How to Avoid Data Silos in Multi Clouds and Hybrid Cloud Integrations
source link: https://www.gigaspaces.com/blog/hybrid-cloud-integration
Go to the source link to view the article. You can view the picture content, updated content and better typesetting reading experience. If the link is broken, please click the button below to view the snapshot at that time.
Key Takeaways
Multi-cloud environments are complex and can lead to data silos which create business barriers to accessing data across different environments and lack of visibility. This in turn limits organizations’ ability to carry out meaningful data analysis and deliver modern data-driven services. An Operational Data Hub can solve these challenges by harmonizing data residing on-premises or in multiple clouds, enabling a cohesive data-driven approach to real-time analytics and new service creation.
Introduction: Challenges of Multi-Cloud Data Integration
As organizations move away from monolithic architecture, most find themselves using various combinations of on-premises and cloud solutions. Hybrid cloud refers to a mixed computing environment that benefits from the best advantages of on-premises data centers, private cloud, and public clouds. Adding to this complexity is multi-cloud, where organizations use more than one cloud based on considerations such as workload optimization, cost and geographic considerations. As noted by Gartner, multi-cloud increases management and governance challenges, increases the complexity and cost of IT, and demands greater skills. The data challenges that organizations face with multi-cloud and hybrid cloud integration include:
- Complexity: Each system may use different data formats
- Security and governance: each system may use different standards, but the organization usually needs a holistic, unified approach to its security; for heavily regulated industries, such as financial and healthcare, this lack of full control over their information systems is especially concerning
- Staff: experts with the required knowledge to integrate and manage data across these ecosystems are in short supply
- Occasional downtime: this can occur when adding or migrating services, or when one component fails for various reasons
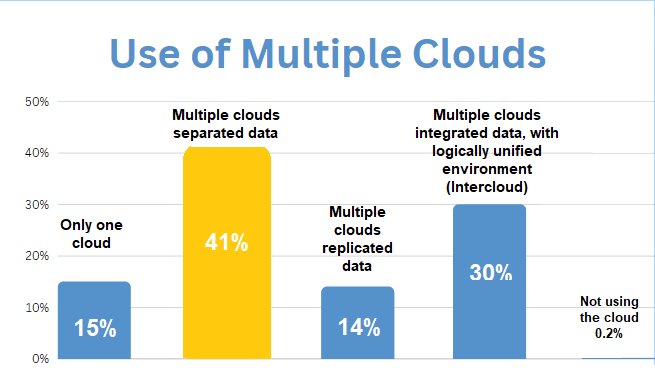
Data presented at the Gartner Data & Analytics Summit, London, 2023
Harmonizing Data Across Multi-Cloud and Hybrid Cloud Integrations
When operating in multi and hybrid cloud environments, enterprises may find that their data and applications are located in isolated or separate repositories that are not easily accessible or integrated with each other.
Data silos create business barriers to accessing data across different environments, leading to lack of visibility and limiting organizations’ ability to carry out meaningful data analysis and to delivering modern data-driven services. This may have a far reaching impact on business outcomes. Take for example, a multinational manufacturing company that was experiencing difficulties with numerous data silos. Their data is collected from over 1,000 technical interfaces, including SAP and other cloud-based and non-cloud systems. Although they use over 20 middleware platforms, the vast majority of this data does not flow through these middleware platforms. Needless to say, they searched for a solution that would consolidate and unify these numerous sources of structured, semi-structured and unstructured data. By incorporating an operational data hub they are able to integrate and centralize their data, and conduct analysis on comprehensive, accurate real-time information, promoting true business insights and faster time to market.
Let’s look at an innovative solution that harmonizes data from multiple cloud-based and on-premises systems which can address the challenges described above. This solution, an operational data hub, offers several advantages for creating a unified data model across hybrid cloud environments, enabling real-time analytics and data access services.
An operational data hub elegantly harmonizes data from systems residing in multiple clouds and hybrid environments, enabling a cohesive data mesh that allows data sharing among consuming apps and stakeholders. It utilizes a low-latency, scalable, high performance data layer to serve data to digital applications through RESTful APIs and events, using low code microservices. Consuming apps and digital services are decoupled from the underlying systems – wherever they reside – eliminating dependencies and ensuring 24×7 real-time availability. The operational data hub’s unified data model eliminates the chaos of numerous, simultaneous requests and responses between multiple systems, and streamlines these processes to enable timely responses.
Some of the key advantages of an operational data hub for hybrid cloud integrations are:
Faster Development and Deployment of Digital Services
With access to consolidated, accurate data, developers and data scientists can leverage the hub’s APIs and query interfaces to easily access data. The operational data hub provides a unified interface and data services layer that abstracts the complexities of the underlying hybrid cloud architecture. This simplifies data access and consumption for applications, analytics tools, and other data-driven services.
Centralized Data Management
An operational data hub consolidates data from on-premises systems and multiple cloud providers into a single hub, providing a unified, near real-time view of the organization’s data. This eliminates siloed data that can lead to incorrect insights based on partial information. Hubs can be colocated to support functional teams or Lines of Business, ensuring that each has control over their own data while being able to share it easily among them.
Real-time data integration from multiple sources into a unified data model
With an operational data hub, organizations can achieve near real-time data integration and synchronization across hybrid cloud environments, utilizing continuous data ingestion, processing, and delivery. Advanced event-driven data integration tools can reduce development overhead by automatically scanning the source schema and metadata, and mapping them to the unified data model. These tools ingest data sources such as relational databases, no-SQL databases, object stores, file systems, or message brokers, and integrate the data in streams and/or in batches.
Enables the Cloud Journey
An operational data hub abstracts modern applications from the underlying systems of record. A cloud strategy can be a lengthy process, starting application-by-application and workload-by-workload. The hub promotes a progressive cloud journey with the gradual migration of appropriate workloads. Organizations can leverage their investment in on-premises and cloud infrastructure, by maintaining their legacy systems for as long as required, and enabling continuation of services from all platforms.
Reverse Migration
Although the cloud continues to offer many benefits, a cloud backlash may have begun. While reducing ROI was a major incentive to migrate to the cloud, ubiquitous cloud adoption has led to cloud sprawl, with out-of-control costs and heightened complexity. Enterprises are now running core compute workloads and storing massive volumes of data in the cloud, all of which leads to escalating cloud expenses. As the price of hard drive storage has moved downwards, while cloud costs have remained relatively stable, moving workloads back on premises looks more attractive. Nvidia estimates that moving large, specialized AI and ML workloads back on premises can yield a 30% savings. This reverse migration can create a new hybrid configuration or maintain an existing hybrid architecture.
An operational data hub enables a progressive cloud journey, maintaining continuing service with no downtime, as various applications and services move to or from the cloud, or to different clouds.
Data Consistency and Quality
By consolidating data in an operational data hub, organizations can centralize data governance policies, data standards, and data quality rules. This centralization enables easier enforcement of data policies and helps to ensure consistent and high-quality data. These unified governance policies reduce the risk of data inconsistencies and errors, despite the fact that the data arrives from many disparate sources of data.
Scalability and Agility
An operational data hub can scale in response to business needs, scaling both vertically and horizontally to handle large volumes of data. This scalability and agility support the growth and evolving requirements of organizations that are in expansion mode. The hub also scales to support spikes in peak usage, ensuring continuous availability.
Disaster Recovery
In the event of a disaster or ransomware attack, the multi-cloud user can restore data stored in their other, separate cloud environment. Since cloud services continue to improve, data recovery can be executed nearly as quickly from a cloud as from on-premises infrastructure. For cloud-native companies keeping data in multiple public clouds reduces the risk of data loss when a single provider keeps both production and backup copies.
Cost Optimization
An operational data hub can reduce cloud costs and also maximize the business value of using the cloud. With centralized data management, organizations can optimize data processing resources, minimize data duplication and reduce data storage costs. An advanced operational data hub should offer tiered storage that automatically assigns data to different categories of storage types balancing performance, availability, cost and recovery options. The hub enables efficient data ingestion and data delivery, which reduces network and bandwidth costs associated with data movement across cloud environments.
Last Words
An operational data hub encourages a data-driven approach for successful application integration in hybrid and multi-cloud environments by:
- Empowering organizations to utilize data efficiently and carry out real-time analytics on data in multiple clouds
- Enabling the delivery of data driven services to modern digital applications that rely on data from diverse systems
Data driven organizations can use Operational Data Hubs to promote data-driven initiatives, enabling organizations to take advantage of all the flavors of cloud computing and legacy systems in an agile and innovative way.
Recommend
About Joyk
Aggregate valuable and interesting links.
Joyk means Joy of geeK