

基础篇-SpringBoot HTTP接口实战
source link: https://blog.51cto.com/u_15773567/5655628
Go to the source link to view the article. You can view the picture content, updated content and better typesetting reading experience. If the link is broken, please click the button below to view the snapshot at that time.
一、相关注解说明
SpringBoot的Controller中经常会用到注解@Controller、@RestController、@RequestMapping、@RequestParam、@PathVariable、@RequestBody等。以下针对这些注解简单使用。
1、@Controller
用于定义控制器类,在spring项目中由控制器负责将用户发来的URL请求转发到对应的服务接口(service层),一般这个注解在类中,通常方法需要配合注解@RequestMapping。
@RequestMapping("/demo")
public class HttpController {
@RequestMapping(value = "/hello")
public String sayHello() {
System.out.println("hello world!");
return "hello";
}
}
2、@RestController
用于定义控制器类,注解是@Controller和@ResponseBody的合集,表示这是个控制器bean,并且是将函数的返回值直接填入HTTP响应体中,是REST风格的控制器。
@RequestMapping("/demo")
public class RestHttpController {
@RequestMapping(value = "/rest")
public Object rest() {
Map<String,Object> resultMap = new HashMap<>(8);
resultMap.put("msg","i am rest controller test");
resultMap.put("code","10000");
return resultMap;
}
}
请求返回:
3、@RequestMapping
作用于类或者方法上,用于映射URL路径,将http的请求地址映射到控制器(controller)类的处理方法上。
参数说明:
- value:定义处理方法的请求的 URL 地址。(重点)
- method:定义处理方法的 http method 类型,如 GET、POST 等。(重点)
- params:定义请求的 URL 中必须包含的参数。或者不包含某些参数。(了解)
- headers:定义请求中 Request Headers 必须包含的参数。或者不包含某些参数。(了解)
衍生注解:
- GetMapping:等价于@RequestMapping(value = “hello”, method = RequestMethod.GET),接收Get请求方法的RequestMapping。
- PostMapping:等价于@RequestMapping(value = “hello”, method = RequestMethod.POST),接收POST请求方法的RequestMapping。
- DeleteMapping:等价于@RequestMapping(value = “hello”, method = RequestMethod.DELETE),接收DELETE请求方法的RequestMapping。
- PutMapping:等价于@RequestMapping(value = “hello”, method = RequestMethod.PUT),接收PUT请求方法的RequestMapping。
- PatchMapping:等价于@RequestMapping(value = “hello”, method = RequestMethod.PATCH),接收PATCH请求方法的RequestMapping。
@RequestMapping("/demo")
public class RestHttpController {
@RequestMapping(value = "/rest")
public Object rest() {
Map<String,Object> resultMap = new HashMap<>(8);
resultMap.put("msg","i am rest controller test");
resultMap.put("code","10000");
return resultMap;
}
@PostMapping("/post")
public Object post(){
Map<String,Object> resultMap = new HashMap<>(8);
resultMap.put("msg","i am post mapping test");
resultMap.put("code","10000");
return resultMap;
}
@GetMapping("/get")
public Object get(){
Map<String,Object> resultMap = new HashMap<>(8);
resultMap.put("msg","i am get mapping test");
resultMap.put("code","10000");
return resultMap;
}
@PutMapping("/put")
public Object put(){
Map<String,Object> resultMap = new HashMap<>(8);
resultMap.put("msg","i am put mapping test");
resultMap.put("code","10000");
return resultMap;
}
@DeleteMapping("/delete")
public Object delete(){
Map<String,Object> resultMap = new HashMap<>(8);
resultMap.put("msg","i am delete mapping test");
resultMap.put("code","10000");
return resultMap;
}
@PatchMapping("/patch")
public Object patch(){
Map<String,Object> resultMap = new HashMap<>(8);
resultMap.put("msg","i am patch mapping test");
resultMap.put("code","10000");
return resultMap;
}
}
4、@RequestParam
作用于方法上,@RequestParam 注解配合 @RequestMapping 一起使用,可以将请求的参数同处理方法的参数绑定在一起。
public Object requestParamTest(@RequestParam("data") String data){
Map<String,Object> resultMap = new HashMap<>(8);
resultMap.put("data","传入参数为:" + data);
resultMap.put("code","10000");
return resultMap;
}
{"code":"10000","data":"传入参数为:test_data"}
5、@RequestBody
作用于形参列表上,用于将前台发送过来固定格式的数据【xml 格式或者 json等】封装为对应的 JavaBean 对象,封装时使用到的一个对象是系统默认配置的 HttpMessageConverter进行解析,然后封装到形参上。
public Object requestBodyTest(@RequestBody UserDTO user){
Map<String,Object> resultMap = new HashMap<>(8);
resultMap.put("data","传入参数为:" + user);
resultMap.put("code","10000");
return resultMap;
}
{"code":"10000","data":"传入参数为:UserDTO{ id='ca56c077-33e7-4b9c-8ca6-72b01d931996' username='Trazen', address='anhui'}"}
6、@PathVariable
和RequestMapping配套使用,负责解析url请求中占位符参数({XXX})的值绑定到方法的形参中。
public Object pathVariableTest(@PathVariable("data") String data){
Map<String,Object> resultMap = new HashMap<>(8);
resultMap.put("data","传入参数为:" + data);
resultMap.put("code","10000");
return resultMap;
}
{"code":"10000","data":"传入参数为:test_data"}
7、@ResponseBody
使用在控制层(controller)的方法上,将方法的返回值,以特定的格式写入到response的body区域,进而将数据返回给客户端。 当方法上面没有写ResponseBody,底层会将方法的返回值封装为ModelAndView对象。如果返回值是字符串,那么直接将字符串写到客户端;如果是一个对象,会将对象转化为json串,然后写到客户端。
二、HTTP接口请求实战
以GET请求为例,POST,PUT,DELETE类似。
1、PathVariable中获取字段
* 通过@PathVariable解析url请求中占位符参数({XXX})的值绑定到方法的形参中
* @param deptId
* @param userId
* @return
*/
@GetMapping("/{deptId}/{userId}")
public Object queryUser(@PathVariable("deptId")String deptId,
@PathVariable("userId")String userId){
Map<String,Object> resultMap = new HashMap<>(8);
resultMap.put("deptId",deptId);
resultMap.put("userId",userId);
return resultMap;
}
请求测试结果:
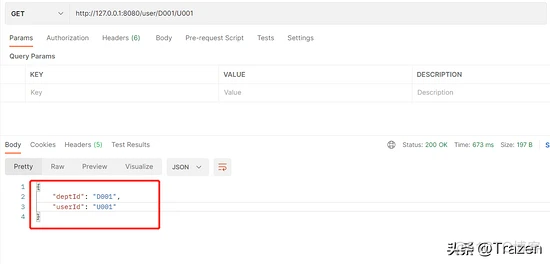
2、params中获取参数
* params中获取参数
* @param pageSize
* @param pageNo
* @return
*/
@GetMapping(value = "/v1/page")
public Object page1(int pageSize,int pageNo){
Map<String,Object> resultMap = new HashMap<>(8);
resultMap.put("pageSize",pageSize);
resultMap.put("pageNo",pageNo);
return resultMap;
}</p
请求测试结果:
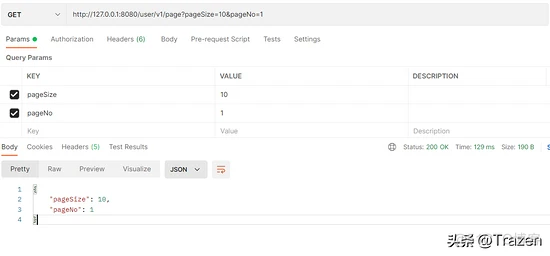
3、通过RequestParam参数设定获取
* 通过RequestParam参数设定获取
* RequestParam可设置默认值
* @param pageSize
* @param pageNo
* @return
*/
@GetMapping(value = "/v2/page")
public Object page2(@RequestParam(defaultValue = "10",name="pageSize") int pageSize,
@RequestParam(defaultValue = "0",name="pageNo") int pageNo){
Map<String,Object> resultMap = new HashMap<>(8);
resultMap.put("pageSize",pageSize);
resultMap.put("pageNo",pageNo);
return resultMap;
}
请求测试结果: 设置默认值后,不传参会使用默认值。
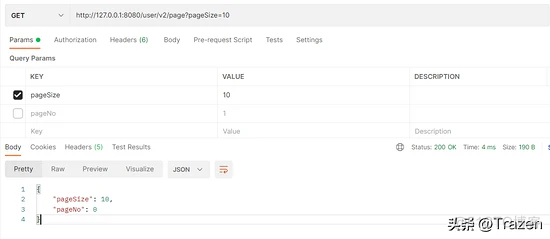
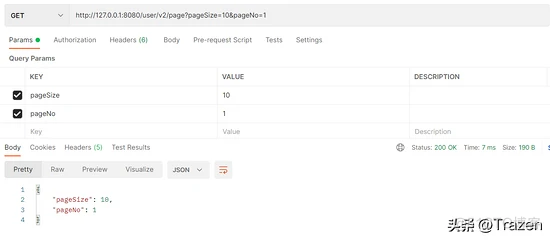
4、通过RequestBody封装为对应的 JavaBean 对象传参
* 通过RequestBody封装为对应的 JavaBean 对象传参
* @param user
* @return
*/
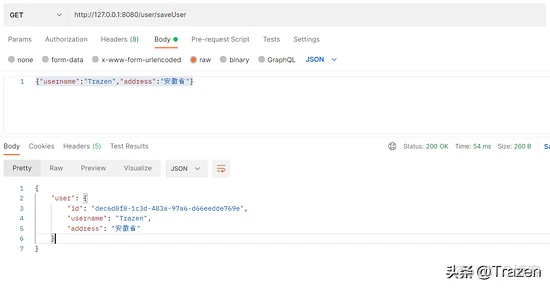
@GetMapping(value = "/saveUser")
public Object saveUser(@RequestBody UserDTO user){
Map<String,Object> resultMap = new HashMap<>(8);
user.setId(UUID.randomUUID().toString());
resultMap.put("user",user);
return resultMap;
}
请求测试结果:
5、header获取参数
* 从header获取参数
* @param accessToken
* @param userId
* @return
*/
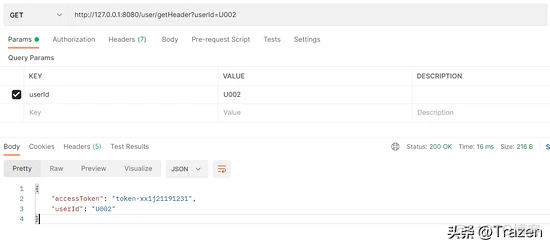
@GetMapping(value = "/getHeader")
public Object getHeader(@RequestHeader("accessToken") String accessToken,String userId){
Map<String,Object> resultMap = new HashMap<>(8);
resultMap.put("accessToken",accessToken);
resultMap.put("userId",userId);
return resultMap;
}
请求测试结果:
6、HttpServletRequest获取请求中的参数
* HttpServletRequest中获取
* @param request
* @return
*/
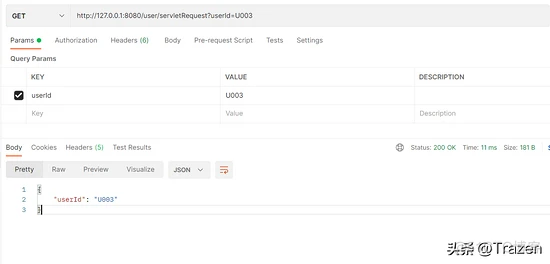
@GetMapping(value ="/servletRequest")
public Object testRequest(HttpServletRequest request){
Map<String,Object> resultMap = new HashMap<>(8);
String userId = request.getParameter("userId");
resultMap.put("userId",userId);
return resultMap;
}
请求测试结果:
Recommend
About Joyk
Aggregate valuable and interesting links.
Joyk means Joy of geeK