

Chaos 测试下的若干 NebulaGraph Raft 问题分析 - NebulaGraph
source link: https://www.cnblogs.com/nebulagraph/p/16981998.html
Go to the source link to view the article. You can view the picture content, updated content and better typesetting reading experience. If the link is broken, please click the button below to view the snapshot at that time.
Raft 是一种广泛使用的分布式共识算法。NebulaGraph 底层采用 Raft 算法实现 metad 和 storaged 的分布式功能。Raft 算法使 NebulaGraph 中的 metad 和 storaged 能够集群化部署、实现了多副本和高可用,同时 storaged 通过 multi-raft 模块实现了数据分片,分散了系统的负载,提升系统的吞吐。
作为分布式系统的基石 Raft 有非常明显的优势,但这也伴随着不小的挑战 —— Raft 算法的实现及其容易出错,同时算法的测试和调试也是一项巨大的挑战。NebulaGraph 目前使用的是自研的 Raft,鉴于 Raft 本身的复杂性我们构造了诸多 Chaos 测试来保障 NebulaGraph Raft 算法的稳定性。本文介绍几个我们使用 Chaos 测试发现的 NebulaGraph Raft 中比较有意思的问题。
Raft 背景知识
Raft 是一种广泛使用的分布式共识算法。一个 Raft 集群中的节点通过运行 Raft 算法保证各个节点之间复制日志序列。算法保证各个节点之间的日志序列是一致的,只要各个节点上的日志序列一致即可保证各个节点上数据的一致性。
Raft 是一种强主算法,系统通过选举产生一个主节点,用户向主节点提交日志,主节点再把日志复制到其他节点上。当一条日志复制到过半数的节点上后,Raft 即可认为这条日志已经提交成功,这条日志将无法被改写,Raft 算法保证这条日志后续能被复制到所有节点上。当一个主节点出现故障时,如 Crash、网络中断等,其他节点会在等待一段时间后发起新的一轮选举选出主节点,后续由这个新的主节点协调集群的工作。
Raft 中有一个 Term 概念,Term 是一个单调递增的非负整数,每个节点都有一个 Term 值,节点在发起选举前会先递增本地的 Term。同一个 Term 内最多只能有一个主节点,否则就意味着 Raft 出现脑裂。「脑裂」在 Raft 中是极其严重的故障,它意味着 Raft 的数据安全无法得到保障——两个主节点可以同时向从节点复制不同的日志数据,而从节点无条件信任主节点的请求。Term 在 Raft 中是一个逻辑时钟的概念,更高值的 Term 意味着 Raft 集群已经进入新时代;当一个 Raft 节点看到更高的 Term 值时需要更新它本地的 Term 值(跟着别人进入新时代),同时转变为从节点;忽略 Term 的更新可能会导致 Raft 集群选举异常,我们后面一个故障的例子即跟这点有关。
NebulaGraph Raft 踩坑记录
在介绍了 Raft 的背景知识后,本节我们介绍几个通过 Chaos 测试发现并处理的 NebulaGraph Raft 故障。
线程池死锁问题
这是在 NebulaGraph v2.6 之前发现的一个很有意思的问题。具体情况是,在一个五节点的集群中运行压测程序,运行我们的设计好的 Chaos 测试,基本上十几分钟后就能看到一个存储节点状态变成离线状态,但查看离线离线节点却发现存储服务还在运行:
(root@nebula) [(none)]> show hosts;
+-----------------+-------+-----------+--------------+----------------------+------------------------+
| Host | Port | Status | Leader count | Leader distribution | Partition distribution |
+-----------------+-------+-----------+--------------+----------------------+------------------------+
| "192.168.15.11" | 33299 | "OFFLINE" | 0 | "No valid partition" | "ttos_3p3r:1" |
+-----------------+-------+-----------+--------------+----------------------+------------------------+
| "192.168.15.11" | 54889 | "ONLINE" | 0 | "No valid partition" | "ttos_3p3r:1" |
+-----------------+-------+-----------+--------------+----------------------+------------------------+
| "192.168.15.11" | 34679 | "ONLINE" | 1 | "ttos_3p3r:1" | "ttos_3p3r:1" |
+-----------------+-------+-----------+--------------+----------------------+------------------------+
| "192.168.15.11" | 57211 | "ONLINE" | 0 | "No valid partition" | "ttos_3p3r:1" |
+-----------------+-------+-----------+--------------+----------------------+------------------------+
| "192.168.15.11" | 35767 | "ONLINE" | 0 | "No valid partition" | "ttos_3p3r:1" |
+-----------------+-------+-----------+--------------+----------------------+------------------------+
| "Total" | | | 1 | "ttos_3p3r:1" | "ttos_3p3r:5" |
+-----------------+-------+-----------+--------------+----------------------+------------------------+
Got 6 rows (time spent 1094/12349 us)
Wed, 03 Nov 2021 11:23:48 CST
# ps aux | grep 33299 | grep -v grep
root 2470607 184 0.0 1385496 159800 ? Ssl 10:55 59:11 /data/src/wwl/nebula/build/bin/nebula-storaged --flagfile /data/src/wwl/test/etc/nebula-storaged.conf --pid_file /data/src/wwl/test/pids/nebula-storaged.pid.4 --meta_server_addrs 192.168.15.11:9559 --heartbeat_interval_secs 1 --raft_heartbeat_interval_secs 1 --minloglevel 3 --log_dir /data/src/wwl/test/logs/storaged.4 --local_ip 192.168.15.11 --port 33299 --ws_http_port 53553 --ws_h2_port 46147 --data_path /data/src/wwl/test/data/storaged.4
通过 gdb attach 到离线的存储服务进程上,我们发现 Raft 向 peer 节点发消息的模块卡在一个条件变量上:
Thread 37 (Thread 0x7fc8d23fd700 (LWP 2470643) "executor-pri3-3"):
...
#11 0x00007fc8e0f159fd in clone () from /lib64/libc.so.6
Thread 36 (Thread 0x7fc8d24fe700 (LWP 2470642) "executor-pri3-2"):
#0 0x00007fc8e11f0a35 in pthread_cond_wait@@GLIBC_2.3.2 () from /lib64/libpthread.so.0
#1 0x0000000004ba7a3c in std::condition_variable::wait(std::unique_lock<std::mutex>&) ()
#2 0x0000000003da583e in std::condition_variable::wait<nebula::raftex::Host::reset()::{lambda()#1}>(std::unique_lock<std::mutex>&, nebula::raftex::Host::reset()::{lambda()#1}) (this=0x7fc8c543d3b0, __lock=..., __p=...) at /data/vesoft/toolset/gcc/7.5.0/include/c++/7.5.0/condition_variable:99
#3 0x0000000003d91965 in nebula::raftex::Host::reset (this=0x7fc8c543d310) at /root/nebula-workspace/nebula/src/kvstore/raftex/Host.h:44
#4 0x0000000003d9da15 in nebula::raftex::RaftPart::handleElectionResponses (this=0x7fc8c54df010, voteReq=..., resps=..., hosts=..., proposedTerm=45) at /root/nebula-workspace/nebula/src/kvstore/raftex/RaftPart.cpp:1145
#5 0x0000000003d9cde0 in nebula::raftex::RaftPart::<lambda(auto:132&&)>::operator()<folly::Try<std::vector<std::pair<long unsigned int, nebula::raftex::cpp2::AskForVoteResponse> > > >(folly::Try<std::vector<std::pair<unsigned long, nebula::raftex::cpp2::AskForVoteResponse>, std::allocator<std::pair<unsigned long, nebula::raftex::cpp2::AskForVoteResponse> > > > &&) (__closure=0x7fc8c4c11320, t=...) at /root/nebula-workspace/nebula/src/kvstore/raftex/RaftPart.cpp:1123
#6 0x0000000003db1421 in folly::Future<std::vector<std::pair<unsigned long, nebula::raftex::cpp2::AskForVoteResponse>, std::allocator<std::pair<unsigned long, nebula::raftex::cpp2::AskForVoteResponse> > > >::<lambda(folly::Executor::KeepAlive<folly::Executor>&&, folly::Try<std::vector<std::pair<long unsigned int, nebula::raftex::cpp2::AskForVoteResponse>, std::allocator<std::pair<long unsigned int, nebula::raftex::cpp2::AskForVoteResponse> > > >&&)>::operator()(folly::Executor::KeepAlive<folly::Executor> &&, folly::Try<std::vector<std::pair<unsigned long, nebula::raftex::cpp2::AskForVoteResponse>, std::allocator<std::pair<unsigned long, nebula::raftex::cpp2::AskForVoteResponse> > > > &&) (__closure=0x7fc8c4c11320, t=...) at /data/src/wwl/nebula/build/third-party/install/include/folly/futures/Future-inl.h:947
查看 src/kvstore/raftex/Host.h:44 的具体代码,通过分析我们可以知道这个函数正在等待当前所有的 append log 请求结束,也就是 44 行对应的 noMoreRequestCV_.wait() 调用,它一直在等待 requestOnGoing_ 变为 false:
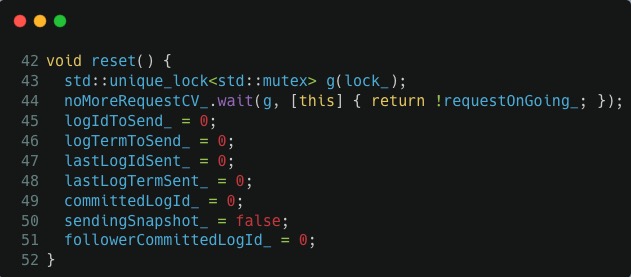
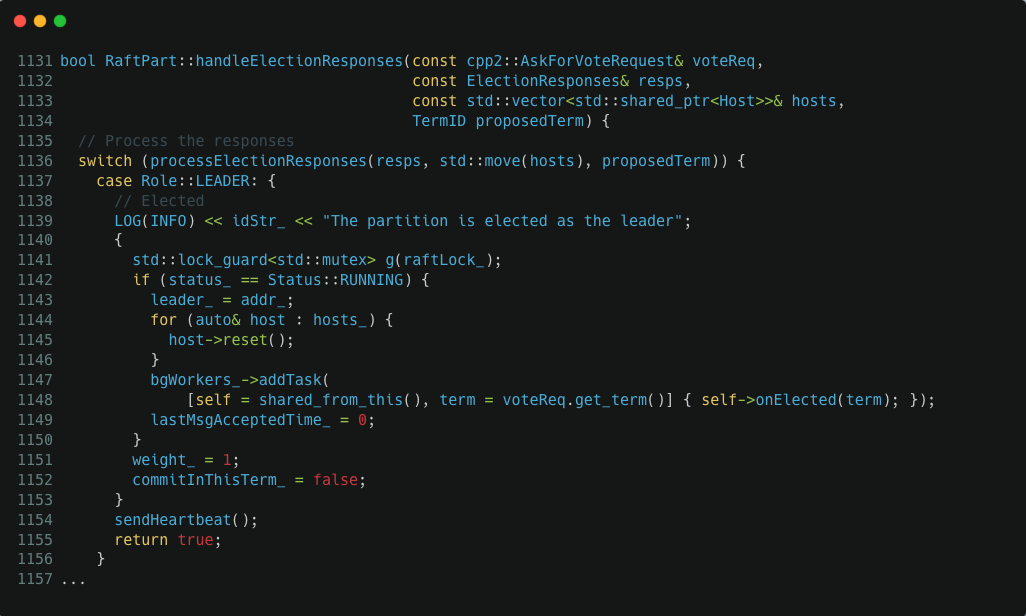
如果我们继续看堆栈上的前一个调用,可以发现 Host.reset() 调用前,RaftPart::handleElectionResponses() 在 1141 这行代码获取了 raftLock_ 这个锁,我们看 src/kvstore/raftex/RaftPart.cpp:1145 中的具体代码:
进程不动,说明 requestOnGoing_ 一直都是 true 状态,通过 gdb attach 进去我们验证了这个猜测:
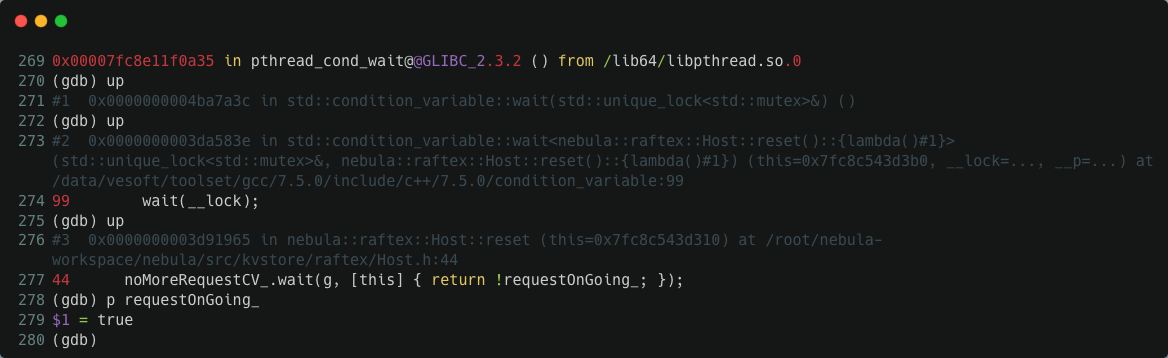
为什么 requestOnGoing_ 一直都是 true 状态呢?通过翻阅 src/kvstore/raftex/Host.cpp 中的代码,我们可以发现当存在 append log 请求时 requestOnGoing_ 在 Host::appendLogs() 函数中会被设置为 true,当 append log 请求都结束时,这个变量在 Host::appendLogsInternal() 函数中会被设置为 fasle。requestOnGoing_ 值一直不变,那么,一个合理的猜测是某个 append log 请求卡在 Host::appendLogsInternal() 上了。这个函数本质上干的活是:
- 通过
sendAppendLogRequest()向 raft peer 发起 append log rpc 请求 - 回调处理 append log rpc 的结果,处理完了顺便在这里吧
requestOnGoing_变量设置为 false
卡住的一种可能是 rpc 回调一直没有返回,但是这边不大可能。因为我们给 rpc 链接请求都设置了超时,所以这一点基本可以排除。再观察这个函数,我们可以看到 sendAppendLogRequest(eb, req) 和它的回调处理用的都是在同一个 eb(EventBase,即 IO 线程)中执行,会不会是回调线程中的操作导致死锁了?
翻了无数遍代码,看不出明显的关联关系,最后想到一个办法是通过打日志进一步观察运行细节。appendLogsInternal() 调用 sendAppendLogRequest() 并在 eb 这个 IO 线程中执行,我们把每个 appendLogsInternal() 请求和当前的时间戳关联。然后设法把 eb 的线程 id 打印出来,并在 sendAppendLogRequest() 处理结果的回调中也打印出对应的 tid(这里还要考虑跑异常的情况)。这样一来,如果 appendLogsInternal() 中没有发生死锁,我们必然能看到结果回调中打印的 eb 的 tid:
void Host::appendLogsInternal(folly::EventBase* eb, std::shared_ptr<cpp2::AppendLogRequest> req) {
using TransportException = apache::thrift::transport::TTransportException;
auto reqId = std::chrono::high_resolution_clock::now().time_since_epoch().count();
pid_t thisTid = syscall(__NR_gettid);
std::cerr << folly::format("append with req: {}, started within thread {}", reqId, thisTid) << std::endl;
eb->runImmediatelyOrRunInEventBaseThreadAndWait([reqId]() {
pid_t tid = syscall(__NR_gettid);
std::cerr << folly::format("append log req {} will run within thread {}", reqId, tid) << std::endl;
});
sendAppendLogRequest(eb, req)
.via(eb)
.thenValue([eb, self = shared_from_this(), reqId](cpp2::AppendLogResponse&& resp) {
pid_t tid = syscall(__NR_gettid);
std::cerr << folly::format("append log req {} done within thread {}", reqId, tid) << std::endl;
...
})
.thenError(folly::tag_t<TransportException>{},
[reqId, self = shared_from_this(), req](TransportException&& ex) {
pid_t tid = syscall(__NR_gettid);
std::cerr << folly::format("append log req {} encounter exception {} within thread {}", reqId, ex.what(), tid) << std::endl;
VLOG(2) << self->idStr_ << ex.what();
cpp2::AppendLogResponse r;
...
return;
})
.thenError(folly::tag_t<std::exception>{}, [self = shared_from_this(), reqId](std::exception&& ex) {
pid_t tid = syscall(__NR_gettid);
std::cerr << folly::format("append log req {} encounter exception {} within thread {}", reqId, ex.what(), tid) << std::endl;
VLOG(2) << self->idStr_ << ex.what();
...
return;
});
}
重新跑测试,很快我们又观察到死锁的情况。通过死锁进程的日志,我们看到 Host::appendLogsInternal() 确实卡住了:
...
append log req 1635908498110971639 done within thread 2470665
append with req: 1635908526021106910, started within thread 2470665
append log req 1635908526021106910 will run within thread 2470665
1635908526021106910 对应的 append 请求运行在线程 2470665 上,处理结果的时候卡住了,gdb attach 进去看 2470665 这个进程在干嘛:
Thread 1 (Thread 0x7fc8c15ff700 (LWP 2470665) "IOThreadPool9"):
#0 0x00007fc8e11f354d in __lll_lock_wait () from /lib64/libpthread.so.0
#1 0x00007fc8e11eee9b in _L_lock_883 () from /lib64/libpthread.so.0
#2 0x00007fc8e11eed68 in pthread_mutex_lock () from /lib64/libpthread.so.0
#3 0x0000000002a655d4 in __gthread_mutex_lock (__mutex=0x7fc8c54df150) at /data/vesoft/toolset/gcc/7.5.0/include/c++/7.5.0/x86_64-vesoft-linux/bits/gthr-default.h:748
#4 0x0000000002a658d6 in std::mutex::lock (this=0x7fc8c54df150) at /data/vesoft/toolset/gcc/7.5.0/include/c++/7.5.0/bits/std_mutex.h:103
#5 0x0000000002a6b43f in std::lock_guard<std::mutex>::lock_guard (this=0x7fc8c15fbbb8, __m=...) at /data/vesoft/toolset/gcc/7.5.0/include/c++/7.5.0/bits/std_mutex.h:162
#6 0x0000000003da1de2 in nebula::raftex::RaftPart::processHeartbeatRequest (this=0x7fc8c54df010, req=..., resp=...) at /root/nebula-workspace/nebula/src/kvstore/raftex/RaftPart.cpp:1650
#7 0x0000000003de1822 in nebula::raftex::RaftexService::async_eb_heartbeat (this=0x7fc8e0a32ab0, callback=..., req=...) at /root/nebula-workspace/nebula/src/kvstore/raftex/RaftexService.cpp:220
#8 0x0000000003e931dd in nebula::raftex::cpp2::RaftexServiceAsyncProcessor::process_heartbeat<apache::thrift::CompactProtocolReader, apache::thrift::CompactProtocolWriter> (this=0x7fc8d1702160, req=..., serializedRequest=..., ctx=0x7fc8c0940b10, eb=0x7fc8c0804000, tm=0x7fc8e0a142b0) at /root/nebula-workspace/nebula/build/src/interface/gen-cpp2/RaftexService.tcc:220
#9 0x0000000003e8ec96 in nebula::raftex::cpp2::RaftexServiceAsyncProcessor::setUpAndProcess_heartbeat<apache::thrift::CompactProtocolReader, apache::thrift::CompactProtocolWriter> (this=0x7fc8d1702160, req=..., serializedRequest=..., ctx=0x7fc8c0940b10, eb=0x7fc8c0804000, tm=0x7fc8e0a142b0) at /root/nebula-workspace/nebula/build/src/interface/gen-cpp2/RaftexService.tcc:198
...
从堆栈上看,它被调度去处理 Raft heartbeat 请求了,然后它卡在 /root/nebula-workspace/nebula/src/kvstore/raftex/RaftPart.cpp:1650 上了,1650 这行代码正要获取 raftLock_ 锁,raft 完美死锁了:
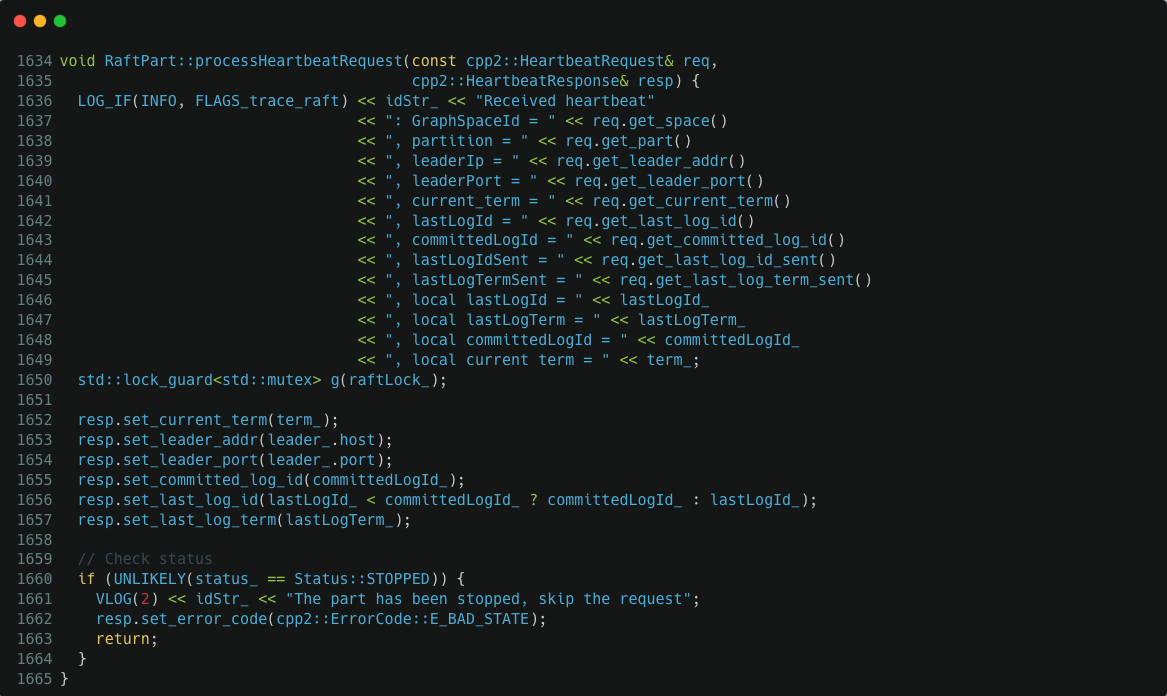
NebulaGraph 大量使用线程池来处理异步回调任务。总结以上问题就是在两个线程池工作线程中:
- worker thread 1 执行以下回调
- 拿到锁 lock,等待在条件变量上;
- worker thread 2 执行以下回调
- 尝试获取,然后执行后续任务;
- 修改数据并激活条件变量;
因为 worker thread 2 先执行任务 a 也就是需要先获取所,再执行回调 b 以激活条件变量,这种调用顺序构成了一个非常隐蔽的死锁场景。在使用线程池处理异步回调的设计中,如果并发加锁的处理稍不留意可能就会踩到类似的坑上,而 NebulaGraph Raft 各项操作都是构建在异步线程池的基础上,并且包含各种复杂的加锁操作。我们在修复这个问题后又陆陆续续在 NebulaGraph 上修复了多起类似的故障。
Raft 缓冲区死锁问题
这也是 v2.6 之前我们通过 Chaos 测试用例发现的一个问题。运行一段时间后终止测试程序,等系统 CPU、磁盘 IO 等各项负载都空闲下来后,我们在 NebulaGraph 执行以一些简单的查询操作,我们发现 NebulaGraph 永远都返回 Leader change 错误。查看 NebulaGraph 日志,我们发现它在疯狂报 Raft buffer overflow 错误:
W1019 08:26:21.220441 539751 RaftPart.cpp:601] [Port: 50944, Space: 3, Part: 1] The appendLog buffer is full. Please slow down the log appending rate.replicatingLogs_ :0
W1019 08:26:54.569221 539751 RaftPart.cpp:601] [Port: 50944, Space: 3, Part: 1] The appendLog buffer is full. Please slow down the log appending rate.replicatingLogs_ :0
W1019 08:27:27.919421 539751 RaftPart.cpp:601] [Port: 50944, Space: 3, Part: 1] The appendLog buffer is full. Please slow down the log appending rate.replicatingLogs_ :0
W1019 08:28:01.268051 539751 RaftPart.cpp:601] [Port: 50944, Space: 3, Part: 1] The appendLog buffer is full. Please slow down the log appending rate.replicatingLogs_ :0
W1019 08:28:34.615942 539751 RaftPart.cpp:601] [Port: 50944, Space: 3, Part: 1] The appendLog buffer is full. Please slow down the log appending rate.replicatingLogs_ :0
rate.replicatingLogs_ :0 表示 raft 没有在复制日志。raft 缓冲区溢出说明有大量数据等待复制,但它却没有在复制日志,看起来就是个 bug。 我们发现稳定下来后 Raft 集群主节点稳定,没有出现切主行为,至少说明 Raft 选举模块还是正常的。所以,从上面的日志看来大概率是日志复制模块被 Chaos 测试玩坏了。
首先我们看 NebulaGraph Raft 中的对 append log 的处理:
folly::Future<AppendLogResult> RaftPart::appendLogAsync(ClusterID source,
LogType logType,
std::string log,
AtomicOp op) {
if (blocking_) {
// No need to block heartbeats and empty log.
if ((logType == LogType::NORMAL && !log.empty()) || logType == LogType::ATOMIC_OP) {
return AppendLogResult::E_WRITE_BLOCKING;
}
}
LogCache swappedOutLogs;
auto retFuture = folly::Future<AppendLogResult>::makeEmpty();
if (bufferOverFlow_) {
LOG_EVERY_N(WARNING, 100) << idStr_
<< "The appendLog buffer is full."
" Please slow down the log appending rate."
<< "replicatingLogs_ :" << replicatingLogs_;
return AppendLogResult::E_BUFFER_OVERFLOW;
}
{
std::lock_guard<std::mutex> lck(logsLock_);
VLOG(2) << idStr_ << "Checking whether buffer overflow";
if (logs_.size() >= FLAGS_max_batch_size) {
// Buffer is full
LOG(WARNING) << idStr_
<< "The appendLog buffer is full."
" Please slow down the log appending rate."
<< "replicatingLogs_ :" << replicatingLogs_;
bufferOverFlow_ = true;
return AppendLogResult::E_BUFFER_OVERFLOW;
}
VLOG(2) << idStr_ << "Appending logs to the buffer";
...
bool expected = false;
if (replicatingLogs_.compare_exchange_strong(expected, true)) {
// We need to send logs to all followers
VLOG(2) << idStr_ << "Preparing to send AppendLog request";
sendingPromise_ = std::move(cachingPromise_);
cachingPromise_.reset();
std::swap(swappedOutLogs, logs_);
bufferOverFlow_ = false;
} else {
VLOG(2) << idStr_ << "Another AppendLogs request is ongoing, just return";
return retFuture;
}
}
...
AppendLogsIterator it(firstId, termId, std::move(sendingLogs_));
appendLogsInternal(std::move(it), termId);
return retFuture;
}
这个函数一旦看到 bufferOverFlow_ 变量值是 true,便认为缓冲区满了,直接报错返回了。否则把要复制的日志先塞到缓冲区 logs_ 中。如果缓冲区满了就设置 bufferOverFlow_ = true。接下来,测试 replicatingLogs_ 这个变量,true 说明已经有活动的异步回调在执行日志复制可以直接返回,否则在函数末尾调用 appendLogsInternal() 真正启动 raft 日志复制操作。另一方面,当向 peer 节点复制日志的操作收到成功的响应后 NebulaGraph raft 会调用 checkAppendLogResult() 来处理结果。这个函数清空 raft 日志缓冲区,把 bufferOverFlow_ 和 replicatingLogs_ 重置为 false。
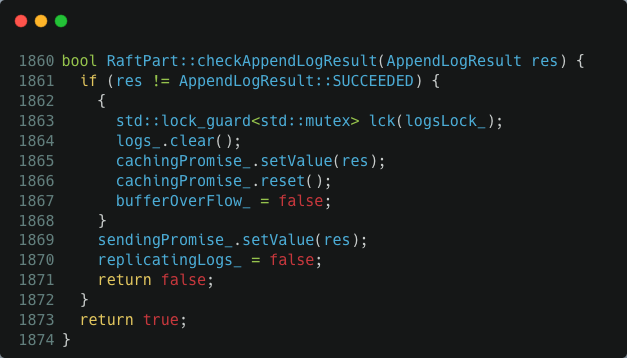
以上是 raft 日志复制的核心操作逻辑。需要注意的是,appendLogAsync() 和 checkAppendLogResult() 都是异步并发执行的,最后意味着 bufferOverFlow_ 和 replicatingLogs_ 变量的更新需要锁的保护,这里用的是 logsLock_ 这个锁。了解这个信息后,我们再来看 checkAppendLogResult() 这个函数就会发现一个非常微妙的加锁问题:replicatingLogs_ = false 这行代码是在没有 logsLock_ 锁保护的情况下执行的。如果客户端的并发请求足够高,那么在 checkAppendLogResult() 释放锁和执行 replicatingLogs_ = false 这个间隙完全有可能把缓冲区打满,然后把 bufferOverFlow_ 设置为 true。这个也就是我们开头看到的,日志缓冲区满了但 raft 却没有在执行日志复制场景,这种情况下所有的操作都会报缓冲区溢出错误,这个几点基本就报销了只能重启。修复也非常容易,把 checkAppendLogResult() 中的 replicatingLogs_ = false 语句放在 logsLock_ 锁的保护下执行即可。
Raft 选举死锁问题
这又是通过 Chaos 测试跑出来的一个 NebulaGraph Raft v2.6 之前版本的故障。我们构造了一个七节点的 Raft 集群,在测试中我们发现,系统挂了三个节点后,另外四个节点再也无法选主了。我们把四个无法选主的节点和对应的服务端口筛选出来:
storage.0 : 54774
storage.2 : 39620
storage.3 : 48140
storage.5 : 33124
通过日志发现了一些很有意思的事情:
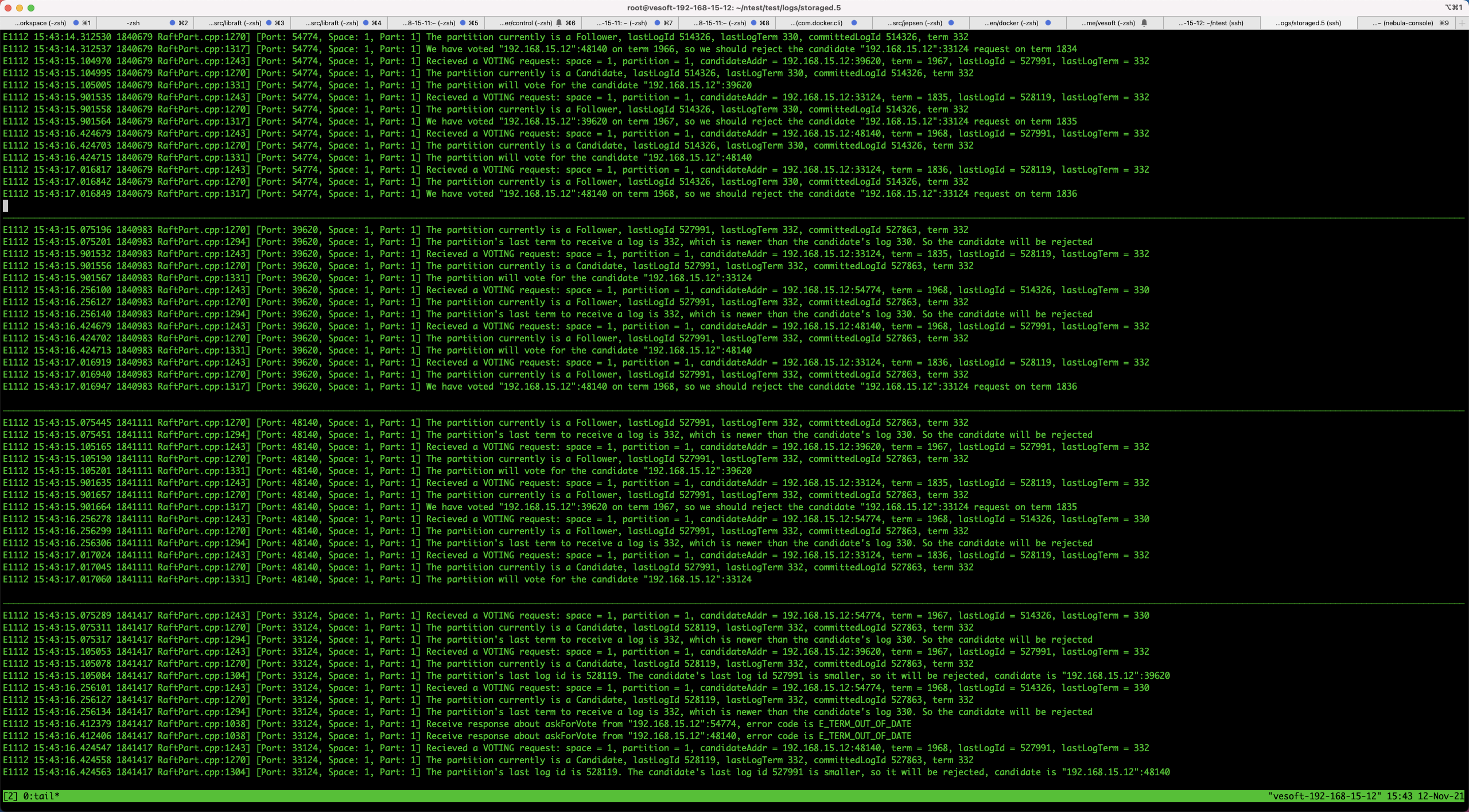
从日志上 storage.0 拒绝了 storage.5 的 vote request,因为 storage.5 的 term 1836 远远落后于其他节点的 term 1967、1968,投票请求被拒绝是意料之中。另一方面 storage.5 上的日志比其他三个节点都新,根据 raft 的选举规则只有 storage.5 才能当选 leader。为什么 storage.5 的 term 上不去,按道理在 storage.5 收到其他节点的 request vote 请求后就应该立即更新本地的 term 了?我们 review NebulaGraph Raft 中对 vote 请求的处理发现了其中的问题:
void RaftPart::processAskForVoteRequest(const cpp2::AskForVoteRequest& req,
cpp2::AskForVoteResponse& resp) {
LOG(ERROR) << idStr_ << "Recieved a VOTING request"
<< ": space = " << req.get_space() << ", partition = " << req.get_part()
<< ", candidateAddr = " << req.get_candidate_addr() << ":" << req.get_candidate_port()
<< ", term = " << req.get_term() << ", lastLogId = " << req.get_last_log_id()
<< ", lastLogTerm = " << req.get_last_log_term();
std::lock_guard<std::mutex> g(raftLock_);
...
// Check the last term to receive a log
if (req.get_last_log_term() < lastLogTerm_) {
LOG(ERROR) << idStr_ << "The partition's last term to receive a log is " << lastLogTerm_
<< ", which is newer than the candidate's log " << req.get_last_log_term()
<< ". So the candidate will be rejected";
resp.set_error_code(cpp2::ErrorCode::E_TERM_OUT_OF_DATE);
return;
}
...
return;
}
我们发现 NebulaGraph Raft 处理选举请求的时候,如果 candidate 的 log 比自己的 log 旧,raft 会直接拒绝这个请求。这个操作逻辑上没问题,但是 Raft 论文里要求一个 Raft 实例一旦遇到比自己 term 大的请求要立马 update 自己的 term,这个函数里执行这步操作了吗?显然没有,判断日志比自己旧后就直接 return 了,这种处理导致集群永远无法选出主节点。这个问题的修复也容易,再处理 request vote 请求的时候及时更新本地 term 即可。不过,如果在集群出问题的时候放任 term 无序递增也不是个好办法。所以,我们在修复这个问题的时候顺便把 Raft prevote 特性也加上去,让 NebulaGraph 的 Raft 更加稳定。
Raft 数据不一致问题
我们的 Chaos 测试发现 v2.6 版本之前的 NebulaGraph Raft 中存在数据不一致的问题,而且可以稳定复现!以下是在一次测试中发现的 NebulaGraph Raft 日志数据和 NebulaGraph 数据不一致的情况:
1c1
< /data/src/nebula-cluster/data/data/store1/nebula/1/wal/1
---
> /data/src/nebula-cluster/data/data/store2/nebula/1/wal/1
293702,293720c293702,293720
< log index: 293701, term: 694, logsz: 55, cluster_id: 0, walfile:
< log index: 293702, term: 694, logsz: 57, cluster_id: 0, walfile:
< log index: 293703, term: 694, logsz: 57, cluster_id: 0, walfile:
< log index: 293704, term: 694, logsz: 55, cluster_id: 0, walfile:
< log index: 293705, term: 694, logsz: 55, cluster_id: 0, walfile:
< log index: 293706, term: 694, logsz: 57, cluster_id: 0, walfile:
< log index: 293707, term: 694, logsz: 57, cluster_id: 0, walfile:
< log index: 293708, term: 694, logsz: 57, cluster_id: 0, walfile:
< log index: 293709, term: 694, logsz: 55, cluster_id: 0, walfile:
< log index: 293710, term: 694, logsz: 57, cluster_id: 0, walfile:
< log index: 293711, term: 694, logsz: 55, cluster_id: 0, walfile:
< log index: 293712, term: 694, logsz: 55, cluster_id: 0, walfile:
< log index: 293713, term: 694, logsz: 55, cluster_id: 0, walfile:
< log index: 293714, term: 694, logsz: 55, cluster_id: 0, walfile:
< log index: 293715, term: 694, logsz: 55, cluster_id: 0, walfile:
< log index: 293716, term: 694, logsz: 55, cluster_id: 0, walfile:
< log index: 293717, term: 694, logsz: 57, cluster_id: 0, walfile:
< log index: 293718, term: 694, logsz: 55, cluster_id: 0, walfile:
< log index: 293719, term: 695, logsz: 0, cluster_id: 0, walfile:
---
> log index: 293701, term: 696, logsz: 53, cluster_id: 0, walfile:
> log index: 293702, term: 696, logsz: 55, cluster_id: 0, walfile:
> log index: 293703, term: 696, logsz: 59, cluster_id: 0, walfile:
> log index: 293704, term: 696, logsz: 57, cluster_id: 0, walfile:
> log index: 293705, term: 696, logsz: 55, cluster_id: 0, walfile:
> log index: 293706, term: 696, logsz: 57, cluster_id: 0, walfile:
> log index: 293707, term: 696, logsz: 57, cluster_id: 0, walfile:
> log index: 293708, term: 696, logsz: 59, cluster_id: 0, walfile:
> log index: 293709, term: 696, logsz: 55, cluster_id: 0, walfile:
> log index: 293710, term: 696, logsz: 57, cluster_id: 0, walfile:
> log index: 293711, term: 696, logsz: 55, cluster_id: 0, walfile:
> log index: 293712, term: 696, logsz: 55, cluster_id: 0, walfile:
> log index: 293713, term: 696, logsz: 55, cluster_id: 0, walfile:
> log index: 293714, term: 696, logsz: 57, cluster_id: 0, walfile:
> log index: 293715, term: 696, logsz: 57, cluster_id: 0, walfile:
> log index: 293716, term: 696, logsz: 57, cluster_id: 0, walfile:
> log index: 293717, term: 696, logsz: 57, cluster_id: 0, walfile:
> log index: 293718, term: 696, logsz: 55, cluster_id: 0, walfile:
> log index: 293719, term: 696, logsz: 53, cluster_id: 0, walfile:
可以看到,同一个 index 下,raft 日志的 term 和 size 值都存在差异,有 19 条 raft log 不一致!
comparing /Users/from-vesoft-with-love/src/toss_integration/data/store1/nebula/1/data to /Users/wenlinwu/src/toss_integration/data/store2/nebula/1/data
size mismatch: 489347, 489348
/Users/from-vesoft-with-love/src/toss_integration/data/store2/nebula/1/data missing keys:
b'\x06\x01\x00\x00key-1-12197-340'
b'\x06\x01\x00\x00key-1-11350-767'
b'\x06\x01\x00\x00key-1-12553-44'
b'\x06\x01\x00\x00key-1-10677-952'
b'\x06\x01\x00\x00key-1-13514-912'
b'\x06\x01\x00\x00key-1-9430-782'
b'\x06\x01\x00\x00key-1-18022-735'
b'\x06\x01\x00\x00key-1-7029-104'
b'\x06\x01\x00\x00key-1-4530-867'
b'\x06\x01\x00\x00key-1-8658-248'
b'\x06\x01\x00\x00key-1-8489-415'
b'\x06\x01\x00\x00key-1-2345-956'
b'\x06\x01\x00\x00key-1-8213-336'
b'\x06\x01\x00\x00key-1-8330-687'
b'\x06\x01\x00\x00key-1-9470-108'
b'\x06\x01\x00\x00key-0-62674-143'
b'\x06\x01\x00\x00key-1-12613-884'
b'\x06\x01\x00\x00key-1-8860-507'
/Users/from-vesoft-with-love/src/toss_integration/data/store1/nebula/1/data missing keys:
b'\x06\x01\x00\x00key-1-9504-429'
b'\x06\x01\x00\x00key-1-15925-489'
b'\x06\x01\x00\x00key-1-17467-978'
b'\x06\x01\x00\x00key-1-14189-663'
b'\x06\x01\x00\x00key-1-6414-170'
b'\x06\x01\x00\x00key-1-11835-136'
b'\x06\x01\x00\x00key-1-10409-874'
b'\x06\x01\x00\x00key-1-6672-385'
b'\x06\x01\x00\x00key-1-17840-561'
b'\x06\x01\x00\x00key-1-13118-1010'
b'\x06\x01\x00\x00key-1-7707-630'
b'\x06\x01\x00\x00key-1-5606-677'
b'\x06\x01\x00\x00key-1-10107-197'
b'\x06\x01\x00\x00key-0-64103-1001'
b'\x06\x01\x00\x00key-1-6373-99'
b'\x06\x01\x00\x00key-1-940-285'
b'\x06\x01\x00\x00key-1-10802-736'
b'\x06\x01\x00\x00key-1-7087-647'
b'\x06\x01\x00\x00key-1-3020-441'
diff 1-2: []
NebulaGraph 写入的数据有 18 条不一致,和 Raft log 中的不一致的数据条目非常接近。Raft 数据不一致的问题处理起来非常棘手。不过,我们通过不断地优化 Chaos 测试用例,让问题可以在短时间内稳定复现。不管是日志还是 gdb 一时都没有太清晰的策略去对付这个问题。后来我们想到了 Mozilla RR。RR 可以把整个程序的执行过程录制下来,然后重复播放执行,而且产生相同的执行结果。我们可以用 RR 把 Raft 数据不一致的故障录制下来。通过 RR 的执行过程回放,我们发现 NebulaGraph Raft 在处理选举请求的时候会错误地把一个本应该变成 follower 的 leader 节点升级成下一个 term 的 leader:
void RaftPart::processAskForVoteRequest(const cpp2::AskForVoteRequest& req,
cpp2::AskForVoteResponse& resp) {
LOG(INFO) << idStr_ << "Received a VOTING request"
<< ": space = " << req.get_space() << ", partition = " << req.get_part()
<< ", candidateAddr = " << req.get_candidate_addr() << ":" << req.get_candidate_port()
<< ", term = " << req.get_term() << ", lastLogId = " << req.get_last_log_id()
<< ", lastLogTerm = " << req.get_last_log_term()
<< ", isPreVote = " << req.get_is_pre_vote();
std::lock_guard<std::mutex> g(raftLock_);
...
auto oldTerm = term_;
// req.get_term() >= term_, we won't update term in prevote
if (!req.get_is_pre_vote()) {
term_ = req.get_term();
}
// Check the last term to receive a log
if (req.get_last_log_term() < lastLogTerm_) {
LOG(INFO) << idStr_ << "The partition's last term to receive a log is " << lastLogTerm_
<< ", which is newer than the candidate's log " << req.get_last_log_term()
<< ". So the candidate will be rejected";
resp.set_error_code(cpp2::ErrorCode::E_TERM_OUT_OF_DATE);
return;
}
...
}
看以上代码,一个 leader 的 term 可能直接被 update 变成下一个 term 的 leader,它本应当变成 follower 的。这样以来 Raft 直接脑裂了,脑裂的两个 leader 分别提交了不一样的数据上去,也就造成了上面的数据不一致问题。
谢谢你读完本文 (///▽///)
如果你想尝鲜图数据库 NebulaGraph,记得去 GitHub 下载、使用、(з)-☆ star 它 -> GitHub;和其他的 NebulaGraph 用户一起交流图数据库技术和应用技能,留下「你的名片」一起玩耍呀~
Recommend
About Joyk
Aggregate valuable and interesting links.
Joyk means Joy of geeK