

Slate 介绍分析与实践
source link: https://coldstone.fun/post/2020/12/13/slate-intro/
Go to the source link to view the article. You can view the picture content, updated content and better typesetting reading experience. If the link is broken, please click the button below to view the snapshot at that time.

Slate 介绍分析与实践
最后更新: 2020-12-13 阅读时间: 19 minSlate 是一个使用 TypeScript 开发富文本编辑器开发框架,诞生于 2016 年,作者是 Ian Storm Taylor。它吸收了 Quill,Prosemirror,Draft.js 的优点,核心数据模型十分精简,具有高度的可扩展性,最新版本为 v0.60.1。
- 插件作为一等公民,能够完全修改编辑器行为
- 数据层和渲染层分离,更新数据触发渲染
- 文档数据类似于 DOM 树,可嵌套
- 具有原子化操作 API,理论上支持协同编辑
- 使用 React 作为渲染层
- 不可变数据结构 Immer
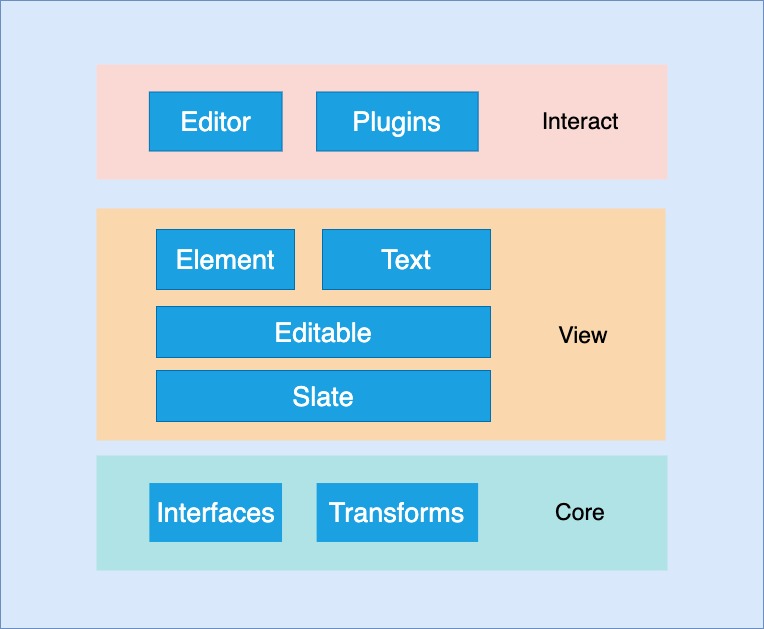
Slate 使用 monorepo 方式管理仓库,packages 目录中有 4 个源码包。
slate
slate 核心仓库,包含抽象数据模型 interfaces,操作节点的方法 transforms,创建实例的方法等。
Interfaces
intefaces 目录下是 Slate 定义的数据模型。
Node 表示 Slate 文档树中不同类型的节点。
1
2
3
4
5
export type BaseNode = Editor | Element | Text
export type Descendant = Element | Text
export type Ancestor = Editor | Element
Editor 对象用于存储编辑器的所有状态,可以通过插件添加辅助函数或实现新行为。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
export interface BaseEditor {
children: Descendant[]
selection: Selection
operations: Operation[]
marks: Omit<Text, 'text'> | null
/// ...
}
Element 对象是 Slate 文档树中包含其他 Element 或 Text 的一种节点,取决于编辑器配置它可以是块级 block 或内联 inline 的。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
export interface ElementInterface {
isAncestor: (value: any) => value is Ancestor
isElement: (value: any) => value is Element
isElementList: (value: any) => value is Element[]
isElementProps: (props: any) => props is Partial<Element>
matches: (element: Element, props: Partial<Element>) => boolean
}
Text 对象表示文档树中的叶子节点,是实际包含文本和格式的节点,它们不能包含其他节点。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
export interface TextInterface {
equals: (text: Text, another: Text, options?: { loose?: boolean }) => boolean
isText: (value: any) => value is Text
isTextList: (value: any) => value is Text[]
isTextProps: (props: any) => props is Partial<Text>
matches: (text: Text, props: Partial<Text>) => boolean
decorations: (node: Text, decorations: Range[]) => Text[]
}
Path 是一个描述节点在文档树中的具体位置的索引列表,一般相对于 Editor 节点,但也可以是其他 Node 节点。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
export interface PathInterface {
ancestors: (path: Path, options?: { reverse?: boolean }) => Path[]
common: (path: Path, another: Path) => Path
compare: (path: Path, another: Path) => -1 | 0 | 1
endsAfter: (path: Path, another: Path) => boolean
endsAt: (path: Path, another: Path) => boolean
endsBefore: (path: Path, another: Path) => boolean
equals: (path: Path, another: Path) => boolean
hasPrevious: (path: Path) => boolean
isAfter: (path: Path, another: Path) => boolean
isAncestor: (path: Path, another: Path) => boolean
isBefore: (path: Path, another: Path) => boolean
isChild: (path: Path, another: Path) => boolean
isCommon: (path: Path, another: Path) => boolean
isDescendant: (path: Path, another: Path) => boolean
isParent: (path: Path, another: Path) => boolean
isPath: (value: any) => value is Path
isSibling: (path: Path, another: Path) => boolean
levels: (
path: Path,
options?: {
reverse?: boolean
}
) => Path[]
next: (path: Path) => Path
parent: (path: Path) => Path
previous: (path: Path) => Path
relative: (path: Path, ancestor: Path) => Path
transform: (
path: Path,
operation: Operation,
options?: { affinity?: 'forward' | 'backward' | null }
) => Path | null
}
Point 对象表示文本节点在文档树中的一个特定位置。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
export interface PointInterface {
compare: (point: Point, another: Point) => -1 | 0 | 1
isAfter: (point: Point, another: Point) => boolean
isBefore: (point: Point, another: Point) => boolean
equals: (point: Point, another: Point) => boolean
isPoint: (value: any) => value is Point
transform: (
point: Point,
op: Operation,
options?: { affinity?: 'forward' | 'backward' | null }
) => Point | null
}
Operation 对象是 Slate 用来更改内部状态的低级指令,Slate 将所有变化表示为 Operation 。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
export interface OperationInterface {
isNodeOperation: (value: any) => value is NodeOperation
isOperation: (value: any) => value is Operation
isOperationList: (value: any) => value is Operation[]
isSelectionOperation: (value: any) => value is SelectionOperation
isTextOperation: (value: any) => value is TextOperation
inverse: (op: Operation) => Operation
}
Transforms
Transforms 是对文档进行操作的辅助函数,包括选区转换,节点转换,文本转换和通用转换。
1
2
3
4
5
6
export const Transforms = {
...GeneralTransforms, // 操作 Operation 命令
...NodeTransforms, // 操作节点
...SelectionTransforms, // 操作选区
...TextTransforms, // 操作文本
}
createEditor
创建编辑器实例的方法,返回一个实现了 Editor 接口的编辑器实例对象。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
/// create-editor.ts
export const createEditor = (): Editor => {
const editor: Editor = {}
/// ...
return editor
}
slate-react
slate-react 编辑器的 React 组件,渲染文档数据。
Slate
组件上下文的包装器,处理 onChange 事件,接受文档数据 value。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
/// Slate.tsx
export const Slate = () => {
/// ...
return (
<SlateContext.Provider value={context}>
<EditorContext.Provider value={editor}>
<FocusedContext.Provider value={ReactEditor.isFocused(editor)}>
{children}
</FocusedContext.Provider>
</EditorContext.Provider>
</SlateContext.Provider>
)
}
Editable
编辑器的主要区域,设置标签属性,处理 DOM 事件。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
/// Editable.tsx
export const Editable = (props: EditableProps) => {
/// ...
return (
<ReadOnlyContext.Provider value={readOnly}>
<Component>
<Children />
</Component>
</ReadOnlyContext.Provider>
)
}
Children
根据编辑器文档数据生成渲染组件。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
/// Children.tsx
const Children = () => {
const children = []
/// ...
return <React.Fragment>{children}</React.Fragment>
}
Element
渲染 Elment 的组件,使用 renderElement 方法渲染元素,使用 Children 组件生成子元素。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
/// Element.tsx
const Element = () => {
/// ...
return (
<SelectedContext.Provider value={!!selection}>
{renderElement({ attributes, children, element })}
</SelectedContext.Provider>
)
}
渲染文本节点组件。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
/// Text.tsx
const Text = () => {
/// ...
return (
<span data-slate-node="text" ref={ref}>
{children}
</span>
)
}
withReact
Slate 插件,添加/重写了编辑器实例的一些方法。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
/// with-react.ts
export const withReact = <T extends Editor>(editor: T) => {
const e = editor as T & ReactEditor
const { apply, onChange } = e
e.apply = () => {
/// ...
}
e.setFragmentData = () => {
/// ...
}
e.insertData = () => {
/// ...
}
e.onChange = () => {
/// ...
}
return e
}
slate-history
slate-history Slate 插件,为编辑器提供 撤销 **和 重做**功能。
History
使用 redos 和 undos 数组存储编辑器所有底层 Operation 命令的对象。
1
2
3
4
5
/// History.ts
export interface History {
redos: Operation[][]
undos: Operation[][]
}
HistoryEditor
带有历史记录功能的编辑器对象,具有操作历史记录的方法。
1
2
3
4
/// HistoryEditor.ts
export const HistoryEditor = {
/// ...
}
withHistory
Slate 编辑器插件,使用 undos 和 redos 栈追踪编辑器操作,实现编辑器的 redo,undo 方法,重写了apply 方法。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
/// with-history.ts
export const withHistory = <T extends Editor>(editor: T) => {
const e = editor as T & HistoryEditor
const { apply } = e
e.history = { undos: [], redos: [] }
e.redo = () => {
/// ...
}
e.undo = () => {
/// ...
}
e.apply = (op: Operation) => {
/// ...
}
return e
}
slate-hyperscript
slate-hyperscript 是一个使用 JSX 编写 Slate 文档的 hyperscript 工具
Slate 的插件只是一个返回 editor 实例的函数,在这个函数中通过重写编辑器实例方法,修改编辑器行为。
在创建编辑器实例的时候调用插件函数即可。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
import { Editor } from 'slate'
const myPlugin = (editor: Editor) => {
// 这里对 editor 的一些方法进行重写, 返回编辑器实例
editor.apply = () => {}
return editor
}
export default myPlugin
1
2
3
4
import { createEditor } from 'slate'
import myPlugin from './myPlugin'
const editor = myPlugin(createEditor())
如此以来插件就能完全控制编辑器行为,正如 Slate 的官方介绍所说
Slate 是一个 完全 可定制的富文本编辑器框架。
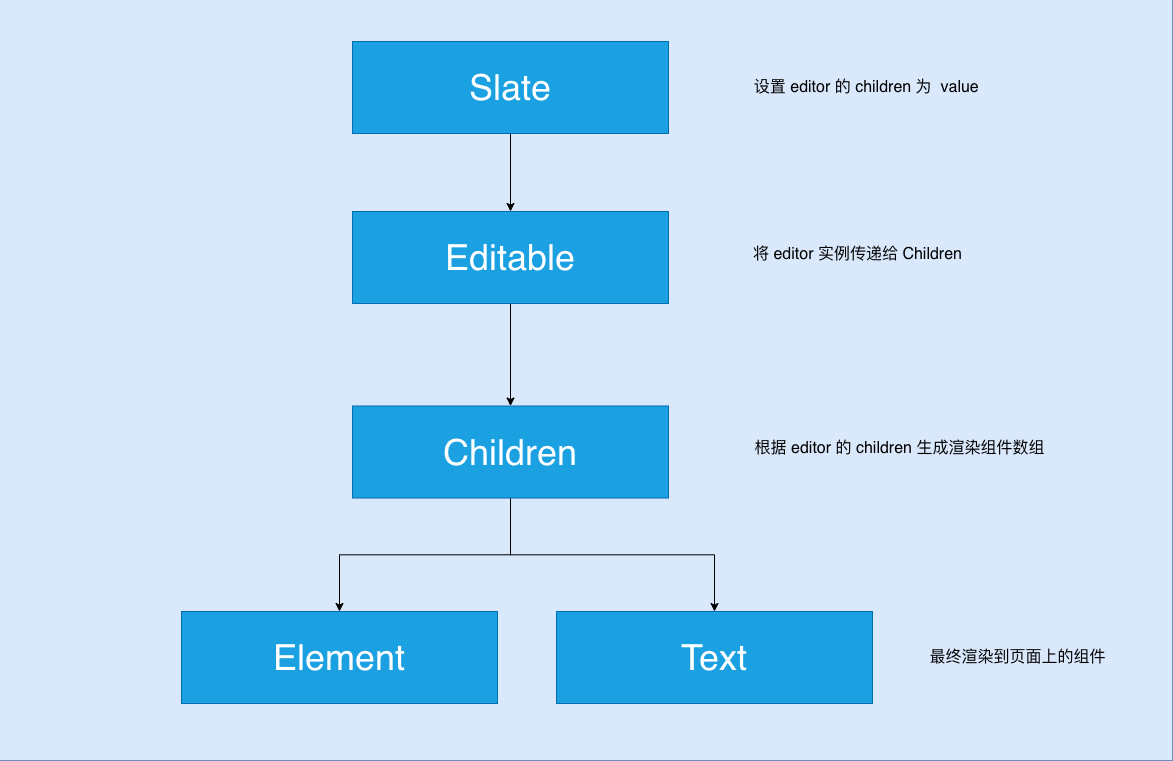
Slate 的文档数据是一颗类似 DOM 的节点树,slate-react 通过递归这颗树生成 children 数组,这个数组有两种类型的组件 Element 和 Text, 最终 raect 将 children 数组中的组件渲染到页面上,步骤如下。
- 设置编辑器实例的
children属性
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
/// Slate.tsx
export const Slate = (props: {
/// ...
}) => {
const { editor, children, onChange, value, ...rest } = props
const context: [ReactEditor] = useMemo(() => {
// 设置 editor 实例的 children 属性为 value
editor.children = value
/// ...
}, [])
/// ...
}
Editable组件传递editor实例给Children
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
/// Editable.tsx
export const Editable = (props: EditableProps) => {
// 获取 editor 实例
const editor = useSlate()
/// ...
return (
<ReadOnlyContext.Provider value={readOnly}>
<Component>
<Children
// 将 editor 传递给 Children 组件
node={editor}
/>
</Component>
</ReadOnlyContext.Provider>
)
}
Children生成渲染数组,交给 React 渲染组件。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
/// Children.tsx
const Children = (props: {
/// ...
}) => {
/// ...
const children = []
// 遍历 editor 实例上的 children 数组
for (let i = 0; i < node.children.length; i++) {
// 判断数据为 Element 或 Text
if (Element.isElement(n)) {
children.push(<ElementComponent />)
} else {
children.push(<TextComponent />)
}
}
return <React.Fragment>{children}</React.Fragment>
}
假设有以下数据
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
;[
{
type: 'paragraph',
children: [
{
text: 'A line of text in a paragraph.',
},
],
},
{
type: 'paragraph',
children: [
{
text: 'Another line of text in a paragraph.',
},
],
},
]
页面显示为

自定义渲染
传递渲染函数 renderElement 和 renderLeaf 给 Editable 组件,对元素和叶子节点进行自定义渲染。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
const Leaf = (props) => {
let { attributes, children, leaf } = props
// 根据属性值设置 HTML 标签
if (leaf.bold) {
children = <strong>{children}</strong>
}
return <span {...attributes}>{children}</span>
}
const Element = (props) => {
const { element } = props
// 根据类型返回组件
switch (element.type) {
case 'custom-type':
return <CustomElement {...props} />
default:
return <DefaultElement {...props} />
}
}
const renderLeaf = props => <Leaf {...props} />
const renderElement = props => <Element {...props} />
<Slate>
<Editable
// 传递自定义渲染函数
renderLeaf={renderLeaf}
renderElement={renderElement}
/>
</Slate>
slate-react 的 withReact 插件会重写编辑器的 onChange 方法,在每次文档数据更新时,调用 onContextChange 函数,执行 setKey(key + 1) 触发 React 重新渲染。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
/// slate.tsx
export const Slate = () => {
const [key, setKey] = useState(0)
const onContextChange = useCallback(() => {
onChange(editor.children)
// 设置 key + 1 触发 React 重新渲染
setKey(key + 1)
}, [key, onChange])
// 设置 onContextChange 函数
EDITOR_TO_ON_CHANGE.set(editor, onContextChange)
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
/// with.react.ts
export const withReact = <T extends Editor>(editor: T) => {
// 重写 onChange 方法
e.onChange = () => {
ReactDOM.unstable_batchedUpdates(() => {
const onContextChange = EDITOR_TO_ON_CHANGE.get(e)
if (onContextChange) {
// 执行 onContextChange 进行 key + 1
onContextChange()
}
onChange()
})
}
return e
}
一个基础的富文本编辑器
- 导入依赖,创建
<MyEditor />组件
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
import { createEditor } from 'slate'
import React, { useMemo, useState } from 'react'
import { Slate, Editable, withReact } from 'slate-react'
const MyEditor = () => {
return null
}
export default MyEditor
- 创建编辑器对象
editor和它的文档数据value,将他们传递给<Slate />。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
// ...
const MyEditor = () => {
const [value, setValue] = useState([])
const editor = useMemo(() => withReact(createEditor()), [])
return (
// Slate 组件保存编辑器的状态,目的是共享状态,使得其他组件比如工具栏也能获取到编辑器状态。
<Slate
editor={editor}
value={value}
onChange={(value) => setValue(value)}
></Slate>
)
}
- 使用
<Editable />渲染编辑器主要区域。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
// ...
const MyEditor = () => {
const [value, setValue] = useState([])
const editor = useMemo(() => withReact(createEditor()), [])
return (
<Slate editor={editor} value={value} onChange={(value) => setValue(value)}>
// Editable 组件是编辑器实际的渲染区域,用户在这里进行交互
<Editable
style={{
width: 500,
height: 300,
padding: 20,
border: '1px solid grey',
}}
placeholder="This is placeholder..."
/>
</Slate>
)
}
- 添加默认值编辑器的默认值,此时页面上应该会出现这行文本。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
/// ...
// 编辑器的值是一个对象数组,slate 会根据它来生成数据模型,交给 slate-react 渲染
const initialValue = [
{
type: 'paragraph',
children: [
{
text: 'A line of text in a paragraph.',
},
],
},
]
const MyEditor = () => {
// 初始化编辑器 value 为 initialValue
const [value, setValue] = useState(initialValue)
const editor = useMemo(() => withReact(createEditor()), [])
return (
<Slate editor={editor} value={value} onChange={(value) => setValue(value)}>
<Editable
style={{
width: 500,
height: 300,
padding: 20,
border: '1px solid grey',
}}
placeholder="This is placeholder..."
/>
</Slate>
)
}

- 创建工具栏组件,添加加粗,斜体,下划线按钮。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
const MyToolbar = () => {
return (
<div
style={{
width: 500,
display: 'flex',
padding: '10px 20px',
alignItems: 'center',
margin: '0 auto',
marginTop: 50,
border: '1px solid grey',
}}
>
<button
style={{
marginRight: 20,
}}
onMouseDown={(event) => {
event.preventDefault()
}}
>
B
</button>
<button
style={{
marginRight: 20,
}}
onMouseDown={(event) => {
event.preventDefault()
}}
>
I
</button>
<button
style={{
marginRight: 20,
}}
onMouseDown={(event) => {
event.preventDefault()
}}
>
U
</button>
</div>
)
}
// ...
;<Slate editor={editor} value={value} onChange={(value) => setValue(value)}>
// 在此处使用
<MyToolbar />
<Editable
style={{
width: 500,
height: 300,
padding: 20,
margin: '0 auto',
border: '1px solid grey',
borderTopWidth: 0,
}}
placeholder="This is placeholder..."
/>
</Slate>
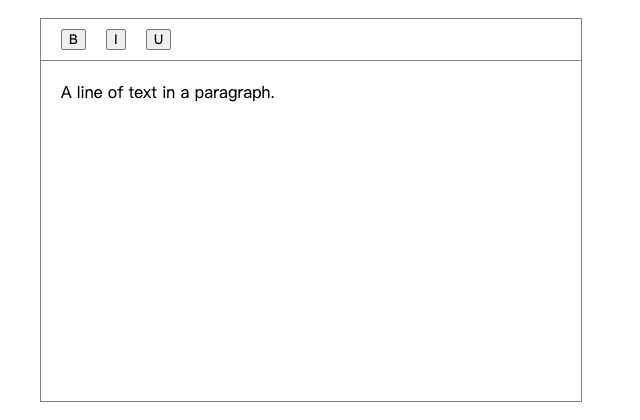
- 设置加粗,斜体,下划线渲染样式,传递
renderLeaf函数给Editable。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
/// MyEditor.jsx
// 定义具体样式如何渲染
const Leaf = (props) => {
let { attributes, children, leaf } = props
if (leaf.bold) {
children = <strong>{children}</strong>
}
if (leaf.italic) {
children = <i>{children}</i>
}
if (leaf.underline) {
children = <u>{children}</u>
}
return <span {...attributes}>{children}</span>
}
const MyEditor = () => {
/// ...
//
const renderLeaf = useCallback((props) => {
return <Leaf {...props} />
}, [])
return (
<Slate editor={editor} value={value} onChange={(value) => setValue(value)}>
<MyToolbar editor={editor} />
<Editable
//
renderLeaf={renderLeaf}
/>
</Slate>
)
}
- 在工具栏上添加转换节点属性的方法,点击时调用。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
/// MyToolbar.jsx
import React from 'react'
import { Text, Editor } from 'slate'
import { Transforms } from 'slate'
// 判断节点的属性值是否为真
const isFormatActive = (editor, format) => {
const [match] = Editor.nodes(editor, {
match: (n) => n[format] === true,
universal: true,
})
return !!match
}
// 根据样式切换属性值
const toggleFormat = (event, editor, format) => {
event.preventDefault()
const isActive = isFormatActive(editor, format)
Transforms.setNodes(
editor,
{ [format]: isActive ? false : true },
{ match: (n) => Text.isText(n), split: true }
)
}
const MyToolbar = ({ editor }) => {
return (
<div
style={{
width: 500,
display: 'flex',
padding: '10px 20px',
alignItems: 'center',
margin: '0 auto',
marginTop: 50,
border: '1px solid grey',
}}
>
<button
style={{
marginRight: 20,
}}
// 在点击事件上调用
onClick={(event) => {
toggleFormat(event, editor, 'bold')
}}
>
B
</button>
/// ...
</div>
)
}

创建一个自定义树型元素
Slate 的强大之处在于它的可扩展性,以下展示如何自定义一个树类型元素。
- 定义树形元素
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
/// TreeElement.jsx
import React, { useState } from 'react'
const TreeElement = ({ attributes, children, element }) => {
const { checked, label } = element
const [isChecked, setIsChecked] = useState(checked)
const onChange = () => {
setIsChecked(!isChecked)
}
return (
<div {...attributes}>
<p
style={{
display: 'flex',
alignItems: 'center',
}}
contentEditable={false}
>
<input
type="checkbox"
style={{
width: 20,
}}
checked={isChecked}
onChange={onChange}
/>
<label>{label}</label>
</p>
{isChecked ? <div style={{ paddingLeft: 20 }}>{children}</div> : null}
</div>
)
}
- 将
renderElement方法传递给<Editable />。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
/// ...
const Element = (props) => {
const { element } = props
switch (element.type) {
case 'tree-item':
return <TreeElement {...props} />
default:
return <DefaultElement {...props} />
}
}
/// ...
const renderElement = useCallback((props) => <Element {...props} />, [])
/// ...
<Editable
renderElement={renderElement}
/>
- 添加树形元素数据
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
const initialValue = [
/// ...
{
type: 'tree-item',
checked: true,
label: 'first level',
children: [
{
type: 'tree-item',
checked: false,
label: 'second level',
children: [
{
type: 'tree-item',
label: 'third level',
checked: false,
children: [
{
type: 'paragraph',
children: [
{
text: 'This is a tree item',
},
],
},
],
},
],
},
],
},
]

创建一个控制输入的插件
以下展示如何定义一个 Slate 插件
- 创建一个
withEmojis插件
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
/// with-emojis.ts
import { ReactEditor } from 'slate-react'
const letterEmojis = {
a: '?',
b: '?',
c: '?',
d: '?',
e: '?',
f: '?',
g: '?',
h: '?',
i: '?',
j: '?',
k: '?',
l: '?',
m: '?',
n: '?',
o: '?',
p: '?',
q: '?',
r: '?',
s: '?',
t: '?',
u: '?',
v: '?',
w: '?',
x: '?',
y: '?',
z: '?',
}
const withEmojis = (editor: ReactEditor) => {
const { insertText } = editor
// 重写 editor 的 insertText 方法
editor.insertText = (text: string) => {
if (letterEmojis[text.toLowerCase()]) {
text = letterEmojis[text]
}
// 执行原有的 insertText 方法
insertText(text)
}
return editor
}
export default withEmojis
- 在新建编辑器对象时使用插件
1
2
3
/// MyEditor.tsx
const editor = useMemo(() => withEmojis(withReact(createEditor())), [])

- 还没有发布正式版,处于 Beta 阶段,API 可能会有变化
- 渲染层目前只有 React,要在其他框架中使用需要自行实现
- 数据渲染分离,需要完全控制用户输入行为,否则可能导致数据和渲染不同步
- 基于 contenteditable 无法突破浏览器的排版效果
- 对中文输入支持不足,详见此 链接
- 社区驱动开发,问题可能得不到及时修复
Slate 是一个设计优秀的富文本编辑器开发框架,具有很高的可扩展性。
如果需要一个能迅速接入并使用的富文本编辑器,那么可以使用 ckeditor4, tinymce, ueditor 这些提供开箱即用功能的编辑器。
如果是要开发一款功能丰富,需要定制化的编辑器那么 Slate 将是你的第一选择。
Recommend
About Joyk
Aggregate valuable and interesting links.
Joyk means Joy of geeK