GitHub - simplesurance/baur: baur manages builds and artifacts in mono repositor...
source link: https://github.com/simplesurance/baur
Go to the source link to view the article. You can view the picture content, updated content and better typesetting reading experience. If the link is broken, please click the button below to view the snapshot at that time.

README.md
baur 
baur is a build management tool for Git based monolithic repositories.
Developers specify in a TOML configuration file:
- what the inputs for the build process are,
- which command must be run to build the application,
- which outputs are generated by the build,
- and where they should be uploaded to.
baur detects which applications need to be build by calculating a digest of the application's build inputs and comparing them with digests from previous builds. If a build with the same build input digest was done in the past, a build is not necessary. If the build input digest differs from the stored ones, baur runs a user-specified command to build the application.
Content
Example Repository
You can find an example monorepository that uses baur at: https://github.com/simplesurance/baur-example. Please follow the quickstart guide at https://github.com/simplesurance/baur-example#quickstart for the example repository.
Quickstart
This chapter describes a quick way to setup baur for experimenting with it without using the Example Repository.
For setting it up in a production environment see the chapter Production Setup.
Install baur by either:
- downloading a release archive from
Release Page and copying
baurinto your$PATHor - install the latest development version by running
go get -u github.com/simplesurance/baur/...
baur uses a PostgreSQL database to store information about builds, the quickest way to setup a PostgreSQL for local testing is with docker:
docker run -p 5432:5432 -e POSTGRES_DB=baur postgres:latest
Afterwards your are ready to create your baur repository configuration. Run in the root directory of your Git repository:
baur init repo
and then follow the printed steps to create the database and application config files. Some commands to start with are:
- List applications in the repository with their build status:
baur ls apps - Build all applications with pending builds, upload their artifacts and
records the results:
baur build - List recorded builds:
baur ls builds all - Show information about an application called "currency-service":
baur show currency-service - Show inputs with their digests of an application called "shop-api":
baur ls inputs --digests shop-api
To get more information about a command pass the --help parameter to baur.
Key Features:
-
Detecting Changed Applications The inputs of applications are specified in the
.app.tomlconfig file for each application. baur calculates a SHA384 digest for all inputs and stores the digest in the database when an application was build and its artifacts uploaded (baur build). The digest is used to detect if a previous build for the same input files exists. If a build exist, the application does not need to be rebuild otherwise a build is done. This allows to selectively run applications through a CI pipeline that changed in a given commit. This approach also prevents that applications are unnecessarily rebuild if commits are reverted in the Git repository. -
Artifact Upload to S3 and Docker Registries baur supports to upload File artifacts that are produced by a build to S3 buckets and produced docker images to docker registries.
-
Managing Applications: baur can be used as management tool in monorepositories to list applications and find their locations.
-
CI Optimized: baur is aimed to be run in CI environments and allows to print relevant output in CSV format to be easily parsed by scripts.
-
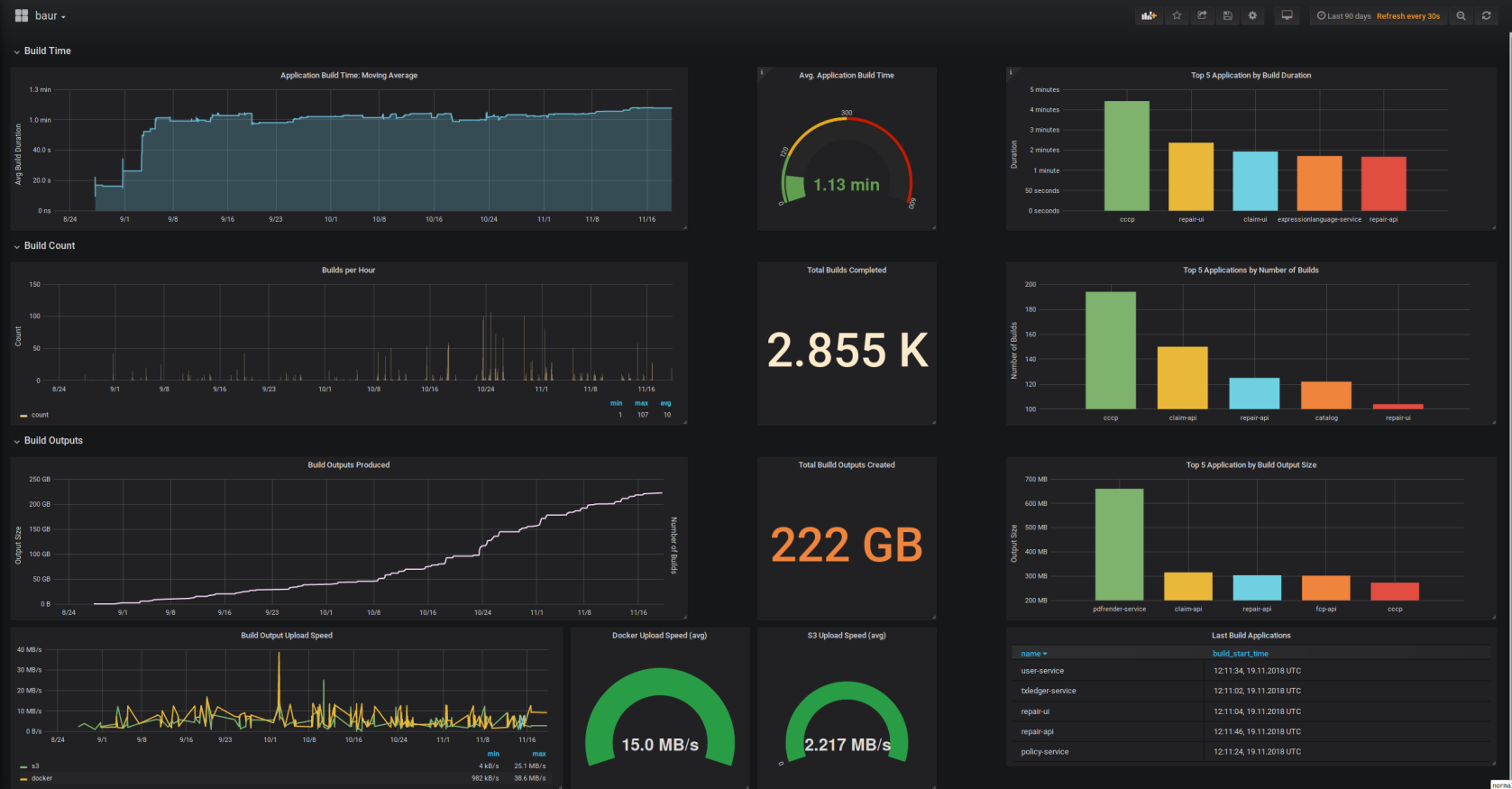
Build Statistics: The data that baur stores in it's PostgreSQL database allows to graph statistics about builds like which application changes most, which produces the biggest build artifacts, which build runs the longest.
Why?
Monorepositories come with new challenges in CI environments. When a Git repository contains only a single applications, every commit can trigger the whole CI workflow of builds, checks, tests and deployments. This is not effective anymore in Monorepositories when an repository can contain hundreds of different applications. Running the whole CI flow for all applications on every commit takes a lot of time and wastes resources. Therefore the CI environment has to detect which application changed to only run those through the CI flow.
When all build inputs per applications are isolated in directories and CI artifacts are always produced for the reference branches, the git-history can be used to determine which files changed. Simpe Shell-Scripts or the mbt build tool can be used for it.
When application in the monorepository share libraries, Protobuf or other files these solutions are not sufficient anymore. Full-fledged build tools like Bazel and pants exist to address those issues in Monorepositories but they come with complex configurations and complex usage. Developers have to get used to define the build steps in those tools instead of relying on their more simple favorite build tools.
baur solves these problems by concentrating on tracking build inputs and build outputs while enabling to use the build tool of your choice.
Documentation
Documentation is available in the wiki.
Graphana Dashboard
The dashboard is available at: https://grafana.com/dashboards/8835
Project Status
baur is used in production CI setups since the first version. It's not considered as API-Stable yet, interface breaking changes can happen in any release.
We are happy to receive Pull Requests, Feature Requests and Bug Reports to further improve baur.
Recommend
About Joyk
Aggregate valuable and interesting links.
Joyk means Joy of geeK