

十张图说清Elasticsearch原理!
source link: http://developer.51cto.com/art/202009/625293.htm
Go to the source link to view the article. You can view the picture content, updated content and better typesetting reading experience. If the link is broken, please click the button below to view the snapshot at that time.
说到 Elasticsearch,其中最明显的一个特点就是 near real-time 准实时,当文档存储在 Elasticsearch 中时,将在 1 秒内以几乎实时的方式对其进行索引和完全搜索。那为什么说 ES 是准实时的呢?

图片来自 Pexels
Lucene 和 ES
Lucene
Lucene 是 Elasticsearch所基于的 Java 库,它引入了按段搜索的概念:
- Segment:也叫段,类似于倒排索引,相当于一个数据集。
- Commit point:提交点,记录着所有已知的段。
- Lucene index:“a collection of segments plus a commit point”。由一堆 Segment 的集合加上一个提交点组成。
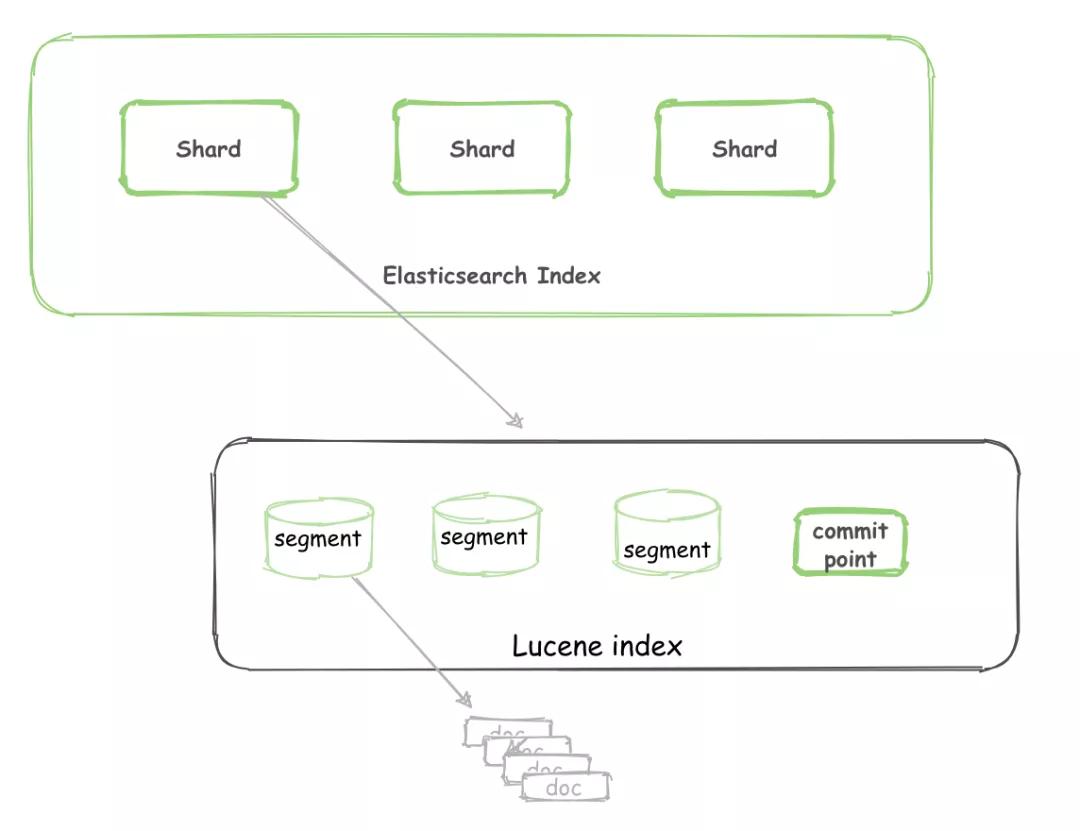
对于一个 Lucene index 的组成,如下图所示:

ES
一个 Elasticsearch Index 由一个或者多个 shard(分片)组成。

而 Lucene 中的 Lucene index 相当于 ES 的一个 shard。
写入过程
写入过程 1.0(不完善)
写入过程 1.0 如下:
- 不断将 Document 写入到 In-memory buffer(内存缓冲区)。
- 当满足一定条件后内存缓冲区中的 Documents 刷新到磁盘。
- 生成新的 segment 以及一个 Commit point 提交点。
- 这个 segment 就可以像其他 segment 一样被读取了。
画图如下:
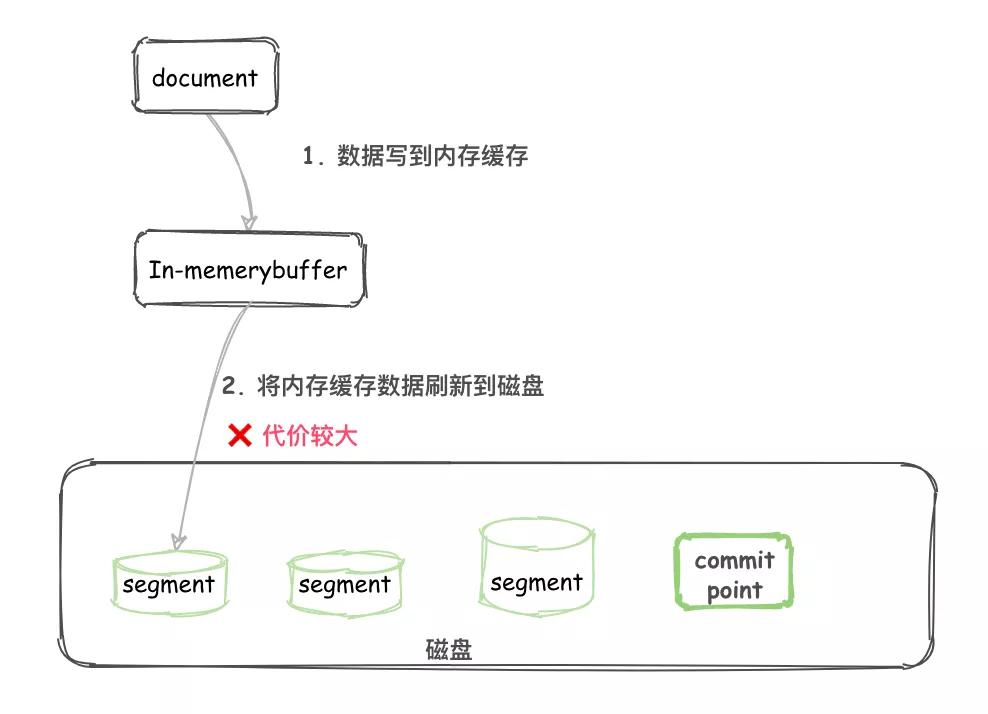
将文件刷新到磁盘是非常耗费资源的,而且在内存缓冲区和磁盘中间存在一个高速缓存(cache),一旦文件进入到 cache 就可以像磁盘上的 segment 一样被读取了。
写入过程 2.0
写入过程 2.0 如下:
- 不断将 Document 写入到 In-memory buffer(内存缓冲区)。
- 当满足一定条件后内存缓冲区中的 Documents 刷新到高速缓存(cache)。
- 生成新的 segment,这个 segment 还在 cache 中。
- 这时候还没有 commit,但是已经可以被读取了。
画图如下:

数据从 buffer 到 cache 的过程是定期每秒刷新一次。所以新写入的 Document 最慢 1 秒就可以在 cache 中被搜索到。
而 Document 从 buffer 到 cache 的过程叫做 ?refresh。一般是 1 秒刷新一次,不需要进行额外修改。
当然,如果有修改的需要,可以参考文末的相关资料。这也就是为什么说 Elasticsearch 是准实时的。
使文档立即可见:
PUT /test/_doc/1?refresh
{"test": "test"}
// 或者
PUT /test/_doc/2?refresh=true
{"test": "test"}
Translog 事务日志
此处可以联想 MySQL 的 binlog,ES 中也存在一个 translog 用来失败恢复:
- Document 不断写入到 In-memory buffer,此时也会追加 translog。
- 当 buffer 中的数据每秒 refresh 到 cache 中时,translog 并没有进入到刷新到磁盘,是持续追加的。
- translog 每隔 5s 会 fsync 到磁盘。
- translog 会继续累加变得越来越大,当 translog 大到一定程度或者每隔一段时间,会执行 flush。

flush 操作会分为以下几步执行:
- buffer 被清空。
- 记录 commit point。
- cache 内的 segment 被 fsync 刷新到磁盘。
- translog 被删除。

值得注意的是:
- translog 每 5s 刷新一次磁盘,所以故障重启,可能会丢失 5s 的数据。
- translog 执行 flush 操作,默认 30 分钟一次,或者 translog 太大也会执行。
手动执行 flush:
POST /my-index-000001/_flush
删除和更新
segment 不可改变,所以 docment 并不能从之前的 segment 中移除或更新。
所以每次 commit, 生成 commit point 时,会有一个 .del 文件,里面会列出被删除的 document(逻辑删除)。
而查询时,获取到的结果在返回前会经过 .del 过滤。更新时,也会标记旧的 docment 被删除,写入到 .del 文件,同时会写入一个新的文件。
此时查询会查询到两个版本的数据,但在返回前会被移除掉一个。

segment 合并
每 1s 执行一次 refresh 都会将内存中的数据创建一个 segment。
segment 数目太多会带来较大的麻烦。每一个 segment 都会消耗文件句柄、内存和 cpu 运行周期。
更重要的是,每个搜索请求都必须轮流检查每个 segment ;所以 segment 越多,搜索也就越慢。
在 ES 后台会有一个线程进行 segment 合并:
- refresh 操作会创建新的 segment 并打开以供搜索使用。
- 合并进程选择一小部分大小相似的 segment,并且在后台将它们合并到更大的 segment 中。这并不会中断索引和搜索。
- 当合并结束,老的 segment 被删。
说明合并完成时的活动:
- 新的 segment 被刷新(flush)到了磁盘。 写入一个包含新 segment 且排除旧的和较小的 segment的新 commit point。
- 新的 segment 被打开用来搜索。
- 老的 segment 被删除。
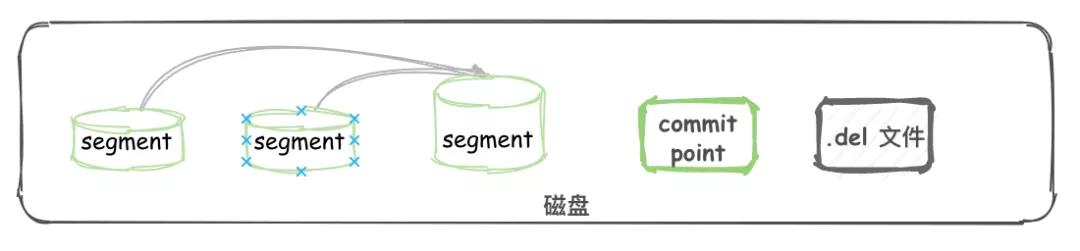
物理删除:在 segment merge 这块,那些被逻辑删除的 document 才会被真正的物理删除。
总结
主要介绍了内部写入和删除的过程,需要了解 refresh、fsync、flush、.del、segment merge 等名词的具体含义。
完整画图如下:

以上就是个人分享的 ES 相关的内容,主要目的是组内技术分享,进行扫盲。不对之处,希望大家留言指正。
相关资料:
- 准实时搜索:
https://www.elastic.co/guide/en/elasticsearch/reference/7.9/near-real-time.html
- Refresh API:
https://www.elastic.co/guide/en/elasticsearch/reference/7.9/indices-refresh.html
- Flush API:
https://www.elastic.co/guide/en/elasticsearch/reference/7.9/indices-flush.html
作者:刘志航
编辑:陶家龙
出处:转载自公众号刘志航(ID:liuzhihangs)

Recommend
About Joyk
Aggregate valuable and interesting links.
Joyk means Joy of geeK