

Build an Uno Platform app with Azure Mobile Apps
source link: https://learn.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/developer/mobile-apps/azure-mobile-apps/quickstarts/uno/
Go to the source link to view the article. You can view the picture content, updated content and better typesetting reading experience. If the link is broken, please click the button below to view the snapshot at that time.
Build an Uno Platform app with Azure Mobile Apps
- Article
- 06/12/2023
In this article
The Uno Platform lets you create .NET UI applications for Windows, macOS, Linux, iOS, Android, and Web Assembly from a single codebase. This tutorial shows you how to add a cloud-based backend service to an Uno Platform Android mobile app by using Azure Mobile Apps and an Azure mobile app backend. You create both a new mobile app backend and a simple Todo list app that stores app data in Azure.
You must complete this tutorial before all other Uno Platform tutorials about using Azure Mobile Apps.
Although the Uno Platform supports a wide variety of platforms, the Azure Mobile Apps library is only supported on mobile and desktop platforms. The tutorial only covers the Android platform.
Prerequisites
To complete this tutorial, you need:
- Visual Studio 2022 with the following workloads.
- ASP.NET and web development
- Azure development
- .NET desktop development
- .NET Multi-platform App UI development
- The Uno Platform for Visual Studio extension.
- An Azure account.
- The Azure CLI.
- Sign in with
az loginand select an appropriate subscription before starting.
- Sign in with
- For Android support, an Android Virtual Device with the following settings:
- Phone: Any phone image - we use the Pixel 5 for testing.
- System Image: Android 11 (API 30 with Google APIs)
This tutorial assumes you are using Windows and Visual Studio 2022. We recommend that you walk through the Uno Platform tutorial to become acquainted with the development process for the Uno Platform.
Download the sample app
Open the azure-mobile-apps repository in your browser.
Open the Code drop-down, then select Download ZIP.
Once the download is complete, open your Downloads folder and locate the
azure-mobile-apps-main.zipfile.Right-click the downloaded file, and select Extract All....
If you prefer, you can use PowerShell to expand the archive:
PowerShellC:\Temp> Expand-Archive azure-mobile-apps-main.zip
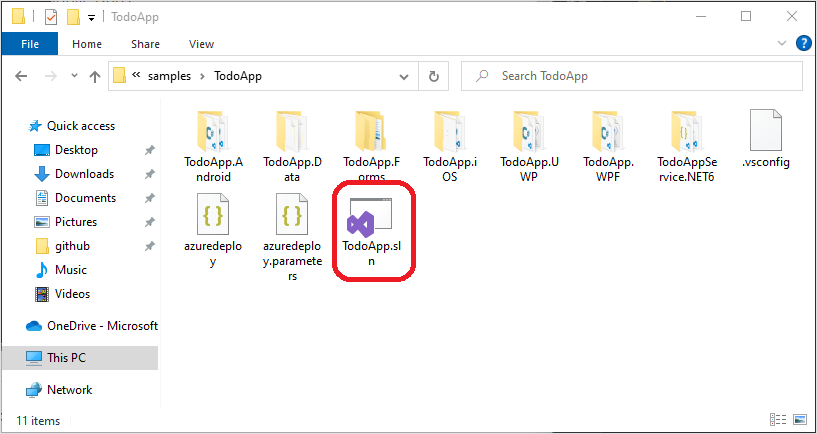
The samples are located in the samples folder within the extracted files. The sample for the quick start is named TodoApp. You can open the sample in Visual Studio by double-clicking the TodoApp.sln file.
Deploy the backend to Azure
If you have already deployed the backend from another quick start, you can use the same backend and skip this step.
To deploy the backend service, we will:
- Use Azure Resource Manager and the Azure CLI to deploy an Azure App Service and Azure SQL Database to Azure.
- Use Visual Studio to publish the service code to the newly created Azure App Service.
Create resources on Azure.
Open a terminal and change directory to the folder containing the
TodoApp.slnfile. This directory also containsazuredeploy.json.Ensure you've signed in and selected a subscription using the Azure CLI.
Create a new resource group:
Azure CLIaz group create -l westus -g quickstartThis command will create the
quickstartresource group in the West US region. You can select any region that you wish, providing you can create resources there. Ensure you use the same name and region wherever they're mentioned in this tutorial.Create the resources using a group deployment:
Azure CLIaz deployment group create -g quickstart --template-file azuredeploy.json --parameters sqlPassword=MyPassword1234Pick a strong password for your SQL Administrator password. You'll need it later on when accessing the database.
Once the deployment is complete, get the output variables as these hold important information you'll need later on:
Azure CLIaz deployment group show -g quickstart -n azuredeploy --query properties.outputsAn example output will be:
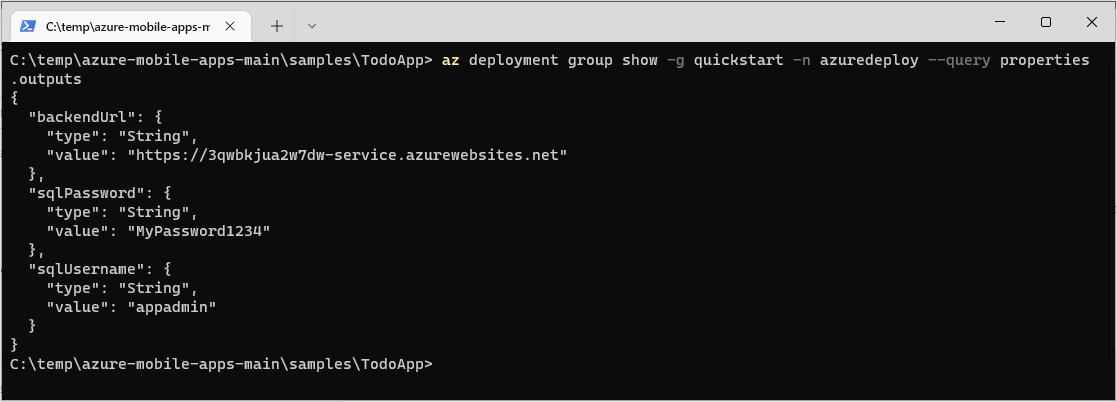
Make a note of each of the values in the outputs for later use.
Publish the service code.
Open the TodoApp.sln in Visual Studio.
In the right-hand pane, select the Solutions Explorer.
Right-click the
TodoAppService.NET6project, then select Set as Startup Project.On the top menu, select Build > Publish TodoAppService.NET6.
In the Publish window, select Target: Azure, then press Next.
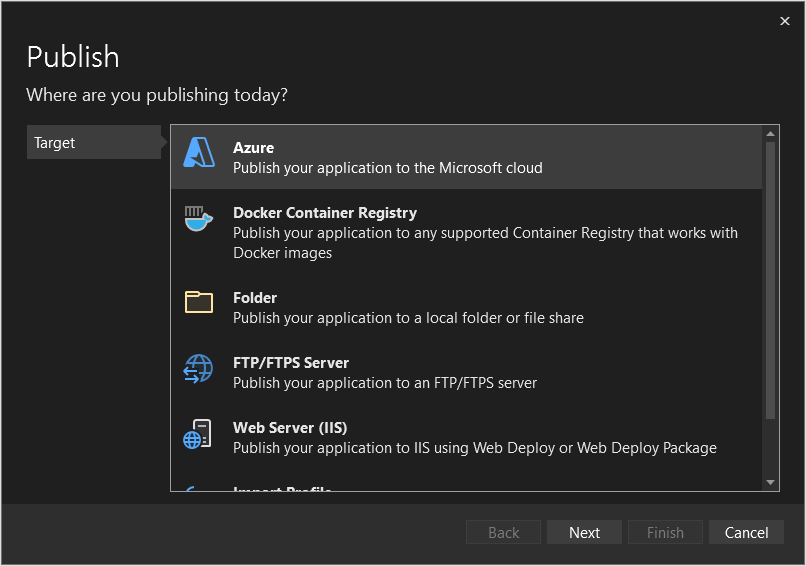
Select Specific target: Azure App Service (Windows), then press Next.
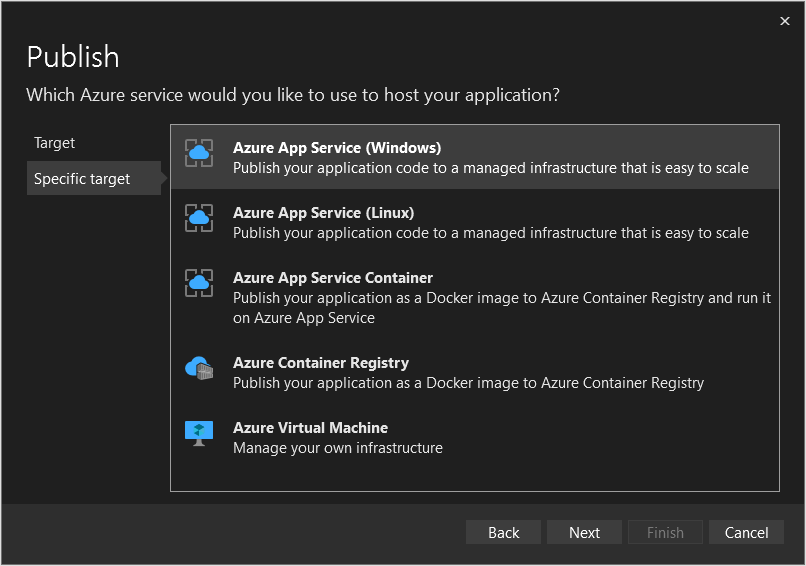
If necessary, sign in and select an appropriate Subscription name.
Ensure View is set to Resource group.
Expand the
quickstartresource group, then select the App Service that was created earlier.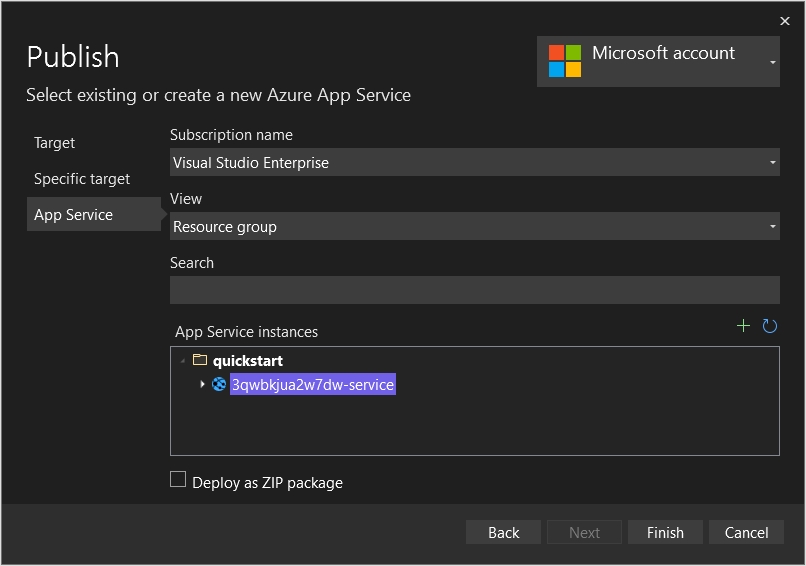
Select Finish.
Once the publish profile creation process has completed, select Close.
Locate the Service Dependencies and select the triple-dots next to the SQL Server Database, then select Connect.
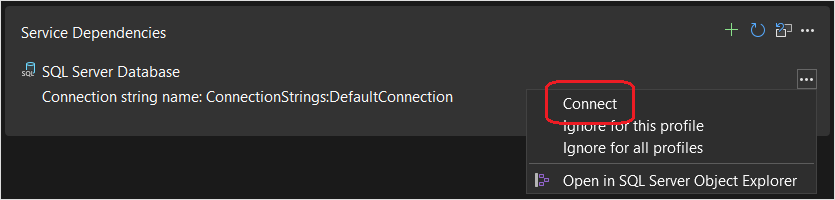
Select Azure SQL Database, then select Next.
Select the quickstart database, then select Next.
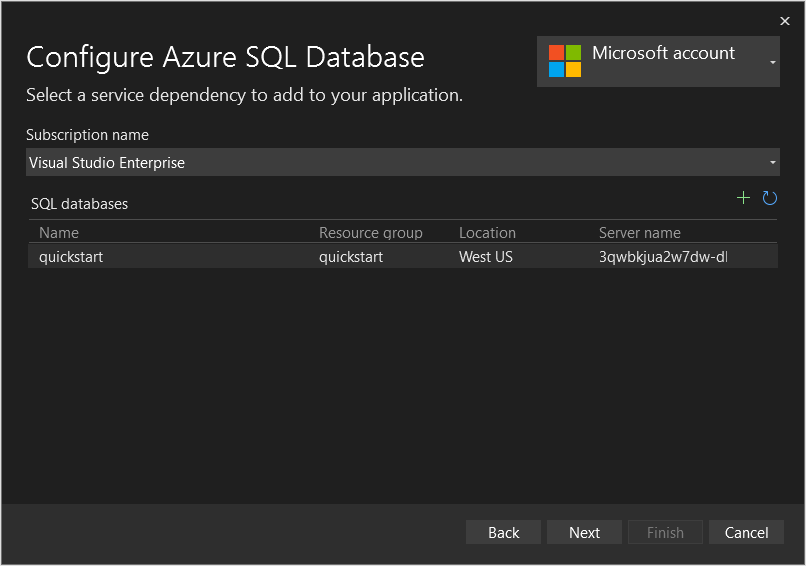
Fill in the form using the SQL username and password that were in the outputs of the deployment, then select Next.
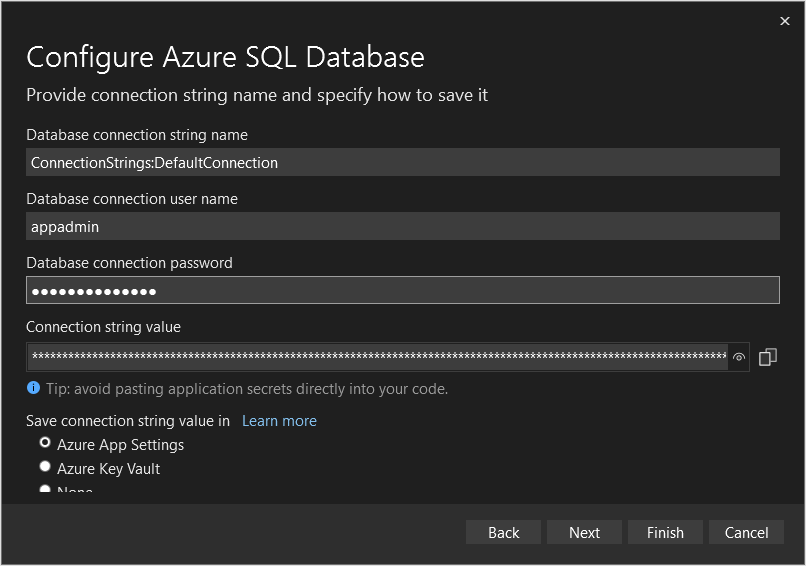
Select Finish.
Select Close when complete.
Select Publish to publish your app to the Azure App Service you created earlier.

Once the backend service is published, a browser will be opened. Add
/tables/todoitem?ZUMO-API-VERSION=3.0.0to the URL: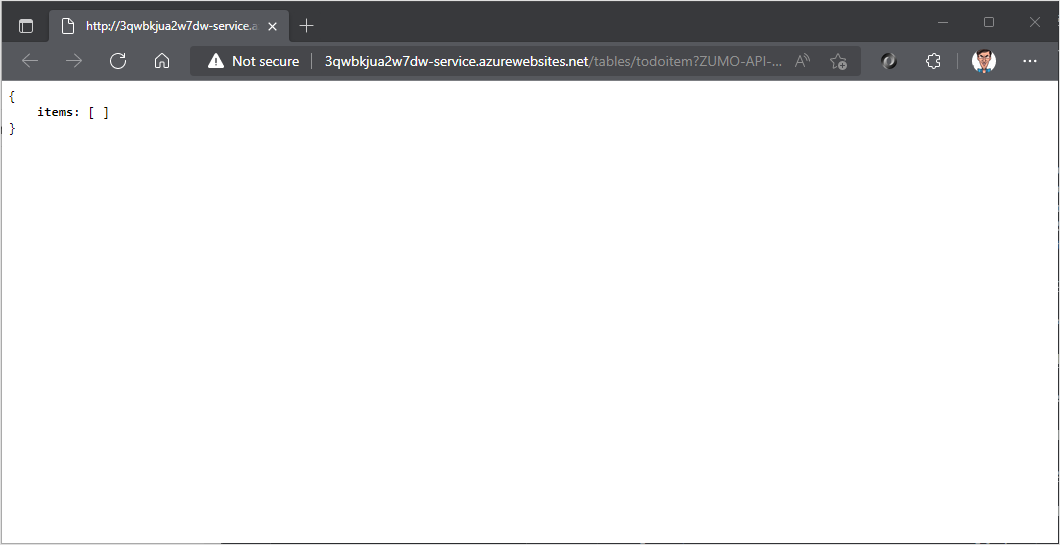
Configure the sample app
Your client application needs to know the base URL of your backend so that it can communicate with it.
Expand the
TodoApp.Dataproject.Right-click on the
TodoApp.Dataproject, then select Add > Class....Enter
Constants.csas the name, then select Add.
Open the
Constants.cs.examplefile and copy the contents (Ctrl-A, followed by Ctrl-C).Switch to
Constants.cs, highlight all text (Ctrl-A), then paste the contents from the example file (Ctrl-V).Replace the
https://APPSERVICENAME.azurewebsites.netwith the backend URL of your service.namespace TodoApp.Data { public static class Constants { /// <summary> /// The base URI for the Datasync service. /// </summary> public static string ServiceUri = "https://demo-datasync-quickstart.azurewebsites.net"; } }You can obtain the backend URL of your service from the Publish tab. Ensure you use a https URL.
Save the file. (Ctrl-S).
Build and run the sample app for Android
In the solutions explorer, expand the
uno/Platformsfolder.Right-click the
TodoApp.Uno.Mobileproject and select Set as Startup Project.In the top bar, select the Any CPU configuration, TodoApp.Uno.Mobile target. Select a suitable Android emulator to run the application:

Press F5 to build and run the project.
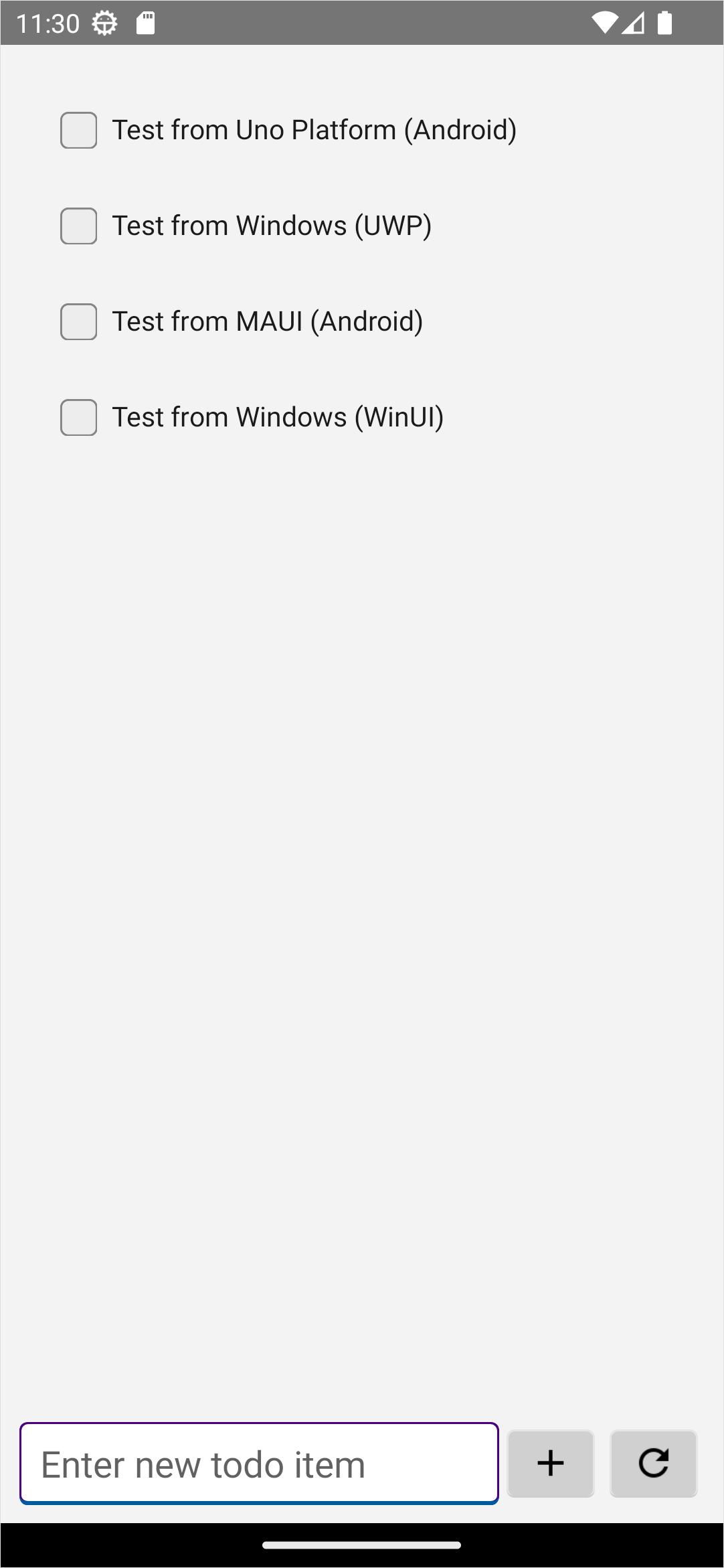
Once the app has started, you see an empty list with a text box. You can:
Enter some text, then press the + icon to add the item.
Set or clear the check box to mark any item as done.
Press the refresh icon to reload data from the service.
Next steps
Continue the tutorial by adding authentication to the app.
Recommend
About Joyk
Aggregate valuable and interesting links.
Joyk means Joy of geeK