Kafka 源码解析之 Consumer 两种 commit 机制和 partition 分配机制(九) | Matt's B...
source link: http://matt33.com/2017/11/19/consumer-two-summary/?
Go to the source link to view the article. You can view the picture content, updated content and better typesetting reading experience. If the link is broken, please click the button below to view the snapshot at that time.

紧接着上篇文章,这篇文章讲述 Consumer 提供的两种 commit 机制和两种 partition 分配机制,具体如何使用是需要用户结合具体的场景进行选择,本文讲述一下其底层实现。
两种 commit 机制
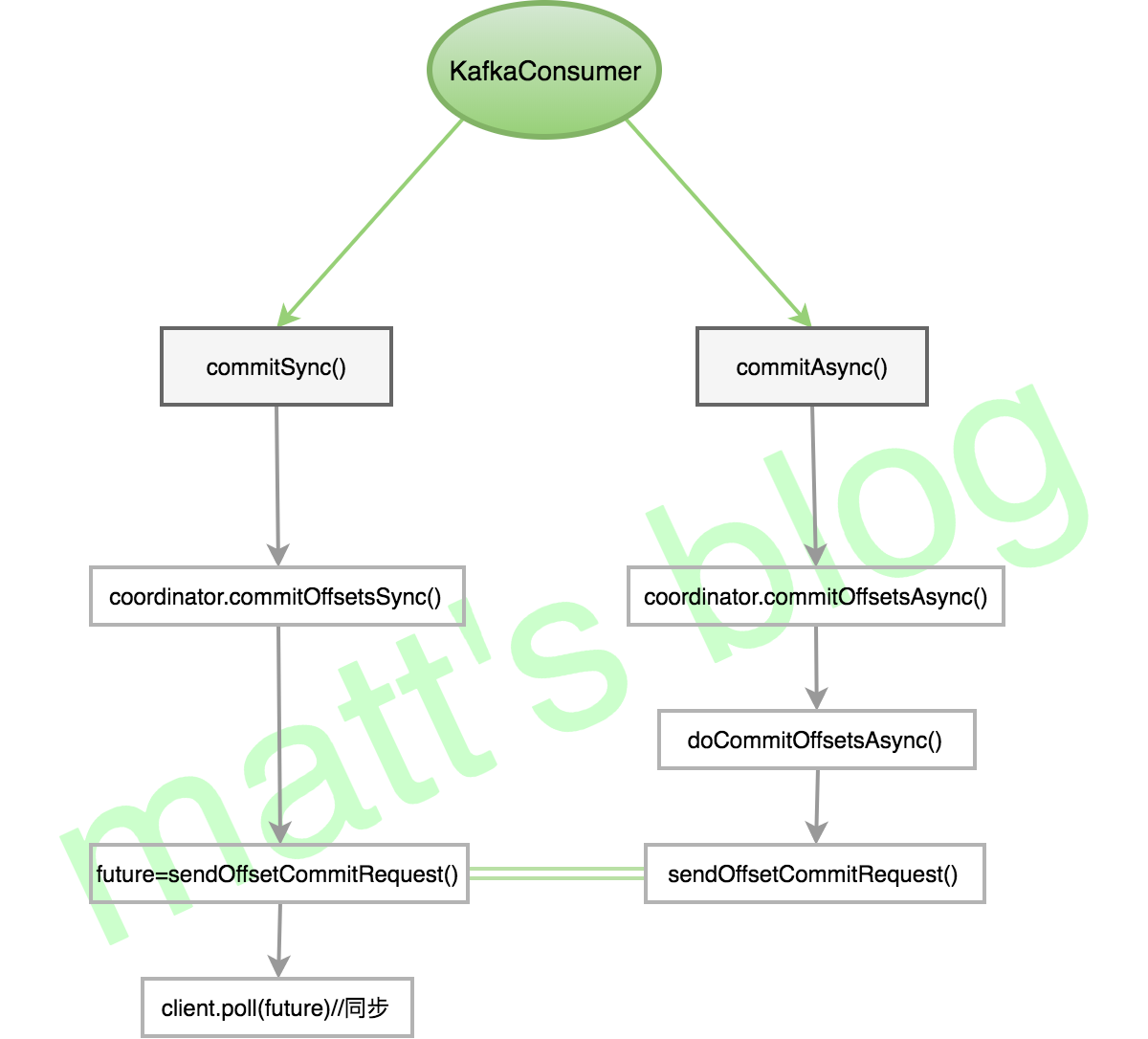
先看下两种不同的 commit 机制,一种是同步 commit,一种是异步 commit,既然其作用都是 offset commit,应该不难猜到它们底层使用接口都是一样的,其调用流程如下图所示:
两种 commit 机制
同步 commit
// 对 poll() 中返回的所有 topics 和 partition 列表进行 commit
// 这个方法只能将 offset 提交 Kafka 中,Kafka 将会在每次 rebalance 之后的第一次拉取或启动时使用同步 commit
// 这是同步 commit,它将会阻塞进程,直到 commit 成功或者遇到一些错误
public void commitSync() {}
// 只对指定的 topic-partition 列表进行 commit
public void commitSync(final Map<TopicPartition, OffsetAndMetadata> offsets) {}
其实,从上图中,就已经可以看出,同步 commit 的实现方式,client.poll() 方法会阻塞直到这个request 完成或超时才会返回。
异步 commit
// 异步 commit
public void commitAsync() {}
public void commitAsync(OffsetCommitCallback callback) {}
public void commitAsync(final Map<TopicPartition, OffsetAndMetadata> offsets, OffsetCommitCallback callback) {}
而对于异步的 commit,最后调用的都是 doCommitOffsetsAsync 方法,其具体实现如下:
//org.apache.kafka.clients.consumer.internals.ConsumerCoordinator
private void doCommitOffsetsAsync(final Map<TopicPartition, OffsetAndMetadata> offsets, final OffsetCommitCallback callback) {
this.subscriptions.needRefreshCommits();
RequestFuture<Void> future = sendOffsetCommitRequest(offsets);//note: 发送 offset-commit 请求
final OffsetCommitCallback cb = callback == null ? defaultOffsetCommitCallback : callback;
future.addListener(new RequestFutureListener<Void>() {
@Override
public void onSuccess(Void value) {
if (interceptors != null)
interceptors.onCommit(offsets);
//note: 添加成功的请求,以唤醒相应的回调函数
completedOffsetCommits.add(new OffsetCommitCompletion(cb, offsets, null));
}
@Override
public void onFailure(RuntimeException e) {
Exception commitException = e;
if (e instanceof RetriableException)
commitException = new RetriableCommitFailedException(e);
//note: 添加失败的请求,以唤醒相应的回调函数
completedOffsetCommits.add(new OffsetCommitCompletion(cb, offsets, commitException));
}
});
}
在异步 commit 中,可以添加相应的回调函数,如果 request 处理成功或处理失败,ConsumerCoordinator 会通过 invokeCompletedOffsetCommitCallbacks() 方法唤醒相应的回调函数。
关于 offset commit 请求的处理见上一篇文章中的Offset Commit 请求处理,对于提交的 offset,GroupCoordinator 会记录在 GroupMetadata 对象中。
两种 partition 分配机制
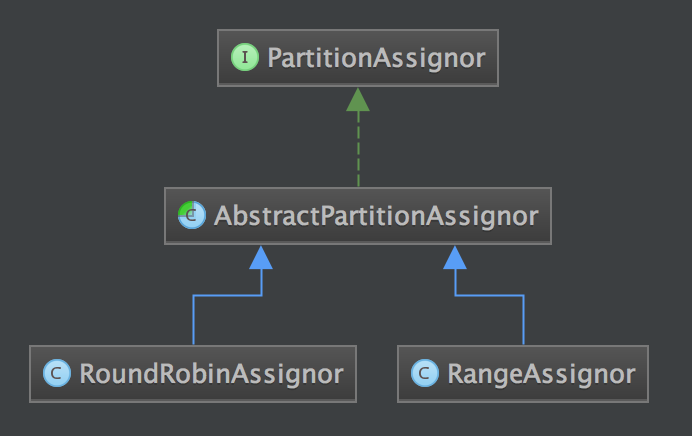
consumer 提供的两种不同 partition 分配策略,可以通过 partition.assignment.strategy 参数进行配置,默认情况下使用的是 org.apache.kafka.clients.consumer.RangeAssignor,Kafka 中提供另一种 partition 的分配策略 org.apache.kafka.clients.consumer.RoundRobinAssignor,它们关系如下图所示:
Kafka 系统内置的两种 partition 分配机制
通过上图可以看出,用户可以自定义相应的 partition 分配机制,只需要继承这个 AbstractPartitionAssignor 抽象类即可。
AbstractPartitionAssignor
AbstractPartitionAssignor 有一个抽象方法,如下所示:
/**
* Perform the group assignment given the partition counts and member subscriptions
* @param partitionsPerTopic The number of partitions for each subscribed topic. Topics not in metadata will be excluded
* from this map.
* @param subscriptions Map from the memberId to their respective topic subscription
* @return Map from each member to the list of partitions assigned to them.
*/
//NOTE: 根据 partitionsPerTopic 和 subscriptions 进行分配,具体的实现会在子类中实现(不同的子类的实现各异)
public abstract Map<String, List<TopicPartition>> assign(Map<String, Integer> partitionsPerTopic,Map<String, List<String>> subscriptions);
assign() 这个方法,有两个参数:
partitionsPerTopic:所订阅的每个 topic 与其 partition 数的对应关系,metadata 没有的 topic 将会被移除;subscriptions:每个 consumerId 与其所订阅的 topic 列表的关系。
RangeAssignor 和 RoundRobinAssignor 通过这个方法 assign() 的实现,来进行相应的 partition 分配。
RangeAssignor 分配模式
直接看一下这个方法的实现:
public Map<String, List<TopicPartition>> assign(Map<String, Integer> partitionsPerTopic,
Map<String, List<String>> subscriptions) {
Map<String, List<String>> consumersPerTopic = consumersPerTopic(subscriptions);//note: (topic, List<consumerId>)
Map<String, List<TopicPartition>> assignment = new HashMap<>();
for (String memberId : subscriptions.keySet())
assignment.put(memberId, new ArrayList<TopicPartition>());//note: 初始化
for (Map.Entry<String, List<String>> topicEntry : consumersPerTopic.entrySet()) {
String topic = topicEntry.getKey();
List<String> consumersForTopic = topicEntry.getValue();
Integer numPartitionsForTopic = partitionsPerTopic.get(topic);
if (numPartitionsForTopic == null)
continue;
Collections.sort(consumersForTopic);
//note: 假设 partition 有 7个,consumer 有5个
int numPartitionsPerConsumer = numPartitionsForTopic / consumersForTopic.size();//note: 1
int consumersWithExtraPartition = numPartitionsForTopic % consumersForTopic.size();//note: 2
List<TopicPartition> partitions = AbstractPartitionAssignor.partitions(topic, numPartitionsForTopic);
for (int i = 0, n = consumersForTopic.size(); i < n; i++) {
//note: i=0, start: 0, length: 2, topic-partition: p0,p1
//note: i=1, start: 2, length: 2, topic-partition: p2,p3
//note: i=2, start: 4, length: 1, topic-partition: p4
//note: i=3, start: 5, length: 1, topic-partition: p5
//note: i=4, start: 6, length: 1, topic-partition: p6
int start = numPartitionsPerConsumer * i + Math.min(i, consumersWithExtraPartition);
int length = numPartitionsPerConsumer + (i + 1 > consumersWithExtraPartition ? 0 : 1);
assignment.get(consumersForTopic.get(i)).addAll(partitions.subList(start, start + length));
}
}
return assignment;
}
假设 topic 的 partition 数为 numPartitionsForTopic,group 中订阅这个 topic 的 member 数为 consumersForTopic.size(),首先需要算出两个值:
numPartitionsPerConsumer = numPartitionsForTopic / consumersForTopic.size():表示平均每个 consumer 会分配到几个 partition;consumersWithExtraPartition = numPartitionsForTopic % consumersForTopic.size():表示平均分配后还剩下多少个 partition 未分配。
分配的规则是:对于剩下的那些 partition 分配到前 consumersWithExtraPartition 个 consumer 上,也就是前 consumersWithExtraPartition 个 consumer 获得 topic-partition 列表会比后面多一个。
在上述的程序中,举了一个例子,假设有一个 topic 有 7 个 partition,group 有5个 consumer,这个5个 consumer 都订阅这个 topic,那么 range 的分配方式如下:
- consumer 0:start: 0, length: 2, topic-partition: p0,p1;
- consumer 1:start: 2, length: 2, topic-partition: p2,p3;
- consumer 2:start: 4, length: 1, topic-partition: p4;
- consumer 3:start: 5, length: 1, topic-partition: p5;
- consumer 4:start: 6, length: 1, topic-partition: p6
而如果 group 中有 consumer 没有订阅这个 topic,那么这个 consumer 将不会参与分配。下面再举个例子,将有两个 topic,一个 partition 有5个,一个 partition 有7个,group 有5个 consumer,但是只有前3个订阅第一个 topic,而另一个 topic 是所有 consumer 都订阅了,那么其分配结果如下:
| consumer | 订阅的 topic1 的列表 | 订阅的 topic2 的列表 |
|---|---|---|
| consumer 0 | t1p0, t1p1 | t2p0, t2p1 |
| consumer 1 | t1p2, t1p3 | t2p2, t2p3 |
| consumer 2 | t1p4 | t2p4 |
| consumer 3 | t2p5 | |
| consumer 4 | t2p6 |
RoundRobinAssignor
这个是 roundrobin 的实现,其实现方法如下:
@Override
public Map<String, List<TopicPartition>> assign(Map<String, Integer> partitionsPerTopic,
Map<String, List<String>> subscriptions) {
Map<String, List<TopicPartition>> assignment = new HashMap<>();
for (String memberId : subscriptions.keySet())
assignment.put(memberId, new ArrayList<TopicPartition>());
CircularIterator<String> assigner = new CircularIterator<>(Utils.sorted(subscriptions.keySet()));//note: 环行迭代
for (TopicPartition partition : allPartitionsSorted(partitionsPerTopic, subscriptions)) {
final String topic = partition.topic();
while (!subscriptions.get(assigner.peek()).contains(topic))//note: 遍历直到找到订阅这个 topic 的 partition
assigner.next();
assignment.get(assigner.next()).add(partition);
}
return assignment;
}
public List<TopicPartition> allPartitionsSorted(Map<String, Integer> partitionsPerTopic,
Map<String, List<String>> subscriptions) {
SortedSet<String> topics = new TreeSet<>();//NOTE: 所有的 topics(有序)
for (List<String> subscription : subscriptions.values())
topics.addAll(subscription);
List<TopicPartition> allPartitions = new ArrayList<>();//NOTE: 订阅的 Topic的所有的 TopicPartition 集合
for (String topic : topics) {
Integer numPartitionsForTopic = partitionsPerTopic.get(topic);
if (numPartitionsForTopic != null)
//note: topic 的所有 partition 都添加进去
allPartitions.addAll(AbstractPartitionAssignor.partitions(topic, numPartitionsForTopic));
}
return allPartitions;
}
roundrobin 的实现原则,简单来说就是:列出所有 topic-partition 和列出所有的 consumer member,然后开始分配,一轮之后继续下一轮,假设有有一个 topic,它有7个 partition,group 有3个 consumer 都订阅了这个 topic,那么其分配方式为:
| consumer | 分配列表 |
|---|---|
| consumer 0 | tp0, tp3, tp6 |
| consumer 1 | tp1, tp4 |
| consumer 2 | tp2, tp5 |
对于多个 topic 的订阅,将有两个 topic,一个 partition 有5个,一个 partition 有7个,group 有5个 consumer,但是只有前3个订阅第一个 topic,而另一个 topic 是所有 consumer 都订阅了,那么其分配结果如下:
| consumer | 订阅的 topic1 的列表 | 订阅的 topic2 的列表 |
|---|---|---|
| consumer 0 | t1p0, t1p3 | t2p0, t2p5 |
| consumer 1 | t1p1, t1p4 | t2p1, t2p6 |
| consumer 2 | t1p2 | t2p2 |
| consumer 3 | t2p3 | |
| consumer 4 | t2p4 |
roundrobin 分配方式与 range 的分配方式还是略有不同。
</div
Recommend
About Joyk
Aggregate valuable and interesting links.
Joyk means Joy of geeK