh(dq_state)) {
dsc->dc_data = (dispatch_wlh_t)dq;
} else {
_dispatch_wait_compute_wlh(upcast(dq)._dl, dsc);
}
if (dsc->dc_data == DISPATCH_WLH_ANON) {
dsc->dsc_override_qos_floor = dsc->dsc_override_qos =
(uint8_t)_dispatch_get_basepri_override_qos_floor();
_dispatch_thread_event_init(&dsc->dsc_event);
}
dx_push(dq, dsc, _dispatch_qos_from_pp(dsc->dc_priority));
_dispatch_trace_runtime_event(sync_wait, dq, 0);
if (dsc->dc_data == DISPATCH_WLH_ANON) {
_dispatch_thread_event_wait(&dsc->dsc_event); // acquire
} else {
_dispatch_event_loop_wait_for_ownership(dsc);
}
if (dsc->dc_data == DISPATCH_WLH_ANON) {
_dispatch_thread_event_destroy(&dsc->dsc_event);
// If _dispatch_sync_waiter_wake() gave this thread an override,
// ensure that the root queue sees it.
if (dsc->dsc_override_qos > dsc->dsc_override_qos_floor) {
_dispatch_set_basepri_override_qos(dsc->dsc_override_qos);
}
}
}
// 展开 _dq_state_drain_locked_by
DISPATCH_ALWAYS_INLINE
static inline bool
_dq_state_drain_locked_by(uint64_t dq_state, dispatch_tid tid)
{
return _dispatch_lock_is_locked_by((dispatch_lock)dq_state, tid);
}
// 然后看一下 _dispatch_lock_is_locked_by
DISPATCH_ALWAYS_INLINE
static inline bool
_dispatch_lock_is_locked_by(dispatch_lock lock_value, dispatch_tid tid)
{
// equivalent to _dispatch_lock_owner(lock_value) == tid
return ((lock_value ^ tid) & DLOCK_OWNER_MASK) == 0;
}
队列push以后就是用_dispatch_lock_is_locked_by判断将要调度的和当前等待的队列是不是同一个,如果相同则返回YES,产生死锁DISPATCH_CLIENT_CRASH;如果没有产生死锁,则执行 _dispatch_trace_item_pop()出队列执行。如何执行调度呢,需要看一下_dispatch_sync_invoke_and_complete_recurse?
DISPATCH_NOINLINE
static void
_dispatch_sync_invoke_and_complete_recurse(dispatch_queue_class_t dq,
void *ctxt, dispatch_function_t func, uintptr_t dc_flags
DISPATCH_TRACE_ARG(void *dc))
{
_dispatch_sync_function_invoke_inline(dq, ctxt, func);
_dispatch_trace_item_complete(dc);
_dispatch_sync_complete_recurse(dq._dq, NULL, dc_flags);
}
// 看一下 _dispatch_sync_function_invoke_inline
DISPATCH_ALWAYS_INLINE
static inline void
_dispatch_sync_function_invoke_inline(dispatch_queue_class_t dq, void *ctxt,
dispatch_function_t func)
{
dispatch_thread_frame_s dtf;
_dispatch_thread_frame_push(&dtf, dq);
_dispatch_client_callout(ctxt, func);
_dispatch_perfmon_workitem_inc();
_dispatch_thread_frame_pop(&dtf);
}
// 看一下 _dispatch_client_callout
void
_dispatch_client_callout(void *ctxt, dispatch_function_t f)
{
@try {
return f(ctxt);
}
@catch (...) {
objc_terminate();
}
}
可以比较清楚的看到最终执行f函数,这个就是外界传过来的回调block。
异步调用 dispatch_async
void
dispatch_async(dispatch_queue_t dq, dispatch_block_t work)
{
dispatch_continuation_t dc = _dispatch_continuation_alloc();
uintptr_t dc_flags = DC_FLAG_CONSUME;
dispatch_qos_t qos;
qos = _dispatch_continuation_init(dc, dq, work, 0, dc_flags);
_dispatch_continuation_async(dq, dc, qos, dc->dc_flags);
}
// 查看 _dispatch_continuation_init 代码,主要进行block初始化
DISPATCH_ALWAYS_INLINE
static inline dispatch_qos_t
_dispatch_continuation_init(dispatch_continuation_t dc,
dispatch_queue_class_t dqu, dispatch_block_t work,
dispatch_block_flags_t flags, uintptr_t dc_flags)
{
void *ctxt = _dispatch_Block_copy(work);
dc_flags |= DC_FLAG_BLOCK | DC_FLAG_ALLOCATED;
if (unlikely(_dispatch_block_has_private_data(work))) {
dc->dc_flags = dc_flags;
dc->dc_ctxt = ctxt;
// will initialize all fields but requires dc_flags & dc_ctxt to be set
return _dispatch_continuation_init_slow(dc, dqu, flags);
}
dispatch_function_t func = _dispatch_Block_invoke(work);
if (dc_flags & DC_FLAG_CONSUME) {
func = _dispatch_call_block_and_release;
}
return _dispatch_continuation_init_f(dc, dqu, ctxt, func, flags, dc_flags);
}
// 另外查看 _dispatch_continuation_async
DISPATCH_ALWAYS_INLINE
static inline void
_dispatch_continuation_async(dispatch_queue_class_t dqu,
dispatch_continuation_t dc, dispatch_qos_t qos, uintptr_t dc_flags)
{
#if DISPATCH_INTROSPECTION
if (!(dc_flags & DC_FLAG_NO_INTROSPECTION)) {
_dispatch_trace_item_push(dqu, dc);
}
#else
(void)dc_flags;
#endif
return dx_push(dqu._dq, dc, qos);
}
// 进一步查看 dx_push
#define dx_push(x, y, z) dx_vtable(x)->dq_push(x, y, z)
// 本质是调用dx_vtable的dq_push(其实就是调用对象的do_push),进一步查看 dq_push,我们假设是global_queue进行异步调用可以看到:
DISPATCH_VTABLE_SUBCLASS_INSTANCE(queue_global, lane,
.do_type = DISPATCH_QUEUE_GLOBAL_ROOT_TYPE,
.do_dispose = _dispatch_object_no_dispose,
.do_debug = _dispatch_queue_debug,
.do_invoke = _dispatch_object_no_invoke,
.dq_activate = _dispatch_queue_no_activate,
.dq_wakeup = _dispatch_root_queue_wakeup,
.dq_push = _dispatch_root_queue_push,
);
可以看到dx_push已经到了_dispatch_root_queue_push,这是可以接着查看_dispatch_root_queue_push:
DISPATCH_NOINLINE
void
_dispatch_root_queue_push(dispatch_queue_global_t rq, dispatch_object_t dou,
dispatch_qos_t qos)
{
#if DISPATCH_USE_KEVENT_WORKQUEUE
dispatch_deferred_items_t ddi = _dispatch_deferred_items_get();
if (unlikely(ddi && ddi->ddi_can_stash)) {
dispatch_object_t old_dou = ddi->ddi_stashed_dou;
dispatch_priority_t rq_overcommit;
rq_overcommit = rq->dq_priority & DISPATCH_PRIORITY_FLAG_OVERCOMMIT;
if (likely(!old_dou._do || rq_overcommit)) {
dispatch_queue_global_t old_rq = ddi->ddi_stashed_rq;
dispatch_qos_t old_qos = ddi->ddi_stashed_qos;
ddi->ddi_stashed_rq = rq;
ddi->ddi_stashed_dou = dou;
ddi->ddi_stashed_qos = qos;
_dispatch_debug("deferring item %p, rq %p, qos %d",
dou._do, rq, qos);
if (rq_overcommit) {
ddi->ddi_can_stash = false;
}
if (likely(!old_dou._do)) {
return;
}
// push the previously stashed item
qos = old_qos;
rq = old_rq;
dou = old_dou;
}
}
#endif
#if HAVE_PTHREAD_WORKQUEUE_QOS
if (_dispatch_root_queue_push_needs_override(rq, qos)) {
return _dispatch_root_queue_push_override(rq, dou, qos);
}
#else
(void)qos;
#endif
_dispatch_root_queue_push_inline(rq, dou, dou, 1);
}
// 多数情况下符合HAVE_PTHREAD_WORKQUEUE_QOS,会执行_dispatch_root_queue_push_override(对比的是qos与root队列的qos是否一致,基本上都不一致的。)
DISPATCH_NOINLINE
static void
_dispatch_root_queue_push_override(dispatch_queue_global_t orig_rq,
dispatch_object_t dou, dispatch_qos_t qos)
{
bool overcommit = orig_rq->dq_priority & DISPATCH_PRIORITY_FLAG_OVERCOMMIT;
dispatch_queue_global_t rq = _dispatch_get_root_queue(qos, overcommit);
dispatch_continuation_t dc = dou._dc;
if (_dispatch_object_is_redirection(dc)) {
// no double-wrap is needed, _dispatch_async_redirect_invoke will do
// the right thing
dc->dc_func = (void *)orig_rq;
} else {
dc = _dispatch_continuation_alloc();
dc->do_vtable = DC_VTABLE(OVERRIDE_OWNING);
dc->dc_ctxt = dc;
dc->dc_other = orig_rq;
dc->dc_data = dou._do;
dc->dc_priority = DISPATCH_NO_PRIORITY;
dc->dc_voucher = DISPATCH_NO_VOUCHER;
}
_dispatch_root_queue_push_inline(rq, dc, dc, 1);
}
// 上面_dispatch_object_is_redirection函数其实就是return _dispatch_object_has_type(dou,DISPATCH_CONTINUATION_TYPE(ASYNC_REDIRECT));所以自定义队列会走这个if语句,如果是dispatch_get_global_queue不会走if语句。展开 _dispatch_root_queue_push_inline。注意_dispatch_root_queue_push_inline中的if把任务装进队列,大多数不走进if语句。但是第一个任务进来之前还是满足这个条件式的,会进入这个条件语句去激活队列来执行里面的任务,后面再加入的任务因为队列被激活了,所以也就不太需要再进入这个队列了,所以相对来说激活队列只要一次
DISPATCH_ALWAYS_INLINE
static inline void
_dispatch_root_queue_push_inline(dispatch_queue_global_t dq,
dispatch_object_t _head, dispatch_object_t _tail, int n)
{
struct dispatch_object_s *hd = _head._do, *tl = _tail._do;
if (unlikely(os_mpsc_push_list(os_mpsc(dq, dq_items), hd, tl, do_next))) {
return _dispatch_root_queue_poke(dq, n, 0);
}
}
// 我们可以看到,我们装入到自定义的任务都被扔到其挂靠的root队列里去了,所以我们我们自己创建的队列只是一个代理人身份,继续查看 _dispatch_root_queue_poke 源码
DISPATCH_NOINLINE
void
_dispatch_root_queue_poke(dispatch_queue_global_t dq, int n, int floor)
{
if (!_dispatch_queue_class_probe(dq)) {
return;
}
#if !DISPATCH_USE_INTERNAL_WORKQUEUE
#if DISPATCH_USE_PTHREAD_POOL
if (likely(dx_type(dq) == DISPATCH_QUEUE_GLOBAL_ROOT_TYPE))
#endif
{
if (unlikely(!os_atomic_cmpxchg2o(dq, dgq_pending, 0, n, relaxed))) {
_dispatch_root_queue_debug("worker thread request still pending "
"for global queue: %p", dq);
return;
}
}
#endif // !DISPATCH_USE_INTERNAL_WORKQUEUE
return _dispatch_root_queue_poke_slow(dq, n, floor);
}
// 继续查看 _dispatch_root_queue_poke_slow
DISPATCH_NOINLINE
static void
_dispatch_root_queue_poke_slow(dispatch_queue_global_t dq, int n, int floor)
{
int remaining = n;
#if !defined(_WIN32)
int r = ENOSYS;
#endif
_dispatch_root_queues_init();
_dispatch_debug_root_queue(dq, __func__);
_dispatch_trace_runtime_event(worker_request, dq, (uint64_t)n);
#if !DISPATCH_USE_INTERNAL_WORKQUEUE
#if DISPATCH_USE_PTHREAD_ROOT_QUEUES
if (dx_type(dq) == DISPATCH_QUEUE_GLOBAL_ROOT_TYPE)
#endif
{
_dispatch_root_queue_debug("requesting new worker thread for global "
"queue: %p", dq);
r = _pthread_workqueue_addthreads(remaining,
_dispatch_priority_to_pp_prefer_fallback(dq->dq_priority));
(void)dispatch_assume_zero(r);
return;
}
#endif // !DISPATCH_USE_INTERNAL_WORKQUEUE
#if DISPATCH_USE_PTHREAD_POOL
dispatch_pthread_root_queue_context_t pqc = dq->do_ctxt;
if (likely(pqc->dpq_thread_mediator.do_vtable)) {
while (dispatch_semaphore_signal(&pqc->dpq_thread_mediator)) {
_dispatch_root_queue_debug("signaled sleeping worker for "
"global queue: %p", dq);
if (!--remaining) {
return;
}
}
}
bool overcommit = dq->dq_priority & DISPATCH_PRIORITY_FLAG_OVERCOMMIT;
if (overcommit) {
os_atomic_add2o(dq, dgq_pending, remaining, relaxed);
} else {
if (!os_atomic_cmpxchg2o(dq, dgq_pending, 0, remaining, relaxed)) {
_dispatch_root_queue_debug("worker thread request still pending for "
"global queue: %p", dq);
return;
}
}
int can_request, t_count;
// seq_cst with atomic store to tail <rdar://problem/16932833>
t_count = os_atomic_load2o(dq, dgq_thread_pool_size, ordered);
do {
can_request = t_count < floor ? 0 : t_count - floor;
if (remaining > can_request) {
_dispatch_root_queue_debug("pthread pool reducing request from %d to %d",
remaining, can_request);
os_atomic_sub2o(dq, dgq_pending, remaining - can_request, relaxed);
remaining = can_request;
}
if (remaining == 0) {
_dispatch_root_queue_debug("pthread pool is full for root queue: "
"%p", dq);
return;
}
} while (!os_atomic_cmpxchgvw2o(dq, dgq_thread_pool_size, t_count,
t_count - remaining, &t_count, acquire));
#if !defined(_WIN32)
pthread_attr_t *attr = &pqc->dpq_thread_attr;
pthread_t tid, *pthr = &tid;
#if DISPATCH_USE_MGR_THREAD && DISPATCH_USE_PTHREAD_ROOT_QUEUES
if (unlikely(dq == &_dispatch_mgr_root_queue)) {
pthr = _dispatch_mgr_root_queue_init();
}
#endif
do {
_dispatch_retain(dq); // released in _dispatch_worker_thread
while ((r = pthread_create(pthr, attr, _dispatch_worker_thread, dq))) {
if (r != EAGAIN) {
(void)dispatch_assume_zero(r);
}
_dispatch_temporary_resource_shortage();
}
} while (--remaining);
#else // defined(_WIN32)
#if DISPATCH_USE_MGR_THREAD && DISPATCH_USE_PTHREAD_ROOT_QUEUES
if (unlikely(dq == &_dispatch_mgr_root_queue)) {
_dispatch_mgr_root_queue_init();
}
#endif
do {
_dispatch_retain(dq); // released in _dispatch_worker_thread
uintptr_t hThread = 0;
while (!(hThread = _beginthreadex(NULL, /* stack_size */ 0, _dispatch_worker_thread_thunk, dq, STACK_SIZE_PARAM_IS_A_RESERVATION, NULL))) {
if (errno != EAGAIN) {
(void)dispatch_assume(hThread);
}
_dispatch_temporary_resource_shortage();
}
#if DISPATCH_USE_PTHREAD_ROOT_QUEUES
if (_dispatch_mgr_sched.prio > _dispatch_mgr_sched.default_prio) {
(void)dispatch_assume_zero(SetThreadPriority((HANDLE)hThread, _dispatch_mgr_sched.prio) == TRUE);
}
#endif
CloseHandle((HANDLE)hThread);
} while (--remaining);
#endif // defined(_WIN32)
#else
(void)floor;
#endif // DISPATCH_USE_PTHREAD_POOL
}
到了这里可以清楚的看到对于全局队列使用_pthread_workqueue_addthreads开辟线程,对于其他队列使用pthread_create开辟新的线程。那么任务执行的代码为什么没看到?其实_dispatch_root_queues_init中会首先执行第一个任务:
DISPATCH_ALWAYS_INLINE
static inline void
_dispatch_root_queues_init(void)
{
dispatch_once_f(&_dispatch_root_queues_pred, NULL,
_dispatch_root_queues_init_once);
}
// 看一下dispatch_once_f就不展开了,可以看一下下面dispatch_once的分析,这里看一下 _dispatch_root_queues_init_once
static void
_dispatch_root_queues_init_once(void *context DISPATCH_UNUSED)
{
_dispatch_fork_becomes_unsafe();
#if DISPATCH_USE_INTERNAL_WORKQUEUE
size_t i;
for (i = 0; i < DISPATCH_ROOT_QUEUE_COUNT; i++) {
_dispatch_root_queue_init_pthread_pool(&_dispatch_root_queues[i], 0,
_dispatch_root_queues[i].dq_priority);
}
#else
int wq_supported = _pthread_workqueue_supported();
int r = ENOTSUP;
if (!(wq_supported & WORKQ_FEATURE_MAINTENANCE)) {
DISPATCH_INTERNAL_CRASH(wq_supported,
"QoS Maintenance support required");
}
if (unlikely(!_dispatch_kevent_workqueue_enabled)) {
r = _pthread_workqueue_init(_dispatch_worker_thread2,
offsetof(struct dispatch_queue_s, dq_serialnum), 0);
#if DISPATCH_USE_KEVENT_WORKLOOP
} else if (wq_supported & WORKQ_FEATURE_WORKLOOP) {
r = _pthread_workqueue_init_with_workloop(_dispatch_worker_thread2,
(pthread_workqueue_function_kevent_t)
_dispatch_kevent_worker_thread,
(pthread_workqueue_function_workloop_t)
_dispatch_workloop_worker_thread,
offsetof(struct dispatch_queue_s, dq_serialnum), 0);
#endif // DISPATCH_USE_KEVENT_WORKLOOP
#if DISPATCH_USE_KEVENT_WORKQUEUE
} else if (wq_supported & WORKQ_FEATURE_KEVENT) {
r = _pthread_workqueue_init_with_kevent(_dispatch_worker_thread2,
(pthread_workqueue_function_kevent_t)
_dispatch_kevent_worker_thread,
offsetof(struct dispatch_queue_s, dq_serialnum), 0);
#endif
} else {
DISPATCH_INTERNAL_CRASH(wq_supported, "Missing Kevent WORKQ support");
}
if (r != 0) {
DISPATCH_INTERNAL_CRASH((r << 16) | wq_supported,
"Root queue initialization failed");
}
#endif // DISPATCH_USE_INTERNAL_WORKQUEUE
}
// 继续查看
DISPATCH_NOINLINE
static void
_dispatch_workloop_worker_thread(uint64_t *workloop_id,
dispatch_kevent_t *events, int *nevents)
{
if (!workloop_id || !dispatch_assume(*workloop_id != 0)) {
return _dispatch_kevent_worker_thread(events, nevents);
}
if (!events || !nevents) {
// events for worker thread request have already been delivered earlier
return;
}
if (!dispatch_assume(*nevents && *events)) return;
dispatch_wlh_t wlh = (dispatch_wlh_t)*workloop_id;
_dispatch_adopt_wlh(wlh);
_dispatch_wlh_worker_thread(wlh, *events, nevents);
_dispatch_preserve_wlh_storage_reference(wlh);
}
// 查看 _dispatch_worker_thread2
static void
_dispatch_worker_thread2(pthread_priority_t pp)
{
bool overcommit = pp & _PTHREAD_PRIORITY_OVERCOMMIT_FLAG;
dispatch_queue_global_t dq;
pp &= _PTHREAD_PRIORITY_OVERCOMMIT_FLAG | ~_PTHREAD_PRIORITY_FLAGS_MASK;
_dispatch_thread_setspecific(dispatch_priority_key, (void *)(uintptr_t)pp);
dq = _dispatch_get_root_queue(_dispatch_qos_from_pp(pp), overcommit);
_dispatch_introspection_thread_add();
_dispatch_trace_runtime_event(worker_unpark, dq, 0);
int pending = os_atomic_dec2o(dq, dgq_pending, relaxed);
dispatch_assert(pending >= 0);
_dispatch_root_queue_drain(dq, dq->dq_priority,
DISPATCH_INVOKE_WORKER_DRAIN | DISPATCH_INVOKE_REDIRECTING_DRAIN);
_dispatch_voucher_debug("root queue clear", NULL);
_dispatch_reset_voucher(NULL, DISPATCH_THREAD_PARK);
_dispatch_trace_runtime_event(worker_park, NULL, 0);
}
// 查看 _dispatch_root_queue_drain
DISPATCH_NOT_TAIL_CALLED // prevent tailcall (for Instrument DTrace probe)
static void
_dispatch_root_queue_drain(dispatch_queue_global_t dq,
dispatch_priority_t pri, dispatch_invoke_flags_t flags)
{
#if DISPATCH_DEBUG
dispatch_queue_t cq;
if (unlikely(cq = _dispatch_queue_get_current())) {
DISPATCH_INTERNAL_CRASH(cq, "Premature thread recycling");
}
#endif
_dispatch_queue_set_current(dq);
_dispatch_init_basepri(pri);
_dispatch_adopt_wlh_anon();
struct dispatch_object_s *item;
bool reset = false;
dispatch_invoke_context_s dic = { };
#if DISPATCH_COCOA_COMPAT
_dispatch_last_resort_autorelease_pool_push(&dic);
#endif // DISPATCH_COCOA_COMPAT
_dispatch_queue_drain_init_narrowing_check_deadline(&dic, pri);
_dispatch_perfmon_start();
while (likely(item = _dispatch_root_queue_drain_one(dq))) {
if (reset) _dispatch_wqthread_override_reset();
_dispatch_continuation_pop_inline(item, &dic, flags, dq);
reset = _dispatch_reset_basepri_override();
if (unlikely(_dispatch_queue_drain_should_narrow(&dic))) {
break;
}
}
// overcommit or not. worker thread
if (pri & DISPATCH_PRIORITY_FLAG_OVERCOMMIT) {
_dispatch_perfmon_end(perfmon_thread_worker_oc);
} else {
_dispatch_perfmon_end(perfmon_thread_worker_non_oc);
}
#if DISPATCH_COCOA_COMPAT
_dispatch_last_resort_autorelease_pool_pop(&dic);
#endif // DISPATCH_COCOA_COMPAT
_dispatch_reset_wlh();
_dispatch_clear_basepri();
_dispatch_queue_set_current(NULL);
}
// 查看 _dispatch_continuation_pop_inline 这个是出队列操作,这里注意一下首先看了有没有vtable(_dispatch_object_has_vtable),这里解释了为什么dispatch_barrier_async尽管主要流程和dispatch_async一模一样但是无法应用到全局队列的原因,因为全局队列没有v_table结构会直接像dispatch_async一样执行
DISPATCH_ALWAYS_INLINE_NDEBUG
static inline void
_dispatch_continuation_pop_inline(dispatch_object_t dou,
dispatch_invoke_context_t dic, dispatch_invoke_flags_t flags,
dispatch_queue_class_t dqu)
{
dispatch_pthread_root_queue_observer_hooks_t observer_hooks =
_dispatch_get_pthread_root_queue_observer_hooks();
if (observer_hooks) observer_hooks->queue_will_execute(dqu._dq);
flags &= _DISPATCH_INVOKE_PROPAGATE_MASK;
if (_dispatch_object_has_vtable(dou)) {
dx_invoke(dou._dq, dic, flags);
} else {
_dispatch_continuation_invoke_inline(dou, flags, dqu);
}
if (observer_hooks) observer_hooks->queue_did_execute(dqu._dq);
}
// 查看 _dispatch_continuation_invoke_inline ,这里`_dispatch_client_callout`就是真正的执行block操作 ,当然还有一种情况这里还不会走就是_dispatch_continuation_with_group_invoke,这个后面的dispatch_group会用到
DISPATCH_ALWAYS_INLINE
static inline void
_dispatch_continuation_invoke_inline(dispatch_object_t dou,
dispatch_invoke_flags_t flags, dispatch_queue_class_t dqu)
{
dispatch_continuation_t dc = dou._dc, dc1;
dispatch_invoke_with_autoreleasepool(flags, {
uintptr_t dc_flags = dc->dc_flags;
// Add the item back to the cache before calling the function. This
// allows the 'hot' continuation to be used for a quick callback.
//
// The ccache version is per-thread.
// Therefore, the object has not been reused yet.
// This generates better assembly.
_dispatch_continuation_voucher_adopt(dc, dc_flags);
if (!(dc_flags & DC_FLAG_NO_INTROSPECTION)) {
_dispatch_trace_item_pop(dqu, dou);
}
if (dc_flags & DC_FLAG_CONSUME) {
dc1 = _dispatch_continuation_free_cacheonly(dc);
} else {
dc1 = NULL;
}
if (unlikely(dc_flags & DC_FLAG_GROUP_ASYNC)) {
_dispatch_continuation_with_group_invoke(dc);
} else {
_dispatch_client_callout(dc->dc_ctxt, dc->dc_func);
_dispatch_trace_item_complete(dc);
}
if (unlikely(dc1)) {
_dispatch_continuation_free_to_cache_limit(dc1);
}
});
_dispatch_perfmon_workitem_inc();
}
另外对于_dispatch_continuation_init的代码中的并没有对其进行展开,其实_dispatch_continuation_init中的func就是_dispatch_call_block_and_release(源码如下),它在dx_push调用时包装进了qos。
void
_dispatch_call_block_and_release(void *block)
{
void (^b)(void) = block;
b();
Block_release(b);
}
dispatch_async代码实现看起来比较复杂,因为其中的数据结构较多,分支流程控制比较复杂。不过思路其实很简单,用链表保存所有提交的 block(先进先出,,在队列本身维护了一个链表新加入block放到链表尾部),然后在底层线程池中,依次取出 block 并执行。
类似的可以看到dispatch_barrier_async源码和dispatch_async几乎一致,仅仅多了一个标记位DC_FLAG_BARRIER,这个标记位用于在取出任务时进行判断,正常的异步调用会依次取出,而如果遇到了DC_FLAG_BARRIER则会返回,所以可以等待所有任务执行结束执行dx_push(不过提醒一下dispatch_barrier_async必须在自定义队列才有用,原因是global队列没有v_table结构,同时不要试图在主队列调用,否则会crash):
void
dispatch_barrier_async(dispatch_queue_t dq, dispatch_block_t work)
{
dispatch_continuation_t dc = _dispatch_continuation_alloc();
uintptr_t dc_flags = DC_FLAG_CONSUME | DC_FLAG_BARRIER;
dispatch_qos_t qos;
qos = _dispatch_continuation_init(dc, dq, work, 0, dc_flags);
_dispatch_continuation_async(dq, dc, qos, dc_flags);
}
单次执行dispatch_once
下面的代码在objc开发中应该很常见,这种方式可以保证instance只会创建一次:
+ (instancetype)sharedInstance {
static MyClass *instance;
static dispatch_once_t onceToken;
dispatch_once(&onceToken, ^{
instance = [[MyClass alloc] init];
});
return instance;
}
不放分析一下dispatch_once的源码:
void
dispatch_once(dispatch_once_t *val, dispatch_block_t block)
{
dispatch_once_f(val, block, _dispatch_Block_invoke(block));
}
// 展开 dispatch_once_f
DISPATCH_NOINLINE
void
dispatch_once_f(dispatch_once_t *val, void *ctxt, dispatch_function_t func)
{
dispatch_once_gate_t l = (dispatch_once_gate_t)val;
#if !DISPATCH_ONCE_INLINE_FASTPATH || DISPATCH_ONCE_USE_QUIESCENT_COUNTER
uintptr_t v = os_atomic_load(&l->dgo_once, acquire);
if (likely(v == DLOCK_ONCE_DONE)) {
return;
}
#if DISPATCH_ONCE_USE_QUIESCENT_COUNTER
if (likely(DISPATCH_ONCE_IS_GEN(v))) {
return _dispatch_once_mark_done_if_quiesced(l, v);
}
#endif
#endif
if (_dispatch_once_gate_tryenter(l)) {
return _dispatch_once_callout(l, ctxt, func);
}
return _dispatch_once_wait(l);
}
// 如果 os_atomic_load为 DLOCK_ONCE_DONE 则直接返回,否则进入_dispatch_once_gate_tryenter,在这里首先判断对象是否存储过,如果存储过则则标记为unlock
DISPATCH_ALWAYS_INLINE
static inline bool
_dispatch_once_gate_tryenter(dispatch_once_gate_t l)
{
return os_atomic_cmpxchg(&l->dgo_once, DLOCK_ONCE_UNLOCKED,
(uintptr_t)_dispatch_lock_value_for_self(), relaxed);
}
// 如果没有存储过则执行 _dispatch_once_callout,主要是执行block
DISPATCH_NOINLINE
static void
_dispatch_once_callout(dispatch_once_gate_t l, void *ctxt,
dispatch_function_t func)
{
_dispatch_client_callout(ctxt, func);
_dispatch_once_gate_broadcast(l);
}
// 执行过block则调用 _dispatch_once_gate_broadcast
DISPATCH_ALWAYS_INLINE
static inline void
_dispatch_once_gate_broadcast(dispatch_once_gate_t l)
{
dispatch_lock value_self = _dispatch_lock_value_for_self();
uintptr_t v;
#if DISPATCH_ONCE_USE_QUIESCENT_COUNTER
v = _dispatch_once_mark_quiescing(l);
#else
v = _dispatch_once_mark_done(l);
#endif
if (likely((dispatch_lock)v == value_self)) return;
_dispatch_gate_broadcast_slow(&l->dgo_gate, (dispatch_lock)v);
}
// 在 _dispatch_once_gate_broadcast 中由于执行完毕,使用_dispatch_once_mark_don毕标记为done
DISPATCH_ALWAYS_INLINE
static inline uintptr_t
_dispatch_once_mark_done(dispatch_once_gate_t dgo)
{
return os_atomic_xchg(&dgo->dgo_once, DLOCK_ONCE_DONE, release);
}
swift中实现dispatch_once
说到这里,从swift3.0以后已经没办法使用dispach_once了,其实原因很简单因为在swift1.x的static var/let属性就已经是dispatch_once在后台执行的了,所以对于单例的创建没有必要显示调用了。但是有时候其他情况我们还是需要使用单次执行怎么办呢?代替方法:使用全局变量(例如创建一个对象实例或者初始化成一个立即执行的闭包:let g = {}();_ = g;),当然习惯于dispatch_once的朋友有时候并不适应这种方法,这里给出一个比较简单的方案:
public extension DispatchQueue {
private static var _onceTracker = [String]()
public class func once(file: String = #file, function: String = #function, line: Int = #line, block:(Void)->Void) {
let token = file + ":" + function + ":" + String(line)
once(token: token, block: block)
}
/**
Executes a block of code, associated with a unique token, only once. The code is thread safe and will
only execute the code once even in the presence of multithreaded calls.
- parameter token: A unique reverse DNS style name such as com.vectorform.<name> or a GUID
- parameter block: Block to execute once
*/
public class func once(token: String, block:(Void)->Void) {
objc_sync_enter(self)
defer { objc_sync_exit(self) }
if _onceTracker.contains(token) {
return
}
_onceTracker.append(token)
block()
}
}
延迟执行 dispatch_after
dispatch_after也是一个常用的延迟执行的方法,比如常见的使用方法是:
dispatch_after(dispatch_time(DISPATCH_TIME_NOW, (int64_t)(1.0 * NSEC_PER_SEC)), dispatch_get_main_queue(), ^{
NSLog(@"...");
});
在查看dispatch_after源码之前先看一下另一个内容事件源dispatch_source_t,其实dispatch_source_t是一个很少让开发者和GCD联想到一起的一个类型,它本身也有对应的创建方法dispatch_source_create(事实上它的使用甚至可以追踪到Runloop)。多数开发者认识dispatch_source_t都是通过定时器,很多文章会教你如何创建一个比较准确的定时器,比如下面的代码:
dispatch_source_t timerSource = dispatch_source_create(DISPATCH_SOURCE_TYPE_TIMER, 0, 0, dispatch_get_global_queue(DISPATCH_QUEUE_PRIORITY_DEFAULT, 0));
dispatch_source_set_timer(timerSource, dispatch_time(DISPATCH_TIME_NOW, 0), 3*NSEC_PER_SEC, 0);
dispatch_source_set_event_handler(timerSource, ^{
NSLog(@"dispatch_source_t...");
});
dispatch_resume(timerSource);
self->source = timerSource;
如果你知道上面一个定时器如何执行的那么下面看一下dispatch_after应该就比较容易明白了:
void
dispatch_after(dispatch_time_t when, dispatch_queue_t queue,
dispatch_block_t work)
{
_dispatch_after(when, queue, NULL, work, true);
}
// 查看 _dispatch_after
DISPATCH_ALWAYS_INLINE
static inline void
_dispatch_after(dispatch_time_t when, dispatch_queue_t dq,
void *ctxt, void *handler, bool block)
{
dispatch_timer_source_refs_t dt;
dispatch_source_t ds;
uint64_t leeway, delta;
if (when == DISPATCH_TIME_FOREVER) {
#if DISPATCH_DEBUG
DISPATCH_CLIENT_CRASH(0, "dispatch_after called with 'when' == infinity");
#endif
return;
}
delta = _dispatch_timeout(when);
if (delta == 0) {
if (block) {
return dispatch_async(dq, handler);
}
return dispatch_async_f(dq, ctxt, handler);
}
leeway = delta / 10; // <rdar://problem/13447496>
if (leeway < NSEC_PER_MSEC) leeway = NSEC_PER_MSEC;
if (leeway > 60 * NSEC_PER_SEC) leeway = 60 * NSEC_PER_SEC;
// this function can and should be optimized to not use a dispatch source
ds = dispatch_source_create(&_dispatch_source_type_after, 0, 0, dq);
dt = ds->ds_timer_refs;
dispatch_continuation_t dc = _dispatch_continuation_alloc();
if (block) {
_dispatch_continuation_init(dc, dq, handler, 0, 0);
} else {
_dispatch_continuation_init_f(dc, dq, ctxt, handler, 0, 0);
}
// reference `ds` so that it doesn't show up as a leak
dc->dc_data = ds;
_dispatch_trace_item_push(dq, dc);
os_atomic_store2o(dt, ds_handler[DS_EVENT_HANDLER], dc, relaxed);
dispatch_clock_t clock;
uint64_t target;
_dispatch_time_to_clock_and_value(when, &clock, &target);
if (clock != DISPATCH_CLOCK_WALL) {
leeway = _dispatch_time_nano2mach(leeway);
}
dt->du_timer_flags |= _dispatch_timer_flags_from_clock(clock);
dt->dt_timer.target = target;
dt->dt_timer.interval = UINT64_MAX;
dt->dt_timer.deadline = target + leeway;
dispatch_activate(ds);
}
代码并不是太复杂,无时间差则直接调用dispatch_async,否则先创建一个dispatch_source_t,不同的是这里的类型并不是DISPATCH_SOURCE_TYPE_TIMER而是_dispatch_source_type_after,查看源码不难发现它只是dispatch_source_type_s类型的一个常量和_dispatch_source_type_timer并没有明显区别:
const dispatch_source_type_s _dispatch_source_type_after = {
.dst_kind = "timer (after)",
.dst_filter = DISPATCH_EVFILT_TIMER_WITH_CLOCK,
.dst_flags = EV_DISPATCH,
.dst_mask = 0,
.dst_timer_flags = DISPATCH_TIMER_AFTER,
.dst_action = DISPATCH_UNOTE_ACTION_SOURCE_TIMER,
.dst_size = sizeof(struct dispatch_timer_source_refs_s),
.dst_create = _dispatch_source_timer_create,
.dst_merge_evt = _dispatch_source_merge_evt,
};
而和dispatch_activate()其实和dispatch_resume() 是一样的开启定时器。那么为什么看不到dispatch_source_set_event_handler来给timer设置handler呢?不放看一下dispatch_source_set_event_handler的源代码:
void
dispatch_source_set_event_handler(dispatch_source_t ds,
dispatch_block_t handler)
{
_dispatch_source_set_handler(ds, handler, DS_EVENT_HANDLER, true);
}
// 查看 _dispatch_source_set_handler
DISPATCH_NOINLINE
static void
_dispatch_source_set_handler(dispatch_source_t ds, void *func,
uintptr_t kind, bool is_block)
{
dispatch_continuation_t dc;
dc = _dispatch_source_handler_alloc(ds, func, kind, is_block);
if (_dispatch_lane_try_inactive_suspend(ds)) {
_dispatch_source_handler_replace(ds, kind, dc);
return _dispatch_lane_resume(ds, false);
}
dispatch_queue_flags_t dqf = _dispatch_queue_atomic_flags(ds);
if (unlikely(dqf & DSF_STRICT)) {
DISPATCH_CLIENT_CRASH(kind, "Cannot change a handler of this source "
"after it has been activated");
}
// Ignore handlers mutations past cancelation, it's harmless
if ((dqf & DSF_CANCELED) == 0) {
_dispatch_ktrace1(DISPATCH_PERF_post_activate_mutation, ds);
if (kind == DS_REGISTN_HANDLER) {
_dispatch_bug_deprecated("Setting registration handler after "
"the source has been activated");
} else if (func == NULL) {
_dispatch_bug_deprecated("Clearing handler after "
"the source has been activated");
}
}
dc->dc_data = (void *)kind;
_dispatch_barrier_trysync_or_async_f(ds, dc,
_dispatch_source_set_handler_slow, 0);
}
可以看到最终还是封装成一个dispatch_continuation_t进行同步或者异步调用,而上面_dispatch_after直接构建了dispatch_continuation_t进行执行。
取消延迟执行的任务
使用dispatch_after还有一个问题就是取消问题,当然通常遇到了这种问题大部分答案就是使用下面的方式:
[self performSelector:@selector(myDelayedMethod) withObject: self afterDelay: desiredDelay];
[NSObject cancelPreviousPerformRequestsWithTarget: self selector:@selector(myDelayedMethod) object: self];
不过如果你使用的是iOS 8及其以上的版本,那么其实是可以取消的(如下),当然如果你还在支持iOS 8以下的版本不妨试试这个自定义的dispatch_cancelable_block_t类:
dispatch_block_t block = dispatch_block_create(DISPATCH_BLOCK_INHERIT_QOS_CLASS, ^{
NSLog(@"dispatch_after...");
});
dispatch_after(dispatch_time(DISPATCH_TIME_NOW, 3*NSEC_PER_SEC), dispatch_get_global_queue(DISPATCH_QUEUE_PRIORITY_DEFAULT, 0), block);
// 取消
dispatch_block_cancel(block);
如果你用的是swift那么恭喜你,很简单:
let dispatchItem = DispatchWorkItem {
handler()
}
DispatchQueue.main.asyncAfter(deadline: DispatchTime.now() + Double(Int64(3 * Double(NSEC_PER_SEC))) / Double(NSEC_PER_SEC), execute: dispatchItem)
// 取消
dispatchItem.cancel()
dispatch_semaphore
信号量是线程同步操作中很常用的一个操作,常用的几个类型:
dispatch_semaphore_t:信号量类型
dispatch_semaphore_create:创建一个信号量
dispatch_semaphore_wait:发送一个等待信号,信号量-1,当信号量为0阻塞线程,大于0则开始执行后面的逻辑(也就是说执行dispatch_semaphore_wait前如果信号量<=0则阻塞,否则正常执行后面的逻辑)
dispatch_semaphore_signal:发送唤醒信号,信号量会+1
比如我们有个操作foo()在异步线程已经开始执行,同时可能用户会手动再次触发动作bar(),但是bar依赖foo完成则可以使用信号量:
- (void)foo {
dispatch_semaphore_t semaphore = dispatch_semaphore_create(0);
dispatch_async(dispatch_get_global_queue(DISPATCH_QUEUE_PRIORITY_DEFAULT, 0), ^{
// 这里执行其他任务。。。
// TODO:
// 执行完发送信号
dispatch_semaphore_signal(semaphore);
});
self->semaphore = semaphore;
}
- (void)bar {
// 等待上面的操作完成,如果60s还没有完成则超时继续执行下面的逻辑
dispatch_semaphore_wait(self.semaphore, dispatch_time(DISPATCH_TIME_NOW, 60*NSEC_PER_SEC));
// 这里执行其他任务。。。但是依赖上面的操作完成
// TODO:
}
那么信号量是如何实现的呢,不妨看一下它的源码:
// 首先看一下dispatch_semaphore_t,没错和上面一样本质就是 dispatch_semaphore_s,dsema_value代表当前信号量,dsema_orig表示初始信号量
DISPATCH_CLASS_DECL(semaphore, OBJECT);
struct dispatch_semaphore_s {
DISPATCH_OBJECT_HEADER(semaphore);
intptr_t volatile dsema_value;
intptr_t dsema_orig;
_dispatch_sema4_t dsema_sema;
};
// 查看 dispatch_semaphore_create 源码,其实并不复杂创建分配DISPATCH_VTABLE结构的空间,设置初始信号量,但是可以清楚的看到同样指定了目标队列,这是一个优先级为`DISPATCH_QUEUE_PRIORITY_DEFAULT`的非过载队列
dispatch_semaphore_t
dispatch_semaphore_create(intptr_t value)
{
dispatch_semaphore_t dsema;
// If the internal value is negative, then the absolute of the value is
// equal to the number of waiting threads. Therefore it is bogus to
// initialize the semaphore with a negative value.
if (value < 0) {
return DISPATCH_BAD_INPUT;
}
dsema = _dispatch_object_alloc(DISPATCH_VTABLE(semaphore),
sizeof(struct dispatch_semaphore_s));
dsema->do_next = DISPATCH_OBJECT_LISTLESS;
dsema->do_targetq = _dispatch_get_default_queue(false);
dsema->dsema_value = value;
_dispatch_sema4_init(&dsema->dsema_sema, _DSEMA4_POLICY_FIFO);
dsema->dsema_orig = value;
return dsema;
}
// 下面看一下 dispatch_semaphore_wait,首先`os_atomic_dec2o`信号量减一,当然递减之后信号量大于等于0它其实什么也不做继续执行就好了,但是如果不满足执行_dispatch_semaphore_wait_slow 等待信号量唤醒或者timeout超时
dispatch_semaphore_wait(dispatch_semaphore_t dsema, dispatch_time_t timeout)
{
long value = os_atomic_dec2o(dsema, dsema_value, acquire);
if (likely(value >= 0)) {
return 0;
}
return _dispatch_semaphore_wait_slow(dsema, timeout);
}
// 看一下 _dispatch_semaphore_wait_slow 源码,这里首先对于两种极端情况:如果是DISPATCH_TIME_NOW则执行信号量+1并返回超时信号,DISPATCH_TIME_FOREVER则一直等待,默认则调用 `_dispatch_sema4_timedwait`
DISPATCH_NOINLINE
static intptr_t
_dispatch_semaphore_wait_slow(dispatch_semaphore_t dsema,
dispatch_time_t timeout)
{
long orig;
_dispatch_sema4_create(&dsema->dsema_sema, _DSEMA4_POLICY_FIFO);
switch (timeout) {
default:
if (!_dispatch_sema4_timedwait(&dsema->dsema_sema, timeout)) {
break;
}
// Try to undo what the fast path did to dsema->dsema_value
DISPATCH_FALLTHROUGH;
case DISPATCH_TIME_NOW:
orig = dsema->dsema_value;
while (orig < 0) {
if (os_atomic_cmpxchgvw2o(dsema, dsema_value, orig, orig + 1,
&orig, relaxed)) {
return _DSEMA4_TIMEOUT();
}
}
// Another thread called semaphore_signal(). Drain the wakeup.
DISPATCH_FALLTHROUGH;
case DISPATCH_TIME_FOREVER:
_dispatch_sema4_wait(&dsema->dsema_sema);
break;
}
return 0;
}
// 查看 _dispatch_sema4_timedwait 调用mach的内核函数semaphore_timedwait等待收到信号直至超时
bool
_dispatch_sema4_timedwait(_dispatch_sema4_t *sema, dispatch_time_t timeout)
{
mach_timespec_t _timeout;
kern_return_t kr;
do {
uint64_t nsec = _dispatch_timeout(timeout);
_timeout.tv_sec = (__typeof__(_timeout.tv_sec))(nsec / NSEC_PER_SEC);
_timeout.tv_nsec = (__typeof__(_timeout.tv_nsec))(nsec % NSEC_PER_SEC);
kr = semaphore_timedwait(*sema, _timeout);
} while (unlikely(kr == KERN_ABORTED));
if (kr == KERN_OPERATION_TIMED_OUT) {
return true;
}
DISPATCH_SEMAPHORE_VERIFY_KR(kr);
return false;
}
// 最后看一下 dispatch_semaphore_signal,首先信号量+1,如果信号量大于0就什么也不做(通常到了这里dispatch_semaphore_wait还没调用),否则执行 _dispatch_semaphore_signal_slow
intptr_t
dispatch_semaphore_signal(dispatch_semaphore_t dsema)
{
long value = os_atomic_inc2o(dsema, dsema_value, release);
if (likely(value > 0)) {
return 0;
}
if (unlikely(value == LONG_MIN)) {
DISPATCH_CLIENT_CRASH(value,
"Unbalanced call to dispatch_semaphore_signal()");
}
return _dispatch_semaphore_signal_slow(dsema);
}
// 查看 _dispatch_semaphore_signal_slow ,调用内核`semaphore_signal`唤醒线程,如apple api描述“如果唤醒线程则返回非0,否则返回0”
DISPATCH_NOINLINE
intptr_t
_dispatch_semaphore_signal_slow(dispatch_semaphore_t dsema)
{
_dispatch_sema4_create(&dsema->dsema_sema, _DSEMA4_POLICY_FIFO);
_dispatch_sema4_signal(&dsema->dsema_sema, 1);
return 1;
}
// 查看 _dispatch_sema4_signal 源码
void
_dispatch_sema4_signal(_dispatch_sema4_t *sema, long count)
{
do {
kern_return_t kr = semaphore_signal(*sema);
DISPATCH_SEMAPHORE_VERIFY_KR(kr);
} while (--count);
}
信号量是一个比较重要的内容,合理使用可以让你的程序更加的优雅,比如说一个常见的情况:大家知道
PHImageManager.requestImage是一个释放消耗内存的方法,有时我们需要批量获取到图片执行一些操作的话可能就没办法直接for循环,不然内存会很快爆掉,因为每个requestImage操作都需要占用大量内存,即使外部嵌套autoreleasepool也不一定可以及时释放(想想for执行的速度,释放肯定来不及),那么requestImage又是一个异步操作,如此只能让一个操作执行完再执行另一个循环操作才能解决。也就是说这个问题就变成for循环内部的异步操作串行执行的问题。要解决这个问题有几种思路:1.使用requestImage的同步请求照片 2.使用递归操作一个操作执行完再执行另外一个操作移除for操作 3.使用信号量解决。当然第一个方法并非普适,有些异步操作并不能轻易改成同步操作,第二个方法相对普适,但是递归调用本身因为要改变原来的代码结构看起来不是那么优雅,自然当前讨论的信号量是更好的方式。我们假设requestImage是一个bar(callback:((_ image)->
Void))操作,整个请求是一个foo(callback:((_ images)->Void))那么它的实现方式如下:
- (void)foo:(CallbackWithImages)callback {
dispatch_queue_t globalQueue = dispatch_get_global_queue(DISPATCH_QUEUE_PRIORITY_DEFAULT, 0);
dispatch_semaphore_t semaphore = dispatch_semaphore_create(0);
dispatch_async(globalQueue, ^{
NSMutableArray *array = [[NSMutableArray alloc] init];
for (int i=0; i<100; ++i) {
[self bar:^(UIImage *image){
[array addObject:image];
dispatch_semaphore_signal(semaphore);
}];
dispatch_semaphore_wait(semaphore, DISPATCH_TIME_FOREVER);
}
dispatch_async(dispatch_get_main_queue(), ^{
callback([array copy]);
});
});
}
- (void)bar:(CallbackWithImage)callback {
dispatch_queue_t globalQueue = dispatch_get_global_queue(DISPATCH_QUEUE_PRIORITY_DEFAULT, 0);
dispatch_async(globalQueue, ^{
callback([UIImage new]);
});
}
信号量常见crash
可以看到信号量在做线程同步时简单易用,不过有时候不经意间容易出错,比如下面的代码会出现EXC_BAD_INSTRUCTION (code=EXC_I386_INVOP, subcode=0x0)错误,原因是之前的信号量还在使用:
dispatch_semaphore_t semaphore = dispatch_semaphore_create(1);
dispatch_semaphore_wait(semaphore, dispatch_time(DISPATCH_TIME_NOW, 1000*NSEC_PER_SEC));
// semaphore = dispatch_semaphore_create(0);
为什么会这样呢?原因和上面dispatch_semaphore_create中的DISPATCH_VTABLE(semaphore)有关系,这个宏我们上面分析过,最终展开就是OS_dispatch_semaphore_class实例的引用,那么它的实例是什么呢?它当然是通过_dispatch_object_alloc创建的,沿着查找_dispatch_object_alloc的源码可以找到下面的代码:
static inline id
_os_objc_alloc(Class cls, size_t size)
{
id obj;
size -= sizeof(((struct _os_object_s *)NULL)->os_obj_isa);
while (unlikely(!(obj = class_createInstance(cls, size)))) {
_dispatch_temporary_resource_shortage();
}
return obj;
}
不难看出就是依靠class_createInstance创建一个OS_dispatch_semaphore_class实例,这个代码在libdispatch是找不到的,它在runtime源码中。不过在这里可以找到它的实例的定义(其实类似的通过vtable结构创建的实例都包含在libdispatch的init.c中):
DISPATCH_VTABLE_INSTANCE(semaphore,
.do_type = DISPATCH_SEMAPHORE_TYPE,
.do_dispose = _dispatch_semaphore_dispose,
.do_debug = _dispatch_semaphore_debug,
.do_invoke = _dispatch_object_no_invoke,
);
不难看出这个对象是包含一个dispose方法的,就是_dispatch_semaphore_dispose,我们可以看到它的源码,其实这里对我们排查问题最重要的就是if条件语句,信号量的当前值小于初始化,会发生闪退,因为信号量已经被释放了,如果此时没有crash其实就会意味着一直有线程在信号量等待:
void
_dispatch_semaphore_dispose(dispatch_object_t dou,
DISPATCH_UNUSED bool *allow_free)
{
dispatch_semaphore_t dsema = dou._dsema;
if (dsema->dsema_value < dsema->dsema_orig) {
DISPATCH_CLIENT_CRASH(dsema->dsema_orig - dsema->dsema_value,
"Semaphore object deallocated while in use");
}
_dispatch_sema4_dispose(&dsema->dsema_sema, _DSEMA4_POLICY_FIFO);
}
dispatch_group
dispatch_group常常用来同步多个任务(注意和dispatch_barrier_sync不同的是它可以是多个队列的同步),所以其实上面先分析dispatch_semaphore也是这个原因,它本身是依靠信号量来完成的同步管理。典型的用法如下:
dispatch_queue_t globalQueue = dispatch_get_global_queue(DISPATCH_QUEUE_PRIORITY_DEFAULT, 0);
dispatch_group_t group = dispatch_group_create();
dispatch_group_async(group, globalQueue, ^{
sleep(10);
NSLog(@"任务1完成");
});
dispatch_group_async(group, globalQueue, ^{
NSLog(@"任务2完成");
});
dispatch_group_notify(group, globalQueue, ^{
NSLog(@"两个任务全部完成");
});
dispatch_async(globalQueue, ^{
// 等待5s超时后继续执行,此时dispatch_group中的任务未必全部完成,注意:dispatch_group_wait是同步操作必须放到异步队列否则阻塞当前线程
dispatch_group_wait(group, dispatch_time(DISPATCH_TIME_NOW, 5*NSEC_PER_SEC));
NSLog(@"等待到了上限,开始执行。。。");
});
下面看一下dispatch_group相关的源码:
// 和其他对象一样,dispatch_group_t的本质就是 dispatch_group_s指针,这里重点关注一下dg_state和dg_bits是一个计数器
struct dispatch_group_s {
DISPATCH_OBJECT_HEADER(group);
DISPATCH_UNION_LE(uint64_t volatile dg_state,
uint32_t dg_bits,
uint32_t dg_gen
) DISPATCH_ATOMIC64_ALIGN;
struct dispatch_continuation_s *volatile dg_notify_head;
struct dispatch_continuation_s *volatile dg_notify_tail;
};
// 查看 dispatch_group_create
dispatch_group_t
dispatch_group_create(void)
{
return _dispatch_group_create_with_count(0);
}
// 展开 _dispatch_group_create_with_count,其实就是一个dispatch_group_s对象,指定了do_targetq是默认队列并且不支持过载
DISPATCH_ALWAYS_INLINE
static inline dispatch_group_t
_dispatch_group_create_with_count(uint32_t n)
{
dispatch_group_t dg = _dispatch_object_alloc(DISPATCH_VTABLE(group),
sizeof(struct dispatch_group_s));
dg->do_next = DISPATCH_OBJECT_LISTLESS;
dg->do_targetq = _dispatch_get_default_queue(false);
if (n) {
os_atomic_store2o(dg, dg_bits,
(uint32_t)-n * DISPATCH_GROUP_VALUE_INTERVAL, relaxed);
os_atomic_store2o(dg, do_ref_cnt, 1, relaxed); // <rdar://22318411>
}
return dg;
}
// 首先看一下 dispatch_group_enter,它的核心就是os_atomic_sub_orig2o对dg_bits进行-1操作
void
dispatch_group_enter(dispatch_group_t dg)
{
// The value is decremented on a 32bits wide atomic so that the carry
// for the 0 -> -1 transition is not propagated to the upper 32bits.
uint32_t old_bits = os_atomic_sub_orig2o(dg, dg_bits,
DISPATCH_GROUP_VALUE_INTERVAL, acquire);
uint32_t old_value = old_bits & DISPATCH_GROUP_VALUE_MASK;
if (unlikely(old_value == 0)) {
_dispatch_retain(dg); // <rdar://problem/22318411>
}
if (unlikely(old_value == DISPATCH_GROUP_VALUE_MAX)) {
DISPATCH_CLIENT_CRASH(old_bits,
"Too many nested calls to dispatch_group_enter()");
}
}
// 然后看一下 dispatch_group_leave,核心就是os_atomic_add_orig2o执行dg_state+1操作,如果+1之后还等于0那么说明之前没有调用`dispatch_group_enter`,就里会crash,当然这里核心在 `_dispatch_group_wake`
void
dispatch_group_leave(dispatch_group_t dg)
{
// The value is incremented on a 64bits wide atomic so that the carry for
// the -1 -> 0 transition increments the generation atomically.
uint64_t new_state, old_state = os_atomic_add_orig2o(dg, dg_state,
DISPATCH_GROUP_VALUE_INTERVAL, release);
uint32_t old_value = (uint32_t)(old_state & DISPATCH_GROUP_VALUE_MASK);
if (unlikely(old_value == DISPATCH_GROUP_VALUE_1)) {
old_state += DISPATCH_GROUP_VALUE_INTERVAL;
do {
new_state = old_state;
if ((old_state & DISPATCH_GROUP_VALUE_MASK) == 0) {
new_state &= ~DISPATCH_GROUP_HAS_WAITERS;
new_state &= ~DISPATCH_GROUP_HAS_NOTIFS;
} else {
// If the group was entered again since the atomic_add above,
// we can't clear the waiters bit anymore as we don't know for
// which generation the waiters are for
new_state &= ~DISPATCH_GROUP_HAS_NOTIFS;
}
if (old_state == new_state) break;
} while (unlikely(!os_atomic_cmpxchgv2o(dg, dg_state,
old_state, new_state, &old_state, relaxed)));
return _dispatch_group_wake(dg, old_state, true);
}
if (unlikely(old_value == 0)) {
DISPATCH_CLIENT_CRASH((uintptr_t)old_value,
"Unbalanced call to dispatch_group_leave()");
}
}
// 查看 _dispatch_group_wake源码,到了这里通常就是出了调度组,如果有notify等待则执行notify遍历并且在对应队列中执行,如果有wait任务则唤醒其执行任务(注意这里比较牛叉的`_dispatch_wake_by_address`可以根据地址进行函数调用,本身是调用的WakeByAddressAll这个系统调用)
DISPATCH_NOINLINE
static void
_dispatch_group_wake(dispatch_group_t dg, uint64_t dg_state, bool needs_release)
{
uint16_t refs = needs_release ? 1 : 0; // <rdar://problem/22318411>
if (dg_state & DISPATCH_GROUP_HAS_NOTIFS) {
dispatch_continuation_t dc, next_dc, tail;
// Snapshot before anything is notified/woken <rdar://problem/8554546>
dc = os_mpsc_capture_snapshot(os_mpsc(dg, dg_notify), &tail);
do {
dispatch_queue_t dsn_queue = (dispatch_queue_t)dc->dc_data;
next_dc = os_mpsc_pop_snapshot_head(dc, tail, do_next);
_dispatch_continuation_async(dsn_queue, dc,
_dispatch_qos_from_pp(dc->dc_priority), dc->dc_flags);
_dispatch_release(dsn_queue);
} while ((dc = next_dc));
refs++;
}
if (dg_state & DISPATCH_GROUP_HAS_WAITERS) {
_dispatch_wake_by_address(&dg->dg_gen);
}
if (refs) _dispatch_release_n(dg, refs);
}
// 查看 dispatch_group_async源码,dispatch_continuation_t仅仅是封装任务,核心是_dispatch_continuation_group_async
void
dispatch_group_async(dispatch_group_t dg, dispatch_queue_t dq,
dispatch_block_t db)
{
dispatch_continuation_t dc = _dispatch_continuation_alloc();
uintptr_t dc_flags = DC_FLAG_CONSUME | DC_FLAG_GROUP_ASYNC;
dispatch_qos_t qos;
qos = _dispatch_continuation_init(dc, dq, db, 0, dc_flags);
_dispatch_continuation_group_async(dg, dq, dc, qos);
}
// 展开 _dispatch_continuation_group_async,这里重点记住以下 dispatch_group_enter()方法,至于_dispatch_continuation_async前面已经介绍过
DISPATCH_ALWAYS_INLINE
static inline void
_dispatch_continuation_group_async(dispatch_group_t dg, dispatch_queue_t dq,
dispatch_continuation_t dc, dispatch_qos_t qos)
{
dispatch_group_enter(dg);
dc->dc_data = dg;
_dispatch_continuation_async(dq, dc, qos, dc->dc_flags);
}
// 继续查看 dispatch_group_notify,注意这里将`dispatch_block_t`存储到了共享数据 dispatch_continuation_t中
void
dispatch_group_notify(dispatch_group_t dg, dispatch_queue_t dq,
dispatch_block_t db)
{
dispatch_continuation_t dsn = _dispatch_continuation_alloc();
_dispatch_continuation_init(dsn, dq, db, 0, DC_FLAG_CONSUME);
_dispatch_group_notify(dg, dq, dsn);
}
// 展开 _dispatch_group_notify,其实最主要的方法就是`_dispatch_group_wake`
DISPATCH_ALWAYS_INLINE
static inline void
_dispatch_group_notify(dispatch_group_t dg, dispatch_queue_t dq,
dispatch_continuation_t dsn)
{
uint64_t old_state, new_state;
dispatch_continuation_t prev;
dsn->dc_data = dq;
_dispatch_retain(dq);
prev = os_mpsc_push_update_tail(os_mpsc(dg, dg_notify), dsn, do_next);
if (os_mpsc_push_was_empty(prev)) _dispatch_retain(dg);
os_mpsc_push_update_prev(os_mpsc(dg, dg_notify), prev, dsn, do_next);
if (os_mpsc_push_was_empty(prev)) {
os_atomic_rmw_loop2o(dg, dg_state, old_state, new_state, release, {
new_state = old_state | DISPATCH_GROUP_HAS_NOTIFS;
if ((uint32_t)old_state == 0) {
os_atomic_rmw_loop_give_up({
return _dispatch_group_wake(dg, new_state, false);
});
}
});
}
}
简单的说就是dispatch_group_async和dispatch_group_notify本身就是和dispatch_group_enter、dispatch_group_leave没有本质区别,后者相对更加灵活。当然这里还有一个重要的操作就是dispatch_group_wait,还没有看:
// os_atomic_rmw_loop2o不断遍历,如果(old_state & DISPATCH_GROUP_VALUE_MASK) == 0表示执行完,直接返回0,如果当前如果超时立即返回,其他情况调用_dispatch_group_wait_slow
intptr_t
dispatch_group_wait(dispatch_group_t dg, dispatch_time_t timeout)
{
uint64_t old_state, new_state;
os_atomic_rmw_loop2o(dg, dg_state, old_state, new_state, relaxed, {
if ((old_state & DISPATCH_GROUP_VALUE_MASK) == 0) {
os_atomic_rmw_loop_give_up_with_fence(acquire, return 0);
}
if (unlikely(timeout == 0)) {
os_atomic_rmw_loop_give_up(return _DSEMA4_TIMEOUT());
}
new_state = old_state | DISPATCH_GROUP_HAS_WAITERS;
if (unlikely(old_state & DISPATCH_GROUP_HAS_WAITERS)) {
os_atomic_rmw_loop_give_up(break);
}
});
return _dispatch_group_wait_slow(dg, _dg_state_gen(new_state), timeout);
}
// 查看 _dispatch_group_wait_slow,最终调用 _dispatch_wait_on_address 直至 __ulock_wait
DISPATCH_NOINLINE
static intptr_t
_dispatch_group_wait_slow(dispatch_group_t dg, uint32_t gen,
dispatch_time_t timeout)
{
for (;;) {
int rc = _dispatch_wait_on_address(&dg->dg_gen, gen, timeout, 0);
if (likely(gen != os_atomic_load2o(dg, dg_gen, acquire))) {
return 0;
}
if (rc == ETIMEDOUT) {
return _DSEMA4_TIMEOUT();
}
}
}
多个异步操作同步
上面第一个dispatch_group例子介绍的情况很简单,任务本身都是同步的,只是将一个同步任务放到了dispatch_group_async中,现实中这个操作可能是一个网络请求,你现在想让10个请求都完成后再执行某个操作怎么办(网络请求假设方法是request(url:String,complete:Callback))?你现在不可能在网络请求方法内部做出修改了,怎么保证操作同步呢?
之前看到过这种操作:
- (void)foo {
dispatch_queue_t globalQueue = dispatch_get_global_queue(DISPATCH_QUEUE_PRIORITY_DEFAULT, 0);
dispatch_group_t group = dispatch_group_create();
dispatch_semaphore_t semaphore = dispatch_semaphore_create(0);
for (int i=0; i<5; ++i) {
dispatch_group_async(group, globalQueue, ^{
[self bar:^{
printf("task\n");
dispatch_semaphore_signal(semaphore);
}];
});
}
dispatch_group_notify(group, globalQueue, ^{
for (int i=0; i<5; ++i) {
dispatch_semaphore_wait(semaphore, DISPATCH_TIME_FOREVER);
}
NSLog(@"complete");
});
}
- (void)bar:(Callback)complete {
dispatch_queue_t queue = dispatch_queue_create(DISPATCH_QUEUE_PRIORITY_DEFAULT, nil);
dispatch_async(queue, ^{
sleep(arc4random_uniform(5));
complete();
});
}
其实这种方法基本没有用dispatch_group,直接用信号量就可以解决,有了上面的分析使用dispatch_enter和dispatch_leave就可以了。
- (void)foo {
dispatch_queue_t globalQueue = dispatch_get_global_queue(DISPATCH_QUEUE_PRIORITY_DEFAULT, 0);
dispatch_group_t group = dispatch_group_create();
for (int i=0; i<5; ++i) {
dispatch_group_enter(group);
[self bar:^{
printf("task\n");
dispatch_group_leave(group);
}];
}
dispatch_group_notify(group, globalQueue, ^{
NSLog(@"complete");
});
}
dispatch_apply
dispatch_apply设计的主要目的是提高并行能力(注意不是并发,等同于Swift中的DispatchQueue.concurrentPerform),所以一般我们用来并行执行多个结构类似的任务,比如:
void
dispatch_apply(size_t iterations, dispatch_queue_t dq, void (^work)(size_t))
{
dispatch_apply_f(iterations, dq, work,
(dispatch_apply_function_t)_dispatch_Block_invoke(work));
}
// 查看 dispatch_apply_f,对于width=1或者单核心数cpu其实这个是一个同步调用,核心方法就是_dispatch_apply_f
DISPATCH_NOINLINE
void
dispatch_apply_f(size_t iterations, dispatch_queue_t _dq, void *ctxt,
void (*func)(void *, size_t))
{
if (unlikely(iterations == 0)) {
return;
}
dispatch_thread_context_t dtctxt =
_dispatch_thread_context_find(_dispatch_apply_key);
size_t nested = dtctxt ? dtctxt->dtc_apply_nesting : 0;
dispatch_queue_t old_dq = _dispatch_queue_get_current();
dispatch_queue_t dq;
if (likely(_dq == DISPATCH_APPLY_AUTO)) {
dq = _dispatch_apply_root_queue(old_dq)->_as_dq;
} else {
dq = _dq; // silence clang Nullability complaints
}
dispatch_qos_t qos = _dispatch_priority_qos(dq->dq_priority) ?:
_dispatch_priority_fallback_qos(dq->dq_priority);
if (unlikely(dq->do_targetq)) {
// if the queue passed-in is not a root queue, use the current QoS
// since the caller participates in the work anyway
qos = _dispatch_qos_from_pp(_dispatch_get_priority());
}
int32_t thr_cnt = (int32_t)_dispatch_qos_max_parallelism(qos,
DISPATCH_MAX_PARALLELISM_ACTIVE);
if (likely(!nested)) {
nested = iterations;
} else {
thr_cnt = nested < (size_t)thr_cnt ? thr_cnt / (int32_t)nested : 1;
nested = nested < DISPATCH_APPLY_MAX && iterations < DISPATCH_APPLY_MAX
? nested * iterations : DISPATCH_APPLY_MAX;
}
if (iterations < (size_t)thr_cnt) {
thr_cnt = (int32_t)iterations;
}
struct dispatch_continuation_s dc = {
.dc_func = (void*)func,
.dc_ctxt = ctxt,
.dc_data = dq,
};
dispatch_apply_t da = (__typeof__(da))_dispatch_continuation_alloc();
da->da_index = 0;
da->da_todo = iterations;
da->da_iterations = iterations;
da->da_nested = nested;
da->da_thr_cnt = thr_cnt;
#if DISPATCH_INTROSPECTION
da->da_dc = _dispatch_continuation_alloc();
*da->da_dc = dc;
da->da_dc->dc_flags = DC_FLAG_ALLOCATED;
#else
da->da_dc = &dc;
#endif
da->da_flags = 0;
if (unlikely(dq->dq_width == 1 || thr_cnt <= 1)) {
return dispatch_sync_f(dq, da, _dispatch_apply_serial);
}
if (unlikely(dq->do_targetq)) {
if (unlikely(dq == old_dq)) {
return dispatch_sync_f(dq, da, _dispatch_apply_serial);
} else {
return dispatch_sync_f(dq, da, _dispatch_apply_redirect);
}
}
dispatch_thread_frame_s dtf;
_dispatch_thread_frame_push(&dtf, dq);
_dispatch_apply_f(upcast(dq)._dgq, da, _dispatch_apply_invoke);
_dispatch_thread_frame_pop(&dtf);
}
// 查看 _dispatch_apply_f
DISPATCH_ALWAYS_INLINE
static inline void
_dispatch_apply_f(dispatch_queue_global_t dq, dispatch_apply_t da,
dispatch_function_t func)
{
int32_t i = 0;
dispatch_continuation_t head = NULL, tail = NULL;
pthread_priority_t pp = _dispatch_get_priority();
// The current thread does not need a continuation
int32_t continuation_cnt = da->da_thr_cnt - 1;
dispatch_assert(continuation_cnt);
for (i = 0; i < continuation_cnt; i++) {
dispatch_continuation_t next = _dispatch_continuation_alloc();
uintptr_t dc_flags = DC_FLAG_CONSUME;
_dispatch_continuation_init_f(next, dq, da, func,
DISPATCH_BLOCK_HAS_PRIORITY, dc_flags);
next->dc_priority = pp | _PTHREAD_PRIORITY_ENFORCE_FLAG;
next->do_next = head;
head = next;
if (!tail) {
tail = next;
}
}
_dispatch_thread_event_init(&da->da_event);
// FIXME: dq may not be the right queue for the priority of `head`
_dispatch_trace_item_push_list(dq, head, tail);
_dispatch_root_queue_push_inline(dq, head, tail, continuation_cnt);
// Call the first element directly
_dispatch_apply_invoke_and_wait(da);
}
// 展开 _dispatch_apply_invoke_and_wait
DISPATCH_NOINLINE
static void
_dispatch_apply_invoke_and_wait(void *ctxt)
{
_dispatch_apply_invoke2(ctxt, DISPATCH_APPLY_INVOKE_WAIT);
_dispatch_perfmon_workitem_inc();
}
// 查看 _dispatch_apply_invoke2,主要是循环使用_dispatch_perfmon_workitem_inc调用任务,同时在最后一个任务调用完恢复线程 _dispatch_thread_event_signal
DISPATCH_ALWAYS_INLINE
static inline void
_dispatch_apply_invoke2(dispatch_apply_t da, long invoke_flags)
{
size_t const iter = da->da_iterations;
size_t idx, done = 0;
idx = os_atomic_inc_orig2o(da, da_index, acquire);
if (unlikely(idx >= iter)) goto out;
// da_dc is only safe to access once the 'index lock' has been acquired
dispatch_apply_function_t const func = (void *)da->da_dc->dc_func;
void *const da_ctxt = da->da_dc->dc_ctxt;
_dispatch_perfmon_workitem_dec(); // this unit executes many items
// Handle nested dispatch_apply rdar://problem/9294578
dispatch_thread_context_s apply_ctxt = {
.dtc_key = _dispatch_apply_key,
.dtc_apply_nesting = da->da_nested,
};
_dispatch_thread_context_push(&apply_ctxt);
dispatch_thread_frame_s dtf;
dispatch_priority_t old_dbp = 0;
if (invoke_flags & DISPATCH_APPLY_INVOKE_REDIRECT) {
dispatch_queue_t dq = da->da_dc->dc_data;
_dispatch_thread_frame_push(&dtf, dq);
old_dbp = _dispatch_set_basepri(dq->dq_priority);
}
dispatch_invoke_flags_t flags = da->da_flags;
// Striding is the responsibility of the caller.
do {
dispatch_invoke_with_autoreleasepool(flags, {
_dispatch_client_callout2(da_ctxt, idx, func);
_dispatch_perfmon_workitem_inc();
done++;
idx = os_atomic_inc_orig2o(da, da_index, relaxed);
});
} while (likely(idx < iter));
if (invoke_flags & DISPATCH_APPLY_INVOKE_REDIRECT) {
_dispatch_reset_basepri(old_dbp);
_dispatch_thread_frame_pop(&dtf);
}
_dispatch_thread_context_pop(&apply_ctxt);
// The thread that finished the last workitem wakes up the possibly waiting
// thread that called dispatch_apply. They could be one and the same.
if (!os_atomic_sub2o(da, da_todo, done, release)) {
_dispatch_thread_event_signal(&da->da_event);
}
out:
if (invoke_flags & DISPATCH_APPLY_INVOKE_WAIT) {
_dispatch_thread_event_wait(&da->da_event);
_dispatch_thread_event_destroy(&da->da_event);
}
if (os_atomic_dec2o(da, da_thr_cnt, release) == 0) {
#if DISPATCH_INTROSPECTION
_dispatch_continuation_free(da->da_dc);
#endif
_dispatch_continuation_free((dispatch_continuation_t)da);
}
}
在GCD中其实总共有两个线程池进行线程管理,一个是主线程池,另一个是除了主线程池之外的线程池。主线程池由序列为1的主队列管理,使用objc.io上的一幅图表示如下:
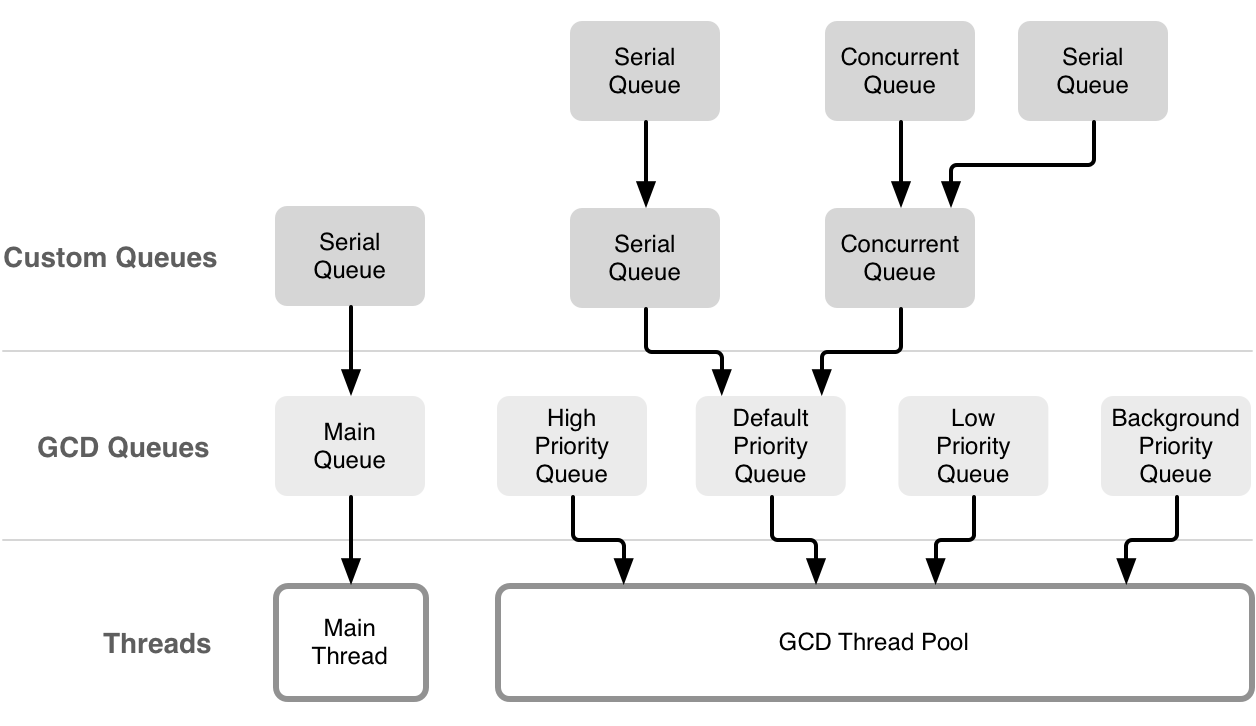
大家都知道使用dispatch_sync很有可能会发生死锁那么这是为什么呢?
不妨回顾一下dispatch_sync的过程:
dispatch_sync
_dispatch_sync_f:区分并发还是串行队列,如果是串行队列
_dispatch_barrier_sync_f:是不是同一个队列,如果是
_dispatch_sync_f_slow
重点在_dq_state_drain_locked_by(dq_state, dsc->dsc_waiter)这个条件,成立则会发生死锁,那么它成立的条件就是((lock_value ^ tid) & DLOCK_OWNER_MASK) == 0首先lock_value和tid进行异或操作,相同为0不同为1,然后和DLOCK_OWNER_MASK(0xfffffffc)进行按位与操作,一个为0则是0,所以若干lock_value和tid相同则会发生死锁。
关于上面源码中的几个宏定义
__builtin_expect
__builtin_expect是一个针对编译器优化的内置函数,让编译更加优化。比如说我们会写这种代码:
if a {
print(a)
} else {
print(b)
}
如果我们更加倾向于使用a那么可将其设为默认值,极特殊情况下才会使用b条件。CPU读取指定是多条一起加载的,可能先加载进来的是a,那么如果遇到执行b的情况则再加载b,那么对于条件a的情况就造成了性能浪费。long __builtin_expect (long EXP, long C) 第一个参数是要预测变量,第二个参数是预测值,这样__builtin_expect(a,false)说明多数情况a应该是false,极少数情况可能是true,这样不至于造成性能浪费。其实对于编译器在汇编时会优化成if !a的形式:
if !a {
print(b)
} else {
print(a)
}
likely和unlikely
#define likely(x) __builtin_expect(!!(x), 1)
#define unlikely(x) __builtin_expect(!!(x), 0)
看了likely和unlikely可以了解,likely表示更大可能成立,unlikely表示更大可能不成立。likely就是 if(likely(x == 0)) 就是if (x==0)。
os_atomic_cmpxchg
第二个参数与第一个参数值比较,如果相等,第三个参数的值替换第一个参数的值。如果不相等,把第一个参数的值赋值到第二个参数上。
#define os_atomic_cmpxchg(p, e, v, m) \
({ _os_atomic_basetypeof(p) _r = (e); \
atomic_compare_exchange_strong_explicit(_os_atomic_c11_atomic(p), \
&_r, v, memory_order_##m, memory_order_relaxed); })
os_atomic_store2o
将第二个参数保存到第一个参数中
#define os_atomic_store2o(p, f, v, m) \
os_atomic_store(&(p)->f, (v), m)
#define os_atomic_store(p, v, m) \
atomic_store_explicit(_os_atomic_c11_atomic(p), v, memory_order_##m)
os_atomic_inc_orig
第一个参数赋值为1
#define os_atomic_inc_orig(p, m) \
os_atomic_add_orig((p), 1, m)
#define os_atomic_add_orig(p, v, m) \
_os_atomic_c11_op_orig((p), (v), m, add, +)
#define _os_atomic_c11_op_orig(p, v, m, o, op) \
atomic_fetch_##o##_explicit(_os_atomic_c11_atomic(p), v, \
memory_order_##m)
os_atomic_inc_orig2o
第二个参数加1并返回
#define os_atomic_inc_orig2o(p, f, m) \
os_atomic_add_orig2o(p, f, 1, m)
#define os_atomic_add_orig2o(p, f, v, m) \
os_atomic_add_orig(&(p)->f, (v), m)
os_atomic_dec2o
第二个参数-1并返回
#define os_atomic_dec2o(p, f, m) \
os_atomic_sub2o(p, f, 1, m)
#define os_atomic_sub2o(p, f, v, m) \
os_atomic_sub(&(p)->f, (v), m)
串行、并发、并行
dispatch_barrier_async
dispatch_apply()
Recommend
About Joyk
Aggregate valuable and interesting links.
Joyk means Joy of geeK