

golang map底层实现
source link: http://yangxikun.com/golang/2019/10/07/golang-map.html?
Go to the source link to view the article. You can view the picture content, updated content and better typesetting reading experience. If the link is broken, please click the button below to view the snapshot at that time.

golang map底层实现
本文学习参考自:map
本文内容基于go1.13.1源码。
在阅读Go map的实现代码时,最好先了解哈希表这种数据结构实现的算法思想,对理解Go map的实现会有帮助,我这里简单总结下:
- map 内部采用的是数组存储 KV,每个数组元素可以认为是一个桶
- key 经过哈希算法后再与 map的数组长度取模映射到某个桶中
- 如果多个 key 映射到了相同的桶,就意味着出现了哈希冲突,解决冲突的方式有两种:开放寻址法和链表法
- 当 KV 过多时,map 就需要扩容(因为数组是固定大小的),扩容的策略是新分配一个更大的数组,然后在插入和删除 key 的时候,将对应的桶的数据搬移到新分配的数组的桶中。这种方式把扩容所需要的 O(n) 时间开销均摊到了 O(1) 的插入和删除操作中。
- map 中用装载因子(map中元素的个数 / map的容量)来表示空闲位置的情况。装载因子越大,说明空闲位置越少,冲突越多。
调试用的go代码map.go:
package main
func main() {
myMap := make(map[string]int, 53)
myMap["key"] = 1
print(myMap["key"])
delete(myMap, "key")
}
- 当 make 的 hint <= 8 时,会直接在栈上分配一个 bucket,一个 bucket 可以存储8对 KV(笔者测试了下将value的类型由int换为[8192]string,也是这样子)
- 当 make 的 hint > 8 && hint <= 52 时,会在堆上分配 bucket,此时不会分配 overflow bucket
- 当 make 的 hint > 52 时,会在堆上分配 bucket 和 overflow bucket
通过对比 hint <= 8 和 hint > 8 生成的"".main汇编代码 go tool compile -N -l -S map.go:
- hint <= 8 直接在
"".main的栈上初始化 hmap 结构体和一个 bucket - hint > 8 会通过调用
runtime.makemap在栈上初始化 hmap 结构体,并在堆上分配bucket
通过dlv debug,可以单步调试代码,并且可以使用si命令,单步执行汇编代码
hmap 结构体如下:
// A header for a Go map.
type hmap struct {
// Note: the format of the hmap is also encoded in cmd/compile/internal/gc/reflect.go.
// Make sure this stays in sync with the compiler's definition.
count int // # live cells == size of map. Must be first (used by len() builtin)
flags uint8
B uint8 // log_2 of # of buckets (can hold up to loadFactor * 2^B items)
noverflow uint16 // approximate number of overflow buckets; see incrnoverflow for details
hash0 uint32 // hash seed
buckets unsafe.Pointer // array of 2^B Buckets. may be nil if count==0.
oldbuckets unsafe.Pointer // previous bucket array of half the size, non-nil only when growing
nevacuate uintptr // progress counter for evacuation (buckets less than this have been evacuated)
extra *mapextra // optional fields
}
// mapextra holds fields that are not present on all maps.
type mapextra struct {
// If both key and elem do not contain pointers and are inline, then we mark bucket
// type as containing no pointers. This avoids scanning such maps.
// However, bmap.overflow is a pointer. In order to keep overflow buckets
// alive, we store pointers to all overflow buckets in hmap.extra.overflow and hmap.extra.oldoverflow.
// overflow and oldoverflow are only used if key and elem do not contain pointers.
// overflow contains overflow buckets for hmap.buckets.
// oldoverflow contains overflow buckets for hmap.oldbuckets.
// The indirection allows to store a pointer to the slice in hiter.
overflow *[]*bmap
oldoverflow *[]*bmap
// nextOverflow holds a pointer to a free overflow bucket.
nextOverflow *bmap
}
func makemap(t *maptype, hint int, h *hmap) *hmap {
// 判断 hint 是否合法
mem, overflow := math.MulUintptr(uintptr(hint), t.bucket.size)
if overflow || mem > maxAlloc {
hint = 0
}
// initialize Hmap
if h == nil {
h = new(hmap)
}
h.hash0 = fastrand()
// Find the size parameter B which will hold the requested # of elements.
// For hint < 0 overLoadFactor returns false since hint < bucketCnt.
// 找到满足 loadFactor * 2^B >= hint 的 B,其中 loadFactor = loadFactorNum / loadFactorDen = 13 / 2 = 6.5
B := uint8(0)
for overLoadFactor(hint, B) {
B++
}
h.B = B
// allocate initial hash table
// if B == 0, the buckets field is allocated lazily later (in mapassign)
// If hint is large zeroing this memory could take a while.
if h.B != 0 {
var nextOverflow *bmap
// makeBucketArray 中会判断 h.B 是否 >= 4,如果是,则会分配 nextOverflow,即overflow bucket
h.buckets, nextOverflow = makeBucketArray(t, h.B, nil)
if nextOverflow != nil {
h.extra = new(mapextra)
h.extra.nextOverflow = nextOverflow
}
}
return h
}
overflow bucket 的作用是用于存储哈希冲突的KV(go map 采用链表法的方式解决哈希冲突))。当 hint = 53 时,分配的 bucket 情况如下:
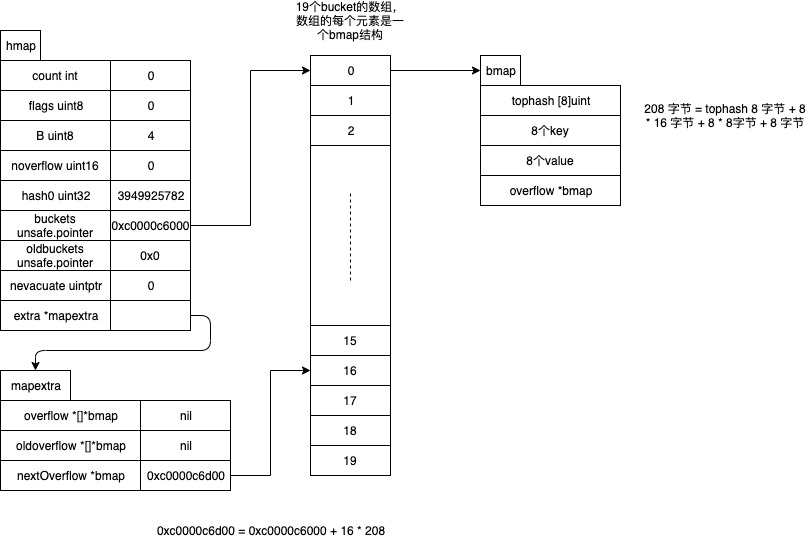
func mapassign_faststr(t *maptype, h *hmap, s string) unsafe.Pointer {
if h == nil {
panic(plainError("assignment to entry in nil map"))
}
if raceenabled {
callerpc := getcallerpc()
racewritepc(unsafe.Pointer(h), callerpc, funcPC(mapassign_faststr))
}
// 不允许并发写
if h.flags&hashWriting != 0 {
throw("concurrent map writes")
}
key := stringStructOf(&s)
// 调用key类型对应的hash算法
hash := t.key.alg.hash(noescape(unsafe.Pointer(&s)), uintptr(h.hash0))
// Set hashWriting after calling alg.hash for consistency with mapassign.
// 异或操作,设置写标记位
h.flags ^= hashWriting
if h.buckets == nil {
h.buckets = newobject(t.bucket) // newarray(t.bucket, 1)
}
again:
// 计算key存储在哪个bucket
bucket := hash & bucketMask(h.B)
if h.growing() {
// 如果map正在扩容,需要确保bucket已经被搬运到hmap.buckets中了
growWork_faststr(t, h, bucket)
}
// 取得对应bucket的内存地址
b := (*bmap)(unsafe.Pointer(uintptr(h.buckets) + bucket*uintptr(t.bucketsize)))
// 取hash的高8位
top := tophash(hash)
// 实际插入的bucket,虽然上面计算出了b,但可能b已经满了,需要插入到b的overflow bucket,或者map需要扩容了
var insertb *bmap
// 插入到bucket中的哪个位置
var inserti uintptr
// bucket中key的地址
var insertk unsafe.Pointer
bucketloop:
for {
// bucketCnt = 8
for i := uintptr(0); i < bucketCnt; i++ {
if b.tophash[i] != top {
if isEmpty(b.tophash[i]) && insertb == nil { // 在b中找到位置i可以存放赋值的KV
insertb = b
inserti = i
// 为何这里不执行break bucketloop?因为有可能K已经存在,需要找到它的位置
}
// 如果余下的位置都是空的,则不需要再往下找了
if b.tophash[i] == emptyRest {
break bucketloop
}
continue
}
// tophash 相同,还需要仔细比较实际的K是否一样
k := (*stringStruct)(add(unsafe.Pointer(b), dataOffset+i*2*sys.PtrSize))
if k.len != key.len {
continue
}
if k.str != key.str && !memequal(k.str, key.str, uintptr(key.len)) {
continue
}
// K已经在map中了
// already have a mapping for key. Update it.
inserti = i
insertb = b
goto done
}
ovf := b.overflow(t)
if ovf == nil {
break
}
b = ovf
}
// K不在map中,需要判断是否进行扩容或者增加overflow bucket
// Did not find mapping for key. Allocate new cell & add entry.
// If we hit the max load factor or we have too many overflow buckets,
// and we're not already in the middle of growing, start growing.
if !h.growing() && (overLoadFactor(h.count+1, h.B) || tooManyOverflowBuckets(h.noverflow, h.B)) {
// 如果map没有扩容,并且负载因子超过阈值或者有太多overflow bucket,则进行扩容
hashGrow(t, h)
// 跳转回again
goto again // Growing the table invalidates everything, so try again
}
// 如果还是没找到空闲的位置存放新的KV,则需要存储到overflow bucket中
if insertb == nil {
// all current buckets are full, allocate a new one.
insertb = h.newoverflow(t, b)
inserti = 0 // not necessary, but avoids needlessly spilling inserti
}
insertb.tophash[inserti&(bucketCnt-1)] = top // mask inserti to avoid bounds checks
// 插入K
insertk = add(unsafe.Pointer(insertb), dataOffset+inserti*2*sys.PtrSize)
// store new key at insert position
*((*stringStruct)(insertk)) = *key
h.count++
done:
// 获取V的地址
elem := add(unsafe.Pointer(insertb), dataOffset+bucketCnt*2*sys.PtrSize+inserti*uintptr(t.elemsize))
if h.flags&hashWriting == 0 {
throw("concurrent map writes")
}
// 清除写标记位
h.flags &^= hashWriting
// 返回V的地址,实际赋值是由编译器生成的汇编代码进行赋值的
return elem
}
当出现 key 冲突时,key 会存储到 overflow bucket 中,以上面的图为例,假设超过8个 key 都 hash 到了索引0的位置:
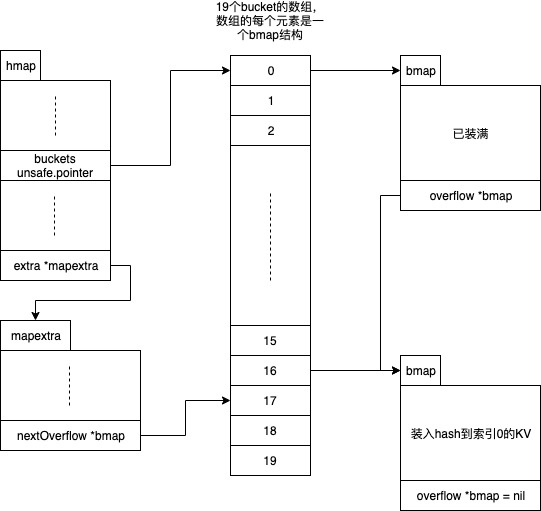
h.mapextra.nextOverflow 指向下一个可用作 overflow bucket 的空闲 bucket。
func mapaccess2_faststr(t *maptype, h *hmap, ky string) (unsafe.Pointer, bool) {
if raceenabled && h != nil {
callerpc := getcallerpc()
racereadpc(unsafe.Pointer(h), callerpc, funcPC(mapaccess2_faststr))
}
// 返回零值,已经false,表示key不存在
if h == nil || h.count == 0 {
return unsafe.Pointer(&zeroVal[0]), false
}
if h.flags&hashWriting != 0 {
throw("concurrent map read and map write")
}
key := stringStructOf(&ky)
if h.B == 0 {
// 只有1个bucket
// One-bucket table.
b := (*bmap)(h.buckets)
if key.len < 32 {
// key比较短,直接进行比较
// short key, doing lots of comparisons is ok
for i, kptr := uintptr(0), b.keys(); i < bucketCnt; i, kptr = i+1, add(kptr, 2*sys.PtrSize) {
k := (*stringStruct)(kptr)
if k.len != key.len || isEmpty(b.tophash[i]) {
// 后面已经没有KV了,不用再找下去了
if b.tophash[i] == emptyRest {
break
}
continue
}
// 找到key
if k.str == key.str || memequal(k.str, key.str, uintptr(key.len)) {
return add(unsafe.Pointer(b), dataOffset+bucketCnt*2*sys.PtrSize+i*uintptr(t.elemsize)), true
}
}
// 未找到,返回零值
return unsafe.Pointer(&zeroVal[0]), false
}
// key 比较长
// long key, try not to do more comparisons than necessary
keymaybe := uintptr(bucketCnt)
for i, kptr := uintptr(0), b.keys(); i < bucketCnt; i, kptr = i+1, add(kptr, 2*sys.PtrSize) {
k := (*stringStruct)(kptr)
if k.len != key.len || isEmpty(b.tophash[i]) {
// 后面已经没有KV了,不用再找下去了
if b.tophash[i] == emptyRest {
break
}
continue
}
// 找到了,内存地址一样
if k.str == key.str {
return add(unsafe.Pointer(b), dataOffset+bucketCnt*2*sys.PtrSize+i*uintptr(t.elemsize)), true
}
// 检查头4字节
// check first 4 bytes
if *((*[4]byte)(key.str)) != *((*[4]byte)(k.str)) {
continue
}
// 检查尾4字节
// check last 4 bytes
if *((*[4]byte)(add(key.str, uintptr(key.len)-4))) != *((*[4]byte)(add(k.str, uintptr(key.len)-4))) {
continue
}
// 走到这里,说明有至少2个key有可能匹配
if keymaybe != bucketCnt {
// Two keys are potential matches. Use hash to distinguish them.
goto dohash
}
keymaybe = i
}
// 有1个key可能匹配
if keymaybe != bucketCnt {
k := (*stringStruct)(add(unsafe.Pointer(b), dataOffset+keymaybe*2*sys.PtrSize))
if memequal(k.str, key.str, uintptr(key.len)) {
return add(unsafe.Pointer(b), dataOffset+bucketCnt*2*sys.PtrSize+keymaybe*uintptr(t.elemsize)), true
}
}
return unsafe.Pointer(&zeroVal[0]), false
}
dohash:
hash := t.key.alg.hash(noescape(unsafe.Pointer(&ky)), uintptr(h.hash0))
m := bucketMask(h.B)
b := (*bmap)(add(h.buckets, (hash&m)*uintptr(t.bucketsize)))
// 判断是否正在扩容
if c := h.oldbuckets; c != nil {
if !h.sameSizeGrow() {
// There used to be half as many buckets; mask down one more power of two.
// 如果不是相同大小的扩容,则需要缩小一倍,因为此时 len(h.buckets) = 2*len(h.oldbuckets)
m >>= 1
}
oldb := (*bmap)(add(c, (hash&m)*uintptr(t.bucketsize)))
// 判断对应的bucket是否已经从h.oldbuckets搬到h.buckets
if !evacuated(oldb) {
// 还没有搬
b = oldb
}
}
top := tophash(hash)
// 在b,以及b的overflow bucket中查找
for ; b != nil; b = b.overflow(t) {
for i, kptr := uintptr(0), b.keys(); i < bucketCnt; i, kptr = i+1, add(kptr, 2*sys.PtrSize) {
k := (*stringStruct)(kptr)
if k.len != key.len || b.tophash[i] != top {
continue
}
if k.str == key.str || memequal(k.str, key.str, uintptr(key.len)) {
return add(unsafe.Pointer(b), dataOffset+bucketCnt*2*sys.PtrSize+i*uintptr(t.elemsize)), true
}
}
}
return unsafe.Pointer(&zeroVal[0]), false
}
func mapdelete_faststr(t *maptype, h *hmap, ky string) {
if raceenabled && h != nil {
callerpc := getcallerpc()
racewritepc(unsafe.Pointer(h), callerpc, funcPC(mapdelete_faststr))
}
if h == nil || h.count == 0 {
return
}
if h.flags&hashWriting != 0 {
throw("concurrent map writes")
}
key := stringStructOf(&ky)
hash := t.key.alg.hash(noescape(unsafe.Pointer(&ky)), uintptr(h.hash0))
// Set hashWriting after calling alg.hash for consistency with mapdelete
h.flags ^= hashWriting
bucket := hash & bucketMask(h.B)
// 如果正在扩容,确保bucket已经从h.oldbuckets搬到h.buckets
if h.growing() {
growWork_faststr(t, h, bucket)
}
b := (*bmap)(add(h.buckets, bucket*uintptr(t.bucketsize)))
bOrig := b
top := tophash(hash)
search:
// 在b,已经b的overflow bucket中查找
for ; b != nil; b = b.overflow(t) {
for i, kptr := uintptr(0), b.keys(); i < bucketCnt; i, kptr = i+1, add(kptr, 2*sys.PtrSize) {
k := (*stringStruct)(kptr)
if k.len != key.len || b.tophash[i] != top {
continue
}
if k.str != key.str && !memequal(k.str, key.str, uintptr(key.len)) {
continue
}
// 找到了
// Clear key's pointer.
k.str = nil
e := add(unsafe.Pointer(b), dataOffset+bucketCnt*2*sys.PtrSize+i*uintptr(t.elemsize))
// 与GC相关
if t.elem.ptrdata != 0 {
memclrHasPointers(e, t.elem.size)
} else {
memclrNoHeapPointers(e, t.elem.size)
}
// 标记当前单元是空闲的
b.tophash[i] = emptyOne
// If the bucket now ends in a bunch of emptyOne states,
// change those to emptyRest states.
// 判断>i的单元是否都是空闲的
if i == bucketCnt-1 {
if b.overflow(t) != nil && b.overflow(t).tophash[0] != emptyRest {
goto notLast
}
} else {
if b.tophash[i+1] != emptyRest {
goto notLast
}
}
// >i的单元都是空闲的,那么将当前单元,以及<i的emptyOne单元都标记为emptyRest
// emptyRest的作用就是在查找的时候,遇到emptyRest就不用再往下找了,加速查找的过程
for {
b.tophash[i] = emptyRest
if i == 0 {
if b == bOrig {
break // beginning of initial bucket, we're done.
}
// Find previous bucket, continue at its last entry.
c := b
for b = bOrig; b.overflow(t) != c; b = b.overflow(t) {
}
i = bucketCnt - 1
} else {
i--
}
if b.tophash[i] != emptyOne {
break
}
}
notLast:
h.count--
break search
}
}
if h.flags&hashWriting == 0 {
throw("concurrent map writes")
}
h.flags &^= hashWriting
}
下图演示了在一个有一个 overflow bucket 的 bucket 中删除 KV,bmap.tophash 标记位变化的过程:

两种情况下会进行扩容:
overLoadFactor(h.count+1, h.B)装载因子过大时,扩容一倍tooManyOverflowBuckets(h.noverflow, h.B))当使用的 overflow bucket 过多时,实际上没有扩容,重新分配了一样大的空间,主要是为了回收空闲的 overflow bucket
启动扩容:
func hashGrow(t *maptype, h *hmap) {
// If we've hit the load factor, get bigger.
// Otherwise, there are too many overflow buckets,
// so keep the same number of buckets and "grow" laterally.
bigger := uint8(1)
if !overLoadFactor(h.count+1, h.B) {
// 如果装载因子没有超过阈值,那么按相同大小的空间“扩容”
bigger = 0
h.flags |= sameSizeGrow
}
oldbuckets := h.buckets
// 分配新空间
newbuckets, nextOverflow := makeBucketArray(t, h.B+bigger, nil)
// 清除 iterator,oldIterator 的标记位
flags := h.flags &^ (iterator | oldIterator)
if h.flags&iterator != 0 {
flags |= oldIterator
}
// commit the grow (atomic wrt gc)
h.B += bigger
h.flags = flags
h.oldbuckets = oldbuckets
h.buckets = newbuckets
h.nevacuate = 0 // 统计搬了多少个bucket
h.noverflow = 0
if h.extra != nil && h.extra.overflow != nil {
// Promote current overflow buckets to the old generation.
if h.extra.oldoverflow != nil {
throw("oldoverflow is not nil")
}
h.extra.oldoverflow = h.extra.overflow
h.extra.overflow = nil
}
if nextOverflow != nil {
if h.extra == nil {
h.extra = new(mapextra)
}
h.extra.nextOverflow = nextOverflow
}
// the actual copying of the hash table data is done incrementally
// by growWork() and evacuate().
}
实际的搬迁bucket:
// 插入和删除的时候,发现正在扩容的话,会调用该方法
func growWork_faststr(t *maptype, h *hmap, bucket uintptr) {
// make sure we evacuate the oldbucket corresponding
// to the bucket we're about to use
evacuate_faststr(t, h, bucket&h.oldbucketmask())
// evacuate one more oldbucket to make progress on growing
if h.growing() {
evacuate_faststr(t, h, h.nevacuate)
}
}
func evacuate_faststr(t *maptype, h *hmap, oldbucket uintptr) {
b := (*bmap)(add(h.oldbuckets, oldbucket*uintptr(t.bucketsize)))
newbit := h.noldbuckets()
// 判断该bucket是否已经搬迁了
if !evacuated(b) {
// TODO: reuse overflow buckets instead of using new ones, if there
// is no iterator using the old buckets. (If !oldIterator.)
// xy contains the x and y (low and high) evacuation destinations.
// xy 指向新空间的高低区间的起点
var xy [2]evacDst
x := &xy[0]
x.b = (*bmap)(add(h.buckets, oldbucket*uintptr(t.bucketsize)))
x.k = add(unsafe.Pointer(x.b), dataOffset)
x.e = add(x.k, bucketCnt*2*sys.PtrSize)
// 如果是扩容一倍,才会用到 y
if !h.sameSizeGrow() {
// Only calculate y pointers if we're growing bigger.
// Otherwise GC can see bad pointers.
y := &xy[1]
y.b = (*bmap)(add(h.buckets, (oldbucket+newbit)*uintptr(t.bucketsize)))
y.k = add(unsafe.Pointer(y.b), dataOffset)
y.e = add(y.k, bucketCnt*2*sys.PtrSize)
}
// 将当前 bucket 以及其 overflow bucket 进行搬迁
for ; b != nil; b = b.overflow(t) {
k := add(unsafe.Pointer(b), dataOffset)
e := add(k, bucketCnt*2*sys.PtrSize)
for i := 0; i < bucketCnt; i, k, e = i+1, add(k, 2*sys.PtrSize), add(e, uintptr(t.elemsize)) {
top := b.tophash[i]
// 这里是不是可以判断到 emptyRest 就停止循环了?
if isEmpty(top) {
b.tophash[i] = evacuatedEmpty
continue
}
if top < minTopHash {
throw("bad map state")
}
var useY uint8
if !h.sameSizeGrow() {
// Compute hash to make our evacuation decision (whether we need
// to send this key/elem to bucket x or bucket y).
hash := t.key.alg.hash(k, uintptr(h.hash0))
if hash&newbit != 0 { // 新的位置位于高区间
useY = 1
}
}
b.tophash[i] = evacuatedX + useY // evacuatedX + 1 == evacuatedY, enforced in makemap
dst := &xy[useY] // evacuation destination
if dst.i == bucketCnt { // 是否要放到 overflow bucket 中
dst.b = h.newoverflow(t, dst.b)
dst.i = 0
dst.k = add(unsafe.Pointer(dst.b), dataOffset)
dst.e = add(dst.k, bucketCnt*2*sys.PtrSize)
}
dst.b.tophash[dst.i&(bucketCnt-1)] = top // mask dst.i as an optimization, to avoid a bounds check
// Copy key.
*(*string)(dst.k) = *(*string)(k)
typedmemmove(t.elem, dst.e, e)
dst.i++
// These updates might push these pointers past the end of the
// key or elem arrays. That's ok, as we have the overflow pointer
// at the end of the bucket to protect against pointing past the
// end of the bucket.
dst.k = add(dst.k, 2*sys.PtrSize)
dst.e = add(dst.e, uintptr(t.elemsize))
}
}
// Unlink the overflow buckets & clear key/elem to help GC.
if h.flags&oldIterator == 0 && t.bucket.ptrdata != 0 {
b := add(h.oldbuckets, oldbucket*uintptr(t.bucketsize))
// Preserve b.tophash because the evacuation
// state is maintained there.
ptr := add(b, dataOffset)
n := uintptr(t.bucketsize) - dataOffset
memclrHasPointers(ptr, n)
}
}
// 统计搬迁的进度,如果数据都搬迁完了,则结束扩容
if oldbucket == h.nevacuate {
advanceEvacuationMark(h, t, newbit)
}
}
关于 map 元素无法取址问题
如果我们尝试对 map 的元素取址,会遇到 cannot take the address of m["a"] 错误。
因为 map 在扩容后m["a"]的地址是会发生改变的。
关于 map 的类型 value 是 struct 或数组类型无法直接修改 value 的某个字段/元素的问题
cannot assign to struct field m["a"].i in map 和 cannot assign to m["a"][0] 错误是在编译阶段就报错的。
如果 key "a" 存在的话,从实现上来讲,是可以做到对 m["a"].i 或 m["a"][0] 进行赋值的。
如果 key "a" 不存在的话,就需要考虑是否抛出 runtime error(返回零值使赋值能成功不太合适,因为需要把零值的key "a" 插入到 map 中,但又感觉又不符合代码的语意)。
关于这个问题在 Go 的代码仓库有个 issue:proposal: spec: cannot assign to a field of a map element directly: m[“foo”].f = x #3117
如果 key 的类型是 struct 或 指针
对于不同类型的 key 会调用相应的runtime.mapassign*和runtime.mapaccess*函数,计算 key 的哈希算法也不一样。
比如type Key struct{a int}会使用与 key 类型为 int 相同的runtime.mapassign_fast64和runtime.mapaccess1_fast64函数,type Key struct{a string}会使用与 key 类型为 string 相同的runtime.mapassign_faststr和runtime.mapaccess1_faststr函数。但是type Key struct{a int; b string}则使用的是runtime.mapassign和runtime.mapaccess1。
- map 并发写的检测是通过判断 h.flags 是否有标记位 hashWriting 这种方式是否不够严谨?
- 相同大小容量的“扩容”,我判断出来的是为了解决过多空闲 overflow bucket 的问题,如果是真的要解决这个问题,是否可以在删除key的时候做回收?
Recommend
About Joyk
Aggregate valuable and interesting links.
Joyk means Joy of geeK