Cars Island ASP .NET Core API secured by Azure AD B2C - part 2
source link: https://daniel-krzyczkowski.github.io/Cars-Island-ASP-NET-Core-API-Secured-By-Azure-AD-B2C/
Go to the source link to view the article. You can view the picture content, updated content and better typesetting reading experience. If the link is broken, please click the button below to view the snapshot at that time.

Introduction
In my previous article, I introduced you to Cars Island car rental on the Azure cloud. I created this fake project to present how to use different Microsoft Azure cloud services and how to their SDKs. I also presented what will be covered in the next articles. Here is the second article from the series where I would like to discuss how Cars Island ASP .NET Core Web API is secured by Azure AD B2C and how Microsoft Identity Web library is used there.
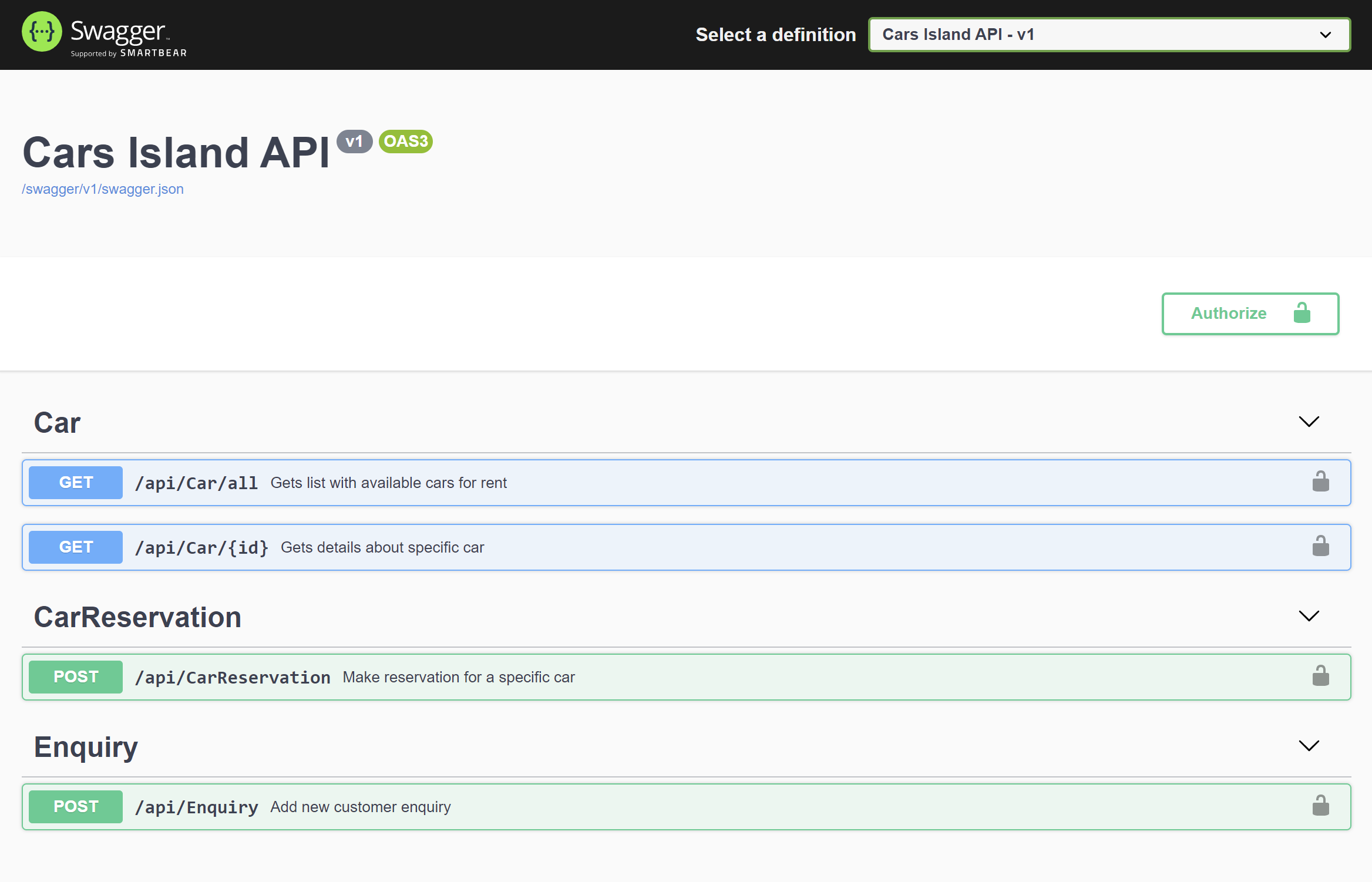
Cars Island Web API provides an Open API definition with a description of all endpoints. Endpoint responsible for handling car reservation requests requires an access token. It means that this endpoint requires the user’s authorization first. This is the topic I am going to discuss in this article.
Cars Island project is available on my GitHub
Azure AD B2C instance and application registration
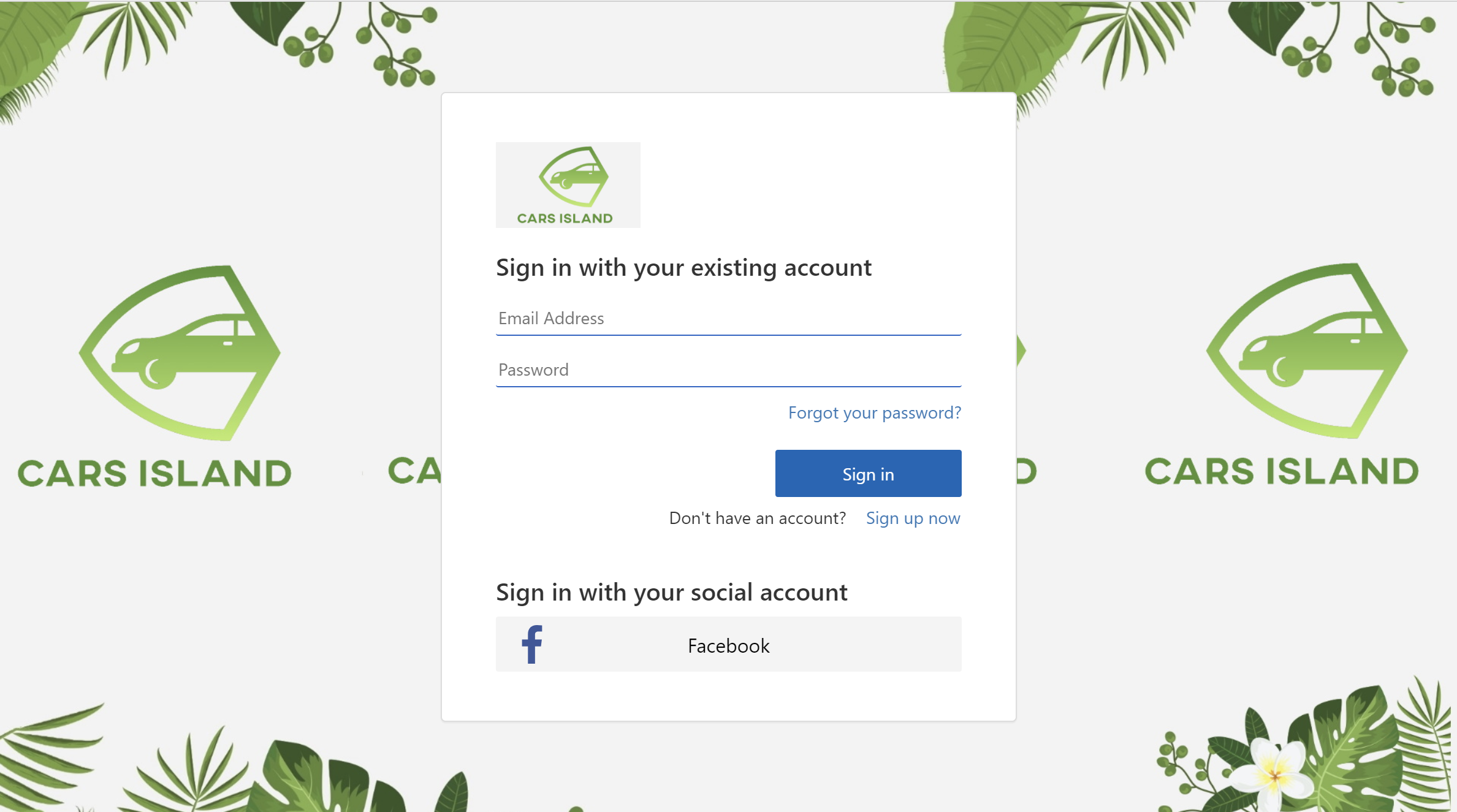
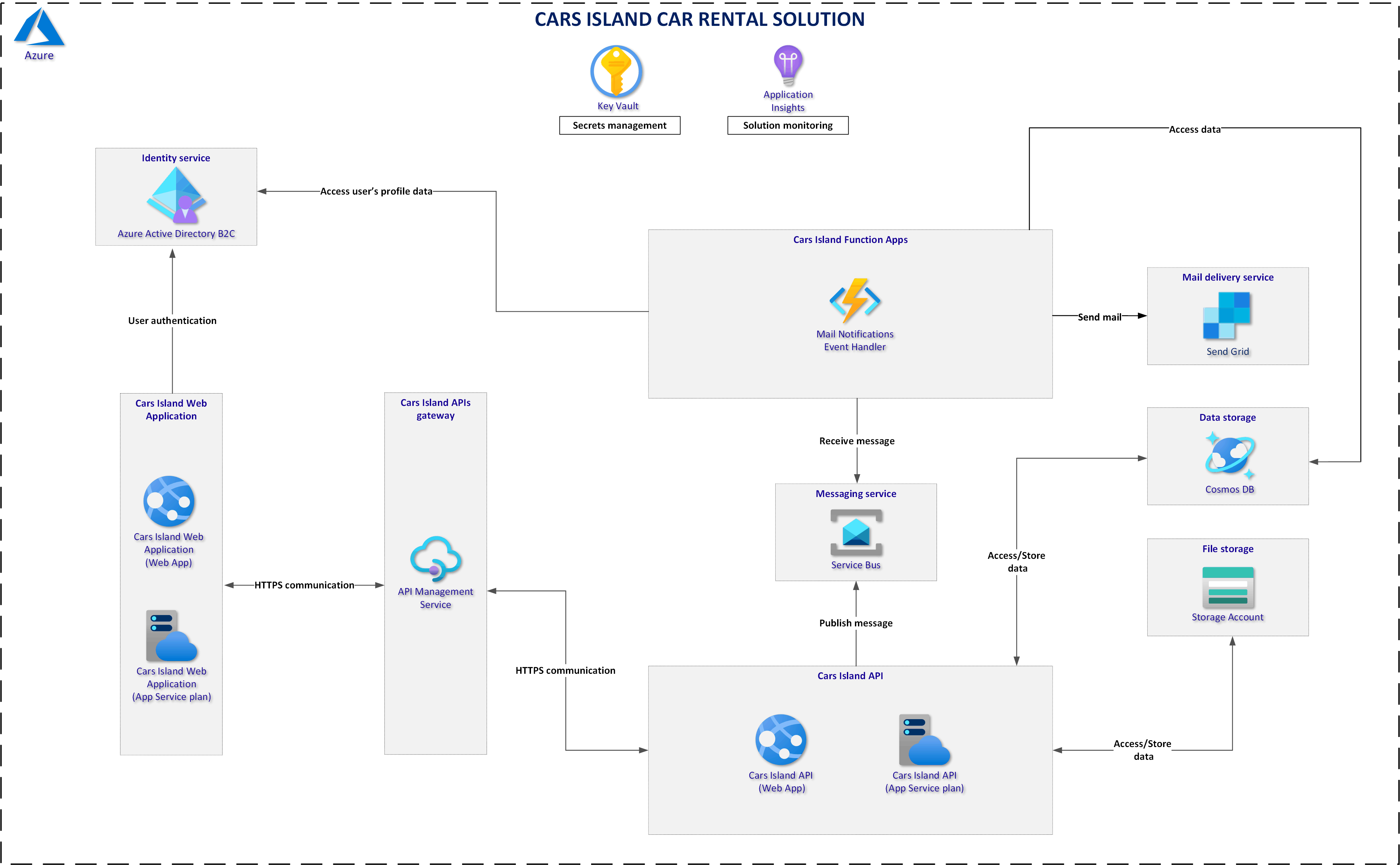
First of all, it is worth reminding the solution architecture. As you can see below, the Azure AD B2C service is used. As I mentioned in the previous article, Azure Active Directory B2C is an identity service in the Azure cloud that enables user authentication and management. It is used in the Cars Island to authenticate users. Web portal and Web API applications are secured by Azure AD B2C. To make a new reservation for a specific car, the user has to login first. If you want to learn more about Azure AD B2C, I recommend checking the official documentation. In the Cars Island solution, I used custom policies and custom branding to adjust the look & feel of login, registration, password reset, and user profile pages.
Web API application registration in the Azure AD B2C
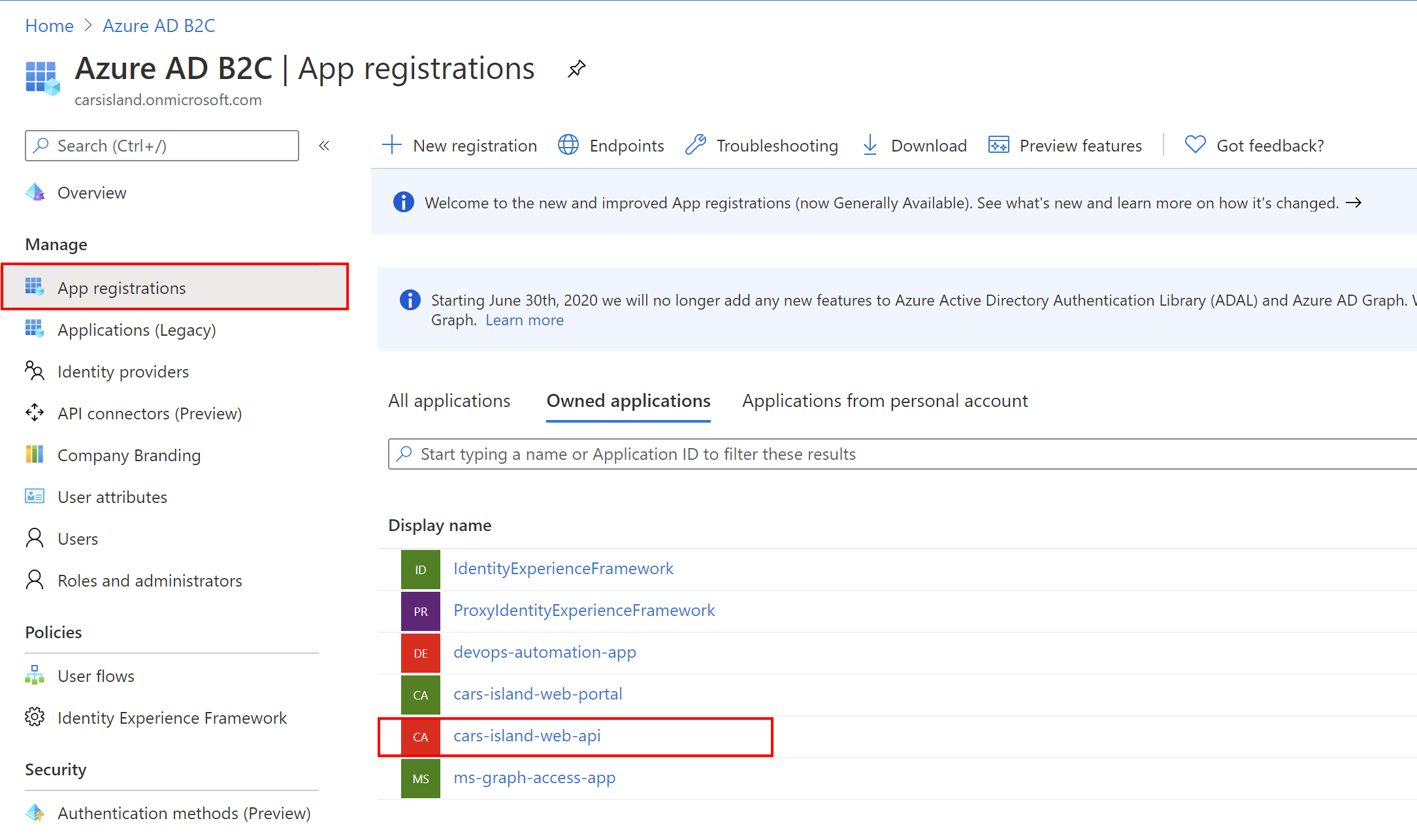
To secure ASP .NET Core Web API application we have to register a new application in the Azure AD B2C directory first.
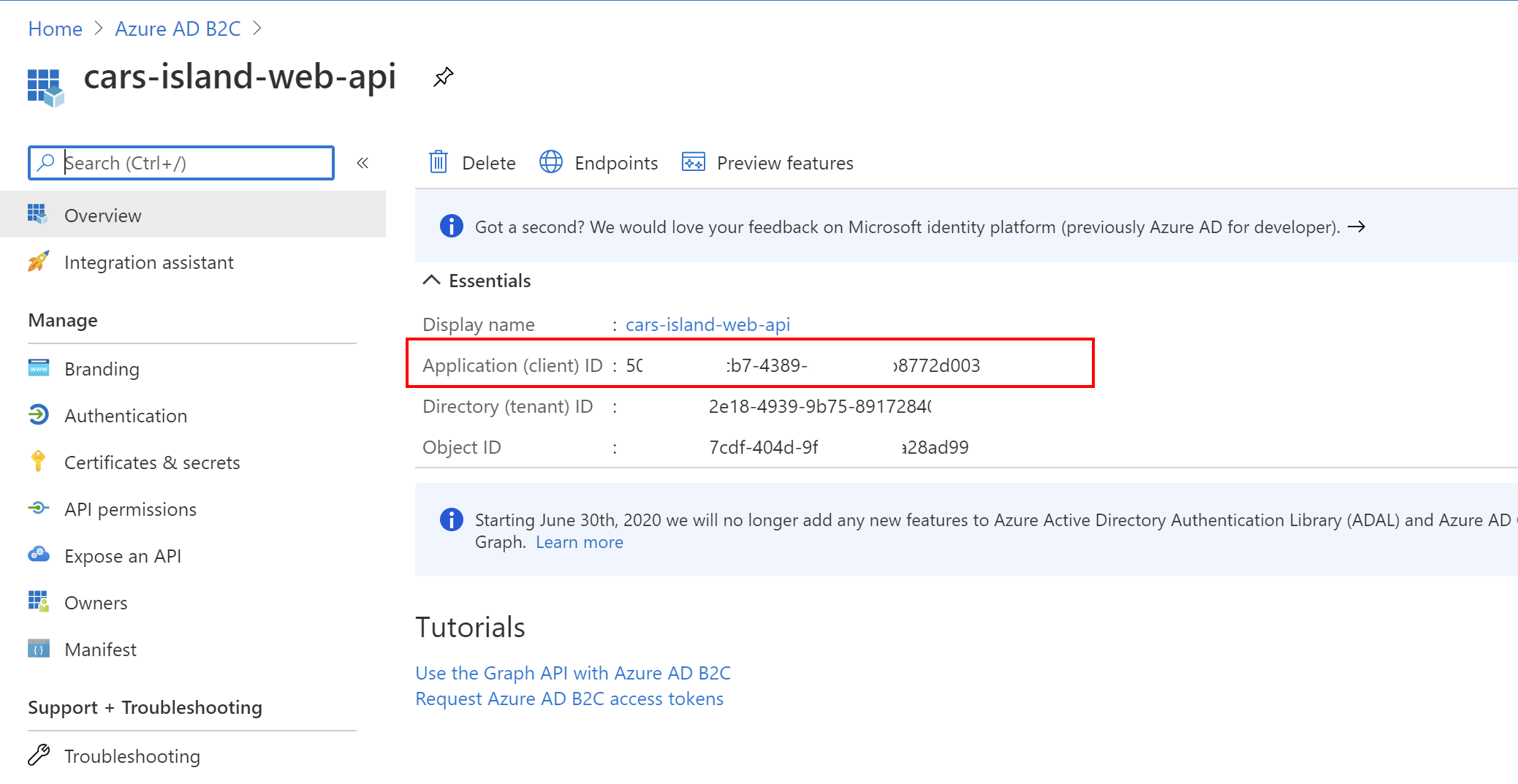
Once the application is created there is Application (client) ID value generated. It is used to uniquely identify the application in the Azure AD B2C tenant.
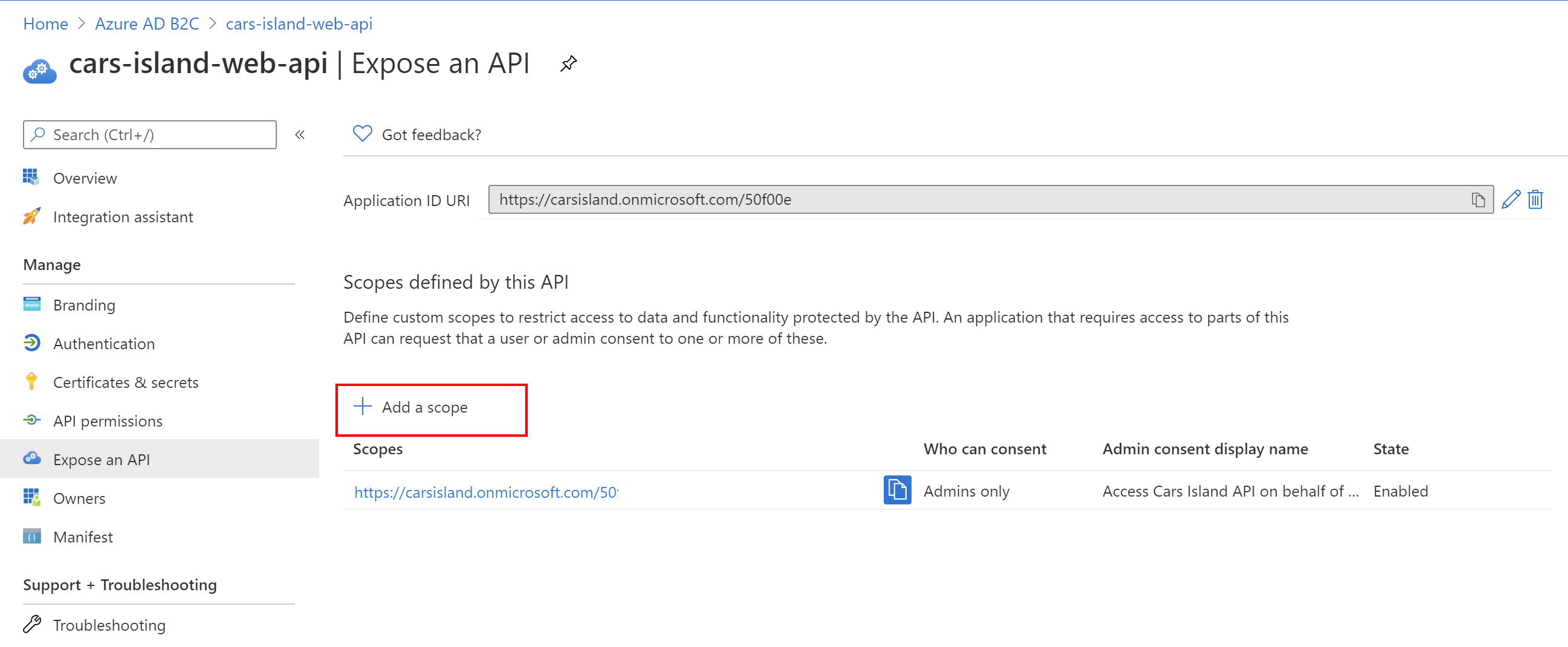
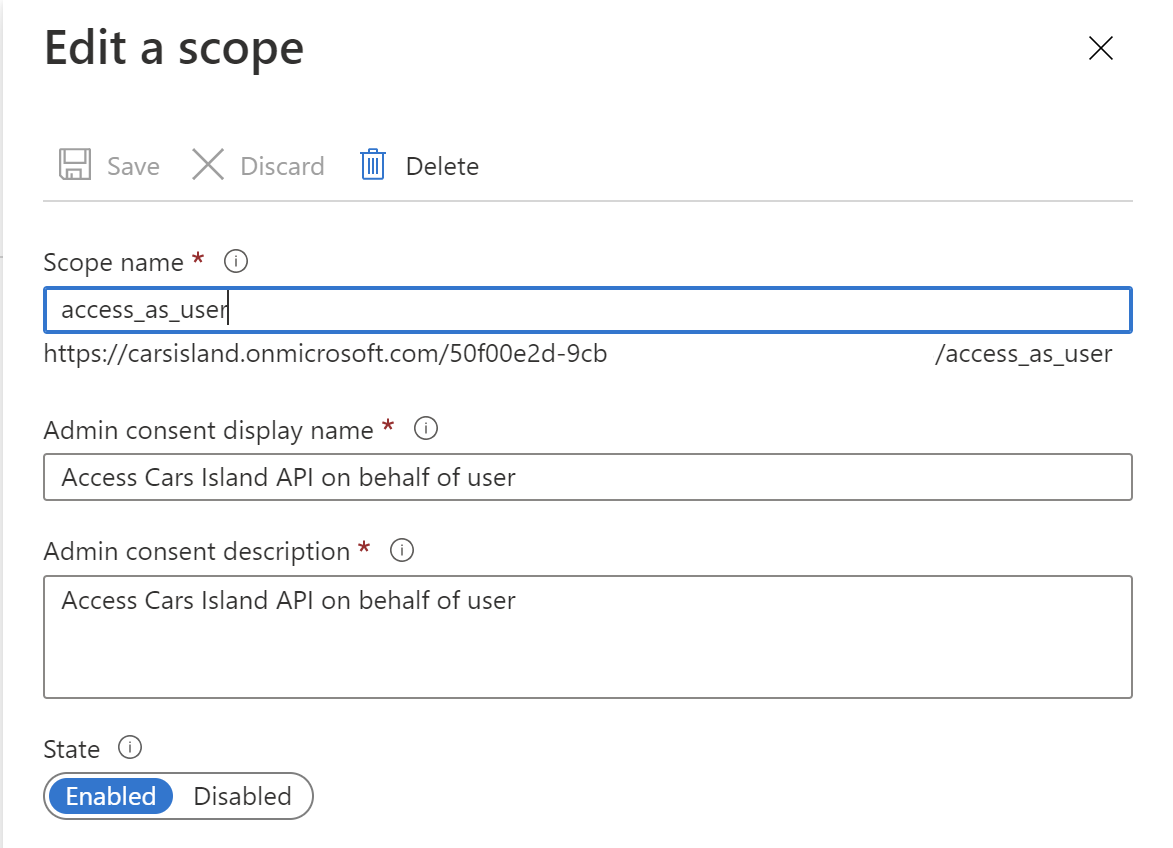
Then we have to expose an API to make it possible to request access token with specific scope. This is why under the Expose an API section we have to add new scope:
That’s it. Now we have an application registered in the Azure AD B2C and we exposed the scope to make it possible to request an access token for this specific Web API (Cars Island API).
Microsoft Identity Web library integration
The next step is to configure authentication and authorization in the ASP .NET Core Web API application. First of all, it is worth mentioning that with new library called Microsoft Identity Web it much easier to do it. This library provides classes and methods to simplify the process of securing the application with Azure Active Directory and Azure Active Directory B2C.
To secure ASP .NET Core Web API with Azure AD B2C, add Microsoft Identity Web NuGet package. Then, in the appsettings.json file include below section:
"AzureAdB2C": {
"Instance": "",
"ClientId": "",
"Domain": "",
"SignUpSignInPolicyId": "B2C_1A_SignUpOrSignin"
},
- Instance - URL of your Azure AD B2C instance, in my case this is https://carsisland.b2clogin.com
- ClientId - ID of the application we registered before in the Azure portal
- Domain - name of your Azure AD B2C tenant, in my case this is carsisland.onmicrosoft.com
- SignUpSignInPolicyId - the name of the Azure AD B2C custom policy responsible for users authentication and registration
Then with one line you can integrate authentication in the source code using the Microsoft Identity Web library extension method:
public static IServiceCollection AddAuthenticationWithAuthorizationSupport(this IServiceCollection services, IConfiguration config)
{
services.AddMicrosoftIdentityWebApiAuthentication(config, "AzureAdB2C");
return services;
}
You can see the above extension method in my GitHub repository where the project is located.
Then in the Startup.cs file we can call this method:
public void ConfigureServices(IServiceCollection services)
{
services.AddAppConfiguration(Configuration)
.AddAuthenticationWithAuthorizationSupport(Configuration)
...
}
Then in the Configure method we have to add these two lines:
public void Configure(IApplicationBuilder app, IWebHostEnvironment env)
{
...
app.UseAuthentication();
app.UseAuthorization();
...
}
In this project I decided to require authenticated users for all available endpoints. To do it in the Startup.cs file, in the ConfigureServices method I added below filter:
services.AddControllers(configure =>
{
...
var policy = new AuthorizationPolicyBuilder()
.RequireAuthenticatedUser()
.Build();
configure.Filters.Add(new AuthorizeFilter(policy));
});
With above filter applied, all enpoints requires authenticated used. To disable this rule for specific endpoints, AllowAnonymous attribute can be applied like I did it in the CarController for instance:
[AllowAnonymous]
[ApiController]
[Route("api/[controller]")]
public class CarController : ControllerBase
...
Authorization setup
As I mentioned before, with Microsoft Identity Web library it is much easier to configure not only authentication but authorization too. In the Cars Island API, there is an endpoint responsible for handling requests related to car reservations. In the CarReservationController class there is attribute: [Authorize(Policy = “AccessAsUser”)]. This attribute underneath verifies if the access token sent in the authorization header to the API contains a specific claim - in this case access_as_user claim we have described in the Azure portal above in the article.
[Authorize(Policy = "AccessAsUser")]
[ApiController]
[Route("api/[controller]")]
public class CarReservationController : ControllerBase
...
Now let’s discuss how this attribute is defined in the source code. In the API project there is a folder called AuthorizationPolicies. This folder contains two classes:
- ScopesRequirement - this class implements IAuthorizationRequirement and has only one property: ScopeName. This property keeps the name of the claim that should be present in the access token sent to the API
- ScopesHandler - this class derives from AuthorizationHandler class and implements HandleRequirementAsync method. Note that this class is generic and in this specific scenario we use ScopesRequirement as a requirement
Below there is the source code of ScopesHandler class. Please note that specific requirement is succeeded only when access_as_user scope is presented in the access token sent to the API:
public class ScopesHandler : AuthorizationHandler<ScopesRequirement>
{
protected override Task HandleRequirementAsync(AuthorizationHandlerContext context,
ScopesRequirement requirement)
{
if (!context.User.Claims.Any(x => x.Type == ClaimConstants.Scope)
&& !context.User.Claims.Any(y => y.Type == ClaimConstants.Scp))
{
return Task.CompletedTask;
}
Claim scopeClaim = context?.User?.FindFirst(ClaimConstants.Scp);
if (scopeClaim == null)
scopeClaim = context?.User?.FindFirst(ClaimConstants.Scope);
if (scopeClaim != null && scopeClaim.Value.Equals(requirement.ScopeName, StringComparison.InvariantCultureIgnoreCase))
{
// Success only when there is a specific claim presented in the access token:
context.Succeed(requirement);
}
return Task.CompletedTask;
}
}
The last step is to specify which claim exactly we expect to be included in the access token. In the Startup.cs file there is below method used:
services.AddAuthorization(options =>
{
options.AddPolicy("AccessAsUser",
policy => policy.Requirements.Add(new ScopesRequirement("access_as_user")));
});
As you can see we require access_as_user to be present as a claim in the access token sent to the API. If there is no access_as_user scope, the request will fail and Unauthorized response will be returned.
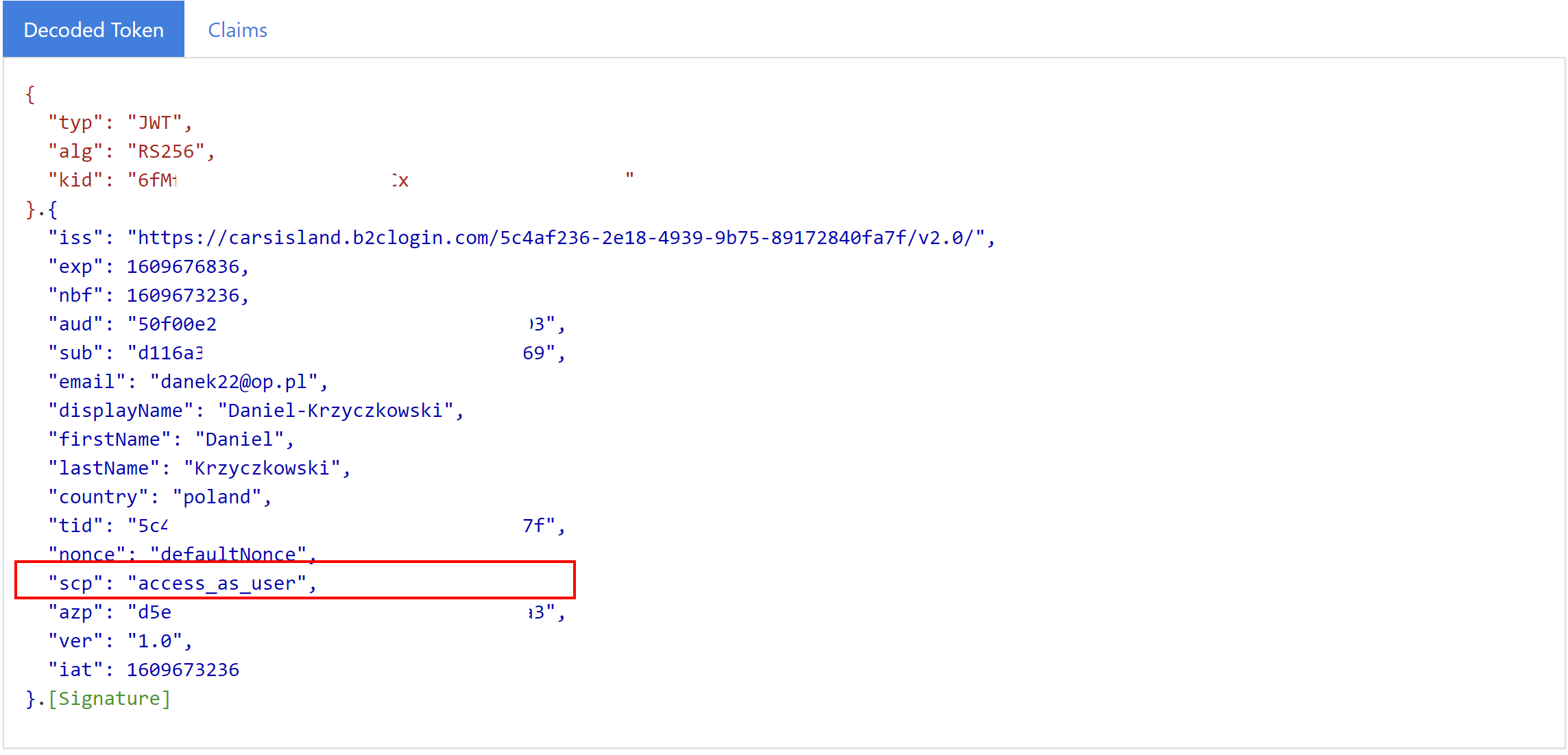
Below I present content of decoded JWT access token returned from the Azure AD B2C service:
As you can see there is access_as_user presented.
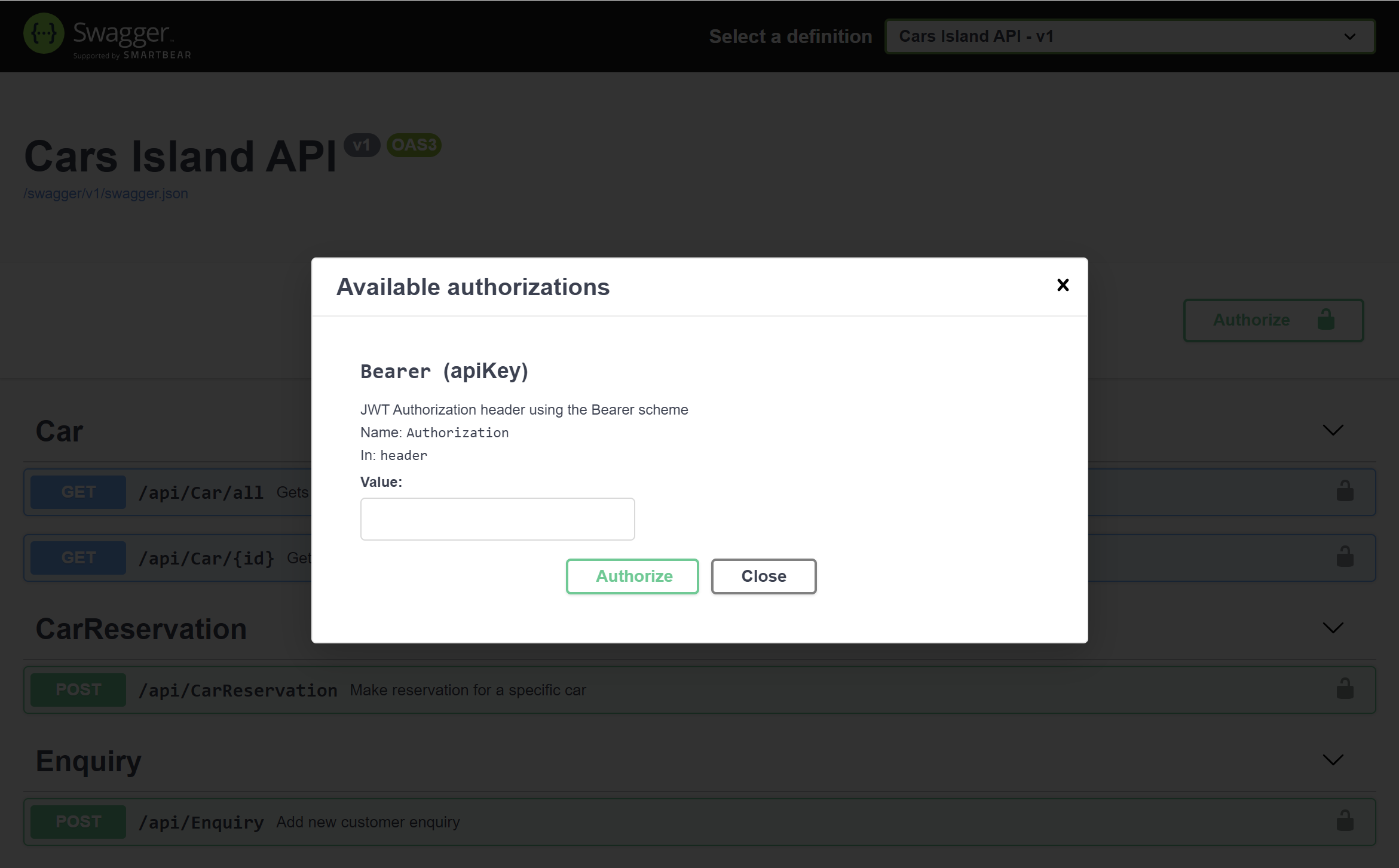
Authorization section in the Swagger UI
To make it easier to develop and verify if authorization works, I decided to add Authorization component to the Swagger UI:
To enable the above functionality, in the SwaggerCollectionExtensions class I wrote the below method where I included handling JWT bearer token:
public static class SwaggerCollectionExtensions
{
public static IServiceCollection AddSwagger(this IServiceCollection services)
{
services.AddSwaggerGen(c =>
{
c.SwaggerDoc("v1", new OpenApiInfo { Title = "Cars Island API", Version = "v1" });
var xmlFile = $"{Assembly.GetExecutingAssembly().GetName().Name}.xml";
var xmlPath = Path.Combine(AppContext.BaseDirectory, xmlFile);
c.IncludeXmlComments(xmlPath);
c.AddSecurityDefinition("Bearer", new OpenApiSecurityScheme
{
Name = "Authorization",
Type = SecuritySchemeType.ApiKey,
Scheme = "Bearer",
BearerFormat = "JWT",
In = ParameterLocation.Header,
Description = "JWT Authorization header using the Bearer scheme"
});
c.AddSecurityRequirement(new OpenApiSecurityRequirement
{
{
new OpenApiSecurityScheme
{
Reference = new OpenApiReference
{
Type = ReferenceType.SecurityScheme,
Id = "Bearer"
}
},
Array.Empty<string>()
}
});
});
return services;
}
}
Once Swagger UI is displayed, JWT token can be added.
Summary
In this article, I described how to secure ASP .NET Core Web API with Azure AD B2C identity service using Microsoft Identity Web library. Source code of the Cars Island solution is available on my GitHub so you can see all implementation details.
If you want to learn more about Azure AD B2C service specifically, please check below resources:

Recommend
-
 33
33
上一节讲到如何在我们的项目中集成Azure AD 保护我们的API资源,以及在项目中集成Swagger,并且如何把Swagger作为一个客户端进行认证和授权去访问我们的WebApi资源的?本节就接着讲如何在我们的项目中集成 Azure AD 保护我们的API资源,使用其他几种授权模式...
-
 13
13
Migrating an ASP.NET Core Web API Project to Azure Function Tuesday, July 7, 2020 China Standard Time - 1034 Reads
-
 11
11
Gunnar Peipman – Programming BlogASP.NET Core, Blazor, .NET, Azure, SharePoint, IoT A portal focused on Operatio...
-
 13
13
Diagnosing ASP.NET Core Startup Issues in Azure App Service (#199)116 views•Feb 16, 2021
-
 8
8
Set a Custom Name Claim Type in Azure AD Secured Web API In this article, we’ll learn how to set a custom name claim type to our ClaimsPrincipal’s primary identity in ASP.NET Core Web API. Our AP...
-
 18
18
Azure Queue Storage with ASP.NET Core Posted by Muhammed Saleem | Updated Date Aug 30, 2021 |
-
 10
10
Secured-Core PC Configuration Lock 10/25/2021 2 minutes to read Applies to Windows 11 In an enterprise organizatio...
-
 8
8
Implement certificate authentication in ASP.NET Core for an Azure B2C API connector This article shows how an ASP.NET Core API can be setup to require certificates for authentication. The API is used to implem...
-
 4
4
December 7, 2021 New Secured-core servers are now available from the Microsoft ecosystem to help secure your infrastructure In the current pandemic-driven remote work environm...
-
 8
8
ASP.NET Core 2.0 Azure AD Authentication Posted on: 04-06-2017
About Joyk
Aggregate valuable and interesting links.
Joyk means Joy of geeK