

用Python的minidom写XML
source link: https://note.qidong.name/2017/11/write-xml-with-minidom/
Go to the source link to view the article. You can view the picture content, updated content and better typesetting reading experience. If the link is broken, please click the button below to view the snapshot at that time.

用Python的minidom写XML
2017-11-22 15:29:30 +08 字数:1543 标签: Python
读、或者说解析XML的需求很常见,而写、或者说生成XML的需求就比较少见。 并且在很多情况下,用字符串手写、拼接,也非常的方便快捷。 然而,总有一些时候,需要用结构化的方式,去写一些复杂的XML。
经过挑选,孤选择了Python的minidom。
XML简介 ¶
XML(eXtensible Markup Language,可扩展标记语言),是一种可用于任何类型的结构化数据的通用型语言。 它被设计来保存与传递数据,是一种W3C推荐的规范。 虽然形式与HTML类似,但XML没有任何预定义的Tag,具备很高的可扩展性。
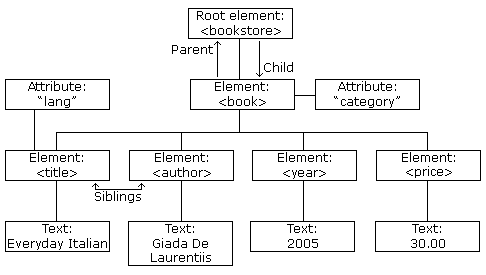
上图与以下代码,都源于XML Tutorial。 这个例子清晰地展示了XML对数据结构的表达。
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<bookstore>
<book category="cooking">
<title lang="en">Everyday Italian</title>
<author>Giada De Laurentiis</author>
<year>2005</year>
<price>30.00</price>
</book>
<book category="children">
<title lang="en">Harry Potter</title>
<author>J K. Rowling</author>
<year>2005</year>
<price>29.99</price>
</book>
<book category="web">
<title lang="en">Learning XML</title>
<author>Erik T. Ray</author>
<year>2003</year>
<price>39.95</price>
</book>
</bookstore>
概念 ¶
要想写XML,需要先知道基本概念。 因为工具都是根据概念来设计的,知道概念就很容易明白有哪些接口、分别是什么功能。
XML的核心概念可以用以下代码片表示。
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<!-- comment -->
<root>
<element attribute="0">text</element>
<sibling attribute="1">text</sibling>
</root>
- XML是树状结构,基本单元是node。 element就是一个node。
- element之间可以有父子关系(parent-child)。 每个element最多只有一个parent,可以有多个child。
- 每一个XML都有且仅有一个特殊的element,是为root。 在父子关系上,它是所有element的祖先。
- element可以有兄弟关系(sibling),它们共享同一个parent。
- 每个element都可以有若干个attribute。
- 每个element都可以有一个text,它也是一个node。
由于是用工具写,而非手写,所以一些语法细节,可以不用关注。 详见XML Syntax。
使用minidom ¶
from xml.dom import minidom
写一个XML,大概过程是:
- 创建Document
- 创建element、定制attribute与text
- 输出Document
创建Document ¶
xml = minidom.Document()
一个Document,其实就是一个XML文件。
创建root ¶
root = xml.createElement('root')
xml.appendChild(root)
要注意两点:
- 需要使用
appendChild,element才真的出现在Document中。 - 一个Document只能有一个root,Document级别的
appendChild只能使用一次。
创建element ¶
child = xml.createElement('child')
root.appendChild(child)
和root相比,普通element都是以root或其它element来调用appendChild。
设置attribute ¶
child.setAttribute('attr', '0')
attribute的值,必须是字符串。
设置text ¶
node = xml.createTextNode('text')
child.appendChild(node)
text也是一个node,要像node一样去操作。
输出 ¶
minidom一共有两种输出方式,一是输出为字符串,二是输出到writer。 但归根结底,还是输出到writer。
def toxml(self, encoding = None):
return self.toprettyxml("", "", encoding)
def toprettyxml(self, indent="\t", newl="\n", encoding = None):
# indent = the indentation string to prepend, per level
# newl = the newline string to append
writer = _get_StringIO()
if encoding is not None:
import codecs
# Can't use codecs.getwriter to preserve 2.0 compatibility
writer = codecs.lookup(encoding)[3](writer)
if self.nodeType == Node.DOCUMENT_NODE:
# Can pass encoding only to document, to put it into XML header
self.writexml(writer, "", indent, newl, encoding)
else:
self.writexml(writer, "", indent, newl)
return writer.getvalue()
从以上源码中可以看出,其实toxml是用toprettyxml实现的,而toprettyxml则是用writexml来实现的。
输出时,可以指定XML的encoding,以及缩进、换行符。
>>> xml.toxml()
'<?xml version="1.0" ?><root><child attr="0">text</child></root>'
>>> print(xml.toprettyxml())
<?xml version="1.0" ?>
<root>
<child attr="0">text</child>
</root>
>>> import sys
>>> xml.writexml(sys.stdout, '', ' ' * 4, '\n', 'UTF-8')
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<root>
<child attr="0">text</child>
</root>
可以看到,之前写的root、child等内容,都在其中。
需要打印到文件时,把上面writexml中的sys.stdout换成文件对象即可。
手写混合 ¶
如果需要混合一些既有的XML片段,到生成到一半的Document中,这时可以使用minidom提供的解析功能。
>>> hello = minidom.parseString('<hello>world</hello>')
>>> root.appendChild(hello.firstChild)
>>> xml.writexml(sys.stdout, '', ' ' * 4, '\n', 'UTF-8')
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<root>
<child attr="0">text</child>
<hello>world</hello>
</root>
总结 ¶
本文只是简单介绍如何生成一个XML文件,相信以上内容就已经足够了。 通过minidom,也可以对既有的XML进行一些解析、查找、修改。
Recommend
-
 37
37
1.问题描述属性无序问题和xml声明不是单独一行# cat HKEX-EPS_20180830_003249795.xml<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?><ETCML><IISHeadline><News Encoding="UTF-8" Language="en-us" TimeStamp="201808301
-
 6
6
Automatic blog publishing using Python and XML-RPCAutomatic blog publishing using Python and XML-RPC Mon 01 December 2008The following piece of code collects links in a Pligg database (but could be any kind of source like RSS feed......
-
 14
14
术→技巧, 研发 Python XML文件格式的解析 钱魏Way · 2020-11-24 ·...
-
 7
7
Parsing XML with Python Minidom November 29, 2019 By Rowell Leave a Comment A core skill...
-
 9
9
python项目练习三:万能的XML 作者:the5fire | 标签: python实战 | 发布:2011-12-20 11:18 p.m. | 阅读量:...
-
 13
13
A Roadmap to XML Parsers in Python – Real PythonChoose the Right XML Parsing Model It turns out that you can process XML documents using a few language-agnostic strategies. Each demonstrates different memory and speed trade-offs, whi...
-
 17
17
PARSE XML/HTML FROM A FILE This post gives a real-world example about how to parse and retrieve data from a XML/HTML file by the use...
-
 5
5
[Python] Use XSL to Transform XML (XSLT) Updated: February 18, 2015 To transform
-
 7
7
python读取xml文件 | K's Life Tag Cloud ...
-
 8
8
Python操作xml打开pycharm项目想使用alfred打开pycharm项目,网上找了下有个python版本的workflow但是我的是 pycharm 2021.1 版本不好使,于是改了一下。pycharm打开的项目信息保存在 ~/Library/Application Support/Jet...
About Joyk
Aggregate valuable and interesting links.
Joyk means Joy of geeK