

Overcoming Imposter Syndrome as a Product Designer: A Guide to Boosting Confiden...
source link: https://uxplanet.org/overcoming-imposter-syndrome-as-a-product-designer-a-guide-to-boosting-confidence-and-achieving-6dd8468ce4e1
Go to the source link to view the article. You can view the picture content, updated content and better typesetting reading experience. If the link is broken, please click the button below to view the snapshot at that time.
Overcoming Imposter Syndrome as a Product Designer: A Guide to Boosting Confidence and Achieving Success
Tips and Strategies for Product Designers to Overcome Imposter Syndrome and Build a Stronger Professional Identity
Imposter syndrome is a pervasive psychological phenomenon that affects many professionals, including product designers. It is a persistent feeling of self-doubt and insecurity, even in the face of success and accomplishments. Imposter syndrome can be particularly debilitating for product designers, who must balance creative expression with practical considerations and business goals. In this article, we will explore the nature of imposter syndrome, its causes, and its impact on product designers. We will also provide practical tips and strategies for overcoming imposter syndrome and building a stronger professional identity.
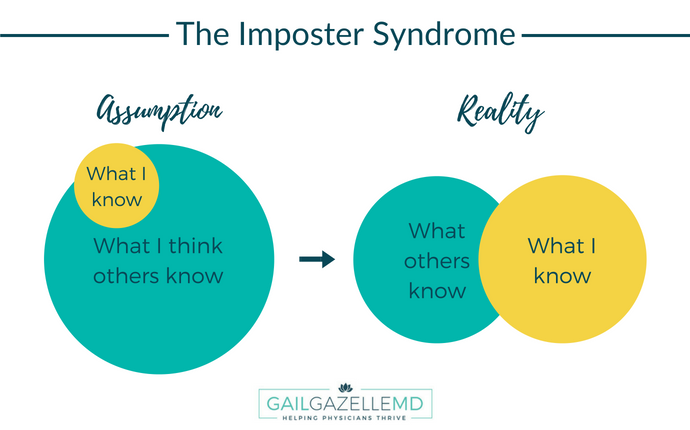
Understanding Imposter Syndrome
Imposter syndrome is a psychological phenomenon in which an individual feels inadequate, incompetent, and unworthy of success, despite evidence to the contrary. It can be characterized by persistent feelings of self-doubt, fear of failure, and anxiety about being exposed as a fraud. Imposter syndrome is not a clinical diagnosis but rather a common experience among high-achieving individuals. Product designers are particularly vulnerable to impostexr syndrome because of the nature of their work, which involves creativity, innovation, and risk-taking.
Source here
Causes of Imposter Syndrome
Imposter syndrome is often caused by a combination of factors, including personality traits, upbringing, and social and cultural norms. Individuals who are perfectionistic, self-critical, and have high expectations of themselves are more likely to experience imposter syndrome. Upbringing can also play a role, as children who were praised for their achievements rather than their effort may internalize the belief that success is based on innate ability rather than hard work. Social and cultural norms that emphasize achievement and success can also contribute to imposter syndrome, as individuals feel pressure to live up to high standards and fear being perceived as failures.
Impact of Imposter Syndrome on Product Designers
Imposter syndrome can have a significant impact on the professional and personal lives of product designers. It can lead to a lack of confidence, which can affect decision-making, communication, and collaboration with others. Product designers who experience imposter syndrome may also avoid taking risks or pursuing new opportunities, which can limit their professional growth and development. Imposter syndrome can also lead to burnout, as individuals feel pressure to constantly prove themselves and may neglect self-care and work-life balance.
Tips and Strategies for Overcoming Imposter Syndrome
While imposter syndrome can be a challenging experience, there are practical strategies and techniques that product designers can use to overcome it. Here are some tips and strategies for building a stronger professional identity and boosting confidence:
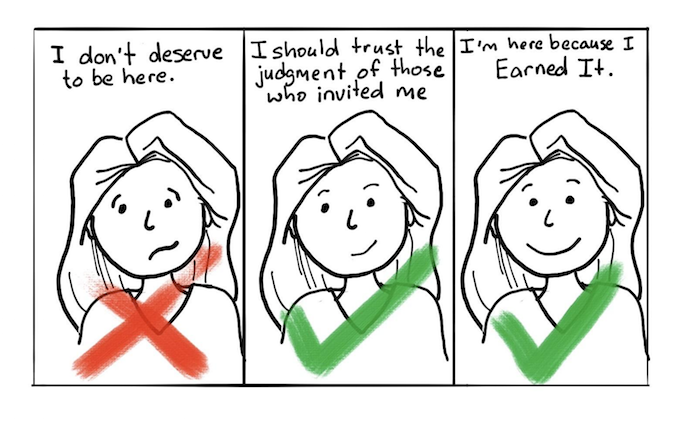
Recognize and Acknowledge Imposter Syndrome
The first step in overcoming imposter syndrome is to recognize and acknowledge it. Product designers should be aware of the symptoms of imposter syndrome and reflect on their own experiences to determine if they are experiencing it. They should also acknowledge that imposter syndrome is a common experience and that they are not alone.
Reframe Negative Thoughts
Product designers can reframe negative thoughts by focusing on their strengths and accomplishments rather than their perceived shortcomings. They should also challenge negative self-talk and replace it with positive affirmations. For example, instead of thinking, “I’m not good enough,” they could think, “I have unique skills and talents that contribute to the success of the team.”
Seek Support and Feedback
Product designers should seek support and feedback from colleagues, mentors, and friends. They can ask for constructive feedback on their work and use it as an opportunity for growth and improvement. They can also seek out mentors who can provide guidance and support as they navigate their careers.
Embrace Failure and Learn from Mistakes
Product designers should embrace failure as an opportunity for growth and learning. They should recognize that failure is a natural part of the design process and that every failure brings them closer to success. By reframing failure as a learning opportunity, product designers can reduce the fear of failure and take risks with greater confidence.
Practice Self-Care
Product designers should prioritize self-care and work-life balance. This includes taking breaks, getting enough sleep, and engaging in activities that bring them joy and fulfillment outside of work. Practicing self-care can help reduce stress and anxiety, and improve overall well-being.
Set Realistic Goals
Product designers should set realistic goals for themselves and their work. This includes breaking down larger projects into smaller, more manageable tasks, and setting achievable deadlines. By setting realistic goals, product designers can reduce the pressure they feel to perform perfectly and improve their sense of accomplishment.
Keep Learning
Product designers should continue to learn and develop their skills and knowledge. This includes attending workshops, conferences, and training sessions, as well as seeking out new experiences and challenges. By continuously learning and growing, product designers can improve their confidence and expertise.
Source here
Conclusion
Imposter syndrome can be a challenging experience for product designers, but it is not insurmountable. By recognizing and acknowledging imposter syndrome, reframing negative thoughts, seeking support and feedback, embracing failure and learning from mistakes, practicing self-care, setting realistic goals, and continuing to learn, product designers can overcome imposter syndrome and build a stronger professional identity. With these strategies in mind, product designers can achieve greater success and fulfillment in their careers, and contribute to the growth and innovation of their teams and organizations.
Recommend
About Joyk
Aggregate valuable and interesting links.
Joyk means Joy of geeK