

Difference Between @Component, @Repository, @Service, and @Controller Annotation...
source link: https://www.geeksforgeeks.org/difference-between-component-repository-service-and-controller-annotations-in-spring/
Go to the source link to view the article. You can view the picture content, updated content and better typesetting reading experience. If the link is broken, please click the button below to view the snapshot at that time.
Difference Between @Component, @Repository, @Service, and @Controller Annotations in Spring
Spring Annotations are a form of metadata that provides data about a program. Annotations are used to provide supplemental information about a program. It does not have a direct effect on the operation of the code they annotate. It does not change the action of the compiled program. Here, we are going to discuss the difference between the 4 most important annotations in Spring, @Component, @Repository, @Service, and @Controller.
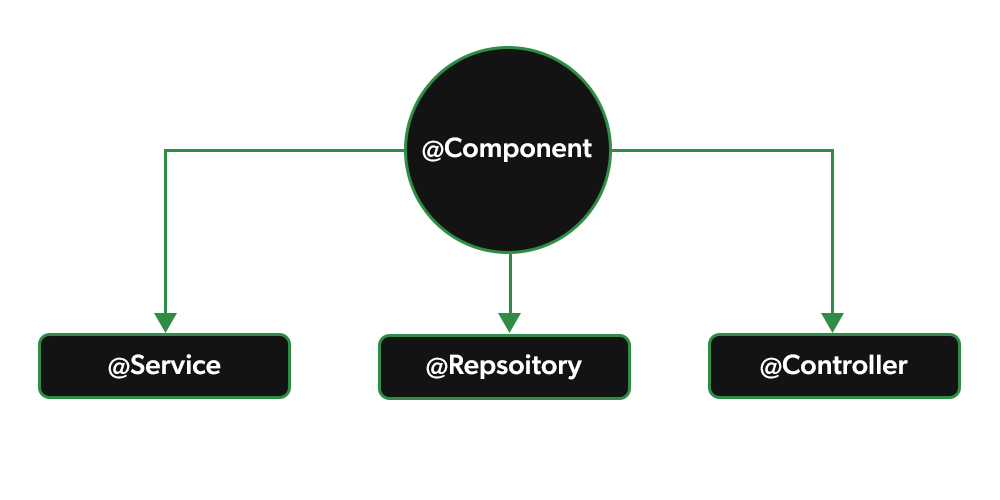
@Component Annotation
@Component is a class-level annotation. It is used to denote a class as a Component. We can use @Component across the application to mark the beans as Spring’s managed components. A component is responsible for some operations. Spring framework provides three other specific annotations to be used when marking a class as a Component.
- @Service
- @Repository
- @Controller
To read more about @Component Annotation refer to the articleSpring @Component Annotation
A. @Service Annotation
In an application, the business logic resides within the service layer so we use the @Service Annotation to indicate that a class belongs to that layer. It is a specialization of @Component Annotation. One most important thing about the @Service Annotation is it can be applied only to classes. It is used to mark the class as a service provider. So overall @Service annotation is used with classes that provide some business functionalities. Spring context will autodetect these classes when annotation-based configuration and classpath scanning is used.
To read more about @Service Annotation refer to the article Spring @Service Annotation
B. @Repository Annotation
@Repository Annotation is also a specialization of @Component annotation which is used to indicate that the class provides the mechanism for storage, retrieval, update, delete and search operation on objects. Though it is a specialization of @Component annotation, so Spring Repository classes are autodetected by the spring framework through classpath scanning. This annotation is a general-purpose stereotype annotation which very close to the DAO pattern where DAO classes are responsible for providing CRUD operations on database tables.
To read more about @Repository Annotation refer to the article Spring @Repository Annotation
C. @Controller Annotation
Spring @Controller annotation is also a specialization of @Component annotation. The @Controller annotation indicates that a particular class serves the role of a controller. Spring Controller annotation is typically used in combination with annotated handler methods based on the@RequestMapping annotation. It can be applied to classes only. It’s used to mark a class as a web request handler. It’s mostly used with Spring MVC applications. This annotation acts as a stereotype for the annotated class, indicating its role. The dispatcher scans such annotated classes for mapped methods and detects @RequestMapping annotations.
To read more about @Controller Annotation refer to the article Spring @Controller Annotation
Similarity
One of the interesting queries that arise in front of a developer is, can @Component, @Repository, @Service, and @Controller annotations be used interchangeably in Spring or do they provide any particular functionality? In other words, if we have a Service class and we change the annotation from @Service to @Component, will it still behave the same way?
So in order to answer the same, it is with respect to scan-auto-detection and dependency injection for BeanDefinition, all these annotations (@Component, @Repository, @Service, and @Controller) are the same. We could use one in place of another and can still get our way around.
By now it is made clear that @Component is a general-purpose stereotype annotation indicating that the class is a spring component and @Repository, @Service, and @Controller annotations are special types of @Component annotation. Now let us finally conclude via plotting the difference table between all annotation types to grasp a better understanding that is as follows:
|
@Service Annotation |
@Repository Annotation |
@Controller Annotation |
|---|---|---|
| @Service annotation is used with classes that provide some business functionalities. | @Repository Annotation is used to indicate that the class provides the mechanism for storage, retrieval, update, delete and search operation on objects. | @Controller annotation indicates that a particular class serves the role of a controller. |
| @Service Annotation is a specialization of @Component Annotation. | @Repository Annotation is also a specialization of @Component Annotation. | @Controller annotation is also a specialization of @Component annotation. |
| It is used to mark the class as a service provider. | It is used to mark the interface as DAO (Data Access Object) provider. | It’s used to mark a class as a web request handler. |
| It is a stereotype for the service layer. | It is also a stereotype for the DAO layer. | It is also a stereotype for the presentation layer (spring-MVC). |
| Switch can be possible. But it is not recommended. | Switch can be possible. But it is not recommended. | We cannot switch this annotation with any other like @Service or @Repository. |
| It is a Stereotype Annotation. | It is also a Stereotype Annotation. | It is also a Stereotype Annotation. |
Feeling lost in the vast world of Backend Development? It's time for a change! Join our Java Backend Development - Live Course and embark on an exciting journey to master backend development efficiently and on schedule.
What We Offer:
- Comprehensive Course
- Expert Guidance for Efficient Learning
- Hands-on Experience with Real-world Projects
- Proven Track Record with 100,000+ Successful Geeks
Recommend
About Joyk
Aggregate valuable and interesting links.
Joyk means Joy of geeK