

Immutable.js及在React中的应用
source link: http://zhenhua-lee.github.io/react/Immutable.html?
Go to the source link to view the article. You can view the picture content, updated content and better typesetting reading experience. If the link is broken, please click the button below to view the snapshot at that time.

1. 为什么需要Immutable.js
1.1 引用带来的副作用
Shared mutable state is the root of all evil(共享的可变状态是万恶之源)
javascript(es5)中存在两类数据结构: primitive value(string、number、boolean、null、undefined)、object(reference)。在编译型语言(例如java)也存在object,但是js中的对象非常灵活、多变,这给我们的开发带来了不少好处,但是也引起了非常多的问题。
业务场景1:
var obj = {
count: 1
};
var clone = obj;
clone.count = 2;
console.log(clone.count) // 2
console.log(obj.count) // 2
业务场景2:
var obj = {
count: 1
};
unKnownFunction(obj);
console.log(obj.count) // 不知道结果是多少?
1.2 深度拷贝的性能问题
针对引用的副作用,有人会提出可以进行深度拷贝(deep clone), 请看下面深度拷贝的代码:
function isObject(obj) {
return typeof obj === 'object';
}
function isArray(arr) {
return Array.isArray(arr);
}
function deepClone(obj) {
if (!isObject(obj)) return obj;
var cloneObj = isArray(obj) ? [] : {};
for(var key in obj) {
if (obj.hasOwnProperty(key)) {
var value = obj[key];
var copy = value;
if (isObject(value)) {
cloneObj[key] = deepClone(value);
} else {
cloneObj[key] = value;
}
}
}
return cloneObj;
}
var obj = {
age: 5,
list: [1, 2, 3]
};
var obj2 = deepClone(obj)
console.log(obj.list === obj2.list) // false
假如仅仅只是对obj.age进行操作,使用深度拷贝同样需要拷贝list字段,而两个对象的list值是相同的,对list的拷贝明显是多余,因此深度拷贝存在性能缺陷的问题。
var obj = {
age: 5,
list: [1, 2, 3]
};
var obj2 = deepClone(obj)
obj2.age = 6;
// 假如仅仅只对age字段操作,使用深度拷贝(deepClone函数)也对list进行了复制,
// 这样明显是多余的,存在性能缺陷
1.3 js本身的无力
在js中实现数据不可变,有两个方法: const(es6)、Object.freeze(es5)。但是这两种方法都是shallow处理,遇到嵌套多深的结构就需要递归处理,又会存在性能上的问题。
2. Immutable的优点
2.1 Persistent data structure
Immutable.js提供了7种不可变的数据类型: List、Map Stack OrderedMap Set OrderedSet Record。对Immutable对象的操作均会返回新的对象,例如:
var obj = {count: 1};
var map = Immutable.fromJS(obj);
var map2 = map.set('count', 2);
console.log(map.get('count')); // 1
console.log(map2.get('count')); // 2
关于Persistent data structure 请查看 wikipedia
2.2 structural sharing
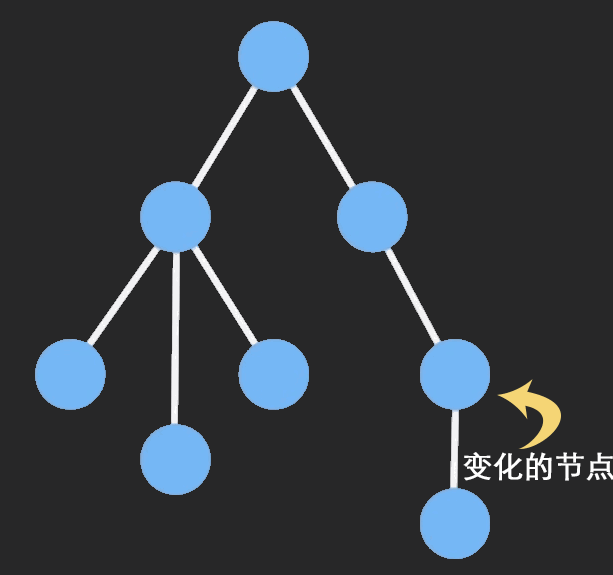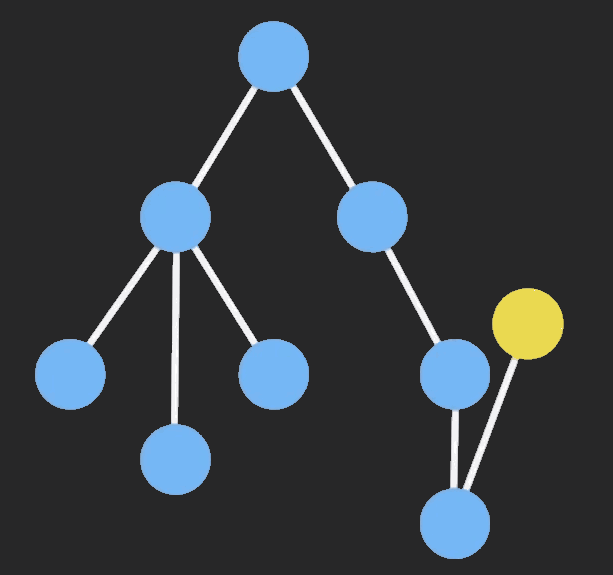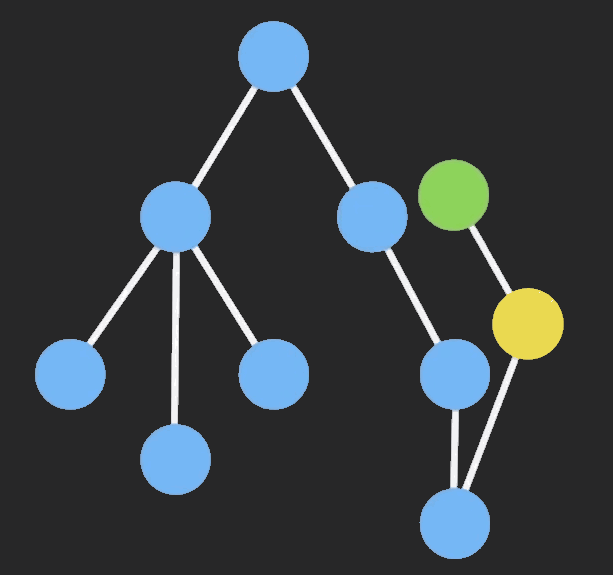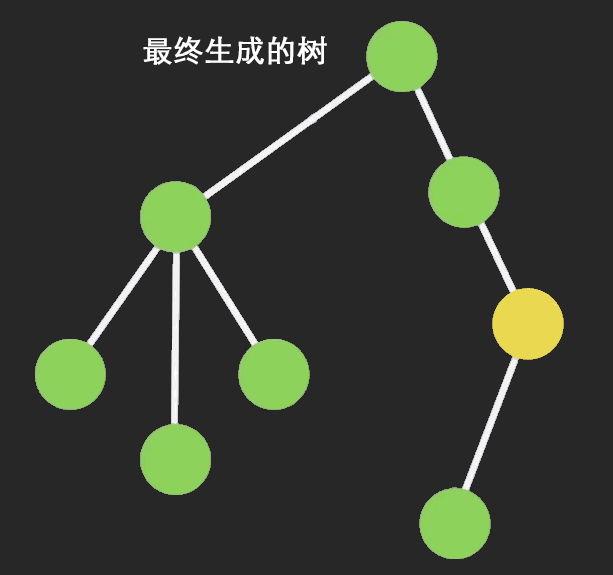
当我们对一个Immutable对象进行操作的时候,ImmutableJS基于哈希映射树(hash map tries)和vector map tries,只clone该节点以及它的祖先节点,其他保持不变,这样可以共享相同的部分,大大提高性能。
var obj = {
count: 1,
list: [1, 2, 3, 4, 5]
}
var map1 = Immutable.fromJS(obj);
var map2 = map1.set('count', 2);
console.log(map1.list === map2.list); // true
从网上找一个图片来说明结构共享的过程:
2.3 support lazy operation
ImmutableJS借鉴了Clojure、Scala、Haskell这些函数式编程语言,引入了一个特殊结构Seq(全称Sequence), 其他Immutable对象(例如List、Map)可以通过toSeq进行转换。
Seq具有两个特征: 数据不可变(Immutable)、计算延迟性(Lazy)。在下面的demo中,直接操作1到无穷的数,会超出内存限制,抛出异常,但是仅仅读取其中两个值就不存在问题,因为没有对map的结果进行暂存,只是根据需要进行计算。
Immutable.Range(1, Infinity)
.map(n => -n)
// Error: Cannot perform this action with an infinite size.
Immutable.Range(1, Infinity)
.map(n => -n)
.take(2)
.reduce((r, n) => r + n, 0);
// -3
2.4 强大的API机制
ImmutableJS的文档很Geek,提供了大量的方法,有些方法沿用原生js的类似,降低学习成本,有些方法提供了便捷操作,例如setIn、UpdateIn可以进行深度操作。
var obj = {
a: {
b: {
list: [1, 2, 3]
}
}
};
var map = Immutable.fromJS(obj);
var map2 = Immutable.updateIn(['a', 'b', 'list'], (list) => {
return list.push(4);
});
console.log(map2.getIn(['a', 'b', 'list']))
// List [ 1, 2, 3, 4 ]
3. 在React中的实践
3.1 快 - 性能优化
React是一个UI = f(state)库,为了解决性能问题引入了virtual dom,virtual dom通过diff算法修改DOM,实现高效的DOM更新。
听起来很完美吧,但是有一个问题: 当执行setState时,即使state数据没发生改变,也会去做virtual dom的diff,因为在React的声明周期中,默认情况下shouldComponentUpdate总是返回true。那如何在shouldComponentUpdate进行state比较?
React的解决方法: 提供了一个PureRenderMixin, PureRenderMixin对shouldComponentUpdate方法进行了覆盖,但是PureRenderMixin里面是浅比较:
var ReactComponentWithPureRenderMixin = {
shouldComponentUpdate: function(nextProps, nextState) {
return shallowCompare(this, nextProps, nextState);
},
};
function shallowCompare(instance, nextProps, nextState) {
return (
!shallowEqual(instance.props, nextProps) ||
!shallowEqual(instance.state, nextState)
);
}
浅比较只能进行简单比较,如果数据结构复杂的话,依然会存在多余的diff过程,说明PureRenderMixin依然不是理想的解决方案。
Immutable来解决: 因为Immutable的结构不可变性&&结构共享性,能够快速进行数据的比较:
shouldComponentUpdate: function(nextProps, nextState) {
return deepCompare(this, nextProps, nextState);
},
function deepCompare(instance, nextProps, nextState) {
return !Immutable.is(instance.props, nextProps) ||
!Immutable.is(instance.state, nextState);
}
3.2 安全 - 保证state操作的安全
当我们在React中执行setState的时候,需要注意的,state merge过程是shallow merge:
getInitState: function () {
return {
count: 1,
user: {
school: {
address: 'beijing',
level: 'middleSchool'
}
}
}
},
handleChangeSchool: function () {
this.setState({
user: {
school: {
address: 'shanghai'
}
}
})
}
render() {
console.log(this.state.user.school);
// {address: 'shanghai'}
}
为了让大家安心,贴上React中关于state merge的源码:
// 在 ReactCompositeComponent.js中完成state的merge,其中merger的方法来源于
// `Object.assign`这个模块
function assign(target, sources) {
....
var to = Object(target);
...
for (var nextIndex = 1; nextIndex < arguments.length; nextIndex++) {
var nextSource = arguments[nextIndex];
var from = Object(nextSource);
...
for (var key in from) {
if (hasOwnProperty.call(from, key)) {
to[key] = from[key];
}
}
}
return to
}
3.3 方便 - 强大的API
ImmutableJS里面拥有强大的API,并且文档写的很Geek,在对state、store进行操作的时候非常方便。
var obj = {
name: 'mt',
info: {
address: 'bj'
}
};
Object.freeze(obj);
obj.name = 'mt&&dp';
obj.info.address = 'bj&&sh';
console.log(obj.name); // 'mt'(no change)
console.log(obj.info.address); // 'bj&&sh'(change)
3.4 历史 - 实现回退
可以保存state的每一个状态,并保证该状态不会被修改,这样就可以实现历史记录的回退。
4. React中引入Immutable.js带来的问题
- 源文件过大: 源码总共有5k多行,压缩后有16kb
- 类型转换: 如果需要频繁地与服务器交互,那么Immutable对象就需要不断地与原生js进行转换,操作起来显得很繁琐
- 侵入性: 例如引用第三方组件的时候,就不得不进行类型转换;在使用react-redux时,connect的
shouldComponentUpdate已经实现,此处无法发挥作用
Recommend
About Joyk
Aggregate valuable and interesting links.
Joyk means Joy of geeK