使用CSS计数器美化有序列表
source link: https://segmentfault.com/a/1190000040836461
Go to the source link to view the article. You can view the picture content, updated content and better typesetting reading experience. If the link is broken, please click the button below to view the snapshot at that time.
在web设计中,使用一种井井有条的方法来展示数据是十分重要的,这样用户就可以很清晰的理解网站所展示的数据结构和内容,使用有序列表就是实现数据有组织的展示的一种简单方法。
如果你需要更加深入地控制有序列表数字的样式,你可能会觉得必须通过增加更多的 html DOM 结构或者通过 JavaScript 才能做到。幸运的是,使用 CSS计数器 可以更加容易的解决这个问题。在本文中,主要介绍什么是 CSS计数器 和一些使用案例。
有序列表的问题
当你写了一个如下的有序列表,浏览器会自动在列表项前面加上数字
<ol> <li>My First Item</li> <li>My Second Item</li> <li>My Third Item</li> </ol>
这看起来很好,但是它不允许你对数字进行样式调整。假如,你需要把列表前的数字放进一个圆圈里来修饰列表,你该怎么做呢?
一种方法是完全删除列表,并自己手动添加数字。
<div> <span>1</span> My First Item </div> <div> <span>2</span> My Second Item </div> <div> <span>3</span> My Third Item </div>
div {
margin-bottom:10px;
}
div span {
display:inline-flex;
align-items:center;
justify-content:center;
width:25px;
height:25px;
border-radius:50%;
background-color:#000;
color:#fff;
}这确实是我们想要做的效果,但是也有一些缺点。首先,手动添加数字是很麻烦的。如果你需要更改一个编号,你必须一个接一个地改变它们。面对这种情况,你可以使用 JavaScript 动态添加 <span> 标签来解决这些问题,但这会为 DOM 添加更多的节点,从而导致大量内存占用。
在大多数情况下,最好使用CSS计数器。让我们来看看原因。
CSS计数器简介
CSS计数器是网页范围变量,其值可以使用 CSS 规则更改。
首先,使用 counter-reset 属性设置计数器。list-number 是此处使用的变量名。
div.list {
counter-reset: list-number;
}接着,使用 counter-increment属性来增加计数器的值。
div.list div {
counter-increment: list-number;
}现在,每次出现 div.listdiv 元素时,list-number 变量都会增加一。
最后,使用含有设置 content属性和 counter()函数的 :before 伪元素来展示数字。
div.list div:before {
content: counter(list-number);
}这里是完整代码:
<div class="list"> <div>My first item</div> <div>My second item</div> <div>My third item</div> </div>
div.list {
counter-reset: list-number;
}
/** 可以在:before 为元素中使用 counter-increment **/
div.list div:before {
counter-increment: list-number;
content: counter(list-number);
}现在我们还没有完全达到目标。让我们对 :before 伪元素进行样式设计,使其看起来更好。
div.list div:before {
counter-increment: list-number;
content: counter(list-number);
margin-right: 10px;
margin-bottom:10px;
width:35px;
height:35px;
display:inline-flex;
align-items:center;
justify-content: center;
font-size:16px;
background-color:#d7385e;
border-radius:50%;
color:#fff;
}<iframe allowfullscreen="true" allowpaymentrequest="true" allowtransparency="true" class="cp_embed_iframe " frameborder="0" height="265" width="100%" name="cp_embed_1" scrolling="no" src="https://codepen.io/SupunKavinda/embed/OJybvoq?height=265&theme-id=dark&default-tab=css%2Cresult&user=SupunKavinda&slug-hash=OJybvoq&pen-title=OJybvoq&name=cp_embed_1" style="width: 100%; overflow:hidden; display:block;" title="OJybvoq" loading="lazy" id="cp_embed_OJybvoq"></iframe>
修改起始数字
默认情况下,counter-reset 会将计数器设置为 0。当第一个 counter-increment 被调用后它的起始变为1 可以通过将一个整数作为 counter-reset 函数的第二个参数来设置初始值。
div.list {
counter-reset: list-number 1;
}如果你想从 0 开始,可以将初始值设置为 -1。
div.list {
counter-reset: list-number -1;
}更改增量值
默认情况下,counter-increment 会使计数器的值增加一。就像 counter-reset 一样,你可以定义 counter-increment 属性的偏移值。
在此示例中,counter-reset 将 list-number 设置为 0。每次调用 counter-increment 时,list-number 数值都会增加 2,因此,你将会看到列表序为 2、4 和 6。
div.list {
counter-reset: list-number;
}
div.list div:before {
counter-increment: list-number 2;
// other styles
}计数器格式
counter() 函数可以有两个参数:counter-name 和 counter-format。对于第二个参数,你可以使用任何有效的列表类型值,包括:
decimal(e.g., 1, 2, 3…)lower-latin(e.g., a, b, c…)lower-roman(e.g., i, ii, iii…)
默认值为数字。
例如,如果你像我一样科学,你可以使用 lower-greek 小写希腊字母作为编号的值。
div.list div:before {
counter-increment: list-number;
content: counter(list-number, lower-greek);
// ... other styles
}计数器嵌套
使用嵌套订单列表时,始终以这种格式显示编号:
如果您需要子列表项目的数字编号(例如,1.1),您可以使用具有 counters() 功能的 CSS计数器。
<ol>
<li>
My First Item
<ol>
<li>My Nested First Item</li>
<li>My Nested Second Item</li>
</ol>
</li>
<li>My Second Item</li>
</ol>ol {
list-style-type:none;
counter-reset:list;
}
ol li:before {
counter-increment:list;
content: counters(list, ".") ". ";
}注意,我们使用的是 counters() 函数,而不是 counter() 函数。
counters() 函数的第二个参数是连接字符串。它还可以有第三个参数来设置格式(例如,希腊数字或罗马数字)。
带标题的嵌套计数器
元素,如 <h1>,<h2> 不嵌套在文档中。它们以不同的元素出现,但仍代表一种层次结构。下面介绍如何将嵌套数字设置到标题中:
body {
counter-reset:h1;
}
h1 {
counter-reset:h2;
}
h1:before {
counter-increment: h1;
content: counter(h1) ". ";
}
h2:before {
counter-increment:h2;
content: counter(h1) "." counter(h2) ". ";
}每次找到<h1>时,<h2>计数器都会重置。<h2> 在文档中获得的编号和 <h1> 相关。
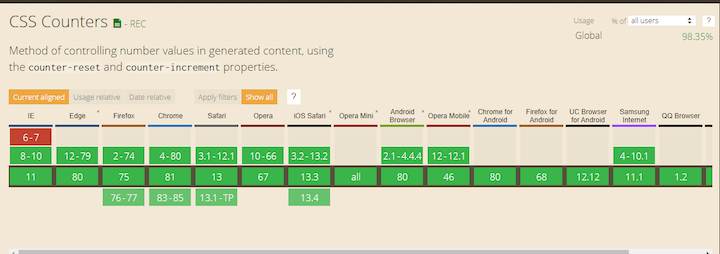
Browser support
值得庆幸的是,CSS 计数器自与 CSS2 一起推出以来,得到了浏览器的广泛支持。虽然在内容以外的属性中使用 counter() 函数仍然是实验性的,但你可以毫不犹豫地执行本教程中涵盖的所有例子。
一个简单挑战
您准备好迎接涉及CSS计数器的简单挑战了吗?
使用 CSS计数器在 10 行代码中显示 1 到 1000 及其罗马字符。
如果你被难倒了,下面是你如何做到这一点:
要创建 1000 个 div 元素,可以使用以下内容。
for (var i = 0; i < 1000; i++) {
document.body.appendChild( document.createElement("div") );
}CSS计数器:
body {
counter-reset:number;
}
div:before {
counter-increment:number;
content: counter(number) " => " counter(number, lower-roman);
}CSS 计数器在 CSS 中是一个鲜为人知的功能,但您会惊讶于它们派上用场的频率。在此教程中,我们讨论了如何以及何时使用 CSS 计数器,并展示了一些示例。
以下是我们使用的属性列表。
属性用法counter-reset重置(或创建)给定值计数器(默认0)counter-increment通过给定偏移增加给定计数器(默认值 1)counter(counter-name, counter-format)从给定格式获取计数器的价值counters(counter-name, counter-string, counter-format)从给定格式获取嵌套计数器的价值CSS计数器 虽然很酷。但有一件事需要明白的是,所有计数器都是全局性的。如果你在一个有很多 CSS 文件的大型项目中使用,你可能无法找到它们的创建、重置和增量位置。不要过度使用它们,一定要使用描述性名称的计数器,以避免冲突。
一些实战例子
<style>
html {
box-sizing: border-box;
font-size: 62.5%;
}
*,
*::before,
*:after {
box-sizing: inherit;
}
body {
font-family: Rambla, sans-serif;
font-size: 2rem;
line-height: 1.5;
color: #03c03c;
}
h1 {
text-align: center;
}
.wrapper {
margin: 0 auto;
width: 85%;
display: -webkit-box;
display: -webkit-flex;
display: -ms-flexbox;
display: flex;
-webkit-justify-content: space-around;
-ms-flex-pack: distribute;
justify-content: space-around;
}
@media (max-width: 1100px) {
.wrapper {
-webkit-box-orient: vertical;
-webkit-box-direction: normal;
-webkit-flex-direction: column;
-ms-flex-direction: column;
flex-direction: column;
-webkit-box-align: center;
-webkit-align-items: center;
-ms-flex-align: center;
align-items: center;
}
}
ol {
counter-reset: li;
margin: 20px 0;
padding-left: 0;
}
ol>li {
position: relative;
margin: 0 0 25px 2em;
padding: 4px 8px 4px 20px;
list-style: none;
}
ol>li::before {
content: counter(li);
counter-increment: li;
position: absolute;
top: -2px;
left: -2em;
width: 2em;
margin-right: 8px;
padding: 4px;
font-weight: bold;
text-align: center;
}
li ol,
li ul {
margin-top: 6px;
}
ol ol li:last-child {
margin-bottom: 0;
}
.disc>li::before {
color: white;
background-color: #03c03c;
border-radius: 50%;
}
.circle>li::before {
color: #03c03c;
border: solid 2px #03c03c;
border-radius: 50%;
}
.angle>li::before {
color: #03c03c;
border-right: solid 3px #03c03c;
border-bottom: solid 3px #03c03c;
}
.shadow>li::before {
color: white;
background: #03c03c;
box-shadow: 5px 5px 0 0 greenyellow;
}
.rombo>li {
margin-bottom: 25px;
}
.rombo>li::before {
color: white;
z-index: 2;
}
.rombo>li::after {
position: absolute;
top: -2px;
left: -2em;
width: 2em;
margin-right: 8px;
padding: 4px;
background-color: #03c03c;
height: 2em;
-webkit-transform: rotate(45deg);
-ms-transform: rotate(45deg);
transform: rotate(45deg);
content: '';
z-index: 1;
}
.underline>li::before {
border-bottom: solid 3px #03c03c;
}
</style>
<body>
<h1>Styling Ordered List Numbers</h1>
<div class="wrapper">
<ol class="disc">
<li>Tomato</li>
<li>Cucumber</li>
<li>Onion</li>
<li>Pepper</li>
</ol>
<ol class="circle">
<li>Tomato</li>
<li>Cucumber</li>
<li>Onion</li>
<li>Pepper</li>
</ol>
<ol class="angle">
<li>Tomato</li>
<li>Cucumber</li>
<li>Onion</li>
<li>Pepper</li>
</ol>
<ol class="shadow">
<li>Tomato</li>
<li>Cucumber</li>
<li>Onion</li>
<li>Pepper</li>
</ol>
<ol class="rombo">
<li>Tomato</li>
<li>Cucumber</li>
<li>Onion</li>
<li>Pepper</li>
</ol>
<ol class="underline">
<li>Tomato</li>
<li>Cucumber</li>
<li>Onion</li>
<li>Pepper</li>
</ol>
</div>
</body>更多优秀案例
https://css-tricks.com/custom...
文章地址:https://www.cnblogs.com/drago... 作者:dragonir
Recommend
About Joyk
Aggregate valuable and interesting links.
Joyk means Joy of geeK