Harlinn.Windows - A Visual Studio 2022 Solution
source link: https://www.codeproject.com/Articles/5319700/Harlinn-Windows-A-Visual-Studio-2022-Solution
Go to the source link to view the article. You can view the picture content, updated content and better typesetting reading experience. If the link is broken, please click the button below to view the snapshot at that time.
Harlinn.Windows - A Visual Studio 2022 Solution






Overview
This article describes Harlinn.Windows, a Visual Studio 2022 solution.
Before you can build the solution, please read the build instructions and configure your environment accordingly.
Introduction
Harlinn.Windows is a collection of libraries that I have put together that serves as a big part of the runtime we use at work. A few are my own; but most are; more or less, well-known open source libraries.
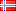
There are currently 439 projects in the solution, and this article provides a high-level overview of what's inside.
Why did I not use cmake and vcpkg?
This is a good question, and initially I tried to do just that, but there were some snags:
- The size of the release build, using vcpkg, for grpc.lib was 325 MB; while the size of the release build of Harlinn.grpc.dll is just 3.7 MB. Currently the combined size of all the native DLLs created for a release build of the solution is 108 MB.
- Some packages relied on different versions of the same package, including their own private copy of a package.
- Some packages were compiled with /sdl on, while others were not. I prefer to turn /sdl and /GS off for release builds, and on for debug builds. This may not be as significant as it used to, but you still get better performance when turning /sdl and /GS off.
- Many packages will not compile with:
- The /std:c++latest option, which enables all currently implemented compiler and standard library features proposed for the next draft standard, as well as some in-progress and experimental features.
- Many packages creates static libraries, not DLLs.
Don't get me wrong; I think CMake and vcpkg are great tools, but putting everything into a single solution makes it easier, at least for me, to understand how everything is tied together.
Why put Harlinn in front of every DLL name?
To avoid naming conflicts. I own the harlinn.com domain, so it is unlikely that anybody would, by accident, put Harlinn in front of the name of their DLL.
What about the unit tests?
A few of those are included, but still just a fraction of those available for the original packages.
In particular, I've included all unit tests, that can be expected to compile on Windows, for:
- Abseil - 4430 tests pass, 26 fails, and 12 tests are disabled
- boringssl
- crypto_test - 910 tests pass, 0 fails, and 0 tests are disabled
- ssl_test - 330 tests pass, 0 fails, and 0 tests are disabled
- gRPC - the tests are implemented as 94 separate executables, using multiple approaches to testing. I think that the tests pass; but I am not certain, since much of the validation was performed manually.
I've also created a fair number of tests for my own projects:
- Harlinn.Common.Core.Tests: 1175
- Harlinn.Windows.Tests: 271
- Harlinn.OCI.Tests: 49
- Harlinn.ODBC.Tests: 9
- Harlinn.Timeseries.Tests: 10
- Harlinn.Julia.Tests: 11
- Harlinn.Common.Config.Tests: 34
All tests can be found under the Tests folder.
What about the examples?
So far I've included 190 example projects.
All Examples can be found under the Examples and DotNet\Examples folders.
How stable is this?
This is a snapshot of the solution, and while most things seems to work, there are bound to be some snags. The most common problem will be a function or variable that is not exported from a DLL, and there are probably other bugs too. Some, probably, created by yours truly.
Still, with this solution you can now:
-
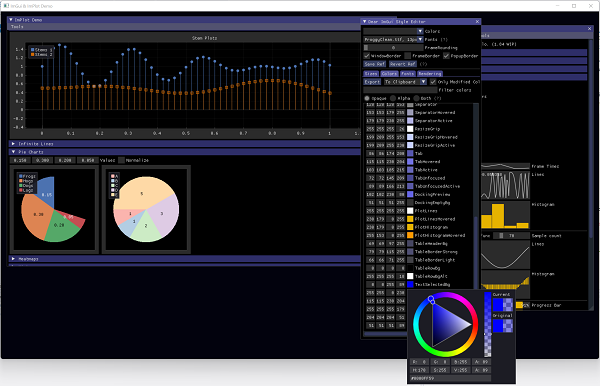
Use Open GL ES to create graphical applications on top of DirectX 3D:
-
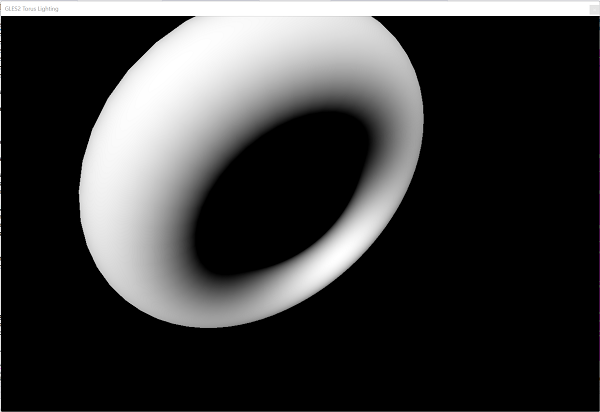
Create nice 2D effects:
-
Create animated 3D visualizations:
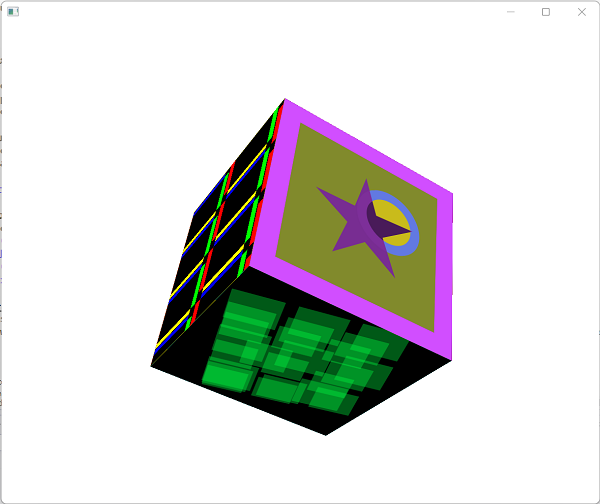
-
Learn a lot about some of the most widely used open source packages available, using Visual Studio 2022 and C++.
Harlinn.Common.Core
Harlinn.Common.Core is a library packaged as a DLL that provide functionality that is useful for most Windows C++ projects.
Dependencies
- The boost C++ libraries
Other 3rd party code included in Harlinn.Common.Core
The Harlinn.Common.Core library contains code from a number of libraries:
- The {fmt} library, version 8.0.1, by Victor Zverovich
- The xxHash library, version 0.8.1
- The CRC-32C (Castagnoli) for C++ library
- The xxhash_cx library
About char, wchar_t, signed char and unsigned char
The library tries to treat char and wchar_t as types used for the sole purpose of representing character data, while signed char and unsigned char are expected to represent signed and unsigned 8-bit integers, respectively.
Normally this is not much of a problem, but consider:
constexpr char buffer1[] = { 1,2,3 };
constexpr unsigned char buffer2[] = { 1,2,3 };
constexpr char buffer3[] = "hello";
constexpr int buffer4[] = { 1,2,3 };
constexpr wchar_t_ buffer5[] = { 1,2,3 };
constexpr wchar_t_ buffer6[] = L"hello";
constexpr auto length1 = LengthOf( buffer1 );
constexpr auto length2 = LengthOf( buffer2 );
constexpr auto length3 = LengthOf( buffer3 );
constexpr auto length4 = LengthOf( buffer4 );
constexpr auto length5 = LengthOf( buffer5 );
constexpr auto length6 = LengthOf( buffer6 );
LengthOf expects buffer1 and buffer5 to be zero-terminated; but since they are not, the compiler will not be able to evaluate LengthOf( buffer1 ) and LengthOf( buffer5 ). LengthOf( buffer3 ) and LengthOf( buffer6 ) evaluate to 5, while LengthOf( buffer2 ) and LengthOf( buffer4 ) evaluate to 3.
The code in HCCPersistent.h, which is used by the code in HCCLogger.h, relies on this, eliminating a significant number of calls to strlen and wcslen at runtime.
Main header files:
- HCC7BitEncoding.h: provides constexpr support for 7-bit encoded values.
-
HCCActiveObject.h: provides:
-
template<typename DerivedT> class ActiveObject:An active object implementation based on
ConcurrentQueue<>.
-
-
HCCApplication.h: provides:
-
class Application:Every program needs to create one, and only one, instance of this class, or a class derived from this class.
Copy Codeint main( int argc, char* argv[], char* envp[] ) { Harlinn::Common::Core::ApplicationOptions options; options.Load( ); Harlinn::Common::Core::Application application( options ); application.Start( ); // your code goes here, perhaps: int result = foo( ); application.Stop( ); return result; }Currently this configures, starts and stops the logging back-end on behalf of the program.
-
-
HCCArray.h: provides:
-
template<typename T, size_t N> ArrayEx:A template derived from std::array that supports constexpr concatenation using operator +.
-
template<typename T, size_t N> class Array:An alternative to std::array that supports constexpr concatenation using operator +.
-
template<size_t N> class ByteArray:A template that supports constexpr serialization of binary data.
-
template<size_t N, bool networkByteOrder = false, bool use7BitEncodedSize = true> class ArrayReader:A template that implements constexpr deserialization of data.
-
template<size_t N, bool networkByteOrder = false, bool use7BitEncodedSize = true> class ArrayWriter:A template that implements constexpr serialization of data.
-
- HCCBinaryReader.h: provides:
BinaryReaderBase:Copy Codetemplate<typename Derived, bool networkByteOrder, bool use7BitEncodedSize> class BinaryReaderBaseA template that can be used to deserialize binary data.BufferedBinaryReader:Copy Codetemplate<typename StreamT, size_t BufferSizeValue, bool networkByteOrder = false, bool use7BitEncodedSize = true> class BufferedBinaryReaderA template that can be used to deserialize binary data from a stream using an internal buffer.BinaryReader:Copy Codetemplate< IO::StreamReader StreamT, bool networkByteOrder = false, bool use7BitEncodedSize = true > class BinaryReaderA template that can be used to deserialize binary data from a stream.
- HCCBinaryWriter.h: provides:
BinaryWriterBase:Copy Codetemplate<typename Derived, bool networkByteOrder, bool use7BitEncodedSize> class BinaryWriterBaseA template that can be used to serialize binary data.BufferedBinaryWriter:Copy Codetemplate<IO::StreamWriter StreamWriterT, size_t BufferSizeValue, bool networkByteOrder = false, bool use7BitEncodedSize = true > class BufferedBinaryWriterA template that can be used to serialize binary data to a stream using an internal buffer.BinaryWriter:Copy Codetemplate<IO::StreamWriter StreamT, bool networkByteOrder = false, bool use7BitEncodedSize = true> class BinaryWriterA template that can be used to serialize binary data to a stream.
- HCCBuffer.h: provides
Blocks::Streama block oriented memory stream. - HCCCom.h: provides:
- HCCConverters.h: provides various overloads of:
Copy Code
template <typename ResultType, typename ArgumentType> inline ResultType ConvertTo( ArgumentType arg )
implementing efficient and 'safe' conversion between basic data types. - HCCCRC.h: provides a few ways of calculating the CRC value for data.
- HCCCrypto.h: provides functionality for working with certificates.
- HCCCurrency.h: declares the
Currencyclass. - HCCDateTime.h: provides functionality for handling date and time, declares:
class TimeSpanclass DateTimeclass Stopwatch
- HCCEnvironment.h: provides easy access to system information
- HCCEse.h: provides C++ classes for working with the Extensible Storage Engine
- HCCException.h: provides a wide range of exception classes.
- HCCGuid.h: functionality for working with UUIDs/GUIDs, declares
class Guid. - HCCHandle.h: declares
template<typename DerivedT, typename HandleT> class Handle - HCCHTTP.h: provides C++ classes for working with the HTTP Server API.
- HCCIO.h: provides file, directory, and stream I/O related C++ classes.
- HCCIOContext.h: declares:
class Context: uses a thread-pool to process asynchronous I/O for an I/O completion portclass ContextHandler: An instance of theContextclass delegates the work for a particular OS handle to theProcessoverride implemented for a class derived fromContextHandler.template<typename DerivedT> FileHandler: A template derived fromContextHandlerused to perform file related asynchronous I/O.class FileRequest: Base class for file related asynchronous I/O requests.class ReadFileRequest: Represents an asynchronous file read request.class WriteFileRequest: Represents an asynchronous file write request.class FileDispatcher: Derived fromFileHandler, broadcasts I/O completion events to callbacks attached toboost::signals2::signal<>handlers.
-
HCCLib.h: provides a number of useful funtions:
ByteSwap:Copy Codetemplate<typename T> requires IsInteger<std::remove_cvref_t<T>> inline constexpr T ByteSwap( T value )Swaps the bytes of the argument, which must be some type of integer. Performs this operation, if possible, at compile-time. If the operation must be performed at runtime, the implementation will call _byteswap_ushort, _byteswap_ulong, _byteswap_uint64, or just return the argument; based on the byte size of the argument type.
ByteSwapforfloat,doubleand enums are implemented as:Copy Codetemplate<typename T> requires (IsFloatingPoint<std::remove_cvref_t<T>> || std::is_enum_v<std::remove_cvref_t<T>> ) inline constexpr T ByteSwap( const T value ) noexcept { using Type = std::remove_cvref_t<T>; using UIntType = MakeUnsigned<Type>; std::bit_cast<Type>( ByteSwap( std::bit_cast<UIntType>( value ) ) ); }-
BitMask:Copy Codetemplate<size_t N> struct BitMask { using type = ... static constexpr type value = ...; };BitMask::type: is the type of the smallest unsigned integer capable of holding a bit-mask of N bits, where N <= 64.BitMask::value: is the value of the bit-mask with the N lowest bits set to 1. LengthOf: returns the number of elements in an array, length of a char or wchar_t zero-terminated string, or the number of elements in a container.template<typename T> inline int Compare( T v1, T v2 ) noexcept: compares two arguments of the same basic type, returning< 0if the first value is considered to be less than the second;0if they are considered equal, and otherwise> 0. Forcharorwchar_tzero-terminated strings,nullptris considered equal to a string with0length.AreNearlyEqual:Copy Codetemplate<typename T> requires std::is_floating_point_v<T> constexpr bool AreNearlyEqual( T a, T b, T smallNumber = static_cast<T>( 0.0001 ) ) noexceptreturnstrueif the absolute value of the difference betweenaandbis less thansmallNumber.class XXH64Hasher: use this class to incrementally generate a hash value from multiple inputs.IsPowerOfTwo: returnstrueif an integer is a power of2.NextPowerOfTwo: returns the next higher value, that is a power of 2, greater than the argument.
- HCCLMDB.h: declares a set of C++ classes for working with LMDB based on 3rdParty\Harlinn.LMDB.
- HCCLogger.h: logger implementation.
- HCCLogging.h: preprocessor macros used for logging.
-
HCCMath.h: constexpr math, namespace:
Harlinn::Common::Core::MathIsSameValue:Copy Codeconstexpr bool IsSameValue( double x, double y ) noexcept; constexpr bool IsSameValue( float x, float y ) noexcept;
Returnstrueifxandyholds the same value, even if they holdNaNvalues.IsZero:Copy Codeconstexpr bool IsZero( double x ) noexcept; constexpr bool IsZero( float x ) noexcept;
Returns true ifxis0.0or-0.0.-
signum:Copy Codetemplate< typename T> requires IsUnsignedInteger<std::remove_cvref_t<T>> || IsBoolean<std::remove_cvref_t<T>> inline constexpr T signum( T val ) noexcept; template< typename T> requires IsSignedInteger<std::remove_cvref_t<T>> inline constexpr T signum( T val ) noexcept; template< typename T> requires IsFloatingPoint<std::remove_cvref_t<T>> inline constexpr T signum( T val ) noexcept;Indicates the sign of
val, returning-1,0, or+1. Deg2Rad:Copy Codetemplate< typename T> requires IsFloatingPoint<std::remove_cvref_t<T>> inline constexpr std::remove_cvref_t<T> Deg2Rad( T angleInDegrees ) noexcept;ConvertangleInDegreesfrom degrees to radians.Rad2Deg:Copy Codetemplate< typename T> requires IsFloatingPoint<std::remove_cvref_t<T>> inline constexpr std::remove_cvref_t<T> Rad2Deg( T angleInRadians ) noexcept;ConvertangleInRadiansfrom radians to degrees.NextAfter:Copy Codeinline constexpr double NextAfter( double x, double y ) noexcept; inline constexpr double NextAfter( float x, float y ) noexcept;
Returns the next representable value of x in the direction of y.NextDown:Copy Codetemplate<typename T> requires IsFloatingPoint<T> inline constexpr std::remove_cvref_t<T> NextDown( T x ) noexcept;Returns the next representable value of x in the direction of negative infinity.NextUp:Copy Codetemplate<typename T> requires IsFloatingPoint<T> inline constexpr std::remove_cvref_t<T> NextUp( T x ) noexcept;Returns the next representable value of x in the direction of positive infinity.-
IsNaN:Copy Codetemplate<typename T> requires IsInteger<T> constexpr inline bool IsNaN( T val ) noexcept; template<typename T> requires IsFloatingPoint<T> constexpr inline bool IsNaN( T val ) noexcept;Returns
trueifvalisNaN. -
IsInf:Copy Codetemplate<typename T> requires IsInteger<T> constexpr inline bool IsInf( T val ) noexcept; template<typename T> requires IsFloatingPoint<T> constexpr inline bool IsInf( T val ) noexcept;Returns
trueifvalis infinite. -
Abs:Copy Codetemplate<typename T> requires IsSignedInteger<T> constexpr inline std::remove_cvref_t<T> Abs( T val ) noexcept; template<typename T> requires IsUnsignedInteger<T> constexpr inline std::remove_cvref_t<T> Abs( T val ) noexcept; template<typename T> requires IsFloatingPoint<T> constexpr inline std::remove_cvref_t<T> Abs( T val ) noexcept;Returns the absolute value of
val. -
SignBit:Copy Codetemplate<typename T> requires IsSignedInteger<T> constexpr inline bool SignBit( T val ) noexcept; template<typename T> requires IsUnsignedInteger<T> constexpr inline bool SignBit( T val ) noexcept; template<typename T> requires IsFloatingPoint<T> constexpr inline bool SignBit( T val ) noexcept;Returns
trueif the value of the sign ofvalis negative, otherwisefalse. -
FRExp:Copy Codetemplate<typename T> requires IsInteger<T> constexpr inline std::pair<double,int> FRExp( T val ) noexcept; template<typename T> requires IsFloatingPoint<T> constexpr inline std::pair<double,int> FRExp( T val ) noexcept; template<typename T> requires IsInteger<T> constexpr inline double FRExp( T val, int* exp ) noexcept; template<typename T> requires IsFloatingPoint<T> constexpr inline std::remove_cvref_t<T> FRExp( T val, int* exp ) noexcept; template<typename T> requires IsInteger<T> constexpr inline double FRExp( T val, int& exp ) noexcept; template<typename T> requires IsFloatingPoint<T> constexpr inline std::remove_cvref_t<T> FRExp( T val, int& exp ) noexcept;Return
(result,exp)such thatresulthas a magnitude in the interval[1/2, 1)or0, and val is equal toresult*2exp. -
ModF:Copy Codetemplate<typename T> requires IsFloatingPoint<T> constexpr inline std::pair<std::remove_cvref_t<T>, std::remove_cvref_t<T>> ModF( T val ) noexcept; template<typename T> requires IsFloatingPoint<T> constexpr inline std::remove_cvref_t<T> ModF( T val, T* integerPart ) noexcept; template<typename T> requires IsFloatingPoint<T> constexpr inline std::remove_cvref_t<T> ModF( T val, T& integerPart ) noexcept;Return a
std::pair<T,T>of the fractional and integral parts of a number. Both parts have the same sign as the argument. -
Min:Copy Codetemplate<typename T> requires IsFloatingPoint<T> constexpr inline std::remove_cvref_t<T> Min( T first, T second ) noexcept; template<typename T> requires IsInteger<T> constexpr inline std::remove_cvref_t<T> Min( T first, T second ) noexcept;Returns the smaller of the argument values.
-
Max:Copy Codetemplate<typename T> requires IsFloatingPoint<T> constexpr inline std::remove_cvref_t<T> Max( T first, T second ) noexcept; template<typename T> requires IsInteger<T> constexpr inline std::remove_cvref_t<T> Max( T first, T second ) noexcept;Returns the greater of the argument values.
-
Trunc:Copy Codetemplate<typename T> requires IsFloatingPoint<T> constexpr inline std::remove_cvref_t<T> Trunc( T val ) noexcept; template<typename T> requires IsInteger<T> constexpr inline std::remove_cvref_t<T> Trunc( T val ) noexcept;Returns the nearest integral value of the same type as
valwhose absolute value is less than or equal to the absolute value ofval. -
Floor:Copy Codetemplate<typename T> requires IsFloatingPoint<T> constexpr inline std::remove_cvref_t<T> Floor( T val ) noexcept; template<typename T> requires IsInteger<T> constexpr inline std::remove_cvref_t<T> Floor( T val ) noexcept;Returns the nearest integral value of the same type as
valthat is less than or equal toval. -
Ceil:Copy Codetemplate<typename T> requires IsFloatingPoint<T> constexpr inline std::remove_cvref_t<T> Ceil( T val ) noexcept; template<typename T> requires IsInteger<T> constexpr inline std::remove_cvref_t<T> Ceil( T val ) noexcept;Returns the nearest integral value of the same type as
valthat is greater than or equal toval. -
Round:Copy Codetemplate<typename T> requires IsFloatingPoint<T> constexpr inline std::remove_cvref_t<T> Round( T val ) noexcept; template<typename T> requires IsInteger<T> constexpr inline std::remove_cvref_t<T> Round( T val ) noexcept;Returns
valrounded to the nearest integral value. -
Clamp:Copy Codetemplate<typename T> requires IsFloatingPoint<T> constexpr inline std::remove_cvref_t<T> Clamp( T val, T minimumValue, T maximumValue ) noexcept; template<typename T> requires ( IsInteger<T> ) constexpr inline std::remove_cvref_t<T> Clamp( T val, T minimumValue, T maximumValue ) noexcept;If
valcompares less thanminimumValue, returnsminimumValue; otherwise ifmaximumValuecompares less thanval, returnsmaximumValue; otherwise returnsval. Lerp:Copy Codetemplate<typename T, typename U> requires ( ( IsInteger<T> || IsFloatingPoint<T> ) && ( IsInteger<U> || IsFloatingPoint<U> ) ) constexpr inline std::conditional_t<IsFloatingPoint<T>, T, std::conditional_t<IsFloatingPoint<U>, U, T>> Lerp( T a, T b, U t ) noexcept;Computes the linear interpolation betweenaandbfor the parametert(or extrapolation, whentis outside the range [0,1]).CopySign:Copy Codetemplate<typename T> requires IsFloatingPoint<T> constexpr inline std::remove_cvref_t<T> CopySign( T magnitude, T signValue ) noexcept;Returns a value with the magnitude ofmagnitudeand the sign ofsignValue.ScaleByN:Copy Codeinline constexpr double ScaleByN( double x, int n ) noexcept; inline constexpr double ScaleByN( float x, int n ) noexcept;
Multiplies a floating point valuexbyFLT_RADIXraised to powern.FMod:Copy Codeinline constexpr double FMod( double x, double y ) noexcept; inline constexpr float FMod( float x, float y ) noexcept;
Computes the floating-point remainder of the division operationx/y.Exp:Copy Codetemplate<typename T> requires IsFloatingPoint<T> constexpr inline std::remove_cvref_t<T> Exp( T x ) noexcept;Computes e (Euler's number, 2.7182818)) raised to the given power ofx.Hypot:Copy Codetemplate<typename T> requires IsFloatingPoint<T> constexpr inline std::remove_cvref_t<T> Hypot( T x, T y ) noexcept;Computes the hypotenuse.Log:Copy Codetemplate<typename T> requires IsFloatingPoint<T> constexpr inline std::remove_cvref_t<T> Log( T x ) noexcept;Computes the natural (base e)) logarithm ofx.Log2:Copy Codetemplate<typename T> requires IsFloatingPoint<T> constexpr inline std::remove_cvref_t<T> Log2( T x ) noexcept;Computes the base 2 logarithm ofx.Log10:Copy Codetemplate<typename T> requires IsFloatingPoint<T> constexpr inline std::remove_cvref_t<T> Log10( T x ) noexcept;Computes the base 10 logarithm ofx.Sin:Copy Codetemplate<typename T> requires IsFloatingPoint<T> constexpr inline std::remove_cvref_t<T> Sin( T x ) noexcept;Computes the sine ofx, wherexis in radians.ASin:Copy Codetemplate<typename T> requires IsFloatingPoint<T> constexpr inline std::remove_cvref_t<T> ASin( T x ) noexcept;Computes the inverse sine ofx, in radians.Cos:Copy Codetemplate<typename T> requires IsFloatingPoint<T> constexpr inline std::remove_cvref_t<T> Cos( T x ) noexcept;Computes cosine ofx, wherexis in radians.ACos:Copy Codetemplate<typename T> requires IsFloatingPoint<T> constexpr inline std::remove_cvref_t<T> ACos( T x ) noexcept;Computes the inverse cosine ofx, with the result in radians.Tan:Copy Codetemplate<typename T> requires IsFloatingPoint<T> constexpr inline std::remove_cvref_t<T> Tan( T x ) noexcept;Computes tangent ofx, wherexis in radians.-
ATan,ATan2:Copy Codetemplate<typename T> requires IsFloatingPoint<T> constexpr inline std::remove_cvref_t<T> ATan( T x ) noexcept; template<typename T> requires IsFloatingPoint<T> constexpr inline std::remove_cvref_t<T> ATan( T x, T y ) noexcept template<typename T> requires IsFloatingPoint<T> constexpr inline std::remove_cvref_t<T> ATan2( T x, T y ) noexceptCompute the inverse tangent of
yory/x, respectively. SinCos:Copy Codetemplate<typename T> requires IsFloatingPoint<T> inline constexpr void SinCos( T x, T& sinResult, T& cosResult ) noexcept;Simultaneously compute the sine and cosine ofx, wherexis in radians.
- HCCObj.h: provides wrapper C++ classes for a wide range of Windows COM interfaces.
- HCCObjBase.h: provides wrapper C++ classes for central Windows COM interfaces.
- HCCObservable.h: declares
template<typename DerivedT> class Observableand a couple macros that can be used to implement observable properties. - HCCPersistent.h: provides a flexible and efficient serialization and deserialization mechanism.
- HCCPersistentDecoder.h: provides a generic decoder for data serialized using the mechanism provided in HCCPersistent.h.
- HCCPipe.h: Synchronous and synchronous I/O using named pipes.
- HCCProcess.h: classes for working with Windows processes.
- HCCPropSys.h: classes for working with the (Windows Property System)[https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/windows/win32/api/_properties/]
- HCCReference.h: support for intrusive reference counted objects.
- HCCSecurity.h: classes for working with Windows Security and identity
- HCCShell.h: classes for working with the Windows Shell API).
- HCCSocket.h: Synchronous and synchronous I/O using sockets.
- HCCSync.h: classes for working with synchronization.
- HCCThread.h: classes for working with threads.
- HCCTraits.h: useful meta programming features.
- HCCTuple.h: yet another tuple implementation.
- HCCVariant.h: provides functionality for working with the VARIANT structure.
- HCCVector.h: yet another vector implementation.
- HCCXml.h: classes for working with the MSXML SDK).
Harlinn.Windows
Harlinn.Windows provides functionality for developing user interfaces in C++.
It is used to implement 73 of the examples.
Main header files:
- HWDXGI.h: provides support for the DirectX Graphics Infrastructure API.
- HWGraphicsD3D12.h: provides support for the Direct3D 12 API.
- HWGraphics.h: provides support for the Direct2D API.
- HWImaging.h: provides support for the Windows Imaging Component API
- HWHandles.h: provides support for the Windows GDI API.
- HWControl.h: provides support for working with Windows Controls
- HWMessage.h: provides the Message class, a simple abstraction for the MSG structure
- HWMenu.h: provides support for working with Windows Menus.
- HWForm.h: provides support for working with top level Windows Controls using the Form class.
- HWApplication.h: provides an Application class and a MessageLoop class.
- HWDXApplication.h: declares some Direct3D 12 utility classes:
class DXMessageLoop: The render/message loop.class DXContext: Initializes and manages interaction with theD3D12Device, theDXGI::SwapChain3, theD3D12GraphicsCommandList, and the few other objects required for interaction with the Direct3D 12 API.class DXApplication: Derived fromWindows::Application, tailored for developing Direct3D 12 usingWindows::Form.
- HWStdCtrls.h: provides a number of classes for working with standard Windows controls. The provided functionality is, unfortunately, quite limited.
- HWFileDialog.h: provides support for the Open and Save As functionality from the Common Dialog Box Library.
- HWEnvironment.h: provides easy access to system information.
- HWSkia.h: provides support for creating Skia based applications.
- HWImGui.h: provides support for creating Dear ImGui based applications.
HWControl.h, HWMessage.h, HWMenu.h, HWForm.h, HWApplication.h, HWStdCtrls.h, HWFileDialog.h, HWSkia.h are meant to be used together, while HWDXGI.h, HWGraphicsD3D12.h, HWGraphics.h, HWImaging.h and HWHandles.h can be used on their own.
These days I often use the slightly modified version of Dear ImGui and ImPlot located under 3rdParty\Harlinn.ImGui to create user interfaces for my Harlinn\:\:Windows\:\:Form based applications.
#include "HWDXApplication.h"
#include "HWImGui.h"
#include "HWmenu.h"
#include "HWstdctrls.h"
#include <iostream>
using namespace Harlinn;
int main()
{
try
{
Windows::ApplicationOptions applicationOptions;
applicationOptions.Load( );
Windows::ImGui::Application application( applicationOptions );
application.Start( );
Windows::ImGui::Form form;
form.SetText( L"ImGui & ImPlot Demo" );
bool showImGuiDemoWindow = true;
bool showImPlotDemoWindow = true;
bool showAnotherWindow = false;
form.OnRender.connect( [&showImGuiDemoWindow,&showImPlotDemoWindow, &showAnotherWindow]( Windows::ImGui::Form* sender )
{
if ( showImGuiDemoWindow )
{
ImGui::ShowDemoWindow( &showImGuiDemoWindow );
}
if ( showImPlotDemoWindow )
{
ImPlot::ShowDemoWindow( &showImPlotDemoWindow );
}
} );
auto result = application.Run( form );
application.Stop( );
return result;
}
catch ( std::exception& exc )
{
std::cout << exc.what( ) << std::endl;
}
catch ( ... )
{
std::cout << "Unknown exception" << std::endl;
}
return 0;
}
Harlinn.OCI
Harlinn.OCI provides high performance access to the Oracle RDBMS using the Oracle OCI API
Harlinn.ODBC
Harlinn.ODBC provides high performance access to database servers and engines through the ODBC API.
Harlinn.Common.Config
This library implements an in-memory hierarchical storage suitable for handling configuration information.
Harlinn.Julia
This library provides easy access to Julia.
3rd party libraries
This solution contains a few useful C and C++ libraries located under the 3rdParty folder.
Header only libraries are contained within ''Static library (.lib)'' projects, everything else creates a DLL.
All C++ code compiles using /std:c++latest and /Zc:__cplusplus
abseil
Version: 20210324.2
Description:
Abseil is an open source collection of C++ libraries drawn from the most fundamental pieces of Google’s internal code-base. These libraries are the nuts-and-bolts that underpin almost everything Google runs. Bits and pieces of these APIs are embedded in most of our open source projects, and Abseil aims to bring them together into one comprehensive project. Abseil encompasses the most basic building blocks of Google’s code-base: code that is production-tested and will be fully maintained for years to come.
Projects:
- Harlinn.abseil
- Tests\3rdParty\abseil\abseil_test
The abseil_test contains the unit tests for the Harlinn.abseil project
libaec - Adaptive Entropy Coding library
Version: master as of 2021.08.26
Description:
Libaec provides fast lossless compression of 1 up to 32 bit wide signed or unsigned integers (samples).
Project: Harlinn.aec
ANGLE - Almost Native Graphics Layer Engine
Version: master as of 2021.09.20
Description:
The goal of ANGLE is to allow users of multiple operating systems to seamlessly run WebGL and other OpenGL ES content by translating OpenGL ES API calls to one of the hardware-supported APIs available for that platform. ANGLE currently provides translation from OpenGL ES 2.0, 3.0 and 3.1 to Vulkan, desktop OpenGL, OpenGL ES, Direct3D 9, and Direct3D 11.
Projects:
- Harlinn.angle
- Harlinn.angle-egl
- Harlinn.angle-gl
- Harlinn.angle-glesv1
- Harlinn.angle-glesv2
- Harlinn.angle-opencl
- Harlinn.angle-util
Alliance for Open Media - AV1 Codec Library
Version: 3.1.2
Description:
AV1 Codec Library
Project: Harlinn.aom
Armadillo: C++ Library for Linear Algebra & Scientific Computing
Version: 10.6.x
Description:
Armadillo is a high quality linear algebra library (matrix maths) for the C++ language, aiming towards a good balance between speed and ease of use
Provides high-level syntax and functionality deliberately similar to Matlab
Useful for algorithm development directly in C++, or quick conversion of research code into production environments
Provides efficient classes for vectors, matrices and cubes; dense and sparse matrices are supported
Integer, floating point and complex numbers are supported
A sophisticated expression evaluator (based on template meta-programming) automatically combines several operations to increase speed and efficiency
Various matrix decompositions (eigen, SVD, QR, etc) are provided through integration with LAPACK, or one of its high performance drop-in replacements (eg. MKL or OpenBLAS)
Can automatically use OpenMP multi-threading (parallelisation) to speed up computationally expensive operations
Distributed under the permissive Apache 2.0 license, useful for both open-source and proprietary (closed-source) software
Can be used for machine learning, pattern recognition, computer vision, signal processing, bioinformatics, statistics, finance, etc
Project: Harlinn.armadillo
BoringSSL
Version: master as of 2021.09.20
Description:
BoringSSL is a fork of OpenSSL that is designed to meet Google's needs.
Projects:
- Harlinn.boringssl
- Tests\3rdParty\boringssl\crypto_test
- Tests\3rdParty\boringssl\ssl_test
Brotli
Version: master as of 2021.08.04
Description:
Brotli is a generic-purpose lossless compression algorithm that compresses data using a combination of a modern variant of the LZ77 algorithm, Huffman coding and 2nd order context modeling, with a compression ratio comparable to the best currently available general-purpose compression methods. It is similar in speed with deflate but offers more dense compression.
Project: Harlinn.brotli
bzip2
Version: 1.0.8
Description:
bzip2 is a freely available, patent free (see below), high-quality data compressor. It typically compresses files to within 10% to 15% of the best available techniques (the PPM family of statistical compressors), whilst being around twice as fast at compression and six times faster at decompression.
Project: Harlinn.bzip2
c-ares is a C library for asynchronous DNS requests (including name resolves)
Version: 1.17.0
Description:
c-ares is a C library for asynchronous DNS requests (including name resolves)
Project: Harlinn.c-ares
CFITSIO - A FITS File Subroutine Library
Version: 4.0.0
Description:
CFITSIO is a library of C and Fortran subroutines for reading and writing data files in FITS (Flexible Image Transport System) data format. CFITSIO provides simple high-level routines for reading and writing FITS files that insulate the programmer from the internal complexities of the FITS format. CFITSIO also provides many advanced features for manipulating and filtering the information in FITS files.
Project: Harlinn.cfitsio
Advanced DXTn texture compression library
Version: 1.04
Description:
crnlib is a lossy texture compression library for developers that ship content using the DXT1/5/N or 3DC compressed color/normal map/cubemap mipmapped texture formats.
It can compress mipmapped 2D textures, normal maps, and cubemaps to approx. 1-1.25 bits/texel, and normal maps to 1.75-2 bits/texel. The actual bitrate depends on the complexity of the texture itself, the specified quality factor/target bitrate, and ultimately on the desired quality needed for a particular texture.
Project: Harlinn.crnlib
libcurl - the multiprotocol file transfer library
Version: 7.78.0
Description:
libcurl is a free and easy-to-use client-side URL transfer library, supporting DICT, FILE, FTP, FTPS, GOPHER, GOPHERS, HTTP, HTTPS, IMAP, IMAPS, LDAP, LDAPS, MQTT, POP3, POP3S, RTMP, RTMPS, RTSP, SCP, SFTP, SMB, SMBS, SMTP, SMTPS, TELNET and TFTP. libcurl supports SSL certificates, HTTP POST, HTTP PUT, FTP uploading, HTTP form based upload, proxies, HTTP/2, HTTP/3, cookies, user+password authentication (Basic, Digest, NTLM, Negotiate, Kerberos), file transfer resume, http proxy tunneling and more!
Project: Harlinn.curl
D3D12 Memory Allocator
Version: 2.0.0-development (2021-07-26)
Description:
Easy to integrate memory allocation library for Direct3D 12
Project: Harlinn.d3d12allocator
libdeflate
Version: 1.8
Description:
libdeflate is a library for fast, whole-buffer DEFLATE-based compression and decompression
Project: Harlinn.deflate
Adobe Digital Negative (DNG) SDK
Version: 1.5.1
Description:
The DNG SDK provides support for reading and writing DNG files as well as for converting DNG data to a format that is easily displayed or processed by imaging applications.
Project: Harlinn.dngsdk
Effcee
Version: main as of 2021.09.27
Description:
Effcee is a C++ library for stateful pattern matching of strings, inspired by LLVM's FileCheck command.
Project: Harlinn.effcee
Expat
Version: 2.4.1
Description:
This is Expat, a C library for parsing XML, started by James Clark in 1997. Expat is a stream-oriented XML parser. This means that you register handlers with the parser before starting the parse. These handlers are called when the parser discovers the associated structures in the document being parsed. A start tag is an example of the kind of structures for which you may register handlers.
Project: Harlinn.expat
Freetype
Version: 2.11.0
Description:
FreeType is a freely available software library to render fonts.
It is written in C, designed to be small, efficient, highly customizable, and portable while capable of producing high-quality output (glyph images) of most vector and bitmap font formats.
Project: Harlinn.freetype
GDAL - Geospatial Data Abstraction Library
Version: 3.4.0
Description:
GDAL is a translator library for raster and vector geospatial data formats that is released under an X/MIT style Open Source License by the Open Source Geospatial Foundation. As a library, it presents a single raster abstract data model and single vector abstract data model to the calling application for all supported formats.
Project: Harlinn.gdal
GEOS - coordinate transformation software library
Version: 3.10.0dev
Description:
GEOS is a C/C++ library for spatial computational geometry of the sort generally used by “geographic information systems” software.
Project: Harlinn.geos
Google gflags
Version: 2.2.2
Description:
Gflags, the commandline flags library used within Google, differs from other libraries, such as getopt(), in that flag definitions can be scattered around the source code, and not just listed in one place such as main(). In practice, this means that a single source-code file will define and use flags that are meaningful to that file. Any application that links in that file will get the flags, and the gflags library will automatically handle that flag appropriately.
There's significant gain in flexibility, and ease of code reuse, due to this technique.
Project: Harlinn.gflags
Giflib
Version: 5.2.1
Project: Harlinn.gif
Description:
giflib is a library for reading and writing gif images.
GLFW - multi-platform library for OpenGL, OpenGL ES and Vulkan development on the desktop
Version: 3.3.4
Description:
GLFW is an Open Source, multi-platform library for OpenGL, OpenGL ES and Vulkan development on the desktop. It provides a simple API for creating windows, contexts and surfaces, receiving input and events.
Project: Harlinn.glfw
Glslang
Version: 2020.07.28
Description:
Reference Validator and GLSL/ESSL -> AST Front End
An OpenGL GLSL and OpenGL|ES GLSL (ESSL) front-end for reference validation and translation of GLSL/ESSL into an internal abstract syntax tree (AST).
HLSL -> AST Front End
An HLSL front-end for translation of an approximation of HLSL to glslang's AST form.
AST -> SPIR-V Back End
Translates glslang's AST to the Khronos-specified SPIR-V intermediate language.
Reflector
An API for getting reflection information from the AST, reflection types/variables/etc. from the HLL source (not the SPIR-V).
Project: Harlinn.glslang
gRPC
Version: 1.41.1
Description:
gRPC is a modern open source high performance Remote Procedure Call (RPC) framework that can run in any environment. It can efficiently connect services in and across data centers with pluggable support for load balancing, tracing, health checking and authentication. It is also applicable in last mile of distributed computing to connect devices, mobile applications and browsers to backend services.
Projects:
- Harlinn.grpc
- Harlinn.grpc-compiler
- Tools\3rdParty\grpc\gen_hpack_tables
- Tools\3rdParty\grpc\grpc_cpp_plugin
- Tools\3rdParty\grpc\grpc_csharp_plugin
- Tools\3rdParty\grpc\grpc_node_plugin
- Tools\3rdParty\grpc\grpc_objective_c_plugin
- Tools\3rdParty\grpc\grpc_php_plugin
- Tools\3rdParty\grpc\grpc_python_plugin
- Tools\3rdParty\grpc\grpc_ruby_plugin
- Tests\3rdParty\gRPC\core\address_utils\grpc_test_core_address_utils_parse_address_test
- Tests\3rdParty\gRPC\core\address_utils\grpc_test_core_address_utils_parse_address_with_named_scope_id_test
- Tests\3rdParty\gRPC\core\address_utils\grpc_test_core_address_utils_sockaddr_utils_test
- Tests\3rdParty\gRPC\core\avl\grpc_test_avl_avl_test
- Tests\3rdParty\gRPC\core\backoff\grpc_test_backoff_backoff_test
- Tests\3rdParty\gRPC\core\bad_client\grpc_test_bad_client_badreq
- Tests\3rdParty\gRPC\core\bad_client\grpc_test_bad_client_bad_streaming_id
- Tests\3rdParty\gRPC\core\bad_client\grpc_test_bad_client_connection_prefix
- Tests\3rdParty\gRPC\core\bad_client\grpc_test_bad_client_duplicate_header
- Tests\3rdParty\gRPC\core\bad_client\grpc_test_bad_client_headers
- Tests\3rdParty\gRPC\core\bad_client\grpc_test_bad_client_head_of_line_blocking
- Tests\3rdParty\gRPC\core\bad_client\grpc_test_bad_client_initial_settings_frame
- Tests\3rdParty\gRPC\core\bad_client\grpc_test_bad_client_large_metadata
- Tests\3rdParty\gRPC\core\bad_client\grpc_test_bad_client_out_of_bounds
- Tests\3rdParty\gRPC\core\bad_client\grpc_test_bad_client_server_registered_method
- Tests\3rdParty\gRPC\core\bad_client\grpc_test_bad_client_simple_request
- Tests\3rdParty\gRPC\core\bad_client\grpc_test_bad_client_unknown_frame
- Tests\3rdParty\gRPC\core\bad_client\grpc_test_bad_client_window_overflow
- Tests\3rdParty\gRPC\core\bad_connection\grpc_test_bad_connection_close_fd_test
- Tests\3rdParty\gRPC\core\bad_ssl\grpc_test_bad_ssl_alpn_server_test
- Tests\3rdParty\gRPC\core\bad_ssl\grpc_test_bad_ssl_bad_ssl_test
- Tests\3rdParty\gRPC\core\bad_ssl\grpc_test_bad_ssl_cert_server_test
- Tests\3rdParty\gRPC\core\channel\grpc_test_channel_channel_args_test
- Tests\3rdParty\gRPC\core\channel\grpc_test_channel_channel_stack_builder_test
- Tests\3rdParty\gRPC\core\channel\grpc_test_channel_channel_stack_test
- Tests\3rdParty\gRPC\core\channel\grpc_test_channel_channel_trace_test
- Tests\3rdParty\gRPC\core\channel\grpc_test_core_channelz_registry_test
- Tests\3rdParty\gRPC\core\channel\grpc_test_core_channelz_test
- Tests\3rdParty\gRPC\core\channel\grpc_test_core_channel_status_util_test
- Tests\3rdParty\gRPC\core\channel\grpc_test_core_minimal_stack_is_minimal_test
- Tests\3rdParty\gRPC\core\client_channel\grpc_test_core_client_channel_certificate_provider_registry_test
- Tests\3rdParty\gRPC\core\client_channel\grpc_test_core_client_channel_retry_throttle_test
- Tests\3rdParty\gRPC\core\client_channel\grpc_test_core_client_channel_service_config_test
- Tests\3rdParty\gRPC\core\client_channel\resolvers\dns_resolver_connectivity_test
- Tests\3rdParty\gRPC\core\client_channel\resolvers\dns_resolver_cooldown_test
- Tests\3rdParty\gRPC\core\client_channel\resolvers\grpc_test_dns_resolver_test
- Tests\3rdParty\gRPC\core\client_channel\resolvers\grpc_test_fake_resolver_test
- Tests\3rdParty\gRPC\core\client_channel\resolvers\grpc_test_sockaddr_resolver_test
- Tests\3rdParty\gRPC\core\compression\grpc_test_core_compression_algorithm_test
- Tests\3rdParty\gRPC\core\compression\grpc_test_core_compression_compression_test
- Tests\3rdParty\gRPC\core\compression\grpc_test_core_compression_message_compress_test
- Tests\3rdParty\gRPC\core\compression\grpc_test_core_compression_stream_compression_test
- Tests\3rdParty\gRPC\core\config\grpc_test_core_config_core_configuration_test
- Tests\3rdParty\gRPC\core\debug\grpc_test_core_debug_stats_test
- Tests\3rdParty\gRPC\core\event_engine\grpc_test_core_event_engine_endpoint_config_test
- Tests\3rdParty\gRPC\core\fling\fling_client
- Tests\3rdParty\gRPC\core\fling\fling_server
- Tests\3rdParty\gRPC\core\fling\grpc_test_core_fling_fling_stream_test
- Tests\3rdParty\gRPC\core\fling\grpc_test_core_fling_fling_test
- Tests\3rdParty\gRPC\core\gpr\grpc_test_core_gpr_alloc_test
- Tests\3rdParty\gRPC\core\gpr\grpc_test_core_gpr_arena_test
- Tests\3rdParty\gRPC\core\gpr\grpc_test_core_gpr_cpu_test
- Tests\3rdParty\gRPC\core\gpr\grpc_test_core_gpr_env_test
- Tests\3rdParty\gRPC\core\gpr\grpc_test_core_gpr_log_test
- Tests\3rdParty\gRPC\core\gpr\grpc_test_core_gpr_murmur_hash_test
- Tests\3rdParty\gRPC\core\gpr\grpc_test_core_gpr_spinlock_test
- Tests\3rdParty\gRPC\core\gpr\grpc_test_core_gpr_string_test
- Tests\3rdParty\gRPC\core\gpr\grpc_test_core_gpr_sync_test
- Tests\3rdParty\gRPC\core\gpr\grpc_test_core_gpr_time_test
- Tests\3rdParty\gRPC\core\gpr\grpc_test_core_gpr_tls_test
- Tests\3rdParty\gRPC\core\gpr\grpc_test_core_gpr_useful_test
- Tests\3rdParty\gRPC\core\gprpp\grpc_test_core_gprpp_bitset_test
- Tests\3rdParty\gRPC\core\gprpp\grpc_test_core_gprpp_capture_test
- Tests\3rdParty\gRPC\core\gprpp\grpc_test_core_gprpp_dual_ref_counted_test
- Tests\3rdParty\gRPC\core\gprpp\grpc_test_core_gprpp_examine_stack_test
- Tests\3rdParty\gRPC\core\gprpp\grpc_test_core_gprpp_fork_test
- Tests\3rdParty\gRPC\core\gprpp\grpc_test_core_gprpp_global_config_env_test
- Tests\3rdParty\gRPC\core\gprpp\grpc_test_core_gprpp_global_config_test
- Tests\3rdParty\gRPC\core\gprpp\grpc_test_core_gprpp_host_port_test
- Tests\3rdParty\gRPC\core\gprpp\grpc_test_core_gprpp_manual_constructor_test
- Tests\3rdParty\gRPC\core\gprpp\grpc_test_core_gprpp_match_test
- Tests\3rdParty\gRPC\core\gprpp\grpc_test_core_gprpp_mpscq_test
- Tests\3rdParty\gRPC\core\gprpp\grpc_test_core_gprpp_orphanable_test
- Tests\3rdParty\gRPC\core\gprpp\grpc_test_core_gprpp_overload_test
- Tests\3rdParty\gRPC\core\gprpp\grpc_test_core_gprpp_ref_counted_ptr_test
- Tests\3rdParty\gRPC\core\gprpp\grpc_test_core_gprpp_ref_counted_test
- Tests\3rdParty\gRPC\core\gprpp\grpc_test_core_gprpp_status_helper_test
- Tests\3rdParty\gRPC\core\gprpp\grpc_test_core_gprpp_stat_test
- Tests\3rdParty\gRPC\core\gprpp\grpc_test_core_gprpp_table_test
- Tests\3rdParty\gRPC\core\gprpp\grpc_test_core_gprpp_thd_test
- Tests\3rdParty\gRPC\core\gprpp\grpc_test_core_gprpp_time_util_test
- Tests\3rdParty\gRPC\core\iomgr\grpc_test_core_iomgr_combiner_test
- Tests\3rdParty\gRPC\core\iomgr\grpc_test_core_iomgr_endpoint_pair_test
- Tests\3rdParty\gRPC\core\iomgr\grpc_test_core_iomgr_error_test
- Tests\3rdParty\gRPC\core\iomgr\grpc_test_core_iomgr_grpc_ipv6_loopback_available_test
- Tests\3rdParty\gRPC\core\iomgr\grpc_test_core_iomgr_load_file_test
- Tests\3rdParty\gRPC\core\iomgr\grpc_test_core_iomgr_mpmcqueue_test
- Tests\3rdParty\gRPC\core\iomgr\grpc_test_core_iomgr_pollset_windows_starvation_test
- Tests\3rdParty\gRPC\core\iomgr\grpc_test_core_iomgr_resolve_address_test
- Tests\3rdParty\gRPC\core\iomgr\grpc_test_core_iomgr_resource_quota_test
- Tests\3rdParty\gRPC\core\iomgr\grpc_test_core_iomgr_threadpool_test
- Tests\3rdParty\gRPC\core\iomgr\grpc_test_core_iomgr_timer_heap_test
- Tests\3rdParty\gRPC\core\iomgr\grpc_test_core_iomgr_timer_list_test
- Tests\3rdParty\gRPC\core\iomgr\grpc_test_core_iomgr_time_averaged_stats_test
- Tests\3rdParty\gRPC\grpc_test_core_util
libgta - Generic Tagged Arrays
Version: 1.2.1
Description:
Libgta, a library that reads and writes GTA files.
Project: Harlinn.gta
GoogleTest
Version: 1.11.0
Description:
GoogleTest is Google’s C++ testing and mocking framework.
Project: Harlinn.gtest
HarfBuzz, a text shaping library
Version: 3.0.0
Description:
HarfBuzz is a text shaping library. Using the HarfBuzz library allows programs to convert a sequence of Unicode input into properly formatted and positioned glyph output—for any writing system and language.
Project: Harlinn.harfbuzz
HDF
Version: 4.2.15
Description:
The Hierarchical Data Format, or HDF, is a multiobject file format for sharing scientific data in a distributed environment. HDF was created at the National Center for Supercomputing Applications, and is now developed and maintained by The HDF Group, to serve the needs of diverse groups of scientists working on projects in various fields
Project: Harlinn.hdf4
HDF5
Version: 1.12.1
Description:
The HDF Group is the developer of HDF5®, a high-performance software library and data format that has been adopted across multiple industries and has become a de facto standard in scientific and research communities.
Project: Harlinn.hdf5
Highway
Version: 0.14.2
Description:
Highway is a C++ library for SIMD (Single Instruction, Multiple Data), i.e. applying the same operation to multiple 'lanes' using a single CPU instruction.
Project: Harlinn.highway
Imath
Version: master as of 2021.08.18
Description:
Imath is a basic, light-weight, and efficient C++ representation of 2D and 3D vectors and matrices and other simple but useful mathematical objects, functions, and data types common in computer graphics applications, including the “half” 16-bit floating-point type.
Project: Harlinn.imath
Dear ImGui and ImPlot
Version: master as of 2021.07.14
Description: Packages Dear ImGui and ImPlot as a single DLL.
Description 'Dear ImGui':
Dear ImGui is a bloat-free graphical user interface library for C++. It outputs optimized vertex buffers that you can render anytime in your 3D-pipeline enabled application.
Description 'ImPlot':
ImPlot is an immediate mode, GPU accelerated plotting library for Dear ImGui. It aims to provide a first-class API that ImGui fans will love. ImPlot is well suited for visualizing program data in real-time or creating interactive plots, and requires minimal code to integrate.
Project: Harlinn.ImGui
JasPer Image Processing/Coding Tool Kit
Version: 2.0.33
Description:
JasPer Image Processing/Coding Tool Kit
Project: Harlinn.jasper
The Independent JPEG Group's JPEG software
Version: 9d
Description:
IJG is an informal group that writes and distributes a widely used free library for JPEG image compression.
Project: Harlinn.jpeg
libjpeg-turbo
Version: 2.1.1
Description:
libjpeg-turbo is a JPEG image codec that uses SIMD instructions (MMX, SSE2, AVX2, Neon, AltiVec) to accelerate baseline JPEG compression and decompression on x86, x86-64, Arm, and PowerPC systems, as well as progressive JPEG compression on x86 and x86-64 systems. On such systems, libjpeg-turbo is generally 2-6x as fast as libjpeg, all else being equal. On other types of systems, libjpeg-turbo can still outperform libjpeg by a significant amount, by virtue of its highly-optimized Huffman coding routines. In many cases, the performance of libjpeg-turbo rivals that of proprietary high-speed JPEG codecs.
libjpeg-turbo implements both the traditional libjpeg API as well as the less powerful but more straightforward TurboJPEG API. libjpeg-turbo also features colorspace extensions that allow it to compress from/decompress to 32-bit and big-endian pixel buffers (RGBX, XBGR, etc.), as well as a full-featured Java interface.
Project: Harlinn.jpeg-turbo
JSON-C - A JSON implementation in C
Version: master as of 2021.08.01
Description:
A JSON implementation in C.
Project: Harlinn.json-c
JsonCpp
Version: 1.9.4
Description:
JsonCpp is a C++ library that allows manipulating JSON values, including serialization and deserialization to and from strings. It can also preserve existing comment in unserialization/serialization steps, making it a convenient format to store user input files.
Project: Harlinn.jsoncpp
JPEG XL reference implementation
Version: 0.5
Description:
A reference implementation of JPEG XL (encoder and decoder), called libjxl.
Project: Harlinn.jxl
kml
Version: 1.3.0
Description:
This is Google's reference implementation of OGC KML 2.2.
Projects:
- Harlinn.kmlbase
- Harlinn.kmlconvenience
- Harlinn.kmldom
- Harlinn.kmlengine
- Harlinn.kmlregionator
- Harlinn.kmlxsd
Little CMS
Version: 2.12
Description:
Little CMS intends to be an OPEN SOURCE small-footprint color management engine, with special focus on accuracy and performance. It uses the International Color Consortium standard (ICC), which is the modern standard when regarding to color management. The ICC specification is widely used and is referred to in many International and other de-facto standards. It was approved as an International Standard, ISO 15076-1, in 2005.
Project: Harlinn.lcms2
LERC - Limited Error Raster Compression
Version: 3.0
Description:
LERC is an open-source image or raster format which supports rapid encoding and decoding for any pixel type (not just RGB or Byte).
Project: Harlinn.Lerc
libde265 - open h.265 codec implementation
Version: 1.0.8
Description:
libde265 is an open source implementation of the h.265 video codec. It is written from scratch and has a plain C API to enable a simple integration into other software.
libde265 supports WPP and tile-based multithreading and includes SSE optimizations. The decoder includes all features of the Main profile and correctly decodes almost all conformance streams
Project: Harlinn.libde265
FLAC - Free Lossless Audio Codec
Version: 1.3.2
Description:
FLAC is an Open Source lossless audio codec
Project: Harlinn.libflac
libheif
Version: 1.12.0
Description:
libheif is an ISO/IEC 23008-12:2017 HEIF and AVIF (AV1 Image File Format) file format decoder and encoder.
HEIF and AVIF are new image file formats employing HEVC (h.265) or AV1 image coding, respectively, for the best compression ratios currently possible.
Project: Harlinn.libheif
liblzma
Version: 5.2.5
Description:
LZMA Utils is an attempt to provide LZMA compression to POSIX-like systems. The idea is to have a gzip-like command line tool and a zlib-like library, which would make it easy to adapt the new compression technology to existing applications.
Project: Harlinn.liblzma
libmysofa
Version: 1.2.1
Description:
This is a simple set of C functions to read AES SOFA files, if they contain HRTFs stored according to the AES69-2015 standard.
Project: Harlinn.libmysofa
libogg
Version: 1.3.5
Description:
Ogg is a multimedia container format, and the native file and stream format for the Xiph.org multimedia codecs.
Project: Harlinn.libogg
LIBSVM -- A Library for Support Vector Machines
Version: 3.16
Description:
LIBSVM is an integrated software for support vector classification, (C-SVC, nu-SVC), regression (epsilon-SVR, nu-SVR) and distribution estimation (one-class SVM). It supports multi-class classification.
Project: Harlinn.libsvm
VMAF - Video Multi-Method Assessment Fusion
Version: 2.2.0
Description:
VMAF is a perceptual video quality assessment algorithm developed by Netflix.
Project: Harlinn.libvmaf
Libxml2
Version: 2.9.12
Description:
Libxml2 is the XML C parser and toolkit developed for the Gnome project.
Project: Harlinn.libxml2
Lightning Memory-Mapped Database
Version: 0.9.70
Description:
An ultra-fast, ultra-compact, crash-proof, key-value, embedded data store
Project: Harlinn.LMDB
LodePNG - PNG encoder and decoder in C and C++, without dependencies
Version: 20200215
Description:
LodePNG is a PNG image decoder and encoder, all in one, no dependency or linkage to zlib or libpng required.
Project: Harlinn.lodepng
LZ4 - Extremely fast compression
Version: 1.9.3
Description:
LZ4 is lossless compression algorithm, providing compression speed > 500 MB/s per core, scalable with multi-cores CPU. It features an extremely fast decoder, with speed in multiple GB/s per core, typically reaching RAM speed limits on multi-core systems.
Project: Harlinn.lz4
LZMA SDK
Version: 21.03
Description:
LZMA / LZMA2 are default and general compression methods of 7z format in the 7-Zip program. LZMA provides a high compression ratio and fast decompression, so it is very suitable for embedded applications.
Project: Harlinn.lzma
Mesh Data Abstraction Library (MDAL)
Version: 0.8.1
Description:
Mesh Data Abstraction Library.
Project: Harlinn.mdal
minizip
Version: 1.1
Description:
This package enables to extract files from a .zip archive file.
Project: Harlinn.minizip
Unidata NetCDF
Version: TBD - this project is currently just a placeholder
Project: Harlinn.netcdf-c
JSON for Modern C++
Version: develop as of 2021.08.16
Description:
JSON for Modern C++
Project: Harlinn.nlohmann-json
OpenAL Soft is an LGPL-licensed, cross-platform, software implementation of the OpenAL 3D audio API.
Version: 1.21.1
Description:
OpenAL Soft is an LGPL-licensed, cross-platform, software implementation of the OpenAL 3D audio API.
OpenAL provides capabilities for playing audio in a virtual 3D environment. Distance attenuation, doppler shift, and directional sound emitters are among the features handled by the API.
Project: Harlinn.openal-soft
OpenCensus - A stats collection and distributed tracing framework
Version: 0.4.0
Description:
OpenCensus is a toolkit for collecting application performance and behavior data. It currently includes an API for tracing and stats.
Project: Harlinn.opencensus
OpenEXR
Version: master as of 2021.08.18
Description:
OpenEXR provides the specification and reference implementation of the EXR file format, the professional-grade image storage format of the motion picture industry.
The purpose of EXR format is to accurately and efficiently represent high-dynamic-range scene-linear image data and associated metadata, with strong support for multi-part, multi-channel use cases.
Projects:
- Harlinn.iex
- Harlinn.ilmthread
- Harlinn.openexr
- Harlinn.openexrcore
- Harlinn.openexrutil
OpenFYBA
Version: 4.1.1
Description:
OpenFYBA is the source code release of the FYBA library, distributed by the National Mapping Authority of Norway (Statens kartverk) to read and write files in the National geodata standard format SOSI.
Project: Harlinn.openfyba
The Preview Image Extractor (PIEX)
Version: master as of 2021.09.24
Description:
The Preview Image Extractor (PIEX) is designed to find and extract the largest JPEG compressed preview image contained in a RAW file.
Project: Harlinn.piex
libpng
Version: 1.6.37
Description:
libpng is the official PNG reference library. It supports almost all PNG features, is extensible, and has been extensively tested for over 23 years.
Project: Harlinn.png
PROJ is a generic coordinate transformation software
Version: 8.1.0
Description:
PROJ is a generic coordinate transformation software that transforms geospatial coordinates from one coordinate reference system (CRS) to another. This includes cartographic projections as well as geodetic transformations.
Project: Harlinn.proj
Protocol Buffers
Version: 3.17.3
Description:
Protocol buffers are Google's language-neutral, platform-neutral, extensible mechanism for serializing structured data – think XML, but smaller, faster, and simpler. You define how you want your data to be structured once, then you can use special generated source code to easily write and read your structured data to and from a variety of data streams and using a variety of languages.
Projects:
- Harlinn.protobuf
- Tools\3rdParty\protobuf\protoc
pthreads4w
Version: 3.0.0
Description:
Also known as "pthreads-win32", POSIX Threads for Windows implements a large subset of the threads related API from the Single Unix Specification Version 3.
Conformance and quality are high priorities of this mature library. Development began in 1998 and has continued with numerous significant professional contributions.
Project: Harlinn.pthreads4w
Qpid Proton - The AMQP messaging toolkit
Version: 0.35.0
Description:
Qpid Proton is a high-performance, lightweight messaging library. It can be used in the widest range of messaging applications, including brokers, client libraries, routers, bridges, proxies, and more. Proton makes it trivial to integrate with the AMQP 1.0 ecosystem from any platform, environment, or language.
Projects:
- Harlinn.qpid-proton
- Harlinn.qpid-proton-cpp
RapidJSON
Version: master as of 2021.09.26
Description:
A fast JSON parser/generator for C++ with both SAX/DOM style API.
Project: Harlinn.RapidJSON
RE2 - a regular expression library
Version: 2021-09-01
Description:
RE2 was designed and implemented with an explicit goal of being able to handle regular expressions from untrusted users without risk. One of its primary guarantees is that the match time is linear in the length of the input string. It was also written with production concerns in mind: the parser, the compiler and the execution engines limit their memory usage by working within a configurable budget – failing gracefully when exhausted – and they avoid stack overflow by eschewing recursion.
Project: Harlinn.re2
RocksDB: A Persistent Key-Value Store for Flash and RAM Storage
Version: 6.22.1
Description:
RocksDB is a storage engine with key/value interface, where keys and values are arbitrary byte streams. It is a C++ library. It was developed at Facebook based on LevelDB and provides backwards-compatible support for LevelDB APIs.
RocksDB supports various storage hardware, with fast flash as the initial focus. It uses a Log Structured Database Engine for storage, is written entirely in C++
Project: Harlinn.rocksdb
Scintilla - a free source code editing component
Version: 5.1.3
Description:
Scintilla is a free source code editing component. It comes with complete source code and a license that permits use in any free project or commercial product.
As well as features found in standard text editing components, Scintilla includes features especially useful when editing and debugging source code. These include support for syntax styling, error indicators, code completion and call tips. The selection margin can contain markers like those used in debuggers to indicate breakpoints and the current line. Styling choices are more open than with many editors, allowing the use of proportional fonts, bold and italics, multiple foreground and background colours and multiple fonts.
Project: Harlinn.scintilla
Simple DirectMedia Layer (SDL) Version 2.0
Version: 2.0.16
Description:
Simple DirectMedia Layer is a cross-platform development library designed to provide low level access to audio, keyboard, mouse, joystick, and graphics hardware via OpenGL and Direct3D.
Project: Harlinn.SDL2
Simple and Fast Multimedia Library
Version: 2.5.1
Description:
SFML provides a simple interface to the various components of your PC, to ease the development of games and multimedia applications. It is composed of five modules: system, window, graphics, audio and network.
Projects:
- Harlinn.sfml-audio
- Harlinn.sfml-graphics
- Harlinn.sfml-network
- Harlinn.sfml-system
- Harlinn.sfml-window
The sjpeg library
Version: master as of 2021.09.11
Description:
sjpeg is a simple encoding library for encoding baseline JPEG files.
Project: Harlinn.sjpeg
skcms
Version: main as of 2021.09.12
Description: Skia Color Management
Project: Harlinn.skcms
Skia - The 2D Graphics Library
Version: 0.31
Description:
Skia is an open source 2D graphics library which provides common APIs that work across a variety of hardware and software platforms. It serves as the graphics engine for Google Chrome and Chrome OS, Android, Flutter, Mozilla Firefox and Firefox OS, and many other products.
Projects:
- Harlinn.skia
- Tools\3rdParty\Skia\skslc
Snappy - a compression/decompression library
Version: master as of 2021.08.02
Description:
Snappy is a compression/decompression library. It does not aim for maximum compression, or compatibility with any other compression library; instead, it aims for very high speeds and reasonable compression. For instance, compared to the fastest mode of zlib, Snappy is an order of magnitude faster for most inputs, but the resulting compressed files are anywhere from 20% to 100% bigger.
Project: Harlinn.snappy
SPIRV-Cross
Version: Version used for MoltenVK 1.1.5 release
Description:
SPIRV-Cross is a tool designed for parsing and converting SPIR-V to other shader languages.
Project: Harlinn.spirv-cross
SPIR-V Headers
Version: 1.5.4
Description: The header files from https://github.com/KhronosGroup/SPIRV-Headers
Project: Harlinn.spirv-headers
SPIR-V Tools
Version: 2021.3
Description:
The project includes an assembler, binary module parser, disassembler, validator, and optimizer for SPIR-V.
Project: Harlinn.spirv-tools
sqlite3
Version: 3.36.0
Description:
SQLite is a C-language library that implements a small, fast, self-contained, high-reliability, full-featured, SQL database engine.
Projects:
- Harlinn.SQLite3
- Tools\3rdParty\SQLite3\sqlite3
Single-file public-domain/open source libraries with minimal dependencies (STB)
Version: master as of 2021.09.10
Description:
Small, easy-to-integrate, portable libraries which are usable from C and/or C++
Project: Harlinn.stb
SuperLU
Version: 5.2.2
Description:
SuperLU is a general purpose library for the direct solution of large, sparse, nonsymmetric systems of linear equations.
Project: Harlinn.superlu
LibTIFF
Version: 4.3.0
Description:
This software provides support for the Tag Image File Format (TIFF), a widely used format for storing image data.
Project: Harlinn.tiff
TinyXML-2
Version: master as of 2021.06.07
Description:
TinyXML-2 is a simple, small, efficient, C++ XML parser that can be easily integrated into other programs.
Project: Harlinn.tinyxml2
μpb: small, fast C protos
Version: master as of 2021.10.21
Description:
μpb (often written 'upb') is a small protobuf implementation written in C.
Projects:
- Harlinn.upb
- Tools\3rdParty\upb\protoc-gen-upb
- Tools\3rdParty\upb\protoc-gen-upbdefs
uriparser
Version: 0.9.5
Description:
uriparser is a strictly RFC 3986 compliant URI parsing and handling library written in C89 ("ANSI C").
Project: Harlinn.uriparser
libvorbis, libvorbisfile and libvorbisenc
Version: 1.3.7
Description:
Vorbis is a general purpose audio and music encoding format contemporary to MPEG-4's AAC and TwinVQ, the next generation beyond MPEG audio layer 3.
Project: Harlinn.vorbis
Vulkan header files
Version: main as of 2021.09.21
Description:
Vulkan header files
Project: Harlinn.vulkan
Vulkan Memory Allocator
Version: 2.3.0
Description:
The Vulkan® Memory Allocator (VMA) library provides a simple and easy to integrate API to help you allocate memory for Vulkan® buffer and image storage.
Project: Harlinn.vulkanmemoryallocator
libwebm
Version: main as of 2021.09.08
Description:
The WebM Project is dedicated to developing a high-quality, open video format for the web that's freely available to everyone.
Project: Harlinn.webm
WebP - An image format for the Web
Version: main as of 2021.09.08
Description:
WebP is a modern image format that provides superior lossless and lossy compression for images on the web. Using WebP, webmasters and web developers can create smaller, richer images that make the web faster.
Project: Harlinn.webp
Xerces-C++ - a validating XML parser
Version: 3.2.3
Description:
Xerces-C++ is a validating XML parser written in a portable subset of C++. Xerces-C++ makes it easy to give your application the ability to read and write XML data.
Project: Harlinn.xerces-c
XMP-Toolkit-SDK
Version: 6.0.0
Description:
The XMP Toolkit allows you to integrate XMP functionality into your product or solution.
Project: Harlinn.xmptoolkitsdk
libyuv
Version: main as of 2021-09-07
Description:
libyuv is an open source project that includes YUV scaling and conversion functionality.
Project: Harlinn.yuv
zlib
Version: 1.2.11
Description:
zlib is designed to be a free, general-purpose, legally unencumbered -- that is, not covered by any patents -- lossless data-compression library for use on virtually any computer hardware and operating system.
Project: Harlinn.zlib
zlib-ng
Version: develop as of 2021.05.08
Description:
zlib data compression library for the next generation systems
Project: Harlinn.zlibng
Zstandard (zstd)
Version: dev as of 2021.08.04
Description:
Zstandard, or zstd as short version, is a fast lossless compression algorithm, targeting real-time compression scenarios at zlib-level and better compression ratios.
Project: Harlinn.zstd
License
This article, along with any associated source code and files, is licensed under The Code Project Open License (CPOL)
Share
About the Author

Specializing in integrated operations and high performance computing solutions.
I’ve been fooling around with computers since the early eighties, I’ve even done work on CP/M and MP/M.
Wrote my first “real” program on a BBC micro model B based on a series in a magazine at that time. It was fun and I got hooked on this thing called programming...
Recommend
About Joyk
Aggregate valuable and interesting links.
Joyk means Joy of geeK