MySQL 5.7 的 JSON 类型 | nullwy's blog
source link: http://nullwy.me/2019/06/mysql-5.7-json/?
Go to the source link to view the article. You can view the picture content, updated content and better typesetting reading experience. If the link is broken, please click the button below to view the snapshot at that time.
MySQL 5.7 的 JSON 类型
2015 年 8 月,MySQL 5.7.8 开始提供对 JSON 的原生支持 [ doc1, doc2 ]。MySQL 对 JSON 的支持可以说是千呼万唤始出来。2009 年开始 NoSQL 逐渐流行起来,相继出现了键值对数据库、文档数据库、列族数据库、图数据库等各类 NoSQL,解决经典关系型数据库无法解决的痛点。其中,对灵活存储半结构化数据的需求,使得类似 MongoDB 这类文档数据库涌现出来。各大主流关系型数据库也在响应趋势,开始支持半结构化数据。早在 2012 年,PostgreSQL 9.2 就已经添加了 JSON 数据类型 [ ref ]。Oracle 也在 2014 年 7 月发布 12c Release 1 后开始支持 JSON [ ref1, ref2 ]。Facebook 在 MySQL 5.7 没发布之前,对 5.6 版本的 MySQL 添加了存储 JSON 功能,这个特性被 Facebook 命名为 DocStore (Document Database for MySQL at Facebook) [ doc, slides ]。另外,SQL 标准组织行动也很快,在 2014 年 3 月已经完成了 SQL/JSON 标准草案(DM32.2 SQL/JSON Proposals, part1, part2)[ slides ]。完整的草案在 2016 年 12 月正式被采纳为标准,即 SQL:2016。
浏览 SQL/JSON 标准草案可以发现,全部作者共有 9 人,这些作者来自两个公司,Oracle 和 IBM,而排前面的作者如 Jim Melton, Fred Zemke, Beda Hammerschmidt 都 Oracle 的专家。正因为 SQL:2016 主要就是 Oracle 参与制定的,目前,Oracle 数据库对 SQL:2016 的支持也是最全的 [ ref ]。
MySQL 对 JSON 的支持,设计文档主要是 WL#7909: Server side JSON functions,另外还有 WL#8132: JSON datatype and binary storage format、WL#8249: JSON comparator、WL#8607: Inline JSON path expressions in SQL 等。在 MySQL 开始 WL#7909 之时,SQL/JSON 标准草案已经公开,WL#7909 中也提及了这份标准,但是如果拿 MySQL 提供 JSON 的功能与 SQL:2016 比较,可以发现 MySQL 虽然融入了部分的设计,但并没有完全参考标准,定义的 JSON 函数多数有区别。
回到正题,下面来看下 MySQL 5.7 的 JSON 的用法。
JSON 函数列表
MySQL 官方列出 JSON 相关的函数,完整列表如下 [ doc ]:
| 分类 | 函数 | 描述 |
|---|---|---|
| json 创建函数 | json_array() | 创建 json 数组 |
| json_object() | 创建 json 对象 | |
| json_quote() | 用双引号包裹 json 文档 | |
| json 查询函数 | json_contains() | 判断是否包含某个 json 值 |
| json_contains_path() | 判断某个路径下是否包 json 值 | |
| json_extract() | 提取 json 值 | |
| column->path | json_extract() 的简洁写法,5.7.9 开始支持 | |
| column->>path | json_unquote(json_extract()) 的简洁写法,5.7.13 开始支持 | |
| json_keys() | 把 json 对象的顶层的全部键提取为 json 数组 | |
| json_search() | 按给定字符串关键字搜索 json,返回匹配的路径 | |
| json 修改函数 | json_append() | 5.7.9 废弃,改名为 json_array_append |
| json_array_append() | 在 josn 文档末尾添加数组元素 | |
| json_array_insert() | 在 josn 数组中插入元素 | |
| json_insert() | 插入值(只插入新值,不替换旧值) | |
| json_merge() | 5.7.22 废弃,与 json_merge_preserve() 同义 | |
| json_merge_patch() | 合并 json 文档,重复键的值将被替换掉 | |
| json_merge_preserve() | 合并 json 文档,保留重复键 | |
| json_remove() | 删除 json 文档中的数据 | |
| json_replace() | 替换值(只替换旧值,不插入新值) | |
| json_set() | 设置值(替换旧值,或插入新值) | |
| json_unquote() | 移除 json 值的双引号包裹 | |
| json 属性函数 | json_depth() | 返回 json 文档的最大深度 |
| json_length() | 返回 json 文档的长度 | |
| json_type() | 返回 json 值的类型 | |
| json_valid() | 判断是否为合法 json 文档 | |
| json 工具函数 | json_pretty() | 美化输出 json 文档,5.7.22 新增 |
| json_storage_size() | 返回 json 文档占用的存储空间,5.7.22 新增 |
官方文档对全部函数都作了充分解释并提供一定的示例代码。下文挑选了部分函数,演示它们的使用方法。
创建与插入 JSON
1 | -- 创建 tbl 表,字段 data 为 json 类型 |
上面的 SQL 示例简单验演示了创建 JSON 列以及写入并查询 JSON 数据,比较简单,就不做解释了。
查询 JSON
json_extract() 与 -> 操作符
如果要查询 JSON 文档中内容,提取 JSON 中的值,可以使用 json_extract() 函数。函数定义如下:
1 | json_extract(json_doc, path[, path] ...) |
先来看下 SQL 示例:
1 | -- 使用 json_extract() 函数查询 json 对象 |
示例中的 $.name,使用的是 JSON 路径语法,用来提取 JSON 文档的内容。JSON 路径语法,源自 Stefan Goessner 的 JsonPath,不过 MySQL 作了简化。路径语法使用 $ 开头来表示整个 JSON 文档。如果要提取部分 JSON 文档,可以在路径后面添加选择符:
- 在路径
path后上追加对象的键名称,可以获取这个键下成员。如果加键名称后,路径表达式非法,需要对键名称用双引号包裹(比如,键名称中包含空格的情况) - 在路径
path后加上追加[N],用于选择数组的第 N 个元素。数组索引从 0 开始。如果path下并不是数组,path[0]获取结果就是path本身。 - 路径可以包含
*和**通配符:.[*]用于获取 JSON 对象的全部成员。[*]用于获取 JSON 数组的全部元素。prefix**suffix表示全部以prefix开始,以suffix结尾的路径。
- 如果路径在 JSON 文档中不存在数据,将返回
NULL。
假设 $ 引用的是如下 JSON 数组:
1 | [3, {"a": [5, 6], "b": 10}, [99, 100]] |
$[0] 获取到的值为 3,$[1] 获取到 {"a": [5, 6], "b": 10},$[2] 获取到 [99, 100],$[3] 获取到 NULL(因为不存在第 4 个元素)。
因为 $[1] 和 $[2] 获取的并非纯量(nonscalar),它们可以进一步使用路径访问到内嵌的值,比如:$[1].a 获取到 [5, 6],$[1].a[1] 获取到 6,$[1].b 获取到 10,$[2][0] 获取到 99。
上文提到,如果追加键值名后,路径表达式非法,需要对键名称用双引号包裹。假设 $ 引用的是如下 JSON 对象:
1 | {"name 1": "Will", "name 2": "Andy"} |
两个键都包含空格,需要加上双引号,才能使用路径表达式访问。$."name 1" 将获取到 Will,而 $."name 2" 将获取到 Andy。
现在来看下通配符的示例,假设 JSON 对象如下:
1 | {"a": {"b": 1}, "c": {"b": 2}, "d": [3, 4, 5]} |
使用 $.* 将获取到 [{"b": 1}, {"b": 2}, [3, 4, 5]];
使用 $.d[*] 将获取到 [3, 4, 5];
使用 $**.b(对应 $.a.b 和 $.c.b)将获取到 [1, 2]。
MySQL 5.7.9 开始,官方支持 json_extract(column, path) 的简洁写法,内联 JSON 路径表达式 column->path(WL#8607)。示例如下:
1 | -- 使用内联 json 路径表达式,查询 json 对象 |
本质上,这种写法是语法糖,column->path 等价于 json_extract(column, path),内联 JSON 路径表达式会在语法解析阶段被转换为 json_extract() 调用。另外,column->path,存在以下限制 [ ref ]
即,1. 数据源必须是表字段,2. 路径表达式必须为字符串,3. SQL 语句中最多只支持一个。
现在来试验下这个限制,如果使用内联 JSON 路径表达式查询 MySQL 变量,将会报语法错误:
1 | mysql> set @j = '["a", "b"]'; |
json_unquote() 与 ->> 操作符
假设数据如下:
1 | mysql> select * from tbl; |
来看下使用 -> 提取获得 JSON 值:
1 | mysql> select data -> '$.id', data -> '$.name', substr(data -> '$.name', 1, 1) from tbl; |
可以看到,对于 string 类型的 JSON 值,使用 json_extract() 或 -> 获取的都是被双引号包裹的字符串。MySQL 提供 json_unquote() 函数,用于去掉双引号包裹。另外,MySQL 支持 column->>path 语法,通过 ->> 操作符获取纯量(scalar)。column->>path 写法等价于 json_unquote( json_extract(column, path) ) 或者 json_unquote(column -> path)。来看下 SQL 示例:
1 | mysql> select data ->> '$.id' as id, data -> '$.name' as name, |
MySQL 这种区分 -> 和 ->> 的写法,怀疑是源自 Postgres。因为 Postgres 也分别提供了 -> 和 ->> 操作符,-> 也是保留双引号(get JSON object field by key),而 ->> 才能获取实际的字符串值(get JSON object field as text)[ doc, stackoverflow ]。
在笔者看来,这种需要通过 json_unquote() 才能获取实际字符串值的写法完全没有必要,因为很难想到有需要保留双引号的使用场景,而就获取实际的字符串值才是多数情况。实际上,SQLite 的开发者也持有相同的想法。2015 年 10 月,SQLite 3.9 发布,开始支持 JSON 类型 [ infoq, doc ]。简单对比下,可以发现 SQLite 提供的 JSON 函数和 MySQL 极其相似,很多函数同名并且同语义。SQLite 也提供了 json_extract() 函数,与 MySQL 不同,SQLite 返回的是移除双引号后的字符串(the dequoted text for a JSON string value)。看下示例:
1 | sqlite> select json_extract('{"id": 1, "name": "Will"}', '$.name'); |
对于提取 JSON 文档中的纯量(scalar),SQL 标准定义了的 json_value() 函数,MySQL 没有支持,但 Oracle、MariaDB、MSSQL 都有支持。MariaDB 在兼容 MySQL 的同时也支持 SQL 标准,json_extract() 和 json_value() 在 MariaDB 下都可用。来看下 SQL 示例:
1 | MariaDB [testdb]> select * from tbl; |
其他查询函数
除了上文的 json_extract() 函数,查询 JSON 文档相关的还有其他函数,如 json_contains()、json_contains_path()、json_keys()、json_search()。示例如下:
1 | mysql> set @j = '{"a": 1, "b": 2, "c": {"d": 4}}'; |
函数的完整定义和用法可以参考官方文档,本文不再一一举例说明。
修改 JSON
对于 MySQL 的 JSON 类型的数据,若要修改数据,可以使用类似如下的 SQL:
1 | mysql> select * from tbl where data->'$.id' = 2; |
如果要修改 JSON 内部数据,是否可以通过 JSON 路径表达式直接赋值呢?答案是,不行,MySQL 不支持。
1 | -- 语法错误,不支持通过 JSON 路径表达式赋值,修改 JSON 数据 |
MySQL 提供了数个函数来修改 JSON 数据。我们先来看看 json_replace()、json_set() 和 json_insert() 这三个函数:
- json_replace():替换值。替换旧值,但不插入新值
- json_set():设置值。替换旧值,或插入新值
- json_insert():插入值。只插入新值,不替换旧值
json_insert() 只能插入数据, json_replace() 只能更新数据,json_set() 能更新或插入数据。
替换值,json_replace() 示例:
1 | -- 使用 json_replace() 函数 |
设置值,json_set() 示例:
1 | -- 使用 json_set() 函数 |
插入值,json_insert() 示例:
1 | -- 使用 json_set() 函数 |
现在,我们来看下修改 JSON 数组的两个函数,json_array_insert() 和 json_array_append(),函数定义如下:
1 | json_array_insert(json_doc, path, val[, path, val] ...) |
json_array_insert(),参数 path 必须指向 JSON 数组某个位置的元素,若该位置存在值,将会把 val 插入该位置,然后其他元素向右移动;若该位置超出数组大小范围,将会把 val 插入到数组末尾。SQL 示例如下:
1 | mysql> set @j = '["a", {"b": [1, 2]}, [3, 4]]'; |
json_array_append(),如果参数 path 指向的 JSON 是数组,将在数组末尾添加元素;如果参数 path 指向的 JSON 是值或对象,该值或对象将被包裹为数组,然后在这个数组末尾添加元素。
1 | mysql> set @j = '["a", {"b": [1, 2]}, [3, 4]]'; |
除了上文提到的函数,还有 json_merge_patch()、json_merge_preserve()、json_remove() 这个些函数,可以参考官方文档的介绍,本文不再一一举例说明。
索引 JSON:生成列
现在来看下根据 JSON 列查询表数据的执行计划,如下:
1 | mysql> explain select * from tbl where data -> "$.id" = 1 \G |
可以看到,因为没有加索引,访问类型是全表扫描 type: ALL。来试下在 JSON 类型的 data 列上添加索引,会提示如下错误:
1 | mysql> alter table tbl add index (data); |
对于索引 JSON 类型列问题,MySQL 文档有如下阐述 [ doc ]:
JSON columns, like columns of other binary types, are not indexed directly; instead, you can create an index on a generated column that extracts a scalar value from the JSON column. See Indexing a Generated Column to Provide a JSON Column Index, for a detailed example.
就是说,不能直接在 JSON 列上创建索引;替代方式是,先创建提取 JSON 纯量的生成列(generated column),然后在这个生成列上创建索引。回过头来,ERROR 3152,这个报错提示信息其实让人有点困惑,对没仔细阅读文档的人来说,可能会误以为 MySQL 不支持索引 JSON 列(Bug #81364)。于是,在 MySQL 8.0 错误提示信息优化为:
ERROR 3152 (42000): JSON column '%s' supports indexing only via generated columns on a specified JSON path.
生成列以及在生成列上创建索引,是 MySQL 5.7 开始支持的新特性。但其实,在 SQL:2003 标准中,生成列就早已经被定义为可选特性,“Optional Features of SQL/Foundation:2003, T175 Generated columns”。这个特性在其他 DBMS 中很早就有支持。2007 年 9 月发布的 Oracle Database 11g 开始支持生成列,不过它们称之为称之为虚拟列(virtual column)。2008 年 8 月发布的 SQL Server 2008 开始支持计算列(computed column),实现的就是 SQL 标准中的生成列。在相近的时间点,MySQL 创建了WL#411: Computed virtual columns as MS SQL server has。之后,MySQL 的社区贡献者 Andrey Zhakov 实现了 WL#411 描述的特性,并发布了实现的代码补丁 [ ref, blog, doc ]。可惜的是 MySQL 官方很长一段时间都没把这个补丁合并进来,直到 2015 年的 MySQL 5.7(7年后)才官方实现 WL#411,同时 WL#411 的标题也被更新为符合 SQL 标准术语的 “Generated columns”。与之相对比的是,2010 年 4 月发布的 MariaDB 5.2 就开始支持虚拟列,实现上同样也是基于 Andrey Zhakov 贡献的代码 [ ref ]。关于生成列或虚拟列,wikipedia 总结了各大 DBMS 的支持情况,可以参阅。总结下,标准 SQL 定义生成列的语法和 SQL Server 2008、Oracle 11g、MariaDB、MySQL 的区别 [ ref1, ref2 ]:
1 | Standard MSSQL 2008 Oracle 11g MariaDB 10.1 MySQL 5.7 |
回到正题,我们现在来试试 MySQL 的生成列:
1 | -- 添加生成列 |
上面的示例,创建生成列 id,生成列对应的表达式是 data -> "$.id"。现在再试试在生成列 id 上,创建索引:
1 | -- 在生成列上创建索引 idx_id |
从上面的执行计划可以看到,查询条件用 id 或者 data -> "$.id" 都能使用索引 idx_id。
JSON 二进制格式
内部实现上,保存到数据库的 JSON 数据并非以 JSON 文本存储,而是二进制格式,具体可以参见,WL#8132: JSON datatype and binary storage format,当然也可以直接阅读源码 json_binary.h、json_binary.cc(doxygen)。
MySQL 的 JSON 二进制格式,其中有一点比较值得注意,WL#8132 提到:
The keys are sorted, so that lookup can use binary search to locate the key quickly.
就是,为了能利用二分搜索快速定位键,存入数据库的JSON 对象的键是被排序过的。来看下下面的 SQL:
1 | mysql> truncate tbl; |
上面的 SQL 可以看到,insert 写入时键并没有按次序排列,而用 select 将 JSON 数据反序列化读出,发现实际保存的键是有序的。排序规则是,先按字符串长度排序,若长度相同按字母排序。同样的,键关联的值,按键排序后的次序排列。对键排序,显然只能针对 JSON 对象,若要存储 JSON 数组,值按索引位置排序。
MySQL 5.7.22 新增 json_storage_size() 函数,用于返回 json 文档二进制表示占用的存储空间。先来看下 SQL 示例:
1 | mysql> select json_storage_size('"abc"'); |
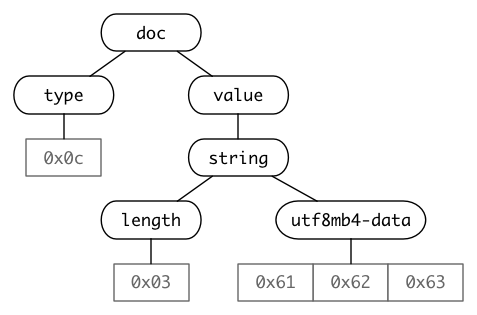
WL#8132 给出了 JSON 二进制格式的 BNF 语法描述。参考这个语法描述,可以推算出上文示例中的 "abc"、[42, "xy", "abc"]、{"b": 42, "a": "xy"} 对应的二进制表示。先来看下 "abc" 纯量,语法推导过程如下:
1 | doc |
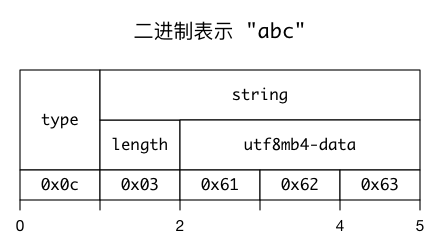
对应的二进制值,共 5 个字节,依次为 0x0c 0x03 0x61 0x62 0x63,其中 0x61 0x62 0x63,就是 16 进制表示的字符串 abc。占用 5个字节,与 json_storage_size() 函数返回的结果一致。相应的语法树如下:
从二进制的角度看,纯量 "abc" 的 JSON 二进制表示如下:
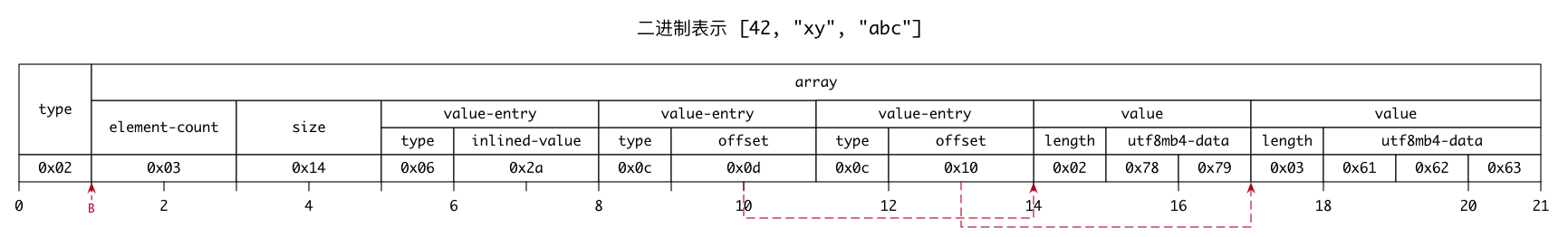
[42, "xy", "abc"] 的推导过程,如下:
1 | doc |
[42, "xy", "abc"] 对应的二进制表示,共 21 个字节,依次为 0x02 0x03 0x00 0x14 0x00 0x06 0x2a 0x00 0x0c 0x0d 0x00 0x0c 0x10 0x00 0x02 0x78 0x79 0x03 0x61 0x62 0x63。如下图:
相对来说,产生式 array ::= element-count size value-entry* value*,是整个JSON 数组二进制表示语法的核心。element-count,表示元素个数。上图中,第 4、5 个字节是 size 字段,十进制值为 20(0x14),是完整二进制表示去掉开头 type 字段后的大小(文档没有明确这个字段的含义,不过通过源码推断出来)。另外,value-entry 由 type 和 offset-or-inlined-value 字段组成。type 很好理解,不做解释。offset-or-inlined-value 字段,官方文档给出了含义,含义如下:
1 | // This field holds either the offset to where the value is stored, |
就是说,如果实际要保存的值足够小,将直接内联在这个字段中,否则将保存偏移量(offset),也就是指向实际值的指针。在示例中,保存 xy 对应的 offset 值为 13(0x0d),指向的相对地址是 14。因为这里的 offset 并不是以相对地址 0 为基准地址,是以相对地址 1 为基准地址(图中箭头 B 指向的位置),所以偏移量是 13 而不是 14(这个字段的明确含义也是从源码推断而来)。类似的,保存 abc 对应的 offset 值为 16(0x10),指向的相对地址是 17。
阅读文档容易发现,element-count、size、offset 字段占用的字节大小是固定的,小 JSON(64KB 以内)是 2 字节,大 JSON 是 4 字节。所以,若要查找 JSON 数组的第 pos 个元素的 value-entry 的偏移量,可以使用下面的式子快速定位:
1 | entry_offset = offset_size * 2 + (1 + offset_size) * pos |
JSON 数组二进制表示的其他字段比较容易理解,文档都有解释,就不展开阐述了。
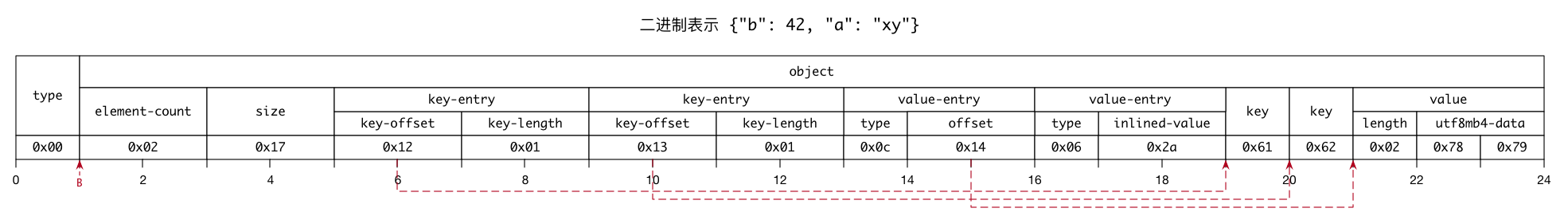
现在来看下,JSON 对象 {"b": 42, "a": "xy"} 的二进制表示,如下图:
对于 JSON 对象二进制表示的语法,核心的产生式是 object ::= element-count size key-entry* value-entry* key* value*。element-count、size 和 value-entry 字段,在 JSON 数组中也有,不再赘述。而 key-entry 字段,类似于 value-entry。key-entry 中的 key-offset 保存的是偏移量,是指向键的指针。另外,正如上文提到的 MySQL 会对 JSON 键排序,所以上图示例的第 20 和 21 个字节值分别是 0x61和 0x62,即 a 和 b,而非 b 和 a。同样的,键关联的值,按键排序后的次序排列,依次是 "xy" 和 42。
- MySQL 5.7 Reference Manual, 12 Data Types, 12.6 The JSON Data Type http://dev.mysql.com/doc/refman/5.7/en/json.html
- MySQL 5.7 Reference Manual, 13 Functions and Operators, 13.16 JSON Functions https://dev.mysql.com/doc/refman/5.7/en/json-functions.html
- 2015-08 MySQL 5.7 Release Notes, Changes in MySQL 5.7.8 https://dev.mysql.com/doc/relnotes/mysql/5.7/en/news-5-7-8.html
- 2015-04 JSON Labs Release: Native JSON Data Type and Binary Format http://mysqlserverteam.com/json-labs-release-native-json-data-type-and-binary-format/
- 2015-04 JSON Labs Release: JSON Functions, Part 1 — Manipulation JSON Data http://mysqlserverteam.com/json-labs-release-json-functions-part-1-manipulation-json-data/
- 2015-04 JSON Labs Release: JSON Functions, Part 2 — Querying JSON Data http://mysqlserverteam.com/mysql-5-7-lab-release-json-functions-part-2-querying-json-data/
- 2015-10 JSON in MariaDB 10.2 https://lists.launchpad.net/maria-developers/msg08954.html
- What is the difference between
->>and->in Postgres SQL? https://stackoverflow.com/a/47270495 - 2018-04 How to Use JSON in MySQL Wrong https://www.slideshare.net/billkarwin/how-to-use-json-in-mysql-wrong
- 2014-10 Generated Columns in MySQL 5.7.5 https://mysqlserverteam.com/generated-columns-in-mysql-5-7-5/
- 2016-03 Indexing JSON documents via Virtual Columns https://mysqlserverteam.com/indexing-json-documents-via-virtual-columns/
- 2016-02 Generated columns in MariaDB and MySQL https://planet.mysql.com/entry/?id=5994068
- 2017-06 What's New in SQL:2016 https://modern-sql.com/blog/2017-06/whats-new-in-sql-2016
Recommend
About Joyk
Aggregate valuable and interesting links.
Joyk means Joy of geeK