

Java集合系列(四):HashMap、Hashtable、LinkedHashMap、TreeMap的使用方法及区别 -...
source link: https://www.cnblogs.com/zwwhnly/p/11304627.html
Go to the source link to view the article. You can view the picture content, updated content and better typesetting reading experience. If the link is broken, please click the button below to view the snapshot at that time.

本篇博客主要讲解Map接口的4个实现类HashMap、Hashtable、LinkedHashMap、TreeMap的使用方法以及四者之间的区别。
注意:本文中代码使用的JDK版本为1.8.0_191
值得注意的是,Map接口是独立的接口,并没有继承Collection接口(这里是重点,面试常问):
public interface Map<K,V> {
......
}
1. HashMap使用
HashMap是Map接口最常用的实现类,存储Key Value键值对,HashMap不保证元素的顺序但保证Key必须唯一。
HashMap类的代码声明如下所示:
public class HashMap<K,V> extends AbstractMap<K,V>
implements Map<K,V>, Cloneable, Serializable {
......
}
1.1 添加元素
使用HashMap添加元素有以下3个方法:
- putIfAbsent
- putAll
首先看下put()方法的使用方法:
HashMap<String, String> platformMap = new HashMap<>();
// 添加元素
System.out.println(platformMap.put("cnblogs.com", "博客园"));
System.out.println(platformMap.put("juejin.im", "掘金"));
System.out.println(platformMap.put("map.weixin.qq.com", "微信公众号"));
System.out.println(platformMap.put("zwwhnly.com", "个人博客"));
// 添加重复的Key,没有添加成功,但是会更新Key对应的Value值
// 不过代码不会报错,而是返回已经存在Key对应的Value
System.out.println(platformMap.put("zwwhnly.com", "个人博客"));
以上代码运行的输出结果是:
调试代码也会发现platformMap只有4个元素,而且元素的顺序和添加的顺序不同:
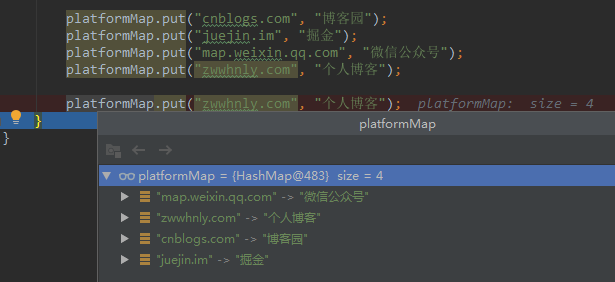
值得注意的是最后一行代码platformMap.put("zwwhnly.com", "个人博客")的返回值是“个人博客”,即之前已存在的Key:zwwhnly.com,对应的Value值。
简单修改下这句代码为:
System.out.println(platformMap.put("zwwhnly.com", "个人博客2"));
再次运行代码,发现输出结果没变,platformMap也还是4个元素,但是platformMap元素的内容变了:
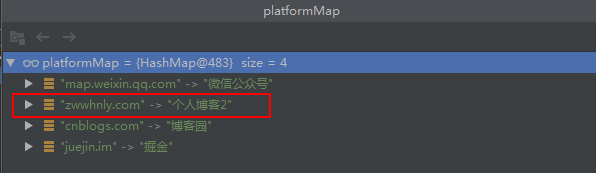
如果Key存在时,不希望Value值被覆盖,可以将代码修改为:
System.out.println(platformMap.putIfAbsent("zwwhnly.com", "个人博客2"));
另外,HashMap还提供了一个putAll()方法来批量添加元素,使用方法如下所示:
HashMap<String, String> platformMap = new HashMap<>();
HashMap<String, String> majorPlatfromMap = new HashMap<>();
// 添加元素
majorPlatfromMap.put("cnblogs.com", "博客园");
majorPlatfromMap.put("juejin.im", "掘金");
HashMap<String, String> otherPlatformMap = new HashMap<>();
otherPlatformMap.put("map.weixin.qq.com", "微信公众号");
otherPlatformMap.put("zwwhnly.com", "个人博客");
otherPlatformMap.put("cnblogs.com", "博客园2");
platformMap.putAll(majorPlatfromMap);
platformMap.putAll(otherPlatformMap);
值得注意的是,由于majorPlatfromMap与otherPlatformMap存在相同的key:cnblogs.com,最终platformMap中Key为”cnblogs.com“的Value值为:“博客园2“,如下图所示:
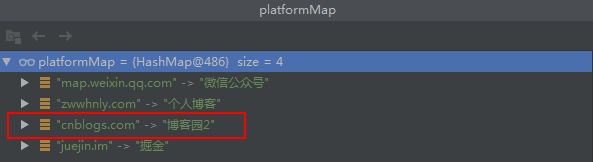
1.2 获取元素
使用HashMap获取元素有以下2个方法:
- get()
- getOrDefault()
首先看下get()方法的使用方法:
System.out.println(platformMap.get("cnblogs.com"));
System.out.println(platformMap.get("csdn.com"));
输出结果:
当key不存在时,如果需要设置默认值,可以使用getOrDefault():
System.out.println(platformMap.getOrDefault("csdn.com", "CSDN"));
上面这句代码的输出结果为:CSDN。
1.3 获取集合元素个数
获取HashMap元素个数的使用方法如下所示:
System.out.println("platformMap的元素个数为:" + platformMap.size());
1.4 删除元素
使用HashMap删除元素有以下2个重载:
public V remove(Object key) {
Node<K,V> e;
return (e = removeNode(hash(key), key, null, false, true)) == null ?
null : e.value;
}
@Override
public boolean remove(Object key, Object value) {
return removeNode(hash(key), key, value, true, true) != null;
}
使用方法如下所示:
System.out.println(platformMap.remove("zwwhnly.com"));
System.out.println(platformMap.remove("zwwhnly.com"));
System.out.println(platformMap.remove("map.weixin.qq.com", "微信公众号"));
System.out.println(platformMap.remove("juejin.im", "博客园"));
上面代码的输出结果为:
false
1.5 修改元素
使用HashMap修改元素有以下2个重载:
@Override
public boolean replace(K key, V oldValue, V newValue) {
Node<K,V> e; V v;
if ((e = getNode(hash(key), key)) != null &&
((v = e.value) == oldValue || (v != null && v.equals(oldValue)))) {
e.value = newValue;
afterNodeAccess(e);
return true;
}
return false;
}
@Override
public V replace(K key, V value) {
Node<K,V> e;
if ((e = getNode(hash(key), key)) != null) {
V oldValue = e.value;
e.value = value;
afterNodeAccess(e);
return oldValue;
}
return null;
}
使用方法如下所示:
System.out.println(platformMap.replace("cnblogs.com", "博客园:https://www.cnblogs.com/zwwhnly/"));
System.out.println(platformMap.replace("juejin.im", "掘金", "掘金:https://juejin.im/user/5c7ce730f265da2dca388167"));
上面代码的输出结果为:
1.6 判断集合是否为空
判断HashMap是否为空的使用方法如下所示:
System.out.println("isEmpty:" + platformMap.isEmpty());
1.7 遍历元素(面试常问)
遍历HashMap的元素主要有以下4种方式:
- 使用keySet获取所有的Key,然后遍历
- 使用Map.entrySet获取所有的元素,然后使用iterator遍历
- 使用Map.entrySet获取所有的元素,然后使用foreach循环遍历
- 直接使用values获取到所有的值,该种方式无法遍历Key
其中2和3的方式,使用的是Set集合的2种遍历方式,因为platformMap.entrySet()返回的类型是一个Set集合,里面的元素类型是Map.Entry<K,V>:
public Set<Map.Entry<K,V>> entrySet() {
Set<Map.Entry<K,V>> es;
return (es = entrySet) == null ? (entrySet = new EntrySet()) : es;
}
使用方法如下所示:
System.out.println("方式1:使用keySet遍历");
for (String key : platformMap.keySet()) {
System.out.println("Key:" + key + ",Value:" + platformMap.get(key));
}
System.out.println();
System.out.println("方式2:通过Map.entrySet使用iterator遍历");
Iterator<Map.Entry<String, String>> iterator = platformMap.entrySet().iterator();
while (iterator.hasNext()) {
Map.Entry<String, String> entry = iterator.next();
System.out.println("Key:" + entry.getKey() + ",Value:" + entry.getValue());
}
System.out.println();
System.out.println("方式3:通过Map.entrySet使用iterator遍历");
for (Map.Entry<String, String> entry : platformMap.entrySet()) {
System.out.println("Key:" + entry.getKey() + ",Value:" + entry.getValue());
}
System.out.println();
System.out.println("方式4:使用values遍历,使用这种方式无法遍历Key");
for (String value : platformMap.values()) {
System.out.println(value);
}
1.8 清空集合
清空HashMap中所有元素的使用方法如下所示:
platformMap.clear();
1.9 完整示例代码
上面讲解的几点,完整代码如下所示:
package collection;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Iterator;
import java.util.Map;
public class MapTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
HashMap<String, String> platformMap = new HashMap<>();
HashMap<String, String> majorPlatfromMap = new HashMap<>();
// 添加元素
majorPlatfromMap.put("cnblogs.com", "博客园");
majorPlatfromMap.put("juejin.im", "掘金");
HashMap<String, String> otherPlatformMap = new HashMap<>();
otherPlatformMap.put("map.weixin.qq.com", "微信公众号");
otherPlatformMap.put("zwwhnly.com", "个人博客");
platformMap.putAll(majorPlatfromMap);
platformMap.putAll(otherPlatformMap);
System.out.println(platformMap.get("cnblogs.com"));
System.out.println(platformMap.get("csdn.com"));
System.out.println(platformMap.getOrDefault("csdn.com", "CSDN"));
System.out.println("platformMap的元素个数为:" + platformMap.size());
System.out.println(platformMap.remove("zwwhnly.com"));
System.out.println(platformMap.remove("zwwhnly.com"));
System.out.println(platformMap.remove("map.weixin.qq.com", "微信公众号"));
System.out.println(platformMap.remove("juejin.im", "博客园"));
System.out.println(platformMap.replace("cnblogs.com", "博客园:https://www.cnblogs.com/zwwhnly/"));
System.out.println(platformMap.replace("juejin.im", "掘金", "掘金:https://juejin.im/user/5c7ce730f265da2dca388167"));
System.out.println("isEmpty:" + platformMap.isEmpty());
System.out.println("方式1:使用keySet遍历");
for (String key : platformMap.keySet()) {
System.out.println("Key:" + key + ",Value:" + platformMap.get(key));
}
System.out.println();
System.out.println("方式2:通过Map.entrySet使用iterator遍历");
Iterator<Map.Entry<String, String>> iterator = platformMap.entrySet().iterator();
while (iterator.hasNext()) {
Map.Entry<String, String> entry = iterator.next();
System.out.println("Key:" + entry.getKey() + ",Value:" + entry.getValue());
}
System.out.println();
System.out.println("方式3:通过Map.entrySet使用iterator遍历");
for (Map.Entry<String, String> entry : platformMap.entrySet()) {
System.out.println("Key:" + entry.getKey() + ",Value:" + entry.getValue());
}
System.out.println();
System.out.println("方式4:使用values遍历,使用这种方式无法遍历Key");
for (String value : platformMap.values()) {
System.out.println(value);
}
platformMap.clear();
System.out.println("isEmpty:" + platformMap.isEmpty());
}
}
输出结果为:
platformMap的元素个数为:4
false
isEmpty:false
方式1:使用keySet遍历
Key:cnblogs.com,Value:博客园:https://www.cnblogs.com/zwwhnly/
Key:juejin.im,Value:掘金:https://juejin.im/user/5c7ce730f265da2dca388167
方式2:通过Map.entrySet使用iterator遍历
Key:cnblogs.com,Value:博客园:https://www.cnblogs.com/zwwhnly/
Key:juejin.im,Value:掘金:https://juejin.im/user/5c7ce730f265da2dca388167
方式3:通过Map.entrySet使用iterator遍历
Key:cnblogs.com,Value:博客园:https://www.cnblogs.com/zwwhnly/
Key:juejin.im,Value:掘金:https://juejin.im/user/5c7ce730f265da2dca388167
方式4:使用values遍历,使用这种方式无法遍历Key
博客园:https://www.cnblogs.com/zwwhnly/
掘金:https://juejin.im/user/5c7ce730f265da2dca388167
isEmpty:true
2. Hashtable使用
Hashtable也是Map接口的实现类,值得注意的是,它的方法都是同步的,即是线程安全的。
public synchronized int size() {
return count;
}
public synchronized boolean isEmpty() {
return count == 0;
}
HashTable类的代码声明如下所示:
public class Hashtable<K,V>
extends Dictionary<K,V>
implements Map<K,V>, Cloneable, java.io.Serializable {
{
......
}
从以上代码也能看出,Hashtable的基类是Dictionary,而HashMap的基类是AbstractMap(这里是重点,面试常问)。
HashTable类的使用方法和HashMap基本一样,只需修改下声明处的代码即可:
Hashtable<String, String> platformMap = new Hashtable<>();
Hashtable<String, String> majorPlatfromMap = new Hashtable<>();
Hashtable<String, String> otherPlatformMap = new Hashtable<>();
3. LinkedHashMap使用
LinkedHashMap也是Map接口的实现类,相比于HashMap,它使用到了链表,因此可以保证元素的插入顺序,即FIFO(First Input First Output 先进先出)。
LinkedHashMap类的代码声明如下所示:
public class LinkedHashMap<K,V>
extends HashMap<K,V>
implements Map<K,V>
{
......
}
从以上代码也能看出,LinkedHashMap类继承了HashMap类。
LinkedHashMap类的使用方法和HashMap基本一样,只需修改下声明处的代码即可:
LinkedHashMap<String, String> platformMap = new LinkedHashMap<>();
LinkedHashMap<String, String> majorPlatfromMap = new LinkedHashMap<>();
LinkedHashMap<String, String> otherPlatformMap = new LinkedHashMap<>();
4. TreeMap使用
TreeMap也是Map接口的实现类,值得注意的是,TreeMap中的元素是有序的,默认的排序规则是按照key的字典顺序升序排序。
TreeMap类的代码声明如下所示:
public class TreeMap<K,V>
extends AbstractMap<K,V>
implements NavigableMap<K,V>, Cloneable, java.io.Serializable
{
......
}
TreeMap类的使用方法和HashMap基本一样,只需修改下声明处的代码即可:
TreeMap<String, String> platformMap = new TreeMap<>();
TreeMap<String, String> majorPlatfromMap = new TreeMap<>();
TreeMap<String, String> otherPlatformMap = new TreeMap<>();
5. HashMap、Hashtable、LinkedHashMap、TreeMap的区别(面试常问)
5.1 相同点
1)HashMap、Hashtable、LinkedHashMap、TreeMap都实现了Map接口
2)四者都保证了Key的唯一性,即不允许Key重复
5.2 不同点
5.2.1 排序
HashMap不保证元素的顺序
Hashtable不保证元素的顺序
LinkHashMap保证FIFO即按插入顺序排序
TreeMap保证元素的顺序,支持自定义排序规则
空口无凭,上代码看效果:
HashMap<String, String> hashMap = new HashMap<>();
Hashtable<String, String> hashtable = new Hashtable<>();
LinkedHashMap<String, String> linkedHashMap = new LinkedHashMap<>();
TreeMap<String, String> treeMap = new TreeMap<>();
String[] letterArray = new String[]{"B", "A", "D", "C", "E"};
for (String letter : letterArray) {
hashMap.put(letter, letter);
hashtable.put(letter, letter);
linkedHashMap.put(letter, letter);
treeMap.put(letter, letter);
}
System.out.println("HashMap(我不保证顺序):" + hashMap);
System.out.println("Hashtable(我不保证顺序):" + hashtable);
System.out.println("LinkedHashMap(我保证元素插入时的顺序):" + linkedHashMap);
System.out.println("TreeMap(我按排序规则保证元素的顺序):" + treeMap);
上面代码的输出结果为:
HashMap(我不保证顺序):{A=A, B=B, C=C, D=D, E=E}
Hashtable(我不保证顺序):{A=A, E=E, D=D, C=C, B=B}
LinkedHashMap(我保证元素插入时的顺序):{B=B, A=A, D=D, C=C, E=E}
TreeMap(我按排序规则保证元素的顺序):{A=A, B=B, C=C, D=D, E=E}
5.2.2 null值
HashMap,LinkedHashMap允许添加null值(Key和Value都允许),所以以下代码是合法的:
HashMap<String, String> hashMap = new HashMap<>();
LinkedHashMap<String, String> linkedHashMap = new LinkedHashMap<>();
hashMap.put(null, null);
linkedHashMap.put(null, null);
TreeMap不允许Key有null值,但允许Value有null值,所以以下代码是合法的:
TreeMap<String, String> treeMap = new TreeMap<>();
treeMap.put("cnblogs.com", null);
但是treeMap.put(null, null);会引发java.lang.NullPointerException异常:
Hashtable不允许添加null值(Key和Value都不允许),添加null值时会抛出java.lang.NullPointerException异常。
Hashtable<String, String> hashtable = new Hashtable<>();
hashtable.put("cnblogs.com", null);
hashtable.put(null, null);
运行上面的代码,报错信息如下所示:
5.2.3 线程安全
HashMap、LinkedHashMap、TreeMap不是线程安全的。
Hashtable是线程安全的,这是它的优点,同时也导致在理论情况下,Hashtable的效率没有HashMap高。
所以如果对线程安全没有要求,建议使用HashMap。
5.2.4 继承
Hashtable的父类是Dictionary。
HashMap的父类是AbstractMap。
LinkedHashMap的父类是HashMap,HashMap的父类是AbstractMap,所以LinkedHashMap也继承了AbstractMap。
TreeMap的父类是AbstractMap。
6. TreeMap的两种排序方式(面试常问)
TreeMap默认的排序规则是按照key的字典顺序升序排序。
先来看下TreeMap存储String类型的例子:
TreeMap<String, String> treeMap = new TreeMap<>();
String[] letterArray = new String[]{"B", "A", "D", "C", "E"};
for (String letter : letterArray) {
treeMap.put(letter, letter);
}
for (String key : treeMap.keySet()) {
System.out.println("key:" + key + ",Value:" + treeMap.get(key));
}
输出结果:
key:A,Value:A
key:B,Value:B
key:C,Value:C
key:D,Value:D
key:E,Value:E
那如果TreeMap中放入的元素类型是我们自定义的引用类型,它的排序规则是什么样的呢?
带着这个疑问,我们新建个Student类如下:
package collection;
public class Student {
private String name;
private int age;
public Student(String name, int age) {
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public int getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(int age) {
this.age = age;
}
}
然后添加如下验证代码:
TreeMap<Student, Student> studentTreeMap = new TreeMap<>();
Student student1 = new Student("zhangsan", 20);
Student student2 = new Student("lisi", 22);
Student student3 = new Student("wangwu", 24);
Student student4 = new Student("zhaoliu", 26);
Student student5 = new Student("zhangsan", 22);
studentTreeMap.put(student1, student1);
studentTreeMap.put(student2, student2);
studentTreeMap.put(student3, student3);
studentTreeMap.put(student4, student4);
studentTreeMap.put(student5, student5);
for (Student student : studentTreeMap.keySet()) {
System.out.println("name:" + student.getName() + ",age:" + student.getAge());
}
满心欢喜的运行代码想看下效果,结果却发现报如下错误:
为什么会这样呢?
这是因为我们并没有给Student类定义任何排序规则,TreeMap说我也不知道咋排序,还是甩锅抛出异常吧,哈哈。
怎么解决呢?有以下两种方式:
- 比较器排序
6.1 自然排序
自然排序的实现方式是让Student类实现接口Comparable,并重写该接口的方法compareTo,该方法会定义排序规则。
package collection;
public class Student implements Comparable<Student> {
// 省略其它代码
@Override
public int compareTo(Student o) {
return 0;
}
}
使用IDEA默认生成的compareTo()方法如上所示。
这个方法会在执行add()方法添加元素时执行,以便确定元素的位置。
如果返回0,代表两个元素相同,只会保留第一个元素
如果返回值大于0,代表这个元素要排在参数中指定元素o的后面
如果返回值小于0,代表这个元素要排在参数中指定元素o的前面
因此如果对compareTo()方法不做任何修改,直接运行之前的验证代码,会发现集合中只有1个元素:
name:zhangsan,age:20
然后修改下compareTo()方法的逻辑为:
@Override
public int compareTo(Student o) {
// 排序规则描述如下
// 按照姓名的长度排序,长度短的排在前面,长度长的排在后面
// 如果姓名的长度相同,按字典顺序比较String
// 如果姓名完全相同,按年龄排序,年龄小的排在前面,年龄大的排在后面
int orderByNameLength = this.name.length() - o.name.length();
int orderByName = orderByNameLength == 0 ? this.name.compareTo(o.name) : orderByNameLength;
int orderByAge = orderByName == 0 ? this.age - o.age : orderByName;
return orderByAge;
}
再次运行之前的验证代码,输出结果如下所示:
name:lisi,age:22
name:wangwu,age:24
name:zhaoliu,age:26
name:zhangsan,age:20
name:zhangsan,age:22
6.2 比较器排序
比较器排序的实现方式是新建一个比较器类,继承接口Comparator,重写接口中的Compare()方法。
注意:使用此种方式Student类不需要实现接口Comparable,更不需要重写该接口的方法compareTo。
package collection;
import java.util.Comparator;
public class StudentComparator implements Comparator<Student> {
@Override
public int compare(Student o1, Student o2) {
// 排序规则描述如下
// 按照姓名的长度排序,长度短的排在前面,长度长的排在后面
// 如果姓名的长度相同,按字典顺序比较String
// 如果姓名完全相同,按年龄排序,年龄小的排在前面,年龄大的排在后面
int orderByNameLength = o1.getName().length() - o2.getName().length();
int orderByName = orderByNameLength == 0 ? o1.getName().compareTo(o2.getName()) : orderByNameLength;
int orderByAge = orderByName == 0 ? o1.getAge() - o2.getAge() : orderByName;
return orderByAge;
}
}
然后修改下验证代码中声明studentTreeSet的代码即可:
TreeMap<Student, Student> studentTreeMap = new TreeMap<>(new StudentComparator());
输出结果和使用自然排序的输出结果完全一样。
7. 源码及参考
Java集合中List,Set以及Map等集合体系详解(史上最全)
原创不易,如果觉得文章能学到东西的话,欢迎点个赞、评个论、关个注,这是我坚持写作的最大动力。
如果有兴趣,欢迎添加我的微信:zwwhnly,等你来聊技术、职场、工作等话题(PS:我是一名奋斗在上海的程序员)。
Recommend
-
 64
64
首先请先阅读这两个的源码。一、hashMap、hashTable都是Map接口的实现类,但是hashMap类继承自抽象类abstractMap类,hashTable继承自Dictionary类,该类在jdk中这样描述:可见该类已经过时。二、hashTable里面的方法都是...
-
 24
24
技术岛公众号 最近同事发现有接口签名验证通不过,查了许久,发现,两边的验签规则不一样。最大的差异在于时间戳是否参与参数的排序。使用较多的版本...
-
 44
44
Hashtable、HashMap、TreeMap都是比较常见的一些Map实现,它们都是 key-value 键值对的形式存储和操作数据的容器类,同时他们的元素中不能有重复的key,一个key也只能映射一个value值。 下面我从不同的维度来分别...
-
 13
13
【Java】HashMap 和 HashTable 的区别到底是什么? 第一、继承不同第一个不同主要是历史原因。Hashtable是基于陈旧的Dictionary类的,HashMap是Java 1.2引进的Map接口的一个实现。 ...
-
 8
8
LruCache 先说结论吧: 由此可见LruCache中维护了一个集合LinkedHashMap,该LinkedHashMap是以访问顺序排序的。当调用put()方法时,就会在结合中添加元素,并调用trimToSize()判断缓存是否已满,如果满了就用LinkedHashMap的迭代器删除队尾元素...
-
 8
8
🔎这里是JAVA成仙路,关注我学习JAVA不迷路 👍如果对你有帮助,给博主一个免费的点赞以示鼓励 欢迎各位🔎点赞👍评论收藏⭐️ 前言:本章具体介绍了HashMap、TreeMap两种集合的基本使用方法和区别,图解穿插代码实现。JAVA成...
-
 8
8
2 年前发表9 个月前更新Code2 分钟读完 (大约351个字)Java HashMap 与 Hashtable 的区别1.HashMap
-
 3
3
Please wait... We are checking your browser... yoursite.com What can I do to prevent this in the f...
-
 8
8
Social Follow us on social media for more news, content and background stories from our authors, editors and events. Share your personal experience with us.
-
 9
9
HashMap vs Hashtable – a comparison of two data structures who share similar functionality but have majorly distinctive features and implementation. Think of HashMap and Hashtable as companions that shine in their own specific use cases instead...
About Joyk
Aggregate valuable and interesting links.
Joyk means Joy of geeK